Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Smoking is considered to be the main cause of COPD. Smoking can also worsen other conditions that cause wheezing.
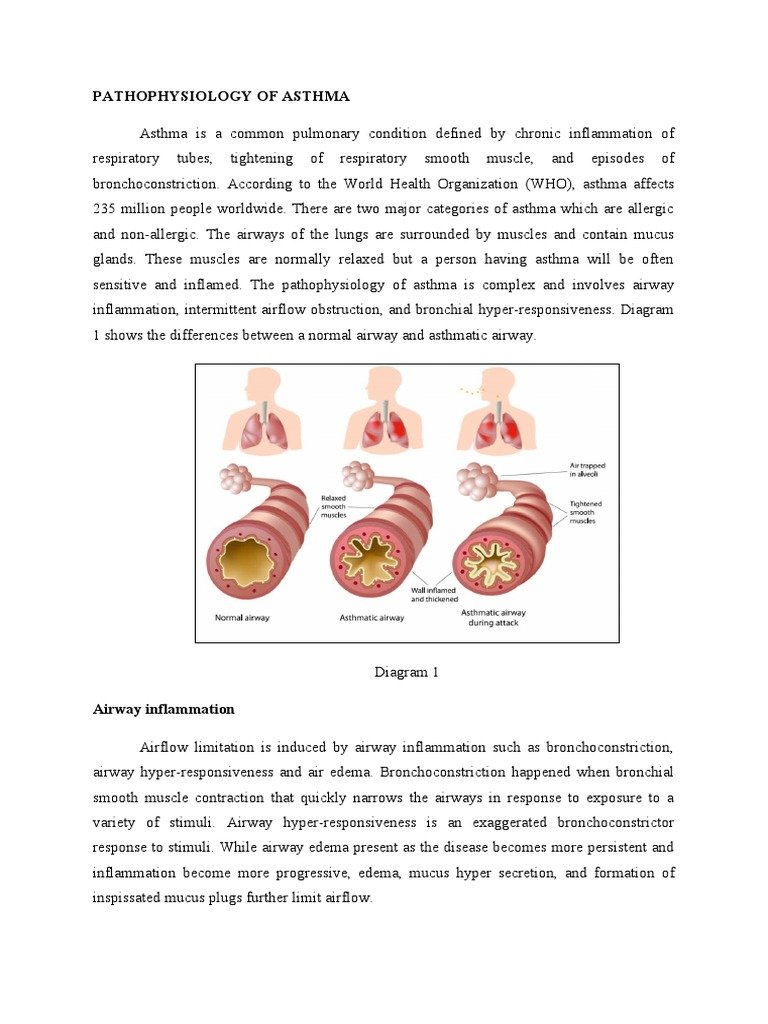
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a progressive lung disease which makes breathing difficult. This can happen because the walls of your air sacs or the walls between air sacs get damaged , or the lining of your airways is constantly irritated leading to the formation of thick mucus , or both.11 Smoking is considered to be the main cause of COPD. Long-term exposure to other things that can irritate your lungs like chemical fumes, air pollution etc. can also lead to COPD. In some cases, people who are genetically deficient in a protein known as alpha-1 antitrypsin can also develop this condition. COPD is usually observed in middle-aged or elderly people.
Other symptoms that indicate COPD include coughing with or without phlegm, shortness of breath that worsens with activity, and fatigue
What to do: COPD causes permanent damage to your lungs, however, there are some measures which can stop this condition from getting worse and help to ease symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe medicine and inhalers that can help you breathe better. Pulmonary rehabilitation exercises can also be helpful in teaching you to breathe better.12
Box : Definition Of A Patient
A patient-reported outcome measure is reported directly by a patient or their carer. It is a measure used to assess the outcome and/or the effect that a particular treatment for a long-term condition has on the quality of life of a patient. These reports might include how the condition affects health-related quality of life, a patient’s perceptions of their health or functional status in relation to their long-term condition and the effect that treatment or care strategies have on the quality of life of the patient.
