Bronchial Asthma And Cardiac Asthma
Bronchial asthma is another name for asthma. The term bronchial is occasionally used to differentiate it from what is sometimes called cardiac asthma, which is not a form of asthma, but actually breathing difficulties caused by heart failure. Although the two conditions have similar symptoms, including shortness of breath and wheezing , they have quite different causes and so treatment differs.
What Is Respiratory Asthma
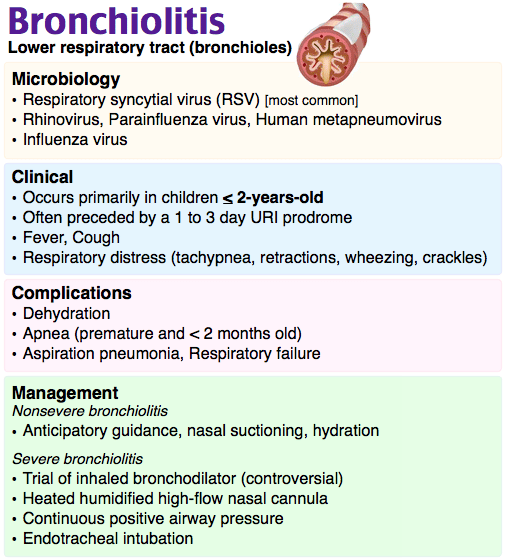
It is actual asthma which is characterised by repeated episodes of cough, shortness of breath, and wheeze. It results from obstruction of the airways, which is reversible in nature. It is also age-specific and generally affects children. It affects about 5-8% of the people. It is classified into three types: mild, moderate and severe asthma. In mild form, symptoms may disappear on their own when the causative agent is removed, moderate and severe forms needs medicines and may be a hospital stay is needed. The cough is mostly nocturnal, meaning occurring at night.
Symptoms include, cough, sputum, intermittent dyspnoea and wheeze. Respiratory Asthma has several precipitating factors, for example, Allergens , cold air, exercise, smoking, pollution, etc.
Cardiac Asthma Vs Bronchial Asthma
Even thought cardiac asthma and bronchial asthma sound very similar, they actually couldnt be more different. Knowing the difference between the two can actually be extremely important in the case of helping someone who is suffering from a true asthma attack versus a cardiac asthma attack. You will need to consider health history, specific symptoms, and recurrence of symptoms to determine if you should speak to a doctor to further examine the root cause of your asthmatic symptoms.
Asthma is treated in different ways depending on the severity of symptoms and how well it responds to treatment. Some people find adequate relief from asthma medications over the counter and other mild remedies such as natural asthma cures. These methods are generally reserved for people who experience symptoms intermittently or seasonally. Some still can find relief from mild symptoms by utilizing simple breathing exercises for asthma, however most often, people end up with inhalers for treating attacks. This is where the differentiation becomes extremely important because using an inhaler for a case of cardiac asthma can be dangerous because it can exacerbate the symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Moderate Persistent Asthma With Exacerbation
Symptoms Of Bronchial Asthma
The symptoms of bronchial asthma include:
- a feeling of tightness in the chest
- difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath
- wheezing or whistling in the chest and
- coughing persistent cough is a common symptom it may be worse at night.
For most people with bronchial asthma, the pattern is they feel well most of the time and can breathe normally, but have periodic attacks of narrowing of their airways and wheezing. However people with severe asthma may alternate between chronic shortness of breath and episodes in which they feel even more breathless than usual.
Difference Between Bronchial Asthma And Cardiac Asthma
August 11, 2011 Posted by Dr.Dinusha
Bronchial Asthma vs Cardiac Asthma
Difficulty in breathing or dyspnoea is described as the increased awareness of ones laborious breathing. Difficulty in breathing is one of the commonest complaints a patient will present with, next to fever and upper respiratory tract infection. It may be a symptom in a varied range of pathological entities and in a similar range of varied body systems. This is sometimes confused with asthma, where there is a component of difficulty breathing, but is associated with an expiratory wheeze. So with regards to the pathophysiology, symptoms, and management we will discuss on the similarities and the dissimilarities of bronchial asthma and cardiac asthma.
Bronchial Asthma
Cardiac Asthma
What is the difference between Bronchial Asthma and Cardiac Asthma?
