Why Is There Overlap Why Does It Occur
Overlapping asthma and COPD could occur for several reasons. Asthma and COPD are two common conditions, and by chance alone there will be overlap. The two conditions may also share common risk factors or origins, which means that one may evolve into the other. One expression of this possibility, the âDutch hypothesisâ, was proposed by Orie who suggested that BHR may be a risk factor for asthma and COPD. Another expression of the common risk hypothesis for overlap syndrome comes from the study of childhood diseases. Epidemiological studies have identified an association between childhood respiratory illness and impaired adult lung function. Airway growth starts in utero and continues throughout childhood into early adult years. Any diseases or exposures that lead to incomplete airway growth may also contribute to impaired adult lung function. In this way, fetal or childhood exposures may contribute to adult asthma and COPD.
Susceptibility genes
Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
The CCDSS is a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in the health insurance registries thus, the CCDSS coverage is near-universal with the exception of some small populations. Case definitions are applied to these linked databases and data are then aggregated at the provincial and territorial level before being submitted to PHAC for reporting at the provincial, territorial and national levels.
The CCDSS has expanded from its initial mandate of diabetes surveillance to include data on several additional chronic diseases and conditions including: hypertension, mental illness, mood and/or anxiety disorders, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, osteoporosis, arthritis and neurological conditions. Asthma and COPD were added to the CCDSS in 2012.
The data presented in this report and subsequent updates can be accessed on the Public Health Agency of Canada’s Public Health Infobase.
Whos Likely To Have Asthma Copd Or Aco
People who smoke or breathe in pollution or chemicals at work for many years have higher chances of having COPD. That’s why the condition often starts in middle age or later in life.
Asthma is sometimes caused by gene changes that are passed down through families. If one of your parents has the disease, you’re more likely to have it.
Symptoms of asthma often start in childhood, and the condition is one of the most widespread long-term illnesses in kids. It affects about 1 in 10 children.
Besides a family history of the condition, a few things can raise your chances of asthma:
- Smoking
- Being around chemicals or other irritants in the air
People who get ACO tend to be over 40 but younger than people with just COPD, and they have allergies .
Read Also: Can I Join The Marines With Asthma
Why Is It Important
There are several reasons why the overlap syndrome is important. First, patients with overlapping asthma and COPD are excluded from clinical trials of treatment. This means that for an increasing proportion of older patients with obstructive lung disease, the data on efficacy of treatment may not be relevant. The clearest example of this comes from the studies on the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. These studies typically exclude smokers with asthma because of the difficulty in separating asthma from COPD in smokers with obstructive lung disease. However, up to 30% of people with asthma are smokers, and this means a substantial proportion of the population are excluded from randomised controlled trials. Extrapolation of the efficacy results for corticosteroids in non-smokers to smokers with asthma is flawed. Smokers with asthma have a relative corticosteroid resistance such that corticosteroids are much less efficacious in smokers with asthma than in non-smokers with asthma. This emphasises the need to study drug efficacy in relevant clinical populations, and the necessity to include overlap syndrome in drug evaluation programmes.
Inflammatory Mediators Involved In Asthma
Chemokines are important in the recruitment of inflammatory cells into the airways and are mainly expressed in airway epithelial cells . Eotaxin is selective for eosinophils, whereas thymus and activationregulated chemokines and macrophage-derived chemokines recruit Th2 cells . Cysteinyl leukotrienes are potent bronchoconstrictors and proinflammatory mediators mainly derived from mast cells and eosinophils . Cytokines orchestrate the inflammatory response in asthma. Key cytokines include IL-1 and TNF, and GM-CSF. Th2-derived cytokines include IL-5, which is required for eosinophil differentiation and survival IL-4, which is important for Th2 cell differentiation and IL-13, needed for IgE formation . Histamine is released from mast cells and contributes to bronchoconstriction and inflammation . Nitric oxide , a potent vasodilator, is produced from syntheses in airway epithelial cells . Exhaled NO is increasingly being used to monitor the effectiveness of asthma treatment . Prostaglandin D2 is a bronchoconstrictor derived predominantly from mast cells and is involved in Th2 cell recruitment to the airways .
