Patients At Risk For Severe Asthma Exacerbations
Careful consideration should be carried out in patients with risk factors for severe asthma exacerbations. Patients with exacerbations that led to endotracheal intubation, previous admissions to the ICU, a history of multiple hospitalizations in the past year or multiple emergency department visits in the past month, the need of chronic oral corticosteroids use, poor access to health care, and frequent use of rescue inhalers are considered to have increased risk of severe asthma exacerbations and death. Patients with asthma and with these characteristics should be evaluated promptly and treated expeditiously. In addition, a minority of patients with asthma may experience a significant decline in lung function without a change in symptoms. These under-perceivers are at higher risk for near-fatal exacerbations. This article focuses on the approach to manage exacerbations of asthma.
Asthma Symptoms In A Severe Allergic Reaction
People having a severe allergic reaction can also have asthma-like symptoms. If the person has an anaphylaxis action plan, follow the instructions. If they have known severe allergies and carry an adrenaline autoinjector , use that before using asthma reliever medication.In case of an emergency, call triple zero and ask for an ambulance.
Also Check: Does Ibuprofen Make Allergies Worse
Will My Wheezing Or Coughing Be Worse
Not necessarily. You might be surprised to learn that you may not have more of these than usual during a severe asthma attack. So donât judge how bad your asthma attack is based on how much you wheeze or cough.
In fact, very severe asthma attacks may affect your airways so much that you donât get enough air in and out of your lungs to make a wheezing sound or cough.
Also Check: Allergy And Asthma Clinic Tuscaloosa
Fungal Infections And Acute Exacerbations Of Bronchial Asthma
The role of fungi and mold in AEBA is much less clear than viral and bacterial infections. It has been shown that fungal sensitization increases the risk of having more severe asthma and the risk of dying in asthma patients increases with increased spore exposure . Additionally, fungal sensitivity to Aspergillus and Clasdosporium species increases the risk of adult-onset asthma . The term severe asthma associated with fungal sensitization has been previously coined to describe patients with fungal sensitivity and persistent severe asthma who have some improvement with antifungal therapy . Denning et al. demonstrated a significant improvement in quality of life in patients with SAFS who were treated with oral itraconazole for 8 months . More specifically, sensitivity to Aspergillus fumigatus has been directly linked to severe persistent asthma in adults and is the cause of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis . Both oral corticosteroids and antifungal therapies have been shown to be partially successful in controlling symptoms of ABPA including improving asthma related symptoms.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of An Asthma Attack
Epidemiology Of Viral Infections In Aeba
Viruses are the most common cause of upper respiratory infections and lower respiratory tract infections in both children and adults. URIs occur frequently in children and most adults experience 24 URIs per year . The role of viral infections in acute exacerbations of asthma is well known with approximately 85 % to 95 % of acute exacerbation of bronchial asthma in children caused by viral infections and up to 60 % of asthma exacerbations in adults related to upper respiratory tract infections . Recent advances in the detection of viral DNA and RNA, e.g., viral respiratory panel, have helped to confirm this data with a significant increase in the weighted average of viral identification noted in patients of all ages with asthma exacerbation . The main features of viruses that may impact asthma are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Main features of viruses that may impact asthma
You May Like: Is Tea Good For Asthma
Recommended Reading: What Are The Worst Cities For Asthma
Asthma Peak Week: How To Exercise Safely With Asthma
The third week of September is known as Asthma Peak Week, the week with the highest numbers of asthma attacks and hospitalizations every year. Allergen levels are at their highest this week, particularly common allergens like ragweed pollen, dust, and mold, and this can make any activity difficult. You might be reluctant to work out, but regular exercise can improve asthma symptoms by increasing lung capacity and reducing inflammation. A well-considered exercise plan guided by a medical professional is vital to ensuring you can exercise safely with asthma, so read on to learn what to discuss with your doctor about creating an exercise plan for you!
You May Like: Asthma Weight Gain
What You Need To Know About Your Childs Asthma
There are many things to think about and plan for when your child has asthma. It is important to learn as much as you can about the condition. Your doctor and pharmacist are there to help you. Talk to them about any concerns you may have about your childs asthma. To manage your childs asthma effectively, it is important to know:
- the pattern of their asthma
- their asthma medications what they do and how to help your child take them properly
- what to do if they have an asthma attack know and follow asthma first aid.
Make sure you have an updated written asthma action plan and understand how to use it.