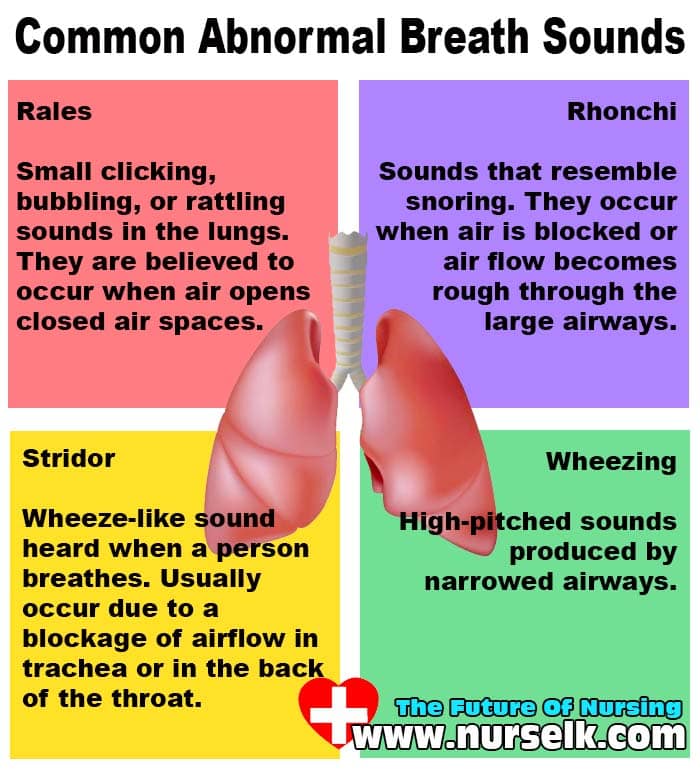
Both these conditions present with dyspnoea and feelings of dread in the patient. Most of the symptoms are similar but with dissimilar past histories. On examination, BA will have rhonchi and CA will have crepitations. The pathophysiology of the two is different with BA having an immune mediated airway narrowing, and CA having a transudative pulmonary oedema. The management of BA is based on bronchodilatation and with CA, the management being the removal of fluids from the alveoli. Both these conditions carry the risk of death with either of them.
You May Like: Whats The Cause Of Asthma
Whats The Treatment For Cardiac Asthma
The treatment for cardiac asthma is essentially to treat the cause of the underlying heart problem, whether it be heart failure or a leaky heart valve, and the excess fluid in the lungs. Medicines may be needed to reduce blood pressure, including diuretics which help reduce fluid retention. If the heart failure can be treated effectively, this may in turn relieve the respiratory symptoms known as cardiac asthma.
People who awaken suddenly in the night with symptoms of cardiac asthma may improve the situation by sitting upright for half an hour. There is no evidence that using bronchodilators will help, and they may even worsen the situation.
How To Diagnose Cardiac Asthma
If you live with heart failure, ask your doctor about the symptoms of cardiac asthma. It can help you identify the problem as soon as it occurs. However, cardiac asthma can be the first obvious symptom of heart failure. In this case, timely diagnosis is imperative.
Several ways exist for diagnosing cardiac asthma and differentiating it from bronchial asthma. Your doctor will likely do or administer the following:
Don’t Miss: Best Ac Air Filters For Allergies And Asthma
Tracheal And Bronchial Lesions
A variety of airway tumors are reported to manifest with symptoms similar to those of asthma. These tumors include endobronchial carcinoid and mucoepidermoid tumors, as shown in the images below. In one case, a 14-year-old boy with hyperlucency in the left lung was ultimately found to have a bronchial carcinoid in the left mainstem bronchus.
Other tracheal lesions can include bronchocentric granulomatosis, subglottic stenosis, subglottic web, tracheal hamartoma, bronchogenic cysts, leiomyoma, and tracheobronchopathia osteoplastica. All these types of tracheal lesions have been reported with symptoms similar to asthma.
Are Your Symptoms Caused By Heart Failure Or Asthma
- Reactions 0 reactions
Asthma is not heart failure. Heart failure is not asthma. The treatment for both conditions is different. Still, they both share common symptoms of shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. So, how do doctors tell the difference between asthma and heart failure? How do they determine which disease to treat you for? Heres what to know.
You May Like: What Does An Asthma Attack Look Like
Assessment Of The Body
People with both conditions may appear to be working hard to breathe. Those experiencing heart failure may have a hard time breathing while lying flat. Their feet and ankles may be swollen. Their stomachs may appear bloated. Asthma usually does not present with a bloated stomach or feet or ankle swelling.7-8
What Causes Cardiac Asthma
Cardiac asthma is caused by heart failure. The most common cause of heart failure in adults is coronary artery disease. Coronary artery disease is when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, unable to deliver blood and even closing completely due to a heart attack. Its usually caused by atherosclerosis, or the buildup of cholesterol and plaque in the blood vessels.