Airway structural cells involved in the pathogenesis of asthma are: airway epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts and airway nerves .
Don’t Miss: Severe Eosinophilic Asthma
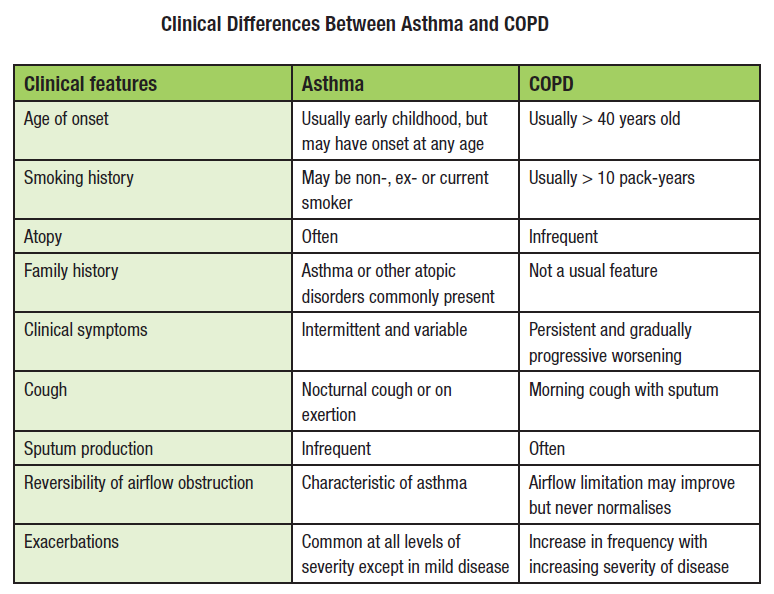
What Is The Difference Between Asthma And Copd
Asthma is a respiratory disease affecting the bronchial tubes, or airways, making them sensitive to allergens or irritants, both of which can bring on an asthma attack. During an asthma attack, it is hard to breathe, and wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness may occur. While COPD can also cause these symptoms, its more likely to experience a consistent cough with phlegm.
Unlike asthma, COPD is a chronic condition caused by damage to the lungs over time, most often from smoking, and it is irreversible. With asthma, breathing returns to normal after an attack, but COPD symptoms are more regular. Usually, COPD develops in people after age 40 and becomes a chronic disease of lung function while asthma may develop in people of almost any age.
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For A Person Copd Vs Asthma
The prognosis for COPD ranges from fair to poor and depends on how rapidly COPD advances over time. In general, individuals with COPD have a decrease in their lifespan according to research.
If you have asthma, the prognosis for most people ranges from fair to excellent, depending upon how well you can identify what triggers your attacks, and your response to medication.
You May Like: Asthma Research Paper
Staging And Treatment Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
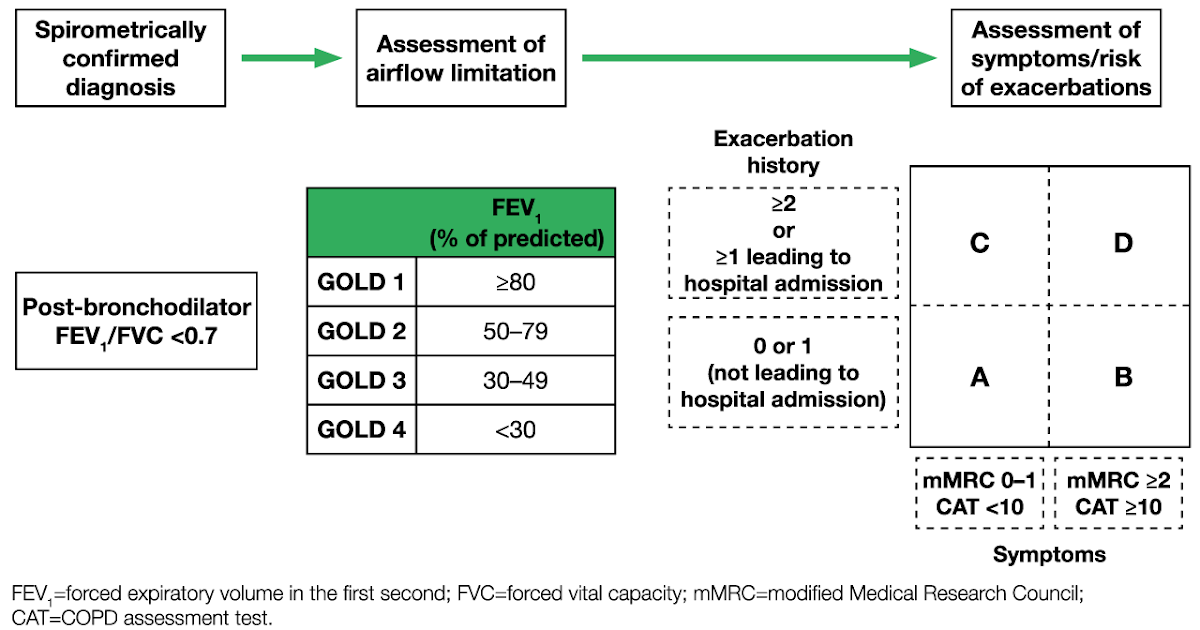
The stages of COPD are defined primarily by lung function . This emphasises the important clinical message that the diagnosis of COPD requires the measurement of lung function. The stages of COPD suggested in the GOLD Guidelines are as follows. Stage 0: At risk, cough or sputum present but lung function normal. Stage 1: Mild COPD, FEV1/forced vital capacity < 70%, with an FEV1 â¥80% predicted, with or without chronic symptoms. Stage 2: Moderate COPD, FEV1/FVC < 70% and FEV1 % pred> 30% and < 80%. Stage 2 is split at an FEV1 of 50% pred since the existing data support the value of inhaled corticosteroids below an FEV1 of 50% pred but not above. Stage 3: Severe COPD, FEV1< 30% pred and FEV1/FVC < 70%.