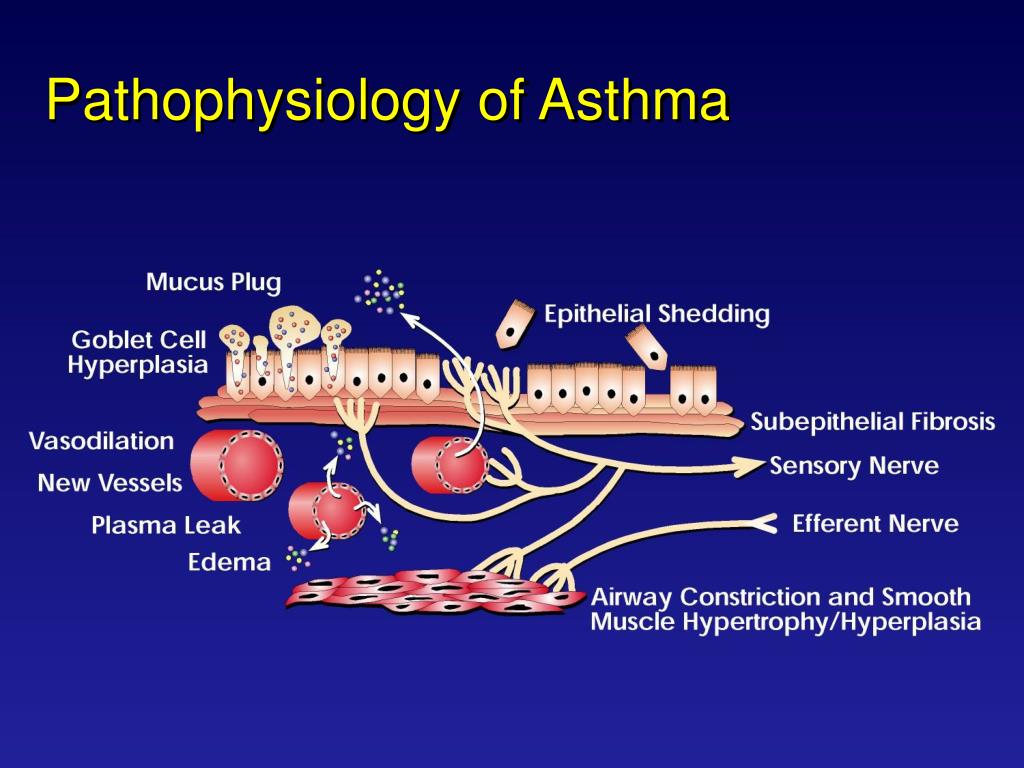
Asm As A Contributor To Airway Inflammation In Asthma
There is evidence that ASM plays a pivotal role in the airway inflammation characteristic of asthma as well. Not just a bystander in this process, ASM releases and expresses several molecular signals that contribute to bronchial inflammation and have become targets of novel therapeutic strategies .
Table 4. Potential new therapeutic targets of inflammation in asthma
| Inflammatory target |
|---|
IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor; IgE, immunoglobulin E.
Don’t Miss: Can Weed Cause Asthma
Similarities Between Intrinsic And Extrinsic Asthma
- Extrinsic Asthma happens when the immune system responds over reactively to an unhealthy product like pollen or dust. An immunoglobin E is released in the body. This antibody release contributes to inflammation and symptoms of Asthma.
- Intrinsic Asthma happens if an immune system reaction affects anything other than allergens. The cause cannot always be identified by people.
Stage : Your Lung Swell In Response To Potential Danger
When the lungs are triggered by allergens, the walls of the passages swell. This eventually blocks the air getting into the lungs and decreases oxygen reaching the body.
Muscles within the breathing tubes of the lungs contract and lead to more narrowing of the airways. This makes it hard the lungs to move and push out air. This difficulty to breathe leads to the typical symptoms of an asthma attack.
Another problem is that extra mucous is made for added protection. If the irritation of the lungs does not stop immediately, this leads to contraction of these muscles and production of thick mucus. Although this may seem strange, the airways are filled with mucus to block more allergens from entering the lungs.