Other conditions that can cause or contribute to the development of heart failure include:
for treating cardiac asthma. Treatment for cardiac asthma involves addressing the underlying heart failure and fluid buildup in the lungs.
You May Like: What To Do Asthma Flare Up
Lung Function And Challenge Test
The pulmonary function test was performed following American Thoracic Society guidelines by a bodyplethysmograph measuring forced vital capacity , forced expiratory volume in one second , total lung capacity and residual volume . FEV1 values < 80% in combination with FEV1/FVC values < 70% were considered to show bronchial obstruction . In this case, patients were given an inhalative betamimetic agent and retested for reversibility after 15min. Reversibility was attested if the FEV1 increased by 12% of the baseline value. Patients with a normal pulmonary function test continued their evaluation with bronchial challenge testing.
Challenge testing was performed by applying the tidal breathing method with doubling concentrations of methacholine up to a concentration of 20mg·mL1, according to published guidelines . Aerosol was inhaled by quiet tidal breathing through the mouth for 2min, using a noseclip. The FEV1 was measured before and 30 and 90s after each inhalation. The challenge test was finished after a 20% fall of FEV1 compared to the baseline value or after completion of the concentration steps. A cut-off point of 16mg·mL1 was used for the provocative concentration producing a 20% fall in the FEV1 to discriminate hyperreactive from nonhyperreactive subjects .
All patients were given an inhalative bronchodilator and hyperreactive patients were asked to perform spirometry measurements in 15-min intervals until they reached approximately their baseline FEV1 value.
What Can I Expect If I Have Cardiac Asthma
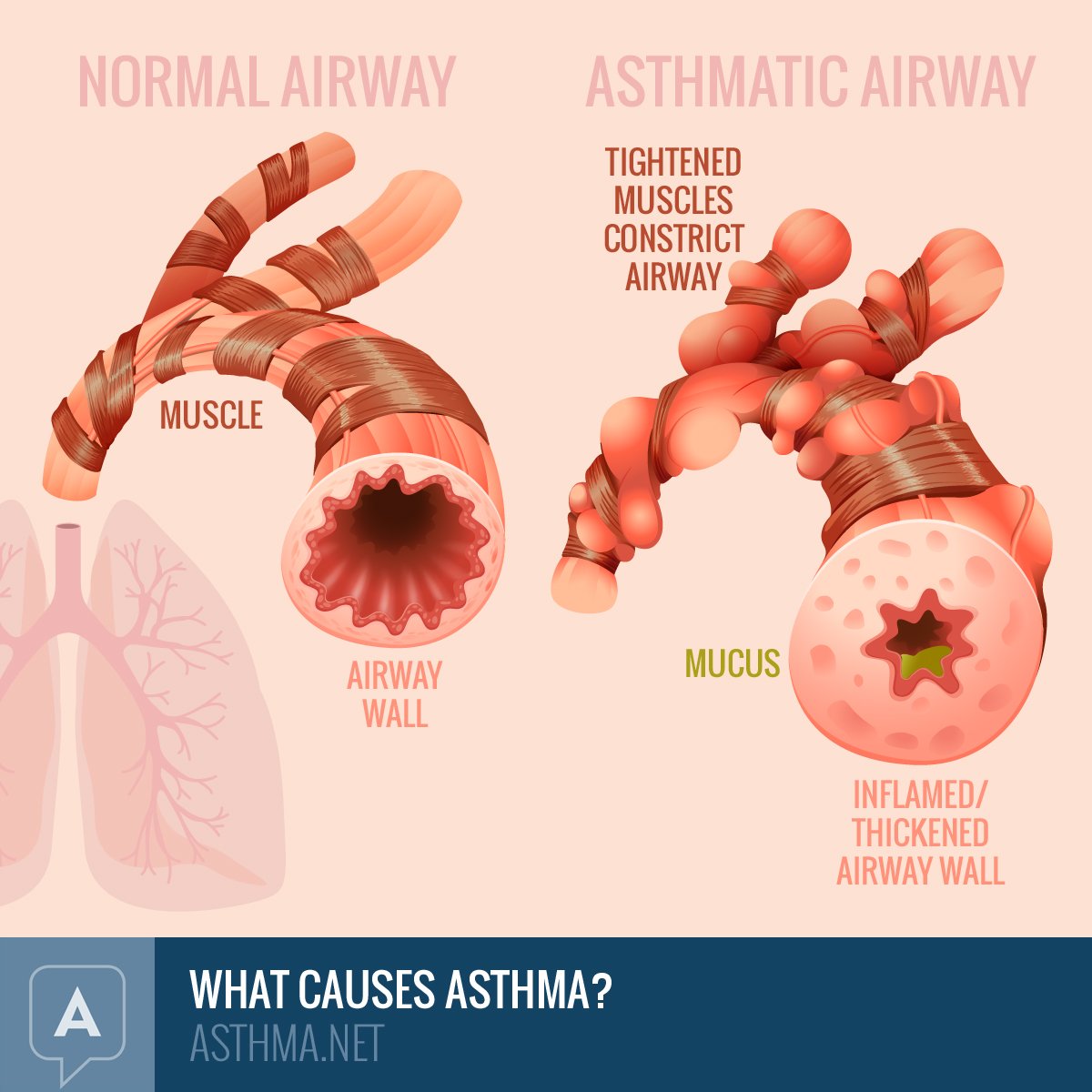
Heart failure, which causes cardiac asthma, keeps getting worse with time. Symptoms can get worse without warning. You can manage heart failure with lifestyle changes and medicines for a while.