Donât Miss: What To Do When Someone Has An Asthma Attack
Also Check: Does Asthma Cause Shortness Of Breath
Initial Therapy Of Asthma Exacerbation In Children Older Than 2 Years
- The first-line therapy: age-related doses of salbutamol through the aerosol metered dose inhaler with a spacer or nebulizer. The inhalation therapy is immediately started with 2-4 doses of the short-acting 2-agonist with aerosol metered dose inhaler with a spacer or nebulizer
- In mild and moderate aggravation, the effectiveness of short-acting beta2-agonists therapy in the form of aerosol metered dose inhaler with a spacer is similar to that of a nebulizer
- If the symptoms are not amenable to treatment with salbutamol, then use Berodual
- Double the dose of basic therapy for 5-7-10-14 days . If exacerbation is severe, you can go a step higher in the treatment for at least 3 months
- If bronchodilators are inefficient , at the time of exacerbation you can add budesonide suspension through the nebulizer
- In children with exacerbation of asthma which is not controlled by inhalation of Berodual through aerosol metered dose inhaler with a spacer to 6-8 doses/day, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Additional doses of bronchodilators are given as needed while waiting for the doctor
- At the time of delivery of a child with a severe asthma attack in the emergency department, a bronchodilator + suspension of budesonide through a nebulizer, inhalation with oxygen are prescribed
- Berodual is canceled if inhalation of short-acting 2-agonists is required more than 4 hours later. In this case, youd better use salbutamol.
Also Check: Do Chihuahuas Help With Allergies
The Role Of Bacterial Infections In Asthma And Aeba
When compared to viral respiratory infections, bacterial infections play a smaller and less significant role. Studies in children reveal that bacterial infections only seem to play a small role in acute asthma exacerbations with only a slightly increased incidence in adult populations. In patients suffering from an AEBA, only 27 % had bacteria isolated in their sputum, with Streptoccoccus pneumoniae, Streptoccoccus aureus, and Moraxella cattarhalis being the most commonly isolated organisms . A more recent study looking for Mycoplasma pneumoniae as an etiology of AEBA found positive sputum cultures in 53 % of patients with acute asthma exacerbations with S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, and M. pneumoniae found in decreasing order of prevalence . However, results of how often bacteria were isolated in controls were not provided.
You May Like: Connecticut Asthma And Allergy Avon
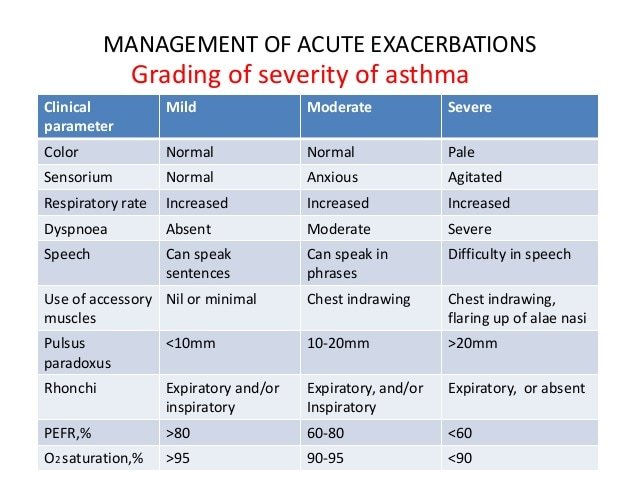
Assessment Of The Severity Of Asthma Attack
The severity of the asthma attack must be rapidly evaluated by the following clinical criteria. Not all signs are necessarily present.
Assessment of severity in children over 2 years and adults
|
Able to talk in sentences Respiratory rate |
Cannot complete sentences in one breathorToo breathless to talk or feed |
Altered level of consciousness Exhaustion Bradycardia in children or arrhythmia/hypotension in adults SpO2 < 92% |
Treatment and follow-up depend on the severity of the attack and the patients response:
Acute Exacerbations Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Similar to asthma exacerbations, most AECOPDs are caused by common respiratory viruses . Because vitamin D-mediated immune mechanisms appear to play a role in the prevention of viral ARI, vitamin D supplementation might be helpful against AECOPD. However, AECOPD is a more complicated phenomenon than asthma exacerbation. For starters, AECOPD often involve both viruses and bacteria . Moreover, the typical COPD patient is older and more likely to suffer from other relevant smoking-related comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disease . Nevertheless, the question remains: does vitamin D supplementation lower the risk of AECOPD?
