Algorithms For Identifying Microscopic Polyangiitis
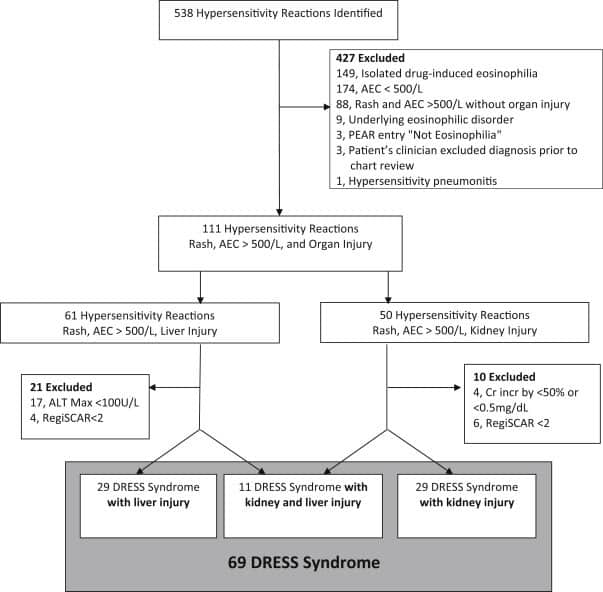
Of the 125 charts reviewed per algorithm-deriving healthcare system, 84 patients from System 1 and 116 patients from System 2 had sufficient data in their medical records to confirm or refute the diagnosis of MPA and were included in the analysis. 27/84 patients had a confirmed diagnosis of MPA at System 1 and 21/116 patients at System 2 based on the ACR criteria or the revised ICHCC definitions. Figure 3 shows the PPV and sensitivity of the 16 constructed case-finding algorithms for MPA. The PPV and sensitivity of the algorithms in each healthcare system are detailed in Supplementary Table 5. An algorithm including patients with one of the following diagnoses: 770.3 , 516.34 , 583.X , 584.X , or 585.X , the encounter type, the physician specialty, and the immunosuppressive medications had the highest average positive predictive value . Adding positivity for pANCA significantly increased the PPV across all algorithms but decreased sensitivity.
36 out of 2,151,960 were identified at System 3 using the algorithm with the highest average PPV listed above. 5 patients were excluded because of insufficient data to confirm or refute the diagnosis. 19/31 had a confirmed diagnosis of MPA. The PPV of this algorithm was 61.2% . Adding positivity for pANCA increased the PPV of this algorithm to 81.2% .
Therapeutics In Eosinophilic Asthma
Current management of eosinophilic asthma begins with standard guideline-based therapy, including inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilators which have been reviewed extensively elsewhere.63 Generally, the presence of eosinophils has been associated with responsiveness to corticosteroids although some patients with eosinophilic asthma have been reported to be steroid-refractory. Specific therapeutics targeting inflammatory mediators are currently under investigation in clinical trials for patients who have failed standard therapy and remain steroid-dependent or refractory.
Who Family Of International Classifications
The World Health Organization maintains several internationally endorsed classifications designed to facilitate the comparison of health related data within and across populations and over time as well as the compilation of nationally consistent data. This “Family of International Classifications” include three main classifications on basic parameters of health prepared by the organization and approved by the World Health Assembly for international use, as well as a number of derived and related classifications providing additional details. Some of these international standards have been revised and adapted by various countries for national use.
Recommended Reading: Atlanta Allergy And Asthma Northlake
Eosinophils In The Pathogenesis Of Asthma
Eosinophils have long been implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma. Post mortem pathologic studies of patients who have died from asthma attacks show airway mucosa infiltrated with activated eosinophils.10 Over 20 years ago, Bousquet et al published their findings demonstrating that chronic asthmatics had an increase in eosinophils in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, along with lung biopsy specimens that correlated with the severity of asthma.11 The presence of eosinophils in the airway lumen, as identified by sputum cell counts, has since been shown to be predictive of loss of asthma control after discontinuation of inhaled corticosteroids.12,13 Further, the persistence of eosinophils in sputum despite high doses of corticosteroids may also be a marker of disease severity.14 Generally, the eosinophilic phenotype is associated with a good response to corticosteroids and to T-helper type 2 targeted therapy, such as anti-interleukin -5 treatments discussed below.1517
Abbreviations: CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor homologous Th2 CystLTs, cysteinyl leukotrienes GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor IL, interleukin ILC2, innate lymphoid cell type 2 IgE, immunoglobulin E PGD2, prostaglandin D2 ROS, reactive oxygen species Siglec-8, sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 8 Th2, T-helper type 2 TGF-, transforming growth factor beta TSLP, thymic stromal lymphoprotein.
