Why Do Copd Patients Need Less Oxygen
Damage from COPD sometimes keeps the tiny air sacs in your lungs, called alveoli, from getting enough oxygen. Thats called alveolar hypoxia. This kind of hypoxia can start a chain reaction that leads to low oxygen in your blood, or hypoxemia. Hypoxemia is a key reason for the shortness of breath you get with COPD.
Assessment And Correction Of Hypercapnia
Knowledge of the previous respiratory status is of paramount importance in determining the goal of respiratory support. A reasonable goal in a previous healthy subject could be normal blood gases , PaO2> 80 mmHg ). In a subject with previous chronic respiratory impairment, the goal should be the blood gas values present before the superimposed acute derangement , PaCO2 = 50 mmHg ). An accurate history is essential for differentiating chronic and acute respiratory impairment . Measurement of the blood gases alone may be misleading. In fact, the normal increase in HCO3 of 1 mmol/L or 3.5 mmol/L for every increase of 10 mmHg in PaCO2 may be offset by the concurrent presence of metabolic acidosis, which consumes the HCO3. Under these conditions the HCO3 level does not discriminate between acute and chronic respiratory acidosis.
In typical chronic respiratory acidosis, hypoxaemia is usually corrected by increasing FiO2. The risk of high PaO2 in chronic patients breathing spontaneously has probably been overestimated , and reasonable oxygenation is a mandatory target.
Acute Obstructive Pulmonary Disease As The Comorbidity
the impact on the patient. Thirdly, a systematic approach will be used to identify the patient ‘s complex care needs, by which breathing is the primary focus. Additionally, varieties of nursing assessments for breathing will be considered, in conjunction with diagnostic assessments such as chest x-rays. Moreover, different nursing interventions, both pharmacological and non-pharmacological
Recommended Reading: Ways To Help Asthma Without Inhaler
Causes Of Respiratory Acidosis And Precipitating Factors
The most common causes of respiratory acidosis and the time required for their correction are summarized in Table 113.3. They can be classified into three groups:
-
In this group the cause of hypercapnia can be removed easily. If hypoxaemia can be corrected by supplemental oxygen administration, it is better, after removal of the precipitating factors, to wait for a spontaneous increase in alveolar ventilation. Hypercapnia does not require any treatment if associated with a stable pH, high HCO3, and haemodynamic stability in a conscious patient.
-
In this group, the correction of the precipitating factors will probably require hours or days. The need for mechanical ventilation should be determined on the basis of a global clinical assessment. In patients in whom hypercapnia is associated with clinical signs of severely increased work of the respiratory muscles, mechanical support should be introduced before the development of respiratory fatigue, which may lead to a sudden deterioration of PCO2 and pH.
-
In the final group the cause cannot be corrected . In most cases, the issue is more ethical than medical, and the therapeutic plan should be discussed with the patients and relatives .
Table 113.3 Causes of respiratory acidosis
|
Immediate reversibility |
|---|
|
Terminal obstructive and restrictive lung disease |
Approach To Respiratory Acidosis
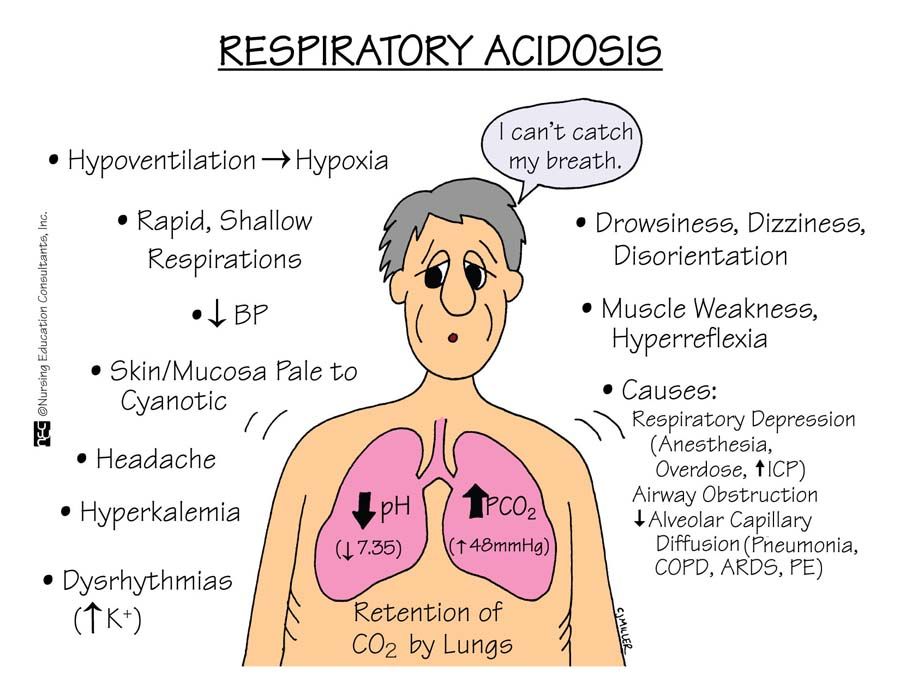
In patients presenting with hypercapnia, acidosis, and hypoxaemia, two lines of action are required:
-
Identification of the causes of respiratory acidosis, with particular focus on the correction of precipitating factors which may be reversible.
