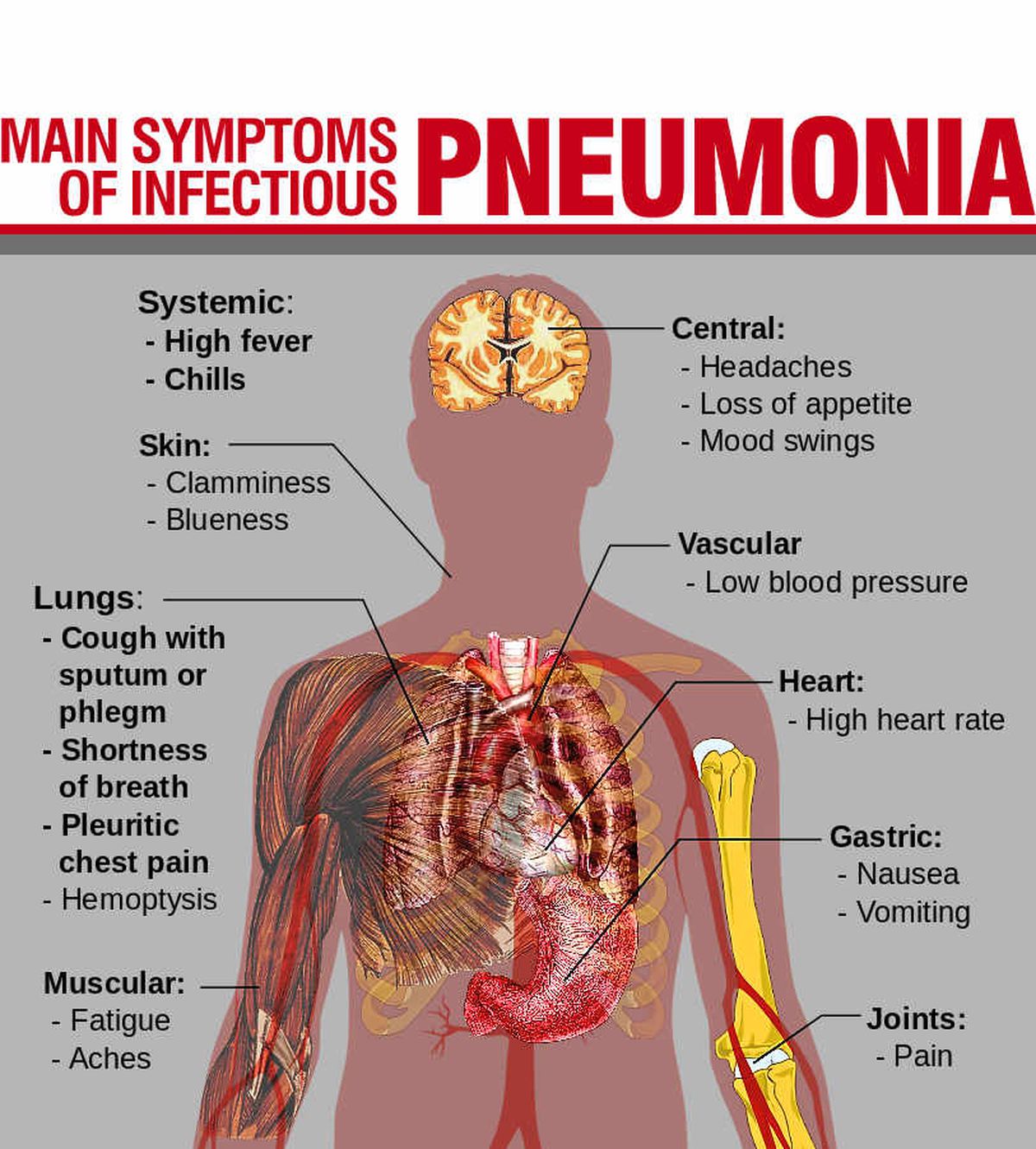
Whos Most Likely To Get It
Anyone can get COVID-19 pneumonia, but its more likely in people who are 65 or older. Those who are 85 or older are at the highest risk.