In the end, the swelling of the lung airways, constriction of the lung muscles, and production of thick mucus all together cause a narrow passageway for air to get through. Eventually, if the trigger is not removed, the lungs will shut down completely and no air will circulate at all.
Read Also: How To Stop Asthma Wheezing Without Inhaler
Airway Remodelling: The Simple Airway Tube Model
The airway can be conceptualized as a simple elastic tube embedded within an elastic lung parenchyma. The elastic airways stretch as the lung stretches, due to parenchymal tethering to the airway adventitia. In health, the elastic properties of the lung parenchyma and airways are well matched , which underlies the relationship between lung volume and airway calibre. Therefore, changes in both the mechanical properties of the lung parenchyma and its attachments to the airway wall may contribute to AHR and fixed airflow obstruction.
Increased tissue mass and altered composition of the airway wall, particularly of the extracellular matrix , may alter the airway wall mechanics and contribute to AHR and non-reversible airway narrowing. Some studies suggest that airways from asthmatic patients are stiffer than those from non-asthmatic patients., This would prevent deep inspirations from dilating airways, but paradoxically it could also resist airway narrowing. Other studies suggest that airway stiffness is not greater in asthma and the role of altered airway compliance remains uncertain. Compliance is not related to the severity of AHR but is related to asthma symptoms. In any event, an in vitro study of intact bronchial segments has shown that the increased thickness of the ASM layer is associated with increased maximal airway narrowing in asthma.
Control Of Triggering Factors
Triggering factors in some patients may be controlled with use of synthetic fiber pillows and impermeable mattress covers and frequent washing of bed sheets, pillowcases, and blankets in hot water. Ideally, upholstered furniture, soft toys, carpets, curtains, and pets should be removed, at least from the bedroom, to reduce dust mites and animal dander. Dehumidifiers should be used in basements and in other poorly aerated, damp rooms to reduce mold. Steam treatment of homes diminishes dust mite allergens. House cleaning and extermination to eliminate cockroach exposure is especially important. Although control of triggering factors is more difficult in urban environments, the importance of these measures is not diminished.
High-efficiency particulate air vacuums and filters may relieve symptoms, but no beneficial effects on pulmonary function and on the need for drugs have been observed.
Sulfite-sensitive patients should avoid sulfite-containing food .
Patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma can use acetaminophen, choline magnesium salicylate, or celecoxib in place of NSAIDs.
Asthma is a relative contraindication to the use of nonselective beta-blockers , including topical formulations, but cardioselective drugs probably have no adverse effects.
Read Also: Homemade Inhaler Spacer
Asthma Epidemiology Pathophysiology And Initial Evaluation
After completing this article, readers should be able to:
Describe the underlying pathophysiology of asthma.
Discuss the role of atopy in the development of asthma.
Identify risk factors for death from asthma.
List conditions to be considered in the differential diagnosis of wheezing in children.
How Is Asthma Classified
Doctors rank how bad asthma is by its symptoms:
Your asthma may be getting worse if:
- You have symptoms more often and they interfere more with your daily life.
- You have a hard time breathing. You can measure this with a device called a peak flow meter.
- You need to use a quick-relief inhaler more often.
Also Check: How To Prevent Asthma Attacks
Asm Role In Airflow Obstruction
It remains unknown whether the mechanism driving ASM hyperaccumulation has a deleterious impact on airway contractile function directly. However, it is clear that excessive ASM mass and airway wall thickening are associated with airway hyperresponsiveness. Furthermore, asthma patients with fixed and severe airflow obstruction have significantly thicker airway walls than those with reversible airflow limitation . Those with fixed airflow obstruction also have longer disease duration , suggesting that airway remodeling contributes to the decline in lung function seen in individuals with asthma. These studies indicate that ASM remodeling contributes to both transient and chronic airflow obstruction in asthma.
Role Of Immune System In Asthma
The development of asthma in response to environment and allergies are closely linked to Th1-type, Th2-type, and IgE immune responses. Th1-type immune responses are linked to fighting infection while Th2-type responses are linked to allergies. In asthma Th2-type responses are more active leading to allergies and asthma. IgE responses are linked to allergies. ;IgE known as immunoglobulin E will bind to the allergen and then to a mast cell, which causes the release of histamine. Histamine causes inflammation and excess mucous production.
