Coding Spotlight: Providers Guide To Coding Respiratory Diseases
Feb 1, 2020State & Federal / Medicaid
Category: Medicaid
ICD-10-CM coding
Respiratory diseases are classified in categories J00 through J99 in Chapter 10, Diseases of the Respiratory System of the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is coded in several ways in ICD-10-CM. Combination codes that account for both pneumonia and the responsible organism are included in Chapter 1, Certain Infectious And Parasitic Diseases and Chapter 10, Diseases of the Respiratory System. Examples of appropriate codes for pneumonia include:
- J15.0 pneumonia due to Klebsiella
- J15.211 pneumonia due to Staphylococcus aureus
- J11.08 + J12.9 viral pneumonia with influenza.
According to ICD-10-CM instructions, when coding J15:
- Code first associated influenza, if applicable
- Code also associated abscess, if applicable
Other types of pneumonia are coded as manifestations of underlying infections classified in chapter 1 two codes are required in such cases. Examples of this dual classification coding include I00 + J17 pneumonia in rheumatic fever. When the diagnostic statement is pneumonia without any further specification and the organism is not identified, the assigned code is J18.9 pneumonia, unspecified organism.
ICD-10-CM classifies influenza as the following categories:
- J09 due to certain identified influenza viruses
- J10 due to other identified influenza virus
- J11 due to unidentified influenza virus.
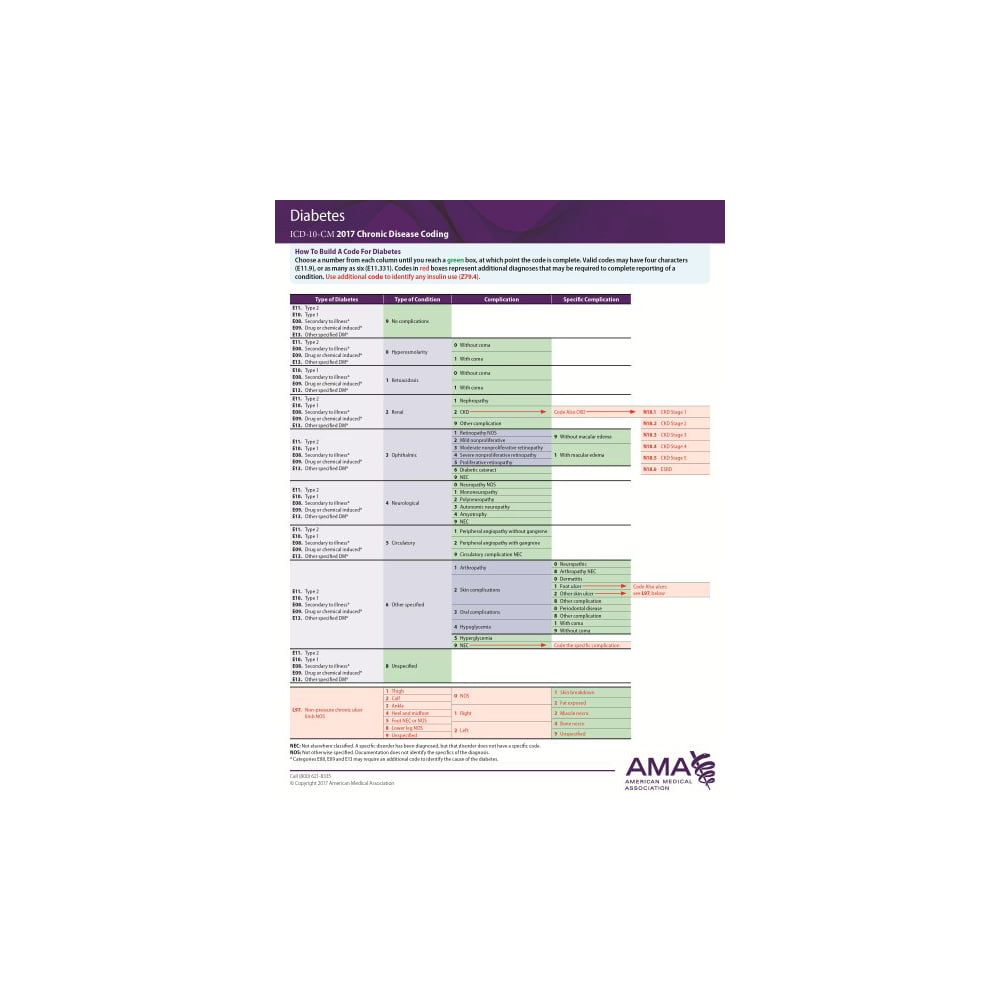
Severity Key To Coding Asthma Encounters
Make sense of fifth digits to complete the picture.