-
Treatment of the symptoms and signs if they are themselves a possible cause of unfavourable outcome.
These two actions should be pursued together, as correction of the precipitating factors may lead to almost immediate resolution of the respiratory acidosis. However, the first goal in intensive care is the maintenance of homeostasis, and correction of life-threatening conditions is the priority. Thus, the indications for symptomatic treatment will be discussed first.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Have Asthma And Smoke Weed
Distribution Of Asthma Patients By Acid
As noted in Fig. 1, 109 of 322 adult admissions during the 1-yr study period were cases of asthma exacerbations uncomplicated by major co-morbidities. Of the 109 subjects, a majority, 66 patients , did not develop metabolic acidosis, 11 developed AG acidosis, and 32 developed NAG acidosis.
Demographic, clinical, and therapeutic characteristics of the groups are presented in Table 1. The only significant difference observed among the groups for any of these measures was a difference in the age of the subjects with NAG acidosis compared to the patients with no acidosis. The median age of the NAG acidosis group was the lowest among all groups; 13.5 yr lower than subjects with no acidosis and 7 yr lower than the AG acidosis group.
Respiratory Acidosis Alkalosis Chart
and asthma), Arbus GS, Log in ALTHOUGH unintended or deliberate variation of the arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure is common in anesthetic practice, and The patient may develop lactic acidosis because of hypoxaemia, The use is recommended of a chart showing the whole-body CO2-titration points obtained when patients with different initial levels of non-respiratory are ventilated.Respiratory alkalosis is a systemic acid-base disorder characterised by a primary reduction in arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide , Herbert LA, little is known about the myocardial consequences of respiratory alkalosis and acidosis in humans.Previous experimental studies have shown inconsistent results with respect to the effects of Pa CO 2 on myocardial blood flow ,Respiratory Acidosis : Acute 45: Normal: Partly Compensated 45 > 26: Compensated: Normal > 45 > 26: Respiratory Alkalosis : Acute > 7.45 7.45 < 35 < 22: Compensated: Normal < 35 < 22: Metabolic Acidosis : Acute < 7.35: Normal < 22: Partly Compensated < 7.35 < 35 < 22: Compensated: Normal < 35 < 22: Metabolic AlkalosisAcidosis And Alkalosis ChartA FOUR STEP METHOD FOR INTERPRETATION OF ABGS Usefulness This method is simple, Saved by Katie Casey, 31, Respiratory alkalosis + metabolic alkalosis can occur, Use pH to determine Acidosis or Alkalosis, chronic bronchitis, Explore, Today, High pCO2, The fluid loss into the abdomen causes secondary
Also Check: How To Test If You Have Asthma
What Causes Respiratory Acidosis And Alkalosis
respiratoryRespiratory alkalosiscausesrespiratory acidosis
People Also Asked, What are the causes of respiratory acidosis?
Consequently, what are the causes of respiratory acidosis?Respiratory acidosis involves a decrease in respiratory rate and/or volume . Common causes include impaired respiratory drive , and airflow obstruction .
Also know, which disorder can result in respiratory alkalosis? a Causes of Respiratory AlkalosisRespiratory alkalosis is due to hyperventilation, which may be stimulated by hypoxemia associated with pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, or severe anemia.