In the GOLD guidelines, Stage 0 is a newly defined stage that was included to give a strong public health message that symptoms of chronic cough and sputum production should alert the clinician to the presence ofan ongoing pathophysiological process even when lung function is normal. This may progress to clinically significant COPD in a proportion of those exposed . The analogy that is perhaps most relevant is that mild hypertension in some but not all , with mild elevation of blood pressure will progress to clinically significant hypertension.
Diagnosing Asthma And Copd
With all the similarities between asthma and COPD symptoms, it can be challenging to diagnose each disease correctly without mistaking one for the other. Asthma is the most common alternative diagnosis for COPD. However, it is important to correctly identify which condition a patient is dealing with so they can receive the proper treatment.
When a patient has symptoms that pertain to both asthma and COPD, there are a few key factors that differentiate the two. To develop an accurate diagnosis, medical professionals will ask patients dealing with breathing issues specific questions about their symptoms, such as what time of day they feel the worst. They will also inquire about the patient’s medical, family and smoking histories and exposure to irritants, as well as gases or vapors.
Don’t Miss: Weed For Asthma
Inflammatory Cells In Copd
Neutrophils are present in sputum of smokers but increased in COPD and related to disease severity. They may be important in mucus hypersecretion and through release of proteases. Macrophages: big numbers are in airway lumen, lung parenchyma, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. They produce increased inflammatory mediators and proteases and may show defective phagocytosis. T lymphocytes: both CD4+ and CD8+ cells are increased in the airway wall and lung parenchyma, with big CD8+/CD4+ ratio. Increased is the number of CD8+ T cells and Th1 cells which secrete interferon- and express the chemokine receptor CXCR3. CD8+ cells may be cytotoxic to alveolar cells. B lymphocytes: are increased in peripheral airways and within lymphoid follicles, possibly as a response to colonization and infection. Eosinophils: increased eosinophil proteins in sputum and eosinophils in airway wall during exacerbations. Epithelial cells: May be activated by cigarette smoke to produce inflammatory mediators .
Differences Between Copd And Asthma
There are a number of other differences between COPD and asthma as well.