Asthma is probably one of the most common conditions your pediatric practice diagnoses and treats. But no matter how familiar you are with the J45 code set, it’s always a good idea to remind yourself what makes the codes so specific.
Coding different asthma conditions accurately is simple if you follow the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute guidelines for asthma diagnoses and know the fifth digit ICD-10 codes for each degree of severity.
So, take a deep breath, read on, and refresh your asthma coding knowledge.
First, Ask Intermittent or Persistent Mild, Moderate or Severe
Unlike many ICD-10 codes, the J45 code set uses the severity of the symptoms rather than the etiology of the condition as its subdivisions. This is consistent with the current asthma guidelines determined by the NHLBI, which classifies the conditions this way.
The chart shows that the condition has four different states – mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent – that correspond exactly with the following four code sets:
- J45.2, Mild intermittent asthma …
- J45.4, Moderate persistent asthma …
- J45.5, Severe persistent asthma …
A fifth code, J45.9 is reserved for forms of the condition that do not fit neatly into the established categories, such as asthmatic bronchitis, childhood asthma, or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
Then, Add 0, 1, or 2 for Full Reimbursement
What Happens To Our Lungsduring Asthma Attack:
During asthma attack, muscles around the airway gets tighten and the lining inside the airways becomes swollen and produce extra mucus. This makes airway to become narrow and partially block airflow in and out of air sacs.
Below picture gives a clear understanding of the position of lungs , normal airway and airway during asthma attack .
Apart from knowing the symptoms and doing a lung physical examination the physician will also do few test measures like X-ray, spirometry, allergy testing, nitric oxide breath test or peak flow to determine the type of asthma and its severity. Hence a coder should definitely pay attention to these areas as well.
Also Check: Moderate Persistent Asthma With Exacerbation
Drg Mapping Rules For J4550
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patients primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patients primary diagnostic code is J45.50, look in the list below to see which MDCs Assignment of Diagnosis Codes is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patients discharge date.
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
The upper airway is defined as the all the structures connecting the glottis to the mouth and nose. The most common upper respiratory tract infection is the common cold. However, infections of specific organs of the upper respiratory tract such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, pharyngitis and laryngitis are also considered upper respiratory tract infections.
Epiglottitis is a bacterial infection of the larynx which causes life-threatening swelling of the epiglottis with a mortality rate of 7% in adults and 1% in children.Haemophilus influenzae is still the primary cause even with vaccinations. Symptoms include drooling, stridor, difficulty breathing and swallowing, and a hoarse voice.
Croup is a viral infection of the vocal cords typically lasting five to six days. The main symptom is a barking cough and low grade fever. On an x-ray, croup can be recognized by the steeple sign, which is a narrowing of the trachea. It most commonly occurs in winter months in children between the ages of 3 months and 5 years. A severe form caused by bacteria is called bacterial tracheitis.