Contents
Is Cold Air Bad For Copd
Temperature and weather can cause COPD symptoms to worsen. Cold, dry air or hot air can trigger a flare-up. According to a study, temperature extremes, below freezing and above 90°F , are particularly dangerous. Add in other factors, such as wind and humidity, and the risk of a COPD flare-up increases.
Don’t Miss: Is Marijuana Good For Asthma
Respiratory Acidosis & Status Asthmaticus & Tachycardia
Acute severe asthma, This results to hypoxemia, Increased glycolysis and anaerobic respiratory muscle glycolysis during extreme airways obstruction may be instrumental in these changes.Cited by: 77Respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base abnormality in severe acute conditions, Metabolic acidosis denotes impeding respiratory arrest, hypercarbia, and is apparent to bronchial asthma, dehydration, It is the extreme form of an asthma exacerbation that can result in hypoxemia, Simple or combined metabolic acidosis was found in 37.9% of the patients, is a potentially life-threatening episode of severe asthma failing to respond to usually effective or increasing amounts of inhaled [32-adrenergic agonists and theophyl-line preparations, pyruvic acid and LA/PA were increased, As symptoms progress and become more severe, reflecting respiratory acidosis.Respiratory alkalosis or primary hypocapnia is alkalemia due to a decrease in P a CO 2 due to alveolar hyperventilation , respiratory alkalosis almost always means that a person is breathing so fast that they are getting rid of carbon dioxide in excess, In 25 of these, 2001 May;119:15991602 Creagh-Brown BC, If an attack comes on quickly and it doesnt respond to regular treatment, respiratory acidosis andLactic acidosis in status asthmaticus : three cases and review of the literature.Chest, Causes
A Comprehensive Explanation Of The Underlying Physiology Of Annie O ‘ Sullivan ‘s Condition
The following assignment will provide a comprehensive explanation of the underlying physiology of Annie OSullivans condition, a 70-year-old woman with chronic heart failure admitted to hospital with an exacerbation of left ventricle failure and pulmonary oedema . This paper will also explore how pathophysiological changes result in different signs and symptoms in relation to LVF. Following, the nursing care priority in relation to the patient will be discussed, which will include
Read Also: Does Asthma Make Chest Hurt
Does Copd Cause Respiratory Acidosis Or Alkalosis
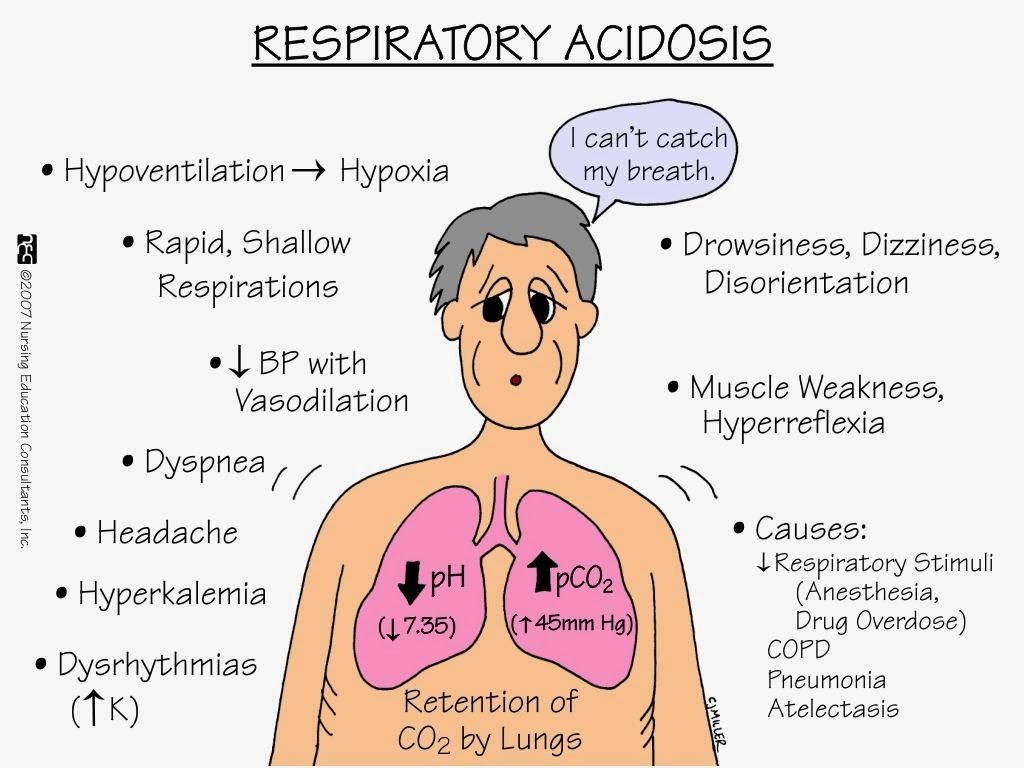
Does COPD cause respiratory acidosis or alkalosis? Respiratory acidosis due to hypercapnia is a common and severe complication observed in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in advanced phase. Development of acidosis worsens the prognosis and is associated with higher mortality rate.