The Icd Code J82 Is Used To Code Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a disease in which an eosinophil, a type of white blood cell, accumulates in the lung. These cells cause disruption of the normal air spaces where oxygen is extracted from the atmosphere. Several different kinds of eosinophilic pneumonia exist and can occur in any age group. The most common symptoms include cough, fever, difficulty breathing, and sweating at night. EP is diagnosed by a combination of characteristic symptoms, findings on a physical examination by a health provider, and the results of blood tests and x-rays. Prognosis is excellent once most EP is recognized and treatment with corticosteroids is begun.
| Specialty: |
Recommended Reading: What Does Advair Do For Asthma
Diseases Of The Digestive Systemtype 2 Excludes
Agents Targeting Corticosteroid Resistance
Several mechanisms that may account for corticosteroid-resistant asthma have been reported including activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and inflammatory genes regulated through transcription factor nuclear factor-B.64 P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is important in the activation of GATA3, the master Th2 cytokine transcription factor.65 Small molecule p38 inhibitors have been demonstrated to attenuate asthmatic features in mice.65 However, clinical trials in humans for the treatment of inflammatory disease have been associated with substantial systemic side effects.66 Phosphoinositide 3-kinase also regulates inflammatory pathways, and activation of the isozyme PI3K by oxidative stress may decrease corticosteroid responsiveness through reductions in histone deacetylase 2, an enzyme targeted by theophylline.67 Other mechanisms for steroid-refractory asthma may include increased expression of the alternatively spliced variant of the glucocorticoid receptor and increased production of macrophage migratory inhibitory factor, which may block the anti-inflammatory effects of corticosteroids.67,68
Also Check: Can You Take Aspirin With Asthma
What Is The Cpt Code For Asthmatic Bronchitis
If the diagnosis is stated as exacerbated or acute chronic asthmatic bronchitis, code J44. 1 is assigned. A diagnosis of asthmatic bronchitis with COPD or chronic asthmatic bronchitis is coded to J44. Interstitial lung disease, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis, an autoimmune disease.
Diagnostic Evaluation Of Eosinophilic Asthma
Traditional guideline-based treatment decisions in asthma target symptoms and lung function, but specific therapies targeting the underlying inflammatory process may be needed in a subset of patients. Sputum eosinophils are an accurate reflection of Th2-dominant mechanisms in uncontrolled asthma, and eosinophilic asthma is generally defined by > 1%3% of eosinophils. Induced sputum is the most reliable measure of inflammatory cell counts although quantitative sputum cell counts are difficult to obtain in routine practice and require access to specific laboratories with trained personnel. The utility of several alternative markers of eosinophilic inflammation are currently being investigated including peripheral blood eosinophil counts, fractional exhaled nitric oxide , serum IgE, and periostin levels.
Recommended Reading: Can Stress Cause An Asthma Attack
Drg Mapping Rules For J8283
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patient’s primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient’s primary diagnostic code is J82.83, look in the list below to see which MDC’s “Assignment of Diagnosis Codes” is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patient’s discharge date.
Preparing For A Doctors Appointment
Patients with asthma or suspected asthma will likely be referred to an allergist or a pulmonologist. These tips may help you be more prepared for your appointment:
- Keep a log of symptoms you are having, even if they are seemingly unrelated.
- Bring a list of any prescription or over-the-counter medications you are taking. Donât forget to list vitamins and supplements, too.
- Jot down a list of questions, such as:
- What tests or procedures will be performed?
- How will my asthma be monitored?
- How should I use my medications? How should they be stored?
- What triggers might cause my asthma to flare? Is there anything I can/should do to reduce my risk of having an asthma attack?
- Will I have an asthma action plan?
- How often do I need follow-up care?
Read Also: What Is Asthma Caused By Smoking
Occupational Exposure To Environmental Tobacco Smoke
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Applicable To
type 1 excludes
Common Terms Found In Medical Record Related To Asthma:
Asthma exacerbation: It is nothing but an acute increase of symptoms in a person with asthma. This can be coded only with the Physician diagnosis.
Status asthmatics : Another term for this is severe asthma exacerbation. It is considered as severe as this may lead to even respiratory failure due to hypoxemia. As soon as a patient comes to emergency room with asthma symptoms, physician treats initially with medicines such as bronchodilators. If patient has status asthmatics they do not respond to these medicines.
Inhaler : Medicine filled inhalers are given to patient to use comfortably at any place when symptoms occurs suddenly.
Nebulizer : Electricity powered machine filled with liquid medication which turns to mist and the patient breath in.
Nasal spray : A bottle with liquid medicine made with the ease of spraying to nose.
PFT : Pulmonary Function Test, use to check the lung function by measuring lung volume, capacity, rates of flow and gas exchange.
Read Also: Can Caffeine Cause Asthma Attack
What Is Eosinophilic Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma is a subtype of asthma that is often severe. It is commonly seen in people who develop asthma in adulthood, although it may occur in children and young adults.
In eosinophilic asthma, the numbers of eosinophils are increased in blood, lung tissue, and mucus coughed up from the respiratory tract . The whole respiratory tract is involved in airflow obstruction from the sinuses to the small or distal airways. Patients with eosinophilic asthma frequently suffer from chronic sinus disease and nasal polyposis.
Research has shown that an elevated number of eosinophils in the blood correlates with future risk and severity of asthma attacks.
Asthma can range in severity and treatment may vary from patient to patient. To help outline the best course of treatment for an asthmatic patient, it is important for a health care provider to determine which subtype of asthma a person might have, because there are now new therapies that target specific subgroups of asthma, like eosinophilic asthma.