Read Also: What To Do If Someone Has An Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
How To Prevent An Asthma Attack
An asthma attack can be dangerous. Breathing is not something that you can do without. And it becomes a serious problem when you can no longer continue with normal daily activities.
When it comes to asthma, the best first line treatment is always lifestyle and environmental changes.;
The best protection against asthma is to identify triggers and avoid and control symptoms. While it may not be impossible to remove all allergens, you can perform simple tasks to decrease your risk of exposure. ;
If the symptoms of an asthma attack are not controlled, the lungs can undergo irreversible changes. This is called ‘airway remodeling’ and it is the reason why some asthmatics need to be carefully monitored by a health care team.;
If you know the cause, you can stay away to prevent asthma attacks. There are some common triggers that can invoke an attack, for example cigarette smoke, pollen, or pet hair and dander. Whenever you can, stay away from these agents that can trigger symptoms or cause full-blown asthma attacks.
Referral To A Specialist
;;;;;; Recognizing when a patient needs to be referred out to a specialist for more advanced care should be of utmost concern to the provider. In patients age 0-4, the EPR-3 guidelines suggest referral with an asthma specialist if step 3 care or higher is required, with consideration at step 2. In older patients, this threshold is step 4 or higher, with consideration in step 3 . GINA guidelines recommend referral to an asthma specialist at step 5, or in the following circumstances:
- Difficulty confirming or doubts regarding the diagnosis
- Suspected occupational asthma
- Persistent uncontrolled asthma or frequent exacerbations
- The presence of any risk factors for asthma-related death, such as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, anaphylaxis or a confirmed food allergy
- Risk for or evidence of significant treatment adverse effects
- Symptoms suggestive of complications or sun-types of asthma, such as aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis .
When treating patients with severe eosinophilic asthma, it is recommended to refer to an Ear, Nose, and Throat specialist to help manage rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis .
Don’t Miss: Stop Asthma Coughing
Effect Of Interventions On Natural History Of Asthma
Two recent studies addressed the possibility that ICSs may prevent the putative declines in lung function believed to occur shortly after the beginning of the disease in adults who have late-onset asthma. A retrospective study reported the results of an observational study of adults who had mild-to-moderate asthma and were treated for 5 years with an ICS. One group, treated early in the disease , had better outcomes in terms of lung function than those who started treatment more than 2 years after diagnosis. The group in which treatment was started more than 2 years after diagnosis, however, had lower levels of lung function at the beginning of the trial. Therefore, it is not possible to determine from these data what the results would have been in a randomized trial. Two recent long-term observational studies report an association between ICS therapy and reduced decline in FEV1 in adults who have asthma . However, long-term RCTs will be necessary to confirm a causal relationship.
The Mycobiome And Asthma
It has been reported by Black et al., in 37 patients admitted to the ICU for an acute asthma attack, that 54% tested positive in a skin test for fungal spores which included Alternaria tenuis, Cladosporium cladosporides, Epicoccum nigrum and Helminthosporium maydis . O Driscoll et al., recruited 181 patients, aged between 16 and 60;years of age and divided them into three groups; severe, moderate and mild, dependent on their number of lifetime hospital admissions. 76% of patients with severe asthma tested positive in a skin test toone or more moulds including Aspergillus fumigatus, Penicillium notatum, Cladosporium herbarum, Alternaria alternata or the yeast Candida albicans in comparison to lower rates of positivity in patients with moderate or mild asthma .
Exposure to fungal allergens can have a devastating impact onasthmatics. Fungi contain proteins which are detrimental to the airway epithelium, enhance additional reactions and also act as allergens . It is possible that the long term fungal colonisation of an atopic patient may provide a chronic source of allergen exposure, propagate airway inflammation and increase severity of asthma phenotype .
Recommended Reading: Best Way To Smoke Weed With Asthma
How Asthma Is Treated
While there is no cure for asthma, there are a number of treatments that can help control the condition.