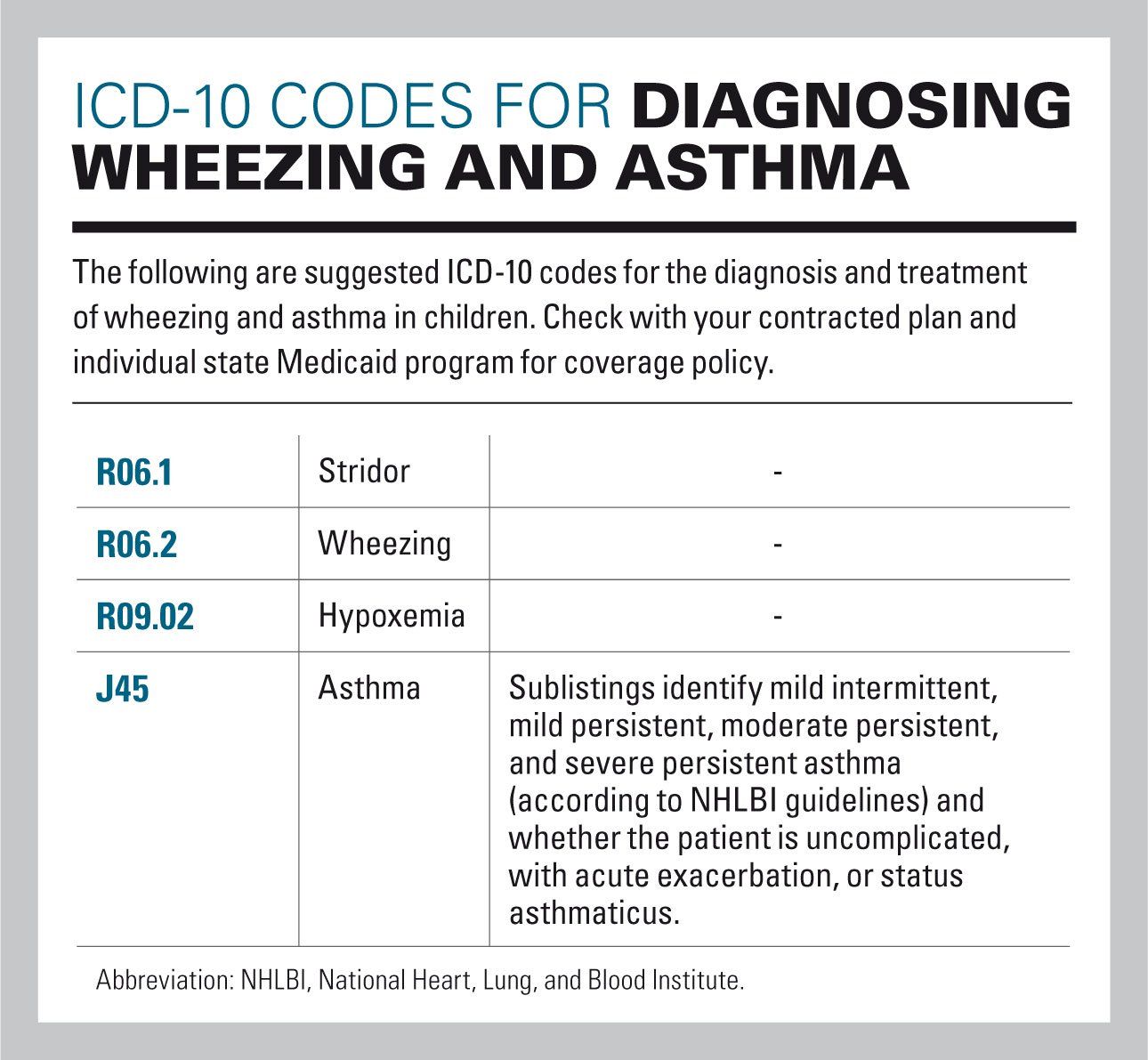
You May Like: Is It Possible To Have Asthma Without Wheezing
What Happens When Your Airways Are Sore
If you have asthma, the inside walls of your airways become sore and swollen. That makes them very sensitive, and they may react strongly to things that you are allergic to or find irritating. When your airways react, they get narrower and your lungs get less air.symptoms of asthma include. wheezing.