Algorithms For Identifying Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Of the 125 charts reviewed per algorithm-deriving healthcare system, 86 patients from System 1 and 117 patients from System 2 had sufficient data in their medical records to confirm or refute the diagnosis of EGPA and were included in the analysis. 19/86 patients had a confirmed diagnosis of EGPA at System 1 and 13/117 patients at System 2 based on the ACR criteria or the revised ICHCC definitions. Figure 2 shows the PPV and sensitivity of the 16 constructed case-finding algorithms for EGPA. The PPV and sensitivity of the algorithms in each healthcare system are detailed in Supplementary Table 3. Two algorithms: i) one including patients with eosinophilia or asthma and including the physician specialty and ii) another including patients with eosinophilia or asthma and including the physician specialty and an immunosuppressive medication had the highest average positive. Adding positivity for pANCA to the algorithms did not significantly increase the PPV and decreased the sensitivity.
58 out of 2,151,960 patients were identified at System 3 using the algorithm with the highest average PPV and the lowest variable numbers listed above . 10 patients were excluded because of insufficient data to confirm or refute the diagnosis. 20/48 remaining patients had a confirmed diagnosis of EGPA. The PPV of this algorithm was: 41.7% indicating a low PPV. However, adding positivity for pANCA to the algorithm increased the PPV to 100.0% .
Also Check: Asthma Vs Reactive Airway Disease
What Happens To Our Lungsduring Asthma Attack:
During asthma attack, muscles around the airway gets tighten and the lining inside the airways becomes swollen and produce extra mucus. This makes airway to become narrow and partially block airflow in and out of air sacs.
Below picture gives a clear understanding of the position of lungs , normal airway and airway during asthma attack .
Apart from knowing the symptoms and doing a lung physical examination the physician will also do few test measures like X-ray, spirometry, allergy testing, nitric oxide breath test or peak flow to determine the type of asthma and its severity. Hence a coder should definitely pay attention to these areas as well.
Pulmonary Eosinophilia Not Elsewhere Classified
- 201620172018201920202021 – Converted to Parent Code20222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- J82 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM J82 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J82 – other international versions of ICD-10 J82 may differ.
type 2 excludes
- pulmonary eosinophilia due to aspergillosis (ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B44
You May Like: Atlanta Allergy And Asthma Lawrenceville Georgia
Diseases Of Esophagus Stomach And Duodenumtype 2 Excludes
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Type 1 Excludes
- eosinophilic gastritis or gastroenteritis
- alcohol abuse and dependence
- Allergic inflammation of the esophagus. Morphologically, it is characterized by the presence of eosinophils infiltrating the esophageal epithelium. Patients present with swallowing difficulty and heartburn.
- Chronic esophagitis characterized by esophageal mucosal eosinophilia. It is diagnosed when an increase in eosinophils are present over the entire esophagus. The reflux symptoms fail to respond to proton pump inhibitors treatment, unlike in gastroesophageal reflux disease. The symptoms are associated with ige-mediated hypersensitivity to food or inhalant allergens.
- 391 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders with mcc
- 392 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders without mcc
Diseases Of The Respiratory Systemnote
- certain conditions originating in the perinatal period
- certain infectious and parasitic diseases
- complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
- congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities
- endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases
- injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes
- symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified
- code, where applicable, to identify:
- exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
- exposure to tobacco smoke in the perinatal period
- history of tobacco dependence
- occupational exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
- cystic fibrosis
Also Check: Does Asthma Prevent Military Service
Algorithms For Identifying Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Of the 125 charts reviewed per algorithm-deriving healthcare system, 97 patients from System 1 and 98 patients from System 2 had sufficient data in their medical records to confirm or refute the diagnosis of GPA and were included in the analysis. 45/97 patients had a confirmed diagnosis of GPA at System 1 and 66/98 patients at System 2 based on the ACR criteria or the revised ICHCC definitions. Figure 1 shows the PPV and sensitivity of the 16 constructed case-finding algorithms for GPA. The PPV and sensitivity of the algorithms in each healthcare system are detailed in Supplementary Table 2. An algorithm excluding patients with eosinophilia or asthma and including the encounter type and physician specialty had the highest average positive predictive value . Adding the cANCA pattern significantly increased the PPV across all algorithms but decreased the sensitivity.
94 patients out of 2,151,960 were identified at the algorithm-verifying healthcare system using the algorithm with the highest average PPV listed above. 23 patients were excluded because of insufficient data to confirm or refute the diagnosis. 61/71 remaining patients had a confirmed diagnosis of GPA. The PPV of this algorithm was 85.9% . Adding positivity for cANCA to the algorithm increased the PPV to 94.4% .
Who Is Affected

The exact prevalence of eosinophilic asthma is unknown, however, it is estimated that approximately 10% of all asthma is categorized as severe. Eosinophilic asthma is most commonly diagnosed in adults 35-50 years old, although it is sometimes seen in even older adults and pediatric patients. Eosinophilic asthma equally affects males and females.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Don’t Treat Asthma