People who live in nursing homes or who have other health problems like these also have higher chances of more severe illness with COVID-19:
- Severe obesity, or a body mass index of 40 or higher
Someone who has a weakened immune system may be more likely to get severe COVID-19 illness, too. This includes smokers, people being treated for cancer, people who have had a bone marrow transplant, people who have HIV or AIDS thats not under control, and anyone who takes medications that slow the immune system, like steroids.
Free COVID testing is available in most communities. Some locations require an appointment while others are drive-up. Check with your local health department about testing availability.
Study Design And Methods
This study was a nationwide register-based cohort analysis of > 900,000 Swedish children to assess the association between pneumonia in infancy and prevalent asthma at 4 years. A secondary aim was to assess if the association has changed after the introduction of nationwide pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunization as this has led to a shift in pneumonia etiology. The study controlled for important confounders, including shared environmental and familial confounding, by using sibling analyses.
What Is The Difference Between Pneumonia And Pneumococcal Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Pneumococcal pneumonia is caused by the bacteria pneumococcus. This means it is a type of bacterial pneumonia. There are numerous other bacteria as well as viruses and fungi that may also cause pneumonia.
Pneumonia can be acquired in different settings. Community-acquired pneumonia can happen to anyone in their homes, communities, and schools. Conversely, healthcare-acquired pneumonia is contracted while people are in a healthcare facility.
Many types of pneumonia can be prevented through vaccines.
Recommended Reading: Does Asthma Act Up In Winter
Whats The Connection Between Asthma And Pneumonia
People who have chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma may be at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
If you have asthma and get the flu, your symptomsand your complicationsmay be worse than they are for someone who doesnt have asthma. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , people with asthma who get the flu are more likely to develop pneumonia as a complication.
One of the treatments for asthma is inhaled corticosteroids. According to one study, these medications may themselves increase the risk of respiratory infections and pneumonia.
Some of the key differences between the conditions can be seen in the table below.
| Asthma |
Pneumonia can be viral or bacterial:
- Viral pneumonia symptoms start out much like those of the flu and include fever, muscle pain, and dry cough. As it progresses, the cough gets worse and you may produce mucus. Shortness of breath and fever can follow.
- Bacterial pneumonia symptoms include a temperature that could go as high as 105°F . Such a high fever can lead to confusion and delirium. Your pulse and breathing rates may rise. Your nail beds and lips may turn blue due to lack of oxygen.
Researchers arent sure exactly what causes asthma. There may be an inherited tendency to develop asthma. There may also be environmental factors.
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of things, such as:
- viruses, including the flu virus
What Are The Symptoms Of Asthma
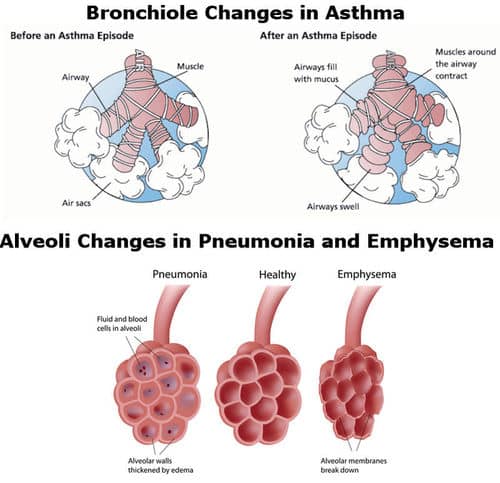
While symptoms vary from person to person, the most common signs of mild asthma include:
- difficulty breathing feeling breathless, even while resting, or being unable to finish full sentences before needing to take another breath
- wheezing making a whistling sound while breathing
- coughing either at specific times or after certain activities
During a severe asthma attack, you may notice more serious symptoms, such as:
- feeling very distressed, exhausted or even limp from trying to breathe
- deep sucking motions at the throat or chest while trying to breathe
Read Also: Does Jeffree Star Have Asthma
Is There A Connection Between Asthma And Pneumonia
Pneumonia and asthma are both considered a type of pulmonary disease affecting the lungs. Yet, asthma is considered a long-term respiratory disease while pneumonia is short-term. Unlike asthma, pneumonia is often contagious and may require antibiotics.
Asthma patients are also more at risk for pneumonia after contracting the flu.
Ive Had Treatment For My Chest Infection But Im Still Having Symptoms What Should I Do Now
The cough from a chest infection is usually the last symptom to go and could last up to three weeks, even after treatment. If you find you’ve still got a cough after your chest infection has cleared up, this might be a sign that your airways are still inflamed, so its worth seeing your doctor.