In 2012, Kunisaki and colleagues analyzed data from an azithromycin trial of exacerbation-prone patients with COPD to examine the longitudinal association between baseline 25D levels and risk of AECOPD over 1 year . Contrary to their hypothesis, baseline 25D levels were unrelated to risk of AECOPD in their observational study of this high-risk population. Similarly null findings were reported in a 2014 study by Puhan and colleagues from the Netherlands and Switzerland and in the previously cited 2015 study by Persson and colleagues in Norway . Taken together, these observational studies do not support a role for vitamin D supplementation in the prevention of AECOPD.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Someone With Asthma Without An Inhaler
Don’t Miss: What Sounds Might You Hear During An Asthma Exacerbation
Assessment Of Respiratory Distress
Effective treatment depends on an accurate and rapid assessment of disease severity and the elimination of other differential diagnoses . Assessment should include:
- Signs and symptoms of respiratory distress and airway obstruction, including documentation of vital signs. Pulse oximetry should be used in all patients. Pulse oxygen saturation of 92% or less on presentation is associated with higher morbidity and ED management failure .
- A focused asthma history recording triggers for exacerbation, previous medications and risk factors for ICU admission and death :
- Previous life-threatening events, admissions to an intensive care unit , intubation
- Hospitalizations or ED visits for asthma in the last year
- Deterioration while on, or recently after stopping, systemic steroids
- Using > 1 canister of salbutamol per month
- Lack of an asthma action plan or poor adherence to treatment
- Low socioeconomic status, psychosocial concerns
Particularly when risk factors are identified, prompt and aggressive treatment is indicated, and caution should be used in determining readiness for discharge. Early consultation with a tertiary care paediatric ED and/or paediatric intensive care unit specialist to discuss patient management and transport when response to treatment is insufficient is advised.
Recommended Reading: Can Asthma Make Your Heart Race
Environmental Factors: Indoor/outdoor Air Pollution And Occupational Factors

Outdoor air pollution is an established risk factor for asthma exacerbations, although the magnitude of effect remains difficult to assess precisely . Diesel exhaust particles and peaks of ambient air pollution, were shown as concomitant factors to emergency department attendance in asthmatics but also could be epidemiologically related to asthma exacerbations and deaths . Work-related exacerbations are probably underestimated, whereas many different non-specific irritants could be identified, such as mineral dusts, gas and fumes, etc. .
Indoor air pollution comprises second-hand tobacco smoke exposure, which is of special interest in children, and other less well-known contributors, such as volatile organic compounds . Open fireplaces, sick building syndrome, cleaning supplies and household products, and inadequate ventilation are also to be integrated into potential sources of indoor air pollution. We propose to test whether facilitating access to air quality data records may prevent asthma exacerbations. The ELF, while reviewing the present manuscript, supports the use of portable air quality sensors, but more research is needed to identify what substances should be monitored and how best to do this.
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Asthma
What Is Asthma Attack
Asthma can flare-ups are when asthma symptoms get worse. They happen when airways get more irritated and inflamed than usual.
During an asthma attack , you might have:
- trouble breathing
- a whistling sound while breathing
- a fast heartbeat
Some flare-ups are serious, but others are mild. Flare-ups can happen suddenly or build up over time, especially if people dont take their asthma medicines as directed.
Things that bring on a flare-up are called triggers. Triggers vary from person to person, but common ones include:
- allergies to things like pollen, mold, and pet dander
- irritants and pollutants in the air
- respiratory infections, like colds or flu
- weather conditions
- gastroesophageal reflux
An important part of managing asthma is avoiding triggers. Your childs doctor will work with you to create a care plan that helps prevent flare-ups as much as possible.
Also Check: How To Treat Asthma Attack
Table 1 Inflammatory Cells Involved In Asthma
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel report 3 : Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma Full Report 2007 pg 16-18 Kraft M. N Engl J Med. 2011 365:1141-1144 Berger A. BMJ. 1999 319:90.
Medications that block interleukins are under investigation right now.10,11 These medications may be helpful for people with moderate to severe asthma and high eosinophil levels.
Recommended Reading: Athletically Induced Asthma
Also Check: Is Asthma An Auto Immune Disease
Types Of Asthma And Biomarkers
Types of asthma and biomarkers
In adults, two common types of asthma are distinguished: allergic asthma, where there is a clear relationship to allergy, and intrinsic or eosinophilic asthma, which usually starts in adulthood without evidence of any relevant allergies.