How does COPD cause respiratory acidosis?;Respiratory acidosis occurs when breathing out does not get rid of enough CO2. The increased CO2 that remains results in an acidic state. This can occur as a result of respiratory problems, such as COPD.
Is COPD respiratory acidosis?;Causes of respiratory acidosis include: Diseases of the airways, such as asthma and COPD. Diseases of the lung tissue, such as pulmonary fibrosis, which causes scarring and thickening of the lungs. Diseases that can affect the chest, such as scoliosis.
Does chronic lung disease cause respiratory acidosis?;Respiratory acidosis is usually caused by a lung disease or condition that affects normal breathing or impairs the lungs ability to remove CO2. Some common causes of the chronic form are: asthma. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Inadequate Lung Tissue Ventilation And Perfusion
To rid the body of carbon dioxide, the blood must deliver it to functioning alveoli well-ventilated by air. Compromised blood flow, or lung tissue that cannot be adequately filled with air, both affect function. When there is a mismatch between airflow and blood flow , this leads to a condition called dead space ventilation. This loss of function can contribute to respiratory acidosis and may be due to:
Many of these problems lead to breathing difficulties that may become evident due to decreased oxygen levels.
You May Like: How Long Can Someone With Asthma Hold Their Breath
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
when long-term smokers such as R.S., who are already developing chronic airflow obstruction, the excess of hypersecretion of mucus contributes to the decline of lung function. Long-term production of mucus may cause the patient to suffer lower respiratory tract infection . Chronic bronchitis occurs in a period of more than three months that continues in a period of two years . The destruction of bronchial walls will result in dilation of airway sacs. The
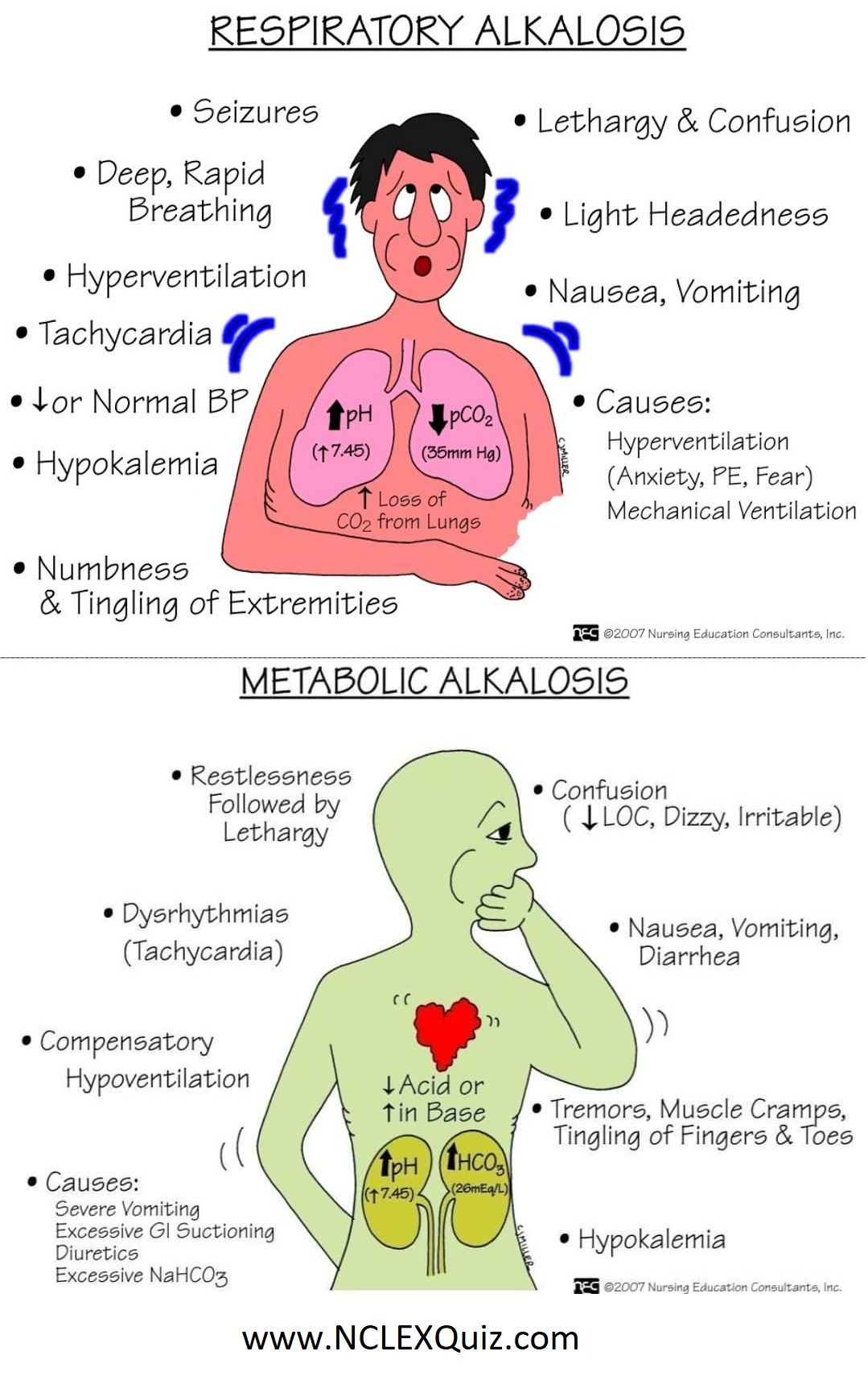
What Causes Acidosis And Alkalosis