Severe Persistent Asthma Uncomplicated
Chapter 10 – Diseases of the respiratory system » Chronic lower respiratory diseases » Severe persistent asthma, uncomplicated
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
You May Like: Does Asthma Affect The Trachea
What Is Asthma Exacerbation
Asthma exacerbation: It is nothing but an acute increase of symptoms in a person with asthma. This can be coded only with the Physician diagnosis. Status asthmatics : Another term for this is severe asthma exacerbation. It is considered as severe as this may lead to even respiratory failure due to hypoxemia.
What Tests Are Done To Determine Asthma
Apart from knowing the symptoms and doing a lung physical examination the physician will also do few test measures like X-ray, spirometry, allergy testing, nitric oxide breath test or peak flow to determine the type of asthma and its severity. Hence a coder should definitely pay attention to these areas as well.
Recommended Reading: What Can Cure Asthma Cough
Sas Code For Calculation Of Asthma Rates By Age Group And Year
- See below for SAS code for calculation of asthma rates by age group and year .Validated work done by Kozyrskyj et al. for children has a slightly different requirement for prescriptions over time. The additional criteria in the drug definition for children is used to help remove individuals with childhood wheezing. The definition is at least one prescription for an inhaled corticosteroid or Chromone or Ketotifen concomitant with an inhaled or oral beta-agonist, or two or more prescriptions for an inhaled or oral beta-agonist. Each of these groups of drugs is identified in the provided code.
Who Is At Risk For Asthma
Asthma affects people of all ages, but it often starts during childhood. Certain factors can raise your risk of having asthma:
Sex.
Also Check: Is Prescribed To Asthma Sufferers
Common Terms Found In Medical Record Related To Asthma:
Asthma exacerbation: It is nothing but an acute increase of symptoms in a person with asthma. This can be coded only with the Physician diagnosis.
Status asthmatics : Another term for this is severe asthma exacerbation. It is considered as severe as this may lead to even respiratory failure due to hypoxemia. As soon as a patient comes to emergency room with asthma symptoms, physician treats initially with medicines such as bronchodilators. If patient has status asthmatics they do not respond to these medicines.
Inhaler : Medicine filled inhalers are given to patient to use comfortably at any place when symptoms occurs suddenly.
Nebulizer : Electricity powered machine filled with liquid medication which turns to mist and the patient breath in.
Nasal spray : A bottle with liquid medicine made with the ease of spraying to nose.
PFT : Pulmonary Function Test, use to check the lung function by measuring lung volume, capacity, rates of flow and gas exchange.
What Are The Treatments For Asthma
If you have asthma, you will work with your health care provider to create a treatment plan. The plan will include ways to manage your asthma symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. It will include
If you have a severe attack and the short-term relief medicines do not work, you will need emergency care.
Your provider may adjust your treatment until asthma symptoms are controlled.
Sometimes asthma is severe and cannot be controlled with other treatments. If you are an adult with uncontrolled asthma, in some cases your provider might suggest bronchial thermoplasty. This is a procedure that uses heat to shrink the smooth muscle in the lungs. Shrinking the muscle reduces your airways ability to tighten and allows you to breathe more easily. The procedure has some risks, so its important to discuss them with your provider.
Also Check: How To Use Asthma Pump Properly
What Causes Asthma
The exact cause of asthma is unknown. Genetics and your environment likely play a role in who gets asthma.
An asthma attack can happen when you are exposed to an asthma trigger. An asthma trigger is something that can set off or worsen your asthma symptoms. Different triggers can cause different types of asthma:
- Allergic asthma is caused by allergens. Allergens are substances that cause an allergic reaction. They can include
- Pollen from grass, trees, and weeds
- Waste from pests such as cockroaches and mice
Asthma triggers may be different for each person and can change over time.