In adults, two common types of asthma are distinguished. The first is allergic asthma, where there is a clear relationship with allergy. Onset is often during childhood or adolescence and often accompanied by allergic rhinitis and/or atopic dermatitis this form is known as early-onset asthma. The second is an intrinsic type, usually with onset in adulthood and usually without evidence of any relevant allergies this form is referred to as adult-onset or late-onset asthma) . In both types of asthma, an increased level of typical cytokines and eosinophil granulocytes is found, together with dysfunction of structural cells characteristics referred to collectively under the name type 2 asthma . The inflammation can be measured through biomarkers . Routine diagnostic procedures covered by statutory health insurance carriers in Germany include blood eosinophil count and allergy markers fractional exhaled NO measurement is available as a self-pay option. It should be noted that these biomarkers can be falsified: for example, eosinophil counts can be greatly reduced by inhaled or oral steroids and FeNO levels by tobacco smoke .
Role Of Chlamydia Pneumonia And M Pneumonia In Aeba
Both C. pneumonia and M. pneumonia have been shown to be the cause of URIs, pneumonia, and acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Their role in AEBA and critical asthma syndrome has not been definitively established. Lieberman et al. demonstrated evidence of acute infection with M. pneumoniae in 18 patients hospitalized for AEBA compared with 3 % in control group. In 10 of these patients, however, there was evidence of infection with at least one additional pathogen , thus their impact is confounded by this co-infection .
Several other studies have implicated chlamydia infection in more serious AEBA. C. pneumoniae has been identified as a single agent in 19 of 58 patients with acute exacerbation of asthma and the presence of CP IgG or IgA titers was fourfold higher in patients with acute asthma when compared to controls . The severity of AEBA has also been shown to be much more severe with C. pneumoniae and M. pneumoniae. Functional impairment on hospital admission, persistent reduction in FEV1, and the proportion of patients with severe AEBA were greater in the group with atypical infections compared to groups without atypical infections . None of the patients in this study met criteria for critical asthma syndrome.
You May Like: Are Chihuahuas Good For Asthma
Inhaled Corticosteroids And Long
In patients with poorly controlled asthma and a history of prior asthma exacerbations, the combination of budesonide and formoterol significantly reduces asthma exacerbations compared with ICS alone.50 ICS/LABA have consistently been shown to prevent exacerbations.69, 70, 71 The benefit of ICS/LABA to prevent exacerbations versus ICS alone is primarily seen in patients requiring higher doses of ICS, thus suggesting that combination therapy to prevent exacerbations should be reserved for patients with more severe disease.
Asthma control can vary even in the face of ongoing ICS/LABA treatment. Consequently, the use of ICS/LABA combinations both for maintenance and symptom relief has been investigated and shown to reduce exacerbations.72, 73, 74 These benefits are also seen in children with a prior history of severe asthma exacerbations and poorly controlled moderate-to-severe persistent asthma despite the use of moderate doses of ICS.75 The use of ICS/LABA as maintenance and reliever treatment should be restricted to formoterol because of its quick onset of action,76 safety profile,77 and dose-response effect.78
The Role Of Antibiotics In Severe Asthma Exacerbations And Critical Asthma Syndrome
The role of antibiotics in acute severe AEBA and critical asthma syndrome is very limited. One study evaluating the value of anti-bacterial antibiotics in 60 adults with AEBA found no difference in length of hospital stay, time taken for 50 % improvement in symptoms and symptoms and respiratory function at the time of discharge . Another study in children admitted with status asthmaticus or critical asthma syndrome without signs of bacterial infection found no benefit in hospital course, complications or duration of hospital stay . However, the additional benefits of antibiotics may play a role that underlies their direct antibacterial effect.
Overall, the role of empiric antibiotic therapy without clear evidence of a bacterial trigger for an acute severe asthma exacerbation and critical asthma syndrome is unclear. Bacterial pathogens play a lesser role when compared to viral agents, but both typical and atypical bacteria are found with relative frequency. During the initial management moments of an acute severe exacerbation or critical asthma syndrome, the etiology, particularly an infectious one, may not be clearly evident. An approach to the use of antibiotics and antiviral therapy in severe AEBA is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1
You May Like: What To Do When Someone Has An Asthma Attack