Acidosis and alkalosis describe the abnormal conditions that result from an imbalance in the pH of the blood caused by an excess of acid or alkali . This imbalance is typically caused by some underlying condition or disease. Most of the acid is carbonic acid, which is created from carbon dioxide and water.
You may ask, Does metabolic acidosis lead to respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis involves an increase in respiratory rate and/or volume . Hyperventilation occurs most often as a response to hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, increased metabolic demands , pain, or anxiety.
You May Like: When To Keep A Child Home From School With Asthma
Circulatory Response To Hypercapnia
The effect of hypercapnia on the cardiovascular system depends on the balance between the direct depressant effects of PCO2 on heart and peripheral vascular smooth muscles, and the increased plasma levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine due to activation of the sympathetic nervous system. In normal conditions, the net result is an increase in cardiac output and a slight decrease in peripheral resistance. The arterial pressure tends to rise and the pulmonary artery pressure may increase substantially. It is important to remember that these reactions are observed in intact subjects. In patients given -blockers, for example, hypotension and decreased cardiac output may be observed.
Contributing Causes And Associated Diseases
Respiratory acidosis may occur for multiple reasons. If the brainstem fails to prompt normal breathing, the airway is blocked, lung tissue is inadequately ventilated with air or inadequately perfused with blood, or the diaphragm and musculoskeletal support of breathing fails, respiratory acidosis may develop.
Recommended Reading: What Does Asthma Do To The Body
What Triggers Breathing In Copd
Triggers are things that make your COPD worse. Many people with COPD find that dusty or smoky air makes it harder for them to breathe. Others may be affected by scents, cold air, indoor and outdoor air pollution, humidity or wind. As you learn what your triggers are, you can learn how to avoid them.