However, you may come to a point when you feel short of breath when youre not exerting yourself at all. This is called advanced heart failure.
Before you get to this point, its good to let your family and healthcare provider know what kind of care you want. For example, if youre having a lot of trouble breathing, would you want a breathing tube in your throat?
How long does cardiac asthma last?
Cardiac asthma lasts as long as you have the condition thats causing it. Usually, that condition is heart failure, which doesnt have a cure. Be sure to explore your treatment options to get the best care available.
You May Like: Does A Humidifier Help With Asthma
What Is Cardiac Asthma
Unlike bronchial asthma, cardiac asthma is difficulty breathing because of pulmonary edema or fluid in your lungs. This fluid comes from pulmonary hypertension, which happens in left-sided heart failure. Heart failure doesnt mean your heart isnt working. It means it cant keep up with your bodys demand for blood.
Cardiac Asthma: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Cardiac asthma is a condition caused by congestive heart failure. While it doesn’t have anything to do with typical bronchial asthma, the symptoms of these two conditions are similar. A person who develops cardiac asthma can experience asthma-like wheezing and coughing that may cause the doctor to misdiagnose the problem.
If left untreated, cardiac asthma could turn into a life-threatening condition. Timely diagnosis is the key to relieving the symptoms and treating the underlying cause of the problem, which is heart failure.
Let’s take a closer look at diagnosing, treating, and preventing cardiac asthma.
Have you considered clinical trials for Asthma?
We make it easy for you to participate in a clinical trial for Asthma, and get access to the latest treatments not yet widely available – and be a part of finding a cure.
Also Check: Does Asthma Get Worse Over Time
How To Prevent Cardiac Asthma
To reduce the risk of cardiac asthma, you can:
-
Keep your heart failure under control
-
Monitor your health to discover heart conditions
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Exercise regularly
-
Take prescribed medication
Not all people who live with heart failure will have cardiac asthma. Speak to your doctor about effective preventive methods.
Difference Between Cardiac Asthma And Respiratory Asthma
Asthma is a disease of lower respiratory tract which causes swelling and contraction in bronchi and bronchioles, parts of lower respiratory pathways. Most commonly Asthma is regarded as a lung disease, lesser known to common man is the fact that Asthma can be due to cardiac problems as well. Both forms of the disease have got specific cause, characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. One similarity between the two forms is that both forms are difficult to cure completely rather management is the rule, or we can say symptomatic treatment along with prevention of further complications. Management of asthma enables a person to lead a normal life with full activities. None of these two forms are transferable from one person to another.
Don’t Miss: How To Use Mullein For Asthma
How Is It Diagnosed
Cardiac asthma can be difficult to diagnose due to its similarity to asthma. Misdiagnosis is common. To differentiate between the two, a doctor will likely start by looking at your medical history and risk factors to determine whether heart failure is the cause.
Tests that may be performed to help diagnose heart failure include:
- Physical exam. The doctor may look for other signs of cardiac asthma and heart failure, such as abnormal sounds in your lungs when breathing and abnormal heart rate.
- Blood tests. The doctor may recommend a blood test to help diagnose conditions that can lead to heart failure, check for markers of increased fluid, and rule out other potential causes for your symptoms.
- Electrocardiogram. An electrocardiogram monitors the electric activity of your heart and helps identify abnormalities in your heart rhythm.
- Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to produce a picture of your heart. The picture can show the doctor how much blood your heart is pumping and screen for irregularities or abnormalities in the pumping function.
- Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can help identify an enlarged heart or fluid in your lungs.