You should also see a doctor if:
- your asthma is waking you at night
- you feel like your chest infection has cleared up, but youre still having asthma symptoms three or more times a week
- your chest infection doesnt get completely better after a course of treatment.
You should phone 111 or 999 if you:
- feel your chest infection symptoms get worse at any point
- develop a fever
Recommended Reading: Allergy And Asthma Lincoln Ne
How Long Is Pneumococcal Pneumonia Contagious
Pneumococcal pneumonia is a contagious disease caused by inhaling infectious droplets. You may encounter these through someone coughing or sneezing. It is typically contagious from 2-14 days. Most people arent considered contagious after being on antibiotics for 2 days. If you have been diagnosed with pneumonia, ask your doctor how long you may be contagious.
What Is Good Asthma Care
Your doctor or nurse will tailor your asthma treatment to your symptoms. Sometimes you may need to be on higher levels of medication than at others.
You should be offered:
- care at your GP surgery provided by doctors and nurses trained in asthma management
- full information about your condition and how to control it
- involvement in making decisions about your treatment
- regular checks to ensure your asthma is under control and your treatment is right for you
- a written personal asthma action plan agreed with your doctor or nurse
It is also important that your GP or pharmacist teaches you how to properly use your inhaler, as this is an important part of good asthma care.
Read Also: Allergic Asthma Treatment Over The Counter
How Soon After Treatment For Pneumonia Will I Begin To Feel Better
How soon you will feel better depends on several factors, including:
- The cause of your pneumonia
- The severity of your pneumonia
- If you have other at-risk conditions
If you are generally healthy, most symptoms of bacterial pneumonia usually begin to improve within 24 to 48 hours after starting treatment. Symptoms of viral pneumonia usually begin to improve within a few days after starting treatment. A cough can last for several weeks. Most people report being tired for about a month after contracting pneumonia.
How Is Pneumonia Diagnosed
If you suspect you may have pneumonia, make an appointment with your doctor. Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms. They will perform a physical exam and conduct testing.
Expect your doctor to listen to your lungs and check your temperature, respiratory rate and pulse oximetry level. If your doctor thinks you may have pneumonia, they may also order a chest X-ray and blood tests to check for infection. For people sick enough to need hospitalization for pneumonia, additional testing may be necessary.
Read Also: Medications For Allergy Induced Asthma
Can Asthma And Pneumonia Be Prevented
Asthma isnt preventable. Good disease management can cut down on asthma attacks, however.
You can get a vaccination for a type of bacterial pneumonia called pneumococcal pneumonia. Doctors recommend this vaccine for certain people at risk of developing the disease. Ask your doctor if you should get the vaccine.
You can also reduce your risk of getting pneumonia by:
- washing your hands regularly to help reduce the spread of germs
- not smoking, since tobacco use can make it more difficult for your lungs to fight off infection
What Is The Outlook For Pneumonia
People who are otherwise healthy often recover quickly when given prompt and proper care. However, pneumonia is a serious condition and can be life-threatening if left untreated and especially for those individuals at increased risk for pneumonia.
Even patients who have been successfully treated and have fully recovered may face long-term health issues. Children who have recovered from pneumonia have an increased risk of chronic lung diseases. Adults may experience:
- General decline in quality of life for months or years
Don’t Miss: Can Asthma Develop Later In Life
Adults 65 Years Or Older
CDC recommends pneumococcal vaccination for all adults 65 years or older. The tables below provide detailed information.
For adults 65 years or older who have not previously received any pneumococcal vaccine, CDC recommends you:
- Give 1 dose of PCV15 or PCV20.
- If PCV15 is used, this should be followed by a dose of PPSV23 at least one year later. The minimum interval is 8 weeks and can be considered in adults with an immunocompromising condition, cochlear implant, or cerebrospinal fluid leak.
- If PCV20 is used, a dose of PPSV23 is NOT indicated.
For adults 65 years or older who have only received PPSV23, CDC recommends you:
- May give 1 dose of PCV15 or PCV20.
- The PCV15 or PCV20 dose should be administered at least one year after the most recent PPSV23 vaccination.
