Pharmacology Of Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
Anticholinergic bronchodilators are antagonistic to parasympathetic activity and exert their effects on acetylcholine receptors on airway smooth muscle and pulmonary parasympathetic nerves . Acetylcholine receptors fall into two familiesnicotinic and muscarinicand it is the M1, M2 and M3 subtypes of the latter that are thought to be primarily involved in the regulation of bronchoconstriction. All subtypes of muscarinic receptors are widely expressed in the brain, the parasympathetic nervous system and the bodys smooth muscle tissues. M1 receptors are broadly distributed throughout the parasympathetic ganglia and regulate cholinergic transmission. M2 receptors are found in prejunctional membranes of neuromuscular junctions of airway smooth muscle and regulate negative feedback to reduce acetylcholine transmission. In a pulmonary context, M3 receptors are predominantly expressed in smooth muscle cells, where they regulate contraction, and also within lung submucosal glands, where they regulate mucus secretion . Thus, it is preferable for antimuscarinic bronchodilators to have a relatively high affinity for M1 and M3 receptors and low affinity for the M2 receptor.
Box : Literature Evaluation Methods
Clinical evidence around long-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators
We performed searches in November 2013 of PubMed, Google Scholar and Cochrane databases and ClinicalTrials.gov .
PubMed searches
All terms restricted to title and abstract, with restriction of results to clinical trials:
-
In November 2013 the searches yielded 209 results search 2 yielded 25 results. PubMed search results were manually reviewed for articles or studies relevant to the topic of short-acting muscarinic agonists or long-acting muscarinic agonists for acute or maintenance therapy
Cochrane database searches
-
Asthma AND anticholinergic, limited to title, abstract and keywords, yielding 39 hits, the titles and abstracts of which were manually reviewed
-
In November 2013 the searches yielded one review relating to the use of anticholinergics for asthma management, and eight reviews of anticholinergics in a variety of acute settings
www.clinicaltrials.gov searches
-
Asthma AND tiotropium OR umeclidinium OR aclidinium OR glycopyrronium OR darotropium OR glycopyrrolate OR QVA149
Pathophysiology and pharmacology
PubMed and Google scholar searches
Interactions Of Anticholinergic Medication With Other Drugs
Anticholinergic medications have potential interactions with many other drugs, especially those with cholinergic actions or anticholinergic side effects. They are best avoided when taking another anticholinergic medication.
Anticholinergic effect is enhanced by:
- Antidepressants, including amitriptyline, nortriptyline, paroxetine, fluoxetine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Antihistamines used to treat asthma, hay fever and urticaria
- Tiotropium, ipratropium bromide and potassium chloride tablets.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used in myasthenia gravis and Alzheimer disease can antagonise the action of anticholinergic medications.
Read Also: How Long Can Someone With Asthma Hold Their Breath
Do Bronchodilator Inhalers Damage My Lungs
Your body may fail to respond to the medicine if you use your bronchodilator too much. Overuse can also cause your body to become overly sensitive to asthma or COPD triggers. Triggers may include smoke, pollution, dust and chemical fumes.
Using steroid inhalers may also increase your risk of developing nontuberculous mycobacteria infections or pneumonia, especially if youre 65 or older.
Who Can Benefit From Long

There are limited step-up treatment options for patients who continue to have frequent symptoms and exacerbations while taking combination ICS/LABA treatment . In addition, there are safety concerns for regular use of 2-agonists in some patients, particularly those with the SNP in the 2-adrenergic receptor gene ADRB2 genotype . Some patients may associate ICSs with systemic side-effects, particularly in children, such as reduced bone density and growth . Long-acting anticholinergics can be a suitable add-on therapy for patients who remain symptomatic despite ICS and LABA therapy or who are unable to receive conventional therapies. The benefits seen with tiotropium add-on therapy in the subgroup analysis in patients with poorly controlled symptomatic asthma also suggest that a broad range of patients can benefit from anticholinergics, irrespective of baseline characteristics .
Recommended Reading: Can Someone With Asthma Take Cough Medicine
Strengths And Limitations Of The Study
This study met most of the methodological criteria suggested for scientific reviews. Similar to all systematic reviews, this meta-analysis is limited by the quality and quantity of existing research and how data are reported. A comprehensive search of the published literature for potentially relevant studies was conducted using a systematic strategy to avoid bias. All of the 32 trials were randomised, and 26 were double blind. Exclusion of trials with lower methodological quality did not affect the conclusions. Assessment of the consistency of effects across studies is an essential part of the review to determine the generalisability of the findings low values of heterogeneity were obtained in all group and subgroup comparisons. The generalisability of study results to different countries should also be considered, particularly with regard to the hospital admission criteria. The decision to admit patients is based on many factors including past asthma and current exacerbation histories and spirometric test results, as well as clinical factors. Important variations in admission criteria could therefore influence the results. However, the results did not change when we analysed only studies with explicit criteria for admission to hospital.