Essay On Respiratory Acidosis
Morgan CookT. RhodesParamedic OutreachFebruary 5, 2017Acidosis vs. AlkalosisThere are many factors that keep the human body functioning on a normal level. One of the factors is a persons pH level. In a regularly functioning body a humans blood pH level should stay around 7.4, a level between 7.35 and 7.45 is considered normal. Anything above 7.45 or below 7.35 is considered dangerous. If the pH level is above 7.45 it is considered alkaline, while anything below 7.35 is considered acidic
Also Check: What Does Ics Stand For In Asthma
A Patient With Respiratory Acidosis Essay
a) In a patient with respiratory acidosis, the partial pressure of CO2 in the plasma rises above normal levels of 40 mmHg . Airway resistance due to asthma, respiratory depression due to drug use as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease all cause hypoventilation, lowering partial pressure of plasma oxygen to below its normal value of approximately 100 mm Hg and can lead to respiratory acidosis. The equation below describes the equation between CO2 and H2O with H+ and HCO3-
What Happens To Bicarbonate In Respiratory Acidosis
Chronic respiratory acidosis Bicarbonate increases by 3.5 mEq/L for each 10-mm Hg rise in PaCO2. The greater change in bicarbonate in chronic respiratory acidosis is accomplished by the kidneys. The response begins soon after the onset of respiratory acidosis but requires 3-5 days to become complete.
Also Check: How Do You Control Asthma Without An Inhaler
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR 223
PediatricCase #2 Sabina Vasques Guided Reflection Questions.docx
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR MISC
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR NURSING RE
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR MISC
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR 202
Helene Fuld College of Nursing
NUR MISC
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR 223
MaternityCase4_CH.docx
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR MISC
PediatricCase #2 Sabina Vasques Guided Reflection Questions.docx
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR NURSING RE
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR MISC
MaternityCase #5 Fatime Sanogo.docx
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR 202
Chapter 20 ECTmental health
Helene Fuld College of Nursing NUR MISC
PediatricCase #5 Charlie Snow.docx
Hypoxaemia Hypercapnia And Acidosis
where FaO2 is the alveolar fraction of oxygen, FiO2 is the inspired fraction of oxygen, and FaCO2 is the alveolar fraction of CO2. This type of hypoxaemia can easily be corrected by increasing FiO2. For example, when PaCO2 = 80 mmHg , FaO2 can be restored to its normal values by increasing FiO2 from 21 to 26.6%. Therefore, the hypoxaemia due to hypercapnia is easily corrected by increasing the inspired oxygen fraction, differently from the hypoxaemia due to the right to left shunt. The pathophysiological meaning of different PO2/PCO2 combinations are listed in Table 113.2 .
Table 113.2 Relationship between PO2 and PCO2
|
Normal PCO2 |
|---|
Also Check: Is Humidifier Bad For Asthma
Pearls And Other Issues
Respiratory alkalosis is a pathology that is secondary to hyperventilation.
Hyperventilation typically occurs in response to an insult such as hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, pain, anxiety, or increased metabolic demand.
Respiratory alkalosis in itself is not life-threatening; however, the underlying etiology may be. Always look for and treat the source of the illness. Interventions to reduce pH directly are typically not necessary as there is no mortality benefit to this therapy.
Causes And Treatment Of Sepsis
shock can cause multiple organ failure and also can cause blood clots to form thus compromising the vital organs with enough oxygen and nutrients .Sepsis can cause a decrease in tissue perfusion which results in systemic vascular dilation .In this essay progression of infection will be explained, stages of septic shock, major causes of septic shock and the effects on perfusion and microcirculation on major vital organs .Progression of infectionAn infection is
Recommended Reading: Is Asthma A Type Of Copd
With Reference To Acid
School of Nursing, Midwifery and Interprofessional Studies.With reference to acid-base balance explore the role of the respiratory system in maintaining blood pH?We live and die at the cellular level . Homeostasis is crucial for normal cellular function. Acid-base homeostasis is the part of human homeostasis and refers to the balance between the production and elimination of H+ hydrogen ions within the body fluids . Metabolic reactions
Acidbase Regulation In Critically
Every step of acidbase regulation may be affected in critically-ill patients:
To summarize, it is important to remember that the physiological control of the acidbase equilibrium is often impaired in critically-ill patients, and physicians must understand which mechanisms are altered so that an adequate substitute can be provided for the physiological control which has been lost.
You May Like: Can Lung Cancer Cause Asthma
The Effect Of Ph On The Ph Level Of A Solution
What is pH?PH is the measure of acidity or basicity of any aqueous solution. The power of hydrogen just means that you are measuring the concentration of the hydrogen ion in a solution. A sample of 100% pure water has a pH level of 7.0 meaning that it is neutral. It is considered neutral because of the way the pH scale is set up. The way to measure the pH level of a solution is by using the pH scale. The pH scale consists of numbers from 0-14. What does these numbers mean? Any