What Are The Icd
Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated ranks at the top of our list with a total of 8,809,971 diagnoses in 2021. The ICD-10 code for asthma, unspecified is J45909.
This chronic condition has a considerable lead in both diagnoses and charges compared to all other ICD-10 codes. While many factors could contribute to why J45909 ranks number one, a likely cause could be problems with documentation. Many of the other codes on this list detail asthma of various degrees of chronicity and severity. A lack of proper documentation, however, could cause medical coders to resort to classifying the diagnosis as unspecified asthma, uncomplicated.
An asthma attack, also called asthma, exacerbation, is another common diagnosis with a few top positions on our list. The ICD-10 codes for these diagnoses are J45901, J4521, J4541 and J4531.
Its also important to note that some physicians may regard asthma classifications as fluid. While this condition cant be cured, a patients lifestyle can make the symptoms of asthma easier or harder to manage. Eliminating smoking habits and exercising regularly, alongside medical treatment, can potentially improve a patients condition. As a result, the classification of asthma a patient is diagnosed with can change over years and decades.
Also Check: What To Do For Asthma Without Inhaler
How Is Asthma Diagnosed
Your health care provider may use many tools to diagnose asthma:
Also Check: How Often Does Asthma Attack Occur
Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
The most common lower respiratory tract infection is pneumonia, an infection of the lungs which is usually caused by bacteria, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae in Western countries. Worldwide, tuberculosis is an important cause of pneumonia. Other pathogens such as viruses and fungi can cause pneumonia, for example severe acute respiratory syndrome, COVID-19 and pneumocystis pneumonia. Pneumonia may develop complications such as a lung abscess, a round cavity in the lung caused by the infection, or may spread to the pleural cavity.
Poor oral care may be a contributing factor to lower respiratory disease, as bacteria from gum disease may travel through airways and into the lungs.
You May Like: Why Does Asthma Get Worse At Night
Also Check: When Beginning An Exercise Program People With Asthma Should Always
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bronchial Infection
Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, and rapid breathing. An attack may be brought on by pet hair, dust, smoke, pollen, mold, exercise, cold air, or stress. A chronic respiratory disease manifested as difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of bronchial passageways.
Coding Tip: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease And Asthma
Kim Boy, RHIT, CDIP, CCS, CCS-P
This Coding Tip was updated on 07/26/2022
Below are some definitions for clarification:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed flow of air from the lungs. The disease is progressive in nature and typically will worsen over time. The most common cause of COPD is smoking tobacco. COPD is increasingly being used to document lung disease. The coder must review the record for further specificity of the disease. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two main conditions of COPD. COPD can also be further clarified to be with acute exacerbation.
Asthma is an inflammatory condition in which the airways narrow and swell and extra mucous is produced. There is no cure for asthma, but symptoms may be prevented by avoiding triggers and using prescribed medications. The cause of asthma is either environmental or genetic. If asthma is present before age 12, the cause is most likely from genetics. If asthma presents after age 12, the cause is more likely to be environmentally induced. Asthma can also be further clarified as to severity as well as status asthmaticus or acute exacerbation.
Status asthmaticus is described as asthma with acute symptoms that do not respond to standard treatment including the use of steroids and bronchodilators.
Exacerbation is a sudden worsening of a disease and typically last several days.
References:
Don’t Miss: Are Bananas Good For Asthma
Diseases Of The Respiratory Systemnote
- certain conditions originating in the perinatal period
- certain infectious and parasitic diseases
- complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
- congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities
- endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases
- injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes
- symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified
- code, where applicable, to identify:
- exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
- exposure to tobacco smoke in the perinatal period
- history of tobacco dependence
- occupational exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
- cystic fibrosis
Occupational Exposure To Environmental Tobacco Smoke
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Applicable To
type 1 excludes
You May Like: How To Test Asthma In Adults