Box : Possible Pathophysiological Reasons Why Long
-
Cholinergic activity is the predominant driver of bronchial smooth muscle contraction, the primary cause of reversible airway obstruction in asthma
-
Patients with asthma have increased basal airway smooth muscle tone, possibly as a result of increased cholinergic tone,
-
Acute treatment with anticholinergic compounds reduces basal airway smooth muscle tone,
-
Local airway inflammatory mediators may have a role in inducing increased cholinergic tone,,
-
Cholinergic activity may have a prominent role in airway smooth muscle remodelling,,
-
Cholinergic receptors on lung submucosal cells regulate mucus secretion,,
-
Increased cholinergic and smooth muscle tone may contribute to airway hyper-responsiveness,,
-
Cholinergic antagonists may have non-neuronal anti-inflammatory actions
-
Patients with asthma may have abnormal muscarinic receptor expression
-
Patients with asthma may have increased release of acetylcholine from cholinergic nerve endings
-
Patients with asthma may have reduced levels of neuromodulators that attenuate cholinergic neurotransmission,
Don’t Miss: Can Seasonal Allergies Trigger Asthma
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms that affect your lungs. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, coughing or wheezing. They can order pulmonary function testing . Lung function tests help diagnose a lung condition that a bronchodilator may treat.
Its also a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider if you need to use SABAs more than twice per week. Using SABAs more than twice a week is a sign of unstable asthma. Your healthcare provider may wish to change the dose of any long-term control medicines that you take.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Lung conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affect your airways. Bronchodilators are medications that can help you control the symptoms of a lung condition.
Always follow your healthcare providers medication plan. If your bronchodilators arent controlling your symptoms, reach out to your healthcare provider right away. They can answer your questions, address any concerns and find the right care plan for you.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/09/2022.
References
Clinical Evidence Of Anticholinergic Bronchodilators In Asthma
Although tiotropium has been indicated for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease for over a decade, no long-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators are currently approved in asthma. A number of compounds exist, including aclidinium, glycopyrronium, glycopyrrolate and darotropium bromide, but, as mentioned, presently only tiotropium and umeclidinium have clinical trials in asthma listed on ClinicalTrials.gov. The latter has been under investigation in two dose-ranging Phase II trials in patients with asthma, as a monotherapy and in combination with fluticasone furoate , although to our knowledge no results from these trials have yet been published.
Early studies with long-acting anticholinergics in asthma were small and underpowered, and failed to detect meaningful responses. However, studies of tiotropium and of glycopyrrolate indicated that long-acting anticholinergics can provide sustained bronchodilation and bronchoprotection.,,,
To date, more thorough clinical evaluation has been performed with tiotropium only, in six Phase II or III studies, involving over 3,500 patients . In an investigator-initiated three-way crossover trial in 210 patients with asthma inadequately controlled by low-dose ICS , tiotropium delivered via the Spiriva HandiHaler device was shown to be superior to a doubling of ICS dose and equal to the addition of salmeterol, as assessed by improvements in lung function .
Read Also: What Is The Best Herbal Medicine For Asthma
Data Abstraction And Validity Assessment
Titles, abstracts, and citations were independently reviewed by two reviewers to assess potential relevance for full review. From the full text, both reviewers independently assessed studies for inclusion based on the criteria for population, intervention, study design and outcomes. Data extraction included the following items: Population: age, sex, number of patients studied, patient demographic data, withdrawals. Intervention: agent, dose, route of delivery, and duration of treatment. Control: concurrent treatments. Outcomes. Design: method of randomisation and allocation concealment. Any disagreement over study inclusion was resolved by consensus. The methodological quality of each trial was evaluated using the 5-point scale described by Jadad et al. This instrument assesses the adequacy of randomisation, blinding, and the handling of withdrawals and drop outs.