Treatment is based on two important goals, which are:
- relieving symptoms;
- preventing future symptoms and attacks
For most people, this will involve the occasional or, more commonly, daily use of medications, usually taken using an inhaler. However, identifying and avoiding possible triggers is also important.
You should have a personal asthma action plan agreed with your doctor or nurse that includes information about the medicines you need to take, how to recognise when your symptoms are getting worse, and what steps to take when they do so.
These symptoms are often worse at night and early in the morning, particularly if the condition is not well controlled. They may also develop or become worse in response to a certain trigger, such as exercise or exposure to an allergen.
Read our page on the;causes of asthma for more information about potential triggers.
Speak to your GP if you think you or your child may have asthma. You should also talk to your doctor or asthma nurse if you have been diagnosed with asthma and you are finding it difficult to control the symptoms.
You May Like: What To Do When Having An Asthma Attack
Increased Asm Mass In Asthma
Another possible mechanism of increased ASM mass is the migration and differentiation of fibrocytes from bone marrow . Fibrocytes exposed in culture to TGF- acquire characteristics of smooth muscle cells , and the number of circulating fibrocytes in the peripheral blood of individuals with asthma with chronic airflow obstruction correlates with their rate of decline in lung function over time . Therefore, interest has developed in TGF- as a therapeutic target in asthma . Animal models of allergen-induced asthma have shown significant reductions in ASM proliferation following TGF- neutralization or inhibition .
Table 3. Potential new therapeutic targets of ASM structural changes in asthma
| ASM Structural Change |
|---|
ASM, airway smooth muscle; FDA, Food and Drug Administration.
Also Check: What Strain Of Weed Is Good For Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology Diagnosis And Management
At the conclusion of this exercise, the learner will be prepared to:
Impact On Asthma Treatment
While there is no cure for asthma, treatment can control its symptoms and slowif not entirely stopits progression.
With the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of asthma in mind, doctors can recommend strategies to either minimize or normalize the response, or prevent it from happening altogether. Given the variety of elements involved in these processes, your asthma management plan will very likely be multi-pronged.
Visit your doctor regularly so they can monitor your respiratory health and alter your treatment plan over time, as needed.
You May Like: Can You Get Into The Military With Asthma
Monitoring Response To Treatment
Guidelines recommend office use of spirometry to measure airflow limitation and assess impairment and risk. Spirometry should be repeated at least every 1 to 2 years in patients with asthma to monitor disease progression, and a step-up in therapy might be required if lung function declines or becomes impaired with evidence of airflow obstruction . Outside the office, home PEF monitoring, in conjunction with patient symptom diaries and the use of an asthma action plan, is especially useful for charting disease progression and response to treatment in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma. When asthma is quiescent, one PEF measurement in the morning suffices. Should PEF measurements fall to <80% of the patients personal best, then twice/day monitoring to assess circadian variation is useful. Circadian variation of > 20% indicates airway instability and the need to re-evaluate the therapeutic regimen.
Remodelling In Severe Asthma
In severe asthma, airway walls are thicker on HRCT, have more fibroblasts, larger mucous glands and increased ASM,- greater epithelial fragility and increased blood vessels in the lamina propria. There is ASM hyperplasia in severe asthma compared with controls, and with less severe asthma. There is also ASM hypertrophy in both severe and less severe asthma compared with controls. ECM is increased in the ASM although this is in proportion to the increase in ASM. Specific ECM proteins are also increased in asthma, although these may vary across the airway wall.,
Although structural changes in postmortem lungs following fatal asthma attacks may not necessarily be generalizable to severe asthma, there are similar changes in postmortem and biopsy tissue of non-fatal but clinically severe asthma, relative to mild cases and non-asthmatic individuals., , There are clear-cut differences in wall thickness in large airways between severe and mild-moderate asthma cases. The differences are less pronounced in the small airways,, possibly due to the small absolute size of the airways and variation in airway number and size. However, the small airways are more susceptible to severe narrowing and closure due to the greater wall area relative to the airway lumen area.
Don’t Miss: Relieving Asthma Without Inhaler