- Breathing tests. Your doctor may recommend breathing tests like a spirometry test or a peak flow test to screen for lung problems.
- Other imaging techniques. A CT or MRI scan may also be used to produce images to assess the health of your heart.
Risk Factors For Asthma
Risk factors for developing bronchial asthma include being exposed early in life to indoor allergens, such as dust mites, moulds and cockroaches, and having a family history of asthma or allergy. Exposure to tobacco smoke before birth or during early childhood also increases the risk of developing bronchial asthma.
Also Check: Are You Born With Asthma Or Can You Develop It
Cardiac Asthma: Not Your Typical Asthma
Clinical Instructor of Pharmacy PracticeSchool of PharmacyPhiladelphia College of Osteopathic MedicineGeorgiaSuwanee, Georgia
Ramon Cereceres, Jr., PharmD
Ashley N. Feik, PharmD Candidate
Katherine E. Iltis, PharmD
University of the Incarnate WordFeik School of Pharmacy
Katelyn E. Horne, PharmD CandidateLoma Linda University
Monica Litzinger BSc, BSc Pharm, RPhOutpatient PharmacistSuwanee, Georgia
US Pharm.
ABSTRACT: Cardiac asthma is a condition secondary to heart failurethat is marked by dyspnea, wheezing, cough, frothy or bloody sputum,and rales.1 These symptoms usually occur at night and aremore prevalent in the elderly population. Because its symptoms aresimilar to those of bronchial asthma, cardiac asthma is oftenmisdiagnosed. However, an accurate diagnosis is imperative becausetreatments for the two conditions differ, and incorrect treatment canexacerbate cardiac asthma.2 IV furosemide, nitroglycerin, and morphine are used for the acute treatment of cardiac asthma.3 If the patient is hypoxic, supplemental oxygen also may be used.3 Outpatient medication regimens focus on treating heart failure.
Vocal Cord Dysfunction Or Inducible Laryngeal Obstruction
Vocal cord dysfunction may exist alone or with asthma, it is caused by paradoxical adduction of the vocal cords during inspiration, and may disappear with panting, speech, or laughing. Patients with chronic symptoms suggestive of asthma, normal spirometry, poor response to asthma medications, and frequent evaluations should be evaluated for vocal cord dysfunction. Usually, the diagnosis can be made using direct laryngoscopy, but only during symptomatic periods or after exercise. The presence of flattening of the inspiratory limb of the flow-volume loop may also suggest vocal cord dysfunction, but this is only seen in 28% of patients at baseline.
Don’t Miss: How To Know If You Are Having An Asthma Attack
Difference Between Bronchial Asthma And Asthma
September 29, 2011 Posted by Dr.Dinusha
Bronchial Asthma vs Asthma
The human respiratory system and its ability to utilize oxygen maximally and transfer it to blood are the reasons why the human society has advanced so much. If it is not for the live giving and preserving oxygen, the human development would be at a standstill. To absorb oxygen maximally, the respiratory system has been subdivided into small branches, ending with alveoli. Thus, the respiratory tubing are a point where the proper oxygen transference is affected to produce hypoxia. Difficulty in respiration can be due to varied reasons from infectious to immunological to neoplastic. Here, we will discuss regarding the terms asthma and bronchial asthma.
Asthma
Among medical professionals, asthma invariably means bronchial asthma, but among the lay individuals, asthma is used in terms of cardiac asthma and skin asthma to name a few. Asthma occurs due to an immunological response leading to restriction of the airways. Thus, asthma is based on the outcome or the clinical features of the condition. Cardiac asthma occurs due to heart failure, and skin asthma is due to atopic conditions leading to allergic reactions with erythematous rashes on the skin and itching. It may be something induced by food or skin contact.
Bronchial Asthma
American Heart Association News Stories
American Heart Association News covers heart disease, stroke and related health issues. Not all views expressed in American Heart Association News stories reflect the official position of the American Heart Association. Statements, conclusions, accuracy and reliability of studies published in American Heart Association scientific journals or presented at American Heart Association scientific meetings are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the American Heart Associations official guidance, policies or positions.
Copyright is owned or held by the American Heart Association, Inc., and all rights are reserved. Permission is granted, at no cost and without need for further request, for individuals, media outlets, and non-commercial education and awareness efforts to link to, quote, excerpt or reprint from these stories in any medium as long as no text is altered and proper attribution is made to American Heart Association News.
Other uses, including educational products or services sold for profit, must comply with the American Heart Associations Copyright Permission Guidelines. See full terms of use. These stories may not be used to promote or endorse a commercial product or service.
Don’t Miss: Southwest Allergy And Asthma Center