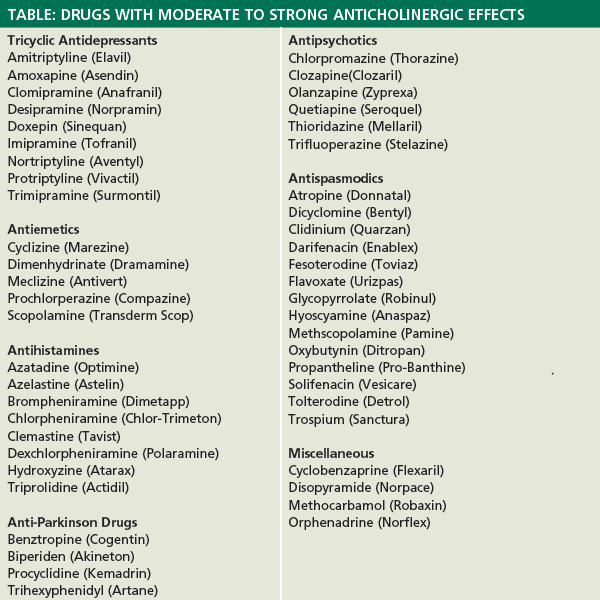
Drugs With Unintended Anticholinergic Effects
There are also drugs that can have anticholinergic effects that are unexpected.
They include certain antidepressants and antipsychotics that increase or decrease dopamine and serotonin, neurotransmitters to alter a persons mood. In some cases, and though unintended, the drugs can block acetylcholine and lead to anticholinergic side effects.
The challenge, of course, is that antidepressants and antipsychotics are often prescribed over the long term, making the management of symptoms all the more difficult.
Speak to your healthcare provider if you experience anticholinergic side effects while on any of these antidepressants or antipsychotics:
That said, there are times when low-dose antidepressants can be used to treat chronic pain and IBS. A similar effect is achieved with certain low-dose antipsychotics and Parkinson’s disease.
Also Check: Does Baby Powder Cause Asthma
Used For Muscle Spasms And Other Issues There Are Notable Cons To Consider
Anticholinergics are any drugs that block the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This chemical messenger is involved in involuntary muscle movements and certain functions of the body, such as digestion and urination.
Anticholinergic drugs can be beneficial in treating a wide array of health conditions ranging from allergies and depression to irritable bowel syndrome and Parkinson’s disease. However, given the extent of anticholinergic effects, these drugs can affect the body negatively too.
Side effects of anticholinergics include blurred vision, impaired coordination, and bowel leakage, to name a few. Long-term use is linked to dementia.
This article discusses different anticholinergic drugs, how they work, and how they are used. It also covers anticholinergic side effects and warnings to consider.
Bronchodilator Effects In Adults
A proof of concept double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover study aiming to evaluate the effects of halving ICS dosage adding salmeterol, or salmeterol plus tiotropium was conducted in 2007 . Eighteen non-smoking severe asthmatics were run-in for 4 weeks on HFA-fluticasone propionate 1000 mcg daily, and were then randomised to 4 weeks of either HFA-fluticasone propionate 500 mcg twice a day + salmeterol 100 mcg twice a day + HFA-tiotropium bromide 18 mcg once a day or fluticasone propionate 500 mcg twice a day + salmeterol 100 mcg twice a day + matched placebo. Spirometry and body plethysmography were performed. Adding salmeterol to half the dose of fluticasone led to a significant improvement vs. baseline in the morning peak expiratory flow and airway resistance . The combination salmeterol/tiotropium produced similar improvements in PEF and RAW, but also significantly improved the forced expiratory volume in the first second by 0.17 l , FVC 0.24 l and reduced fraction exhaled NO by 2.86 ppb .
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Dupixent Work For Asthma
Clinical Data Of Anticholinergics In Airway Inflammation And Remodelling
There are limited clinical data to explain the role of anticholinergics in airway inflammation and remodelling in patients with asthma. A clinical study in patients with symptomatic asthma receiving ICS and LABA assessed the effect of tiotropium on airway geometry and inflammation. Tiotropium significantly decreased airway wall area and thickness, corrected for body surface area , and improved airflow obstruction. These data suggest a potential protective effect of tiotropium against bronchoconstriction and airway remodelling . Patients with severe asthma have shown improved symptoms and lung function with tiotropium add-on to ICS, which suggests a role in reducing airway inflammation . The clinical data of anticholinergics in asthma are summarised later in this review.
Why It Is Used
Inhaled anticholinergics are usually used for severeasthma attacks. They are sometimes used in the home, but they are not used as daily maintenance treatment for persistentasthma. And they are sometimes used with another medicine.
Anticholinergics may be used:
- Along with short-acting beta2-agonists to treat severe asthma attacks orstatus asthmaticus, a long-lasting and severe asthma attack that does not respond to standard treatment.
- As an added medicine used after short-acting beta2-agonists during an asthma attack. The combination may relieve symptoms for a longer period of time.