-
Often diagnosed during childhood or adolescence
-
Symptoms more likely to occur episodically and/or at night
-
Commonly triggered by allergens, cold air, exercise
-
People who have asthma are more commonly nonsmokers
-
Comorbid conditions include eczema and allergic rhinitis
-
Treatment usually involves inhaled steroids
-
Airflow restriction mostly reversible
-
Likely to cause morning cough, increased sputum, and persistent symptoms
-
Exacerbations commonly triggered by pneumonia and flu or pollutants
-
Most people who have COPD have smoked or had significant secondhand smoke exposure
-
Comorbid conditions include coronary heart disease or osteoporosis
-
Treatment usually involves pulmonary rehabilitation
-
Airflow restriction is permanent or only partially reversible
Once you develop COPD, your symptoms will generally be chronic. Over time, with COPD, you are likely to experience symptoms that are not typical for asthmalosing weight, decreased strength, and diminished endurance, functional capacity, and quality of life.
Read Also: Does Ibuprofen Make Asthma Worse
Is It Asthma Copd Or Both
Both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, make breathing difficult. In fact, they share many similarities. However, they are different lung diseases. Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome is diagnosed when you have symptoms of both asthma and COPD. ACOS is not a separate disease, but rather a way for doctors to recognize the mix of symptoms and select a treatment plan that is most appropriate for you.
Symptoms And Signs Of Copd And Asthma
COPD
COPD symptoms differ on the basis of disease severity . Most patients with COPD usually first develop a chronic productive cough. However, dyspnea is the hallmark symptom of COPD and usually prompts patients to seek medical care. As disease severity progresses, cough and dyspnea result in decreased exercise tolerance and increased disability. COPD mainly affects the lungs however, notable systemic effects are also associated with COPD. Patients with COPD often experience changes in their metabolism and in caloric intake. Indeed, 50% of patients with severe disease experience weight loss, which is associated with a poorer prognosis.3 Patients with COPD also develop decreased strength, decreased exercise capacity and a reduced quality of life.3 COPD is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, respiratory infections, osteoporosis and glaucoma.
Asthma
Physiologic changes associated with asthma include bronchoconstriction, airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation. Therefore, patients with asthma typically develop wheezing, shortness of breath and cough. Because asthma is also characterized by reversible airway obstruction, its symptoms are intermittent and cover a spectrum from mild-to-severe disease.
Several symptoms overlap in patients with COPD and asthma. Nevertheless, a history of wheezing strongly suggests a diagnosis of asthma, whereas chronic cough productive of sputum is more indicative of COPD.
Also Check: Asthmatic Bronchitis Definition
Causes Of Copd And Asthma
Host Factors
Risk factors for both COPD and asthma can be categorized as host and environmental factors. The genetic risk factor that has been most closely linked to COPD is a rare deficiency of 1-antitrypsin. Because only 15% of smokers go on to develop COPD, genetics and other susceptibility factors are thought to play an important role. Polymorphisms in genes related to proteases, antioxidants and inflammation have been found to relate to some of the features characteristic of COPD. Polymorphisms in any of three classes of proteases, the serine proteases, cysteine proteases, and matrix metalloproteinases may lead to development of COPD.15 Antioxidant enzymes known to be present in the airways include glutathione-S-transferase, superoxide dismutase and catalase. Cigarettes smoke causes a large number of free radicals, and alterations in these enzymes may also raise susceptibility to COPD. Many pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-a, IL-1, IL6 and TGF-ß are also felt to be important in the development of COPD. A candidate genethe promoter polymorphism-1111 in the interleukin-13 genewas identified in populations with either COPD or asthma. This finding provides additional evidence in support of a genetic susceptibility to COPD and asthma.
Infection with rhinovirus especially in children who have a persistent allergic diathesis is the more common infection to lead to airway hyperactivity .
Environmental Factors
Symptoms And Signs: 6 Similarities Between Copd Vs Asthma
COPD is caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants that damage lung cells. The main cause of COPD in the United States is cigarette smoke followed by other tobacco smoke . Other possible causes of COPD include chemical or toxic fumes, and inherited factors, like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, but these causes are far less common than cigarette smoking.
Although cigarette smoke may trigger asthma in some patients, asthma triggers are different from person to person, and most commonly include airborne substances such as pollen, dust, mites, mold spores, pet dander, and/or many other substances. Inflammatory immune reactions to asthma triggers in the airways is the main cause of asthma.