Medicine treatment for asthma depends on a person’s age, his or her type of asthma, and how well the treatment is controlling asthma symptoms.
- Children up to age 4 usually are treated a little differently from those 5 to 11 years old.
- The least amount of medicine that controls the asthma symptoms is used.
- The amount of medicine and number of medicines are increased in steps. So if asthma is not controlled at a low dose of one controller medicine, the dose may be increased. Or another medicine may be added.
- If the asthma has been under control for several months at a certain dose of medicine, the dose may be reduced. This can help find the least amount of medicine that will control the asthma.
- Quick-relief medicine is used to treat asthma attacks. But if you or your child needs to use quick-relief medicine a lot, the amount and number of controller medicines may be changed.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Rid Of Asthma
Is There A Role For Long
Is it possible to determine to which patients, and in which clinical situations, long-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators might offer clinical benefits? Phase III investigation has found that tiotropium add-on therapy offers advantages to adults with severe asthma who are failing to gain control on ICS and LABA combinations. This, and the fact that the benefit:risk ratio of ICS falls at high ICS doses,,,,, suggests that addition of long-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators to ICS plus a LABA is likely to be a useful option for patients with poorly controlled severe asthma, and an alternative to further increases in ICS dose.
Whether long-acting anticholinergics will be appropriate as alternatives to LABAs is a harder question to answer. Nevertheless, tiotropium add-on to medium-dose ICS has been shown to provide lung function and ACQ-7 improvements that were comparable with those of salmeterol,, indicating that, in patients for whom LABAs may be unsuitable, long-acting anticholinergics could be a helpful alternative.
It is yet to be determined in Phase III investigation whether long-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators offer similar benefits to adults with mild asthma or to children or adolescents, although several Phase III trials are underway with tiotropium in these populations .
Downstream Effects Of Increased Acetylcholine Signalling: Mechanisms And Therapeutic Implications
Bronchoconstriction
In a guinea pig model of acute allergic asthma, tiotropium even reverses and protects against allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness . A clinical study comparing the effectiveness of indacaterol/tiotropium and indacaterol ) on mannitol-induced airway responsiveness found no additional effect of tiotropium on top of indacaterol on mannitol median effective dose , whereas sulfur dioxide-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic subjects is subject to cholinergic control . Thus, whereas it is clear that acetylcholine contributes to bronchoconstriction in asthma, the contribution of the cholinergic reflex arc to airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma is not extensively reported and needs further study.
Increased mucus secretion
In vivo data have shown that when sensitised M3 receptor-deficient mice were exposed to allergen challenge, they had a 30% lower increase in goblet cells compared with wild-type mice . They also showed a significantly lower increase in the mucus-producing gene MUC5AC compared with wild-type mice . Treatment with tiotropium in sensitised guinea pigs also completely prevented allergen-induced mucus gland hypertrophy , a finding that was also reported for house dust mite-induced responses in mice . Repeated exposure of mice to cholinergic agonists also promoted goblet cell presence in the airway epithelium .
Airway inflammation
Airway remodelling
Read Also: What Do You Do When You Have An Asthma Attack
How Do I Use A Bronchodilator Inhaler
Its important to use your bronchodilator inhaler properly to get the full medication dosage. The following steps will help you properly use your bronchodilator inhaler:
Pharmacologic Characteristics Of Tiotropium Bromide And Its Administration
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter which is released from the neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system in several tissues, including the lung. Acetylcholine stimulates smooth muscle contraction and mucus secretion through M1 to M5 muscarinic receptors .
Beyond bronchoconstriction, acetylcholine also regulates airway inflammation and remodeling .
Anticholinergic agents are antiasthma medications. Initially, most of the literature was focused on the use of the short-acting anticholinergic ipratropium bromide, a medication predominantly used in combination with SABA to treat bronchoconstriction during asthma exacerbations . In 1989, the tiotropium bromide was patented and then approved for medical use in the form of inhalation powder in 2002 as LAMA bronchodilator drug .
Figure 1. Moulecular structure of tiotropium.
A pharmacokinetic study in children aged 611 years old demonstrated that tiotropium bromide is rapidly absorbed following inhalation and then excreted into urine , confirming that systemic exposure of children to the medication is within the range observed in adults .
Tiotropium bromide is administered through the Respimat© inhaler . Most children aged 6 years can use a Respimat© inhaler without a valved spacer device but younger children should use the Respimat in combination with a valved spacer .
Figure 2. Externarl structure of Respimat© inhaler.
Figure 3. Internal structure of Respimat© inhaler.
Don’t Miss: Is Asthma Dangerous During Pregnancy