Also Check: Diy Inhaler
Staging And Treatment Of Asthma
The goals of long-term management of asthma should include the following: 1) achievement and maintenance of control of symptoms 2) prevention of asthma exacerbations 3) maintenance of pulmonary function as close to normal levels as possible 4) maintenance of normal activity levels, including exercise 5) avoidance of adverse effects from asthma medications 6) prevention of the development of irreversible airflow limitation and 7) prevention of asthma mortality.
The recommended GINA treatment algorithm, together with the clinical features and staging of severity of asthma, are available on the GINA website . It is important to note that the forced expiratory volume in one second levels are before treatment, i.e. in the unmedicated state.
Until the advent of anti-inflammatory drugs, asthma was treated on an as-needed basis and treated as an acute disease rather than a chronic disease. With the recognition that asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease, there has been a gradual move towards treating it more aggressively and earlier in the hope that this may change the natural history of asthma and prevent some of the remodelling that sometimes occurs.
Prevention Of Copd And Asthma
COPD
COPD is a preventable disease. Although primary prevention hinges on tobacco cessation strategies, secondary prevention of COPD centers on early diagnosis, risk factor modification and treatment. However, early diagnosis of COPD is often delayed. In 2002, the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 7 reported that approximately 24 million adults in the USA have evidence of impaired lung function on spirometry however, only about 50% of these patients have physician-diagnosed COPD, most of which is moderately advanced disease. At this late stage of disease, only tertiary prevention, aimed at preventing the complications of COPD, is effective. Therefore, primary and secondary prevention strategies need to be improved.
Better prevention of COPD can be achieved through compliance with guidelines. Numerous guidelines exist to assist physicians in early diagnosis, prevention of disease progression and management of COPD, including those of GOLD, the American Thoracic Society, the National Collaborating Center for Chronic Conditions and the Canadian Thoracic Society.
Asthma
Numerous guidelines are also available to aid physicians and other healthcare professionals to better prevent and manage asthma. Two frequently referenced guidelines are those of the NAEPP and the Global Initiative for Asthma .
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Which Is Worse: Copd Or Asthma
COPD is worse than asthma. With a well-designed treatment plan, asthma symptoms can be controlled sufficiently to return lung function to normal, or very close to normal, so the condition is generally considered reversible. Though COPD symptoms can be well-managed with various treatments, the respiratory disease is irreversible, so any damage impairing lung function that has occurred cannot be restored.
Airflow Limitation In Copd
The chronic airflow limitation of COPD is caused by a mixture of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction , the relative contributions of which vary from person to person . Chronic inflammation causes structural changes and narrowing of small airways. Destruction of the lung parenchyma, also by inflammatory processes, leads to the loss of alveolar attachments to the small airways and decreases lung elastic recoil in turn these changes diminish the ability of the airways to remain open during expiration .
So in COPD inflammation causes small airway disease and parenchymal destruction that all lead to airflow limitation .
Read Also: What Can Cause Asthma Exacerbation
Whats The Difference Between Copd And Asthma
They may cause similar symptoms, but COPD and asthma are far from the same condition. Find out about important COPD-asthma differences.
Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are just as familiar with these symptoms as people with asthma are, but the two conditions are actually very different from each other.
Its easy to mistake one condition for the other at first. After all, they have one big thing in common: The inability to get enough air into the lungs. Theyre also treated with some of the same medicines. So what makes them different?
Physical Changes: Common Threads, Distinct Differences
In some respects, the changes in the body that cause shortness of breath are similar between COPD and asthma. But a number of other COPD-asthma differences set the two conditions apart.
People who have COPD because of emphysema, meanwhile, have damaged air sacs in their lungs, which can lead to hyperinflation, or the inability of the lungs to return to their normal shape after expelling air. The lungs become swollen or expanded, says Anil Singh, MD, a pulmonary critical care specialist with Allegheny Health Network in Pittsburgh. That makes it hard to feel like youve caught your breath. Most people with COPD have a combination of both chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Age of Onset: Youngsters and Adults
Causes: Genetics, Habits, and More
Treatment: The Meds Are the Same, Other Therapies Differ