- Regardless of if PCV15 or PCV20 is given, an additional dose of PPSV23 is not recommended since they already received it.
For adults 65 years or older who have only received PCV13, CDC recommends you:
- Give PPSV23 as previously recommended.* See Pneumococcal Vaccine Timing for Adults for specific guidance. The incremental public health benefits of providing PCV15 or PCV20 to adults who have received PCV13 only or both PCV13 and PPSV23 have not been evaluated.
* For adults who have received PCV13 but have not completed their recommended pneumococcal vaccine series with PPSV23, one dose of PCV20 may be used if PPSV23 is not available. If PCV20 is used, their pneumococcal vaccinations are complete.
Flu & People With Asthma
People with asthma are at higher risk of developing serious flu complications, even if their asthma is mild or their symptoms are well-controlled by medication. People with asthma can develop swollen and sensitive airways, and flu can cause further inflammation of the airways and lungs. Flu infections can trigger asthma attacks and cause worsening of asthma symptoms. Flu also can lead to pneumonia and other acute respiratory diseases. In fact, adults and children with asthma are more likely to develop pneumonia after getting sick with flu than people who do not have asthma. Asthma is the most common medical condition among children hospitalized with flu and one of the more common medical conditions among adults hospitalized with flu. More information about reported underlying health conditions among people hospitalized with flu is available from the FluView Interactive application.
You May Like: Can Asthma Cause Blue Lips
What Is The Treatment For Pneumococcal Pneumonia
For many people, pneumonia can be treated at home. Since pneumococcal pneumonia is bacterial, the primary treatment is antibiotics. Antibiotics are normally taken one or more times a day for around a week. Make sure to know how often you need to take antibiotics and for how long.
It is important to complete your entire course of antibiotics to prevent the pneumonia from returning. If you do not feel better when you complete your antibiotics, you need to see your doctor. About 30% of pneumococcal bacteria are resistant to one or more antibiotics. Sometimes your pneumonia may require additional treatment.
See: Ask the Allergist: I Had the Flu ShotWhat About the Pneumonia Shot?
Your doctor may also recommend over-the-counter medications to help with fever and muscle aches. They may also suggest over-the-counter or prescription cough medicine. Ask about what medications may be safe for you.
For patients with asthma, some may ask about inhaled or oral corticosteroids. If you are on either medication to manage your asthma, do not stop them without discussing with your doctor. We do know that inhaled corticosteroids put you at greater risk for developing pneumonia, particularly in higher doses. Work with your doctor to ensure you are on the lowest dose of inhaled corticosteroids to safely manage your asthma. Some doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids for patients with pneumonia.
and work with your doctor or health care team.
8229 Boone Blvd, Suite 260,Vienna, VA 22182
People With Asthma Have An Altered Pneumococcal Antibody Response
Children with asthma who have been recurrently exposed to bacteria such as S. pneumoniae have low antibody levels, including those with recurrent clinical infection. In a study by Rose et al., putatively protective levels were seen in between 20% and 54% of young children depending on serotype. Vaccination of these children with PCV was apparently more effective than PPV in raising antibody titres to putatively protective levels. A further study by this group investigating sequential immunization with PCV then PPV showed that around 80% children did not have an initial protective level of 0.35âμL/mL.
Similarly, a Korean study measured IgG levels to six serotypes before and after PPV in children aged 2â14âyears. They also found that children with asthma had a lower baseline antibody level, although the fold increase post-vaccination was similar to that seen in healthy children.
Read Also: Is Spiriva For Asthma Or Copd
How Can Adult Onset Asthma Be Managed
If you manage your asthma, you can expect to lead a normal lifestyle. Basically, there are four key steps to managing asthma successfully:
1. Learn about asthma and stay up-to-date on new developments.
2. Take prescribed medications. Dont make any changes until you check with your physician. Dont use over- the-counter medications unless prescribed by your physician!
3. Check your lungs daily at home by using a peak flow meter. Asthma patients often can detect lung changes with a peak flow meter before they actually experience any changes. Visit your physician regularly for further in-office tests. Lung testing is painless and provides valuable data that helps your physician make adjustments in your medication.
4. Make an asthma management plan with your physician. A plan establishes guidelines that tell you what to do if your asthma symptoms get worse.
Availability Of Data And Materials
The dataset is still subject to further analyses, but will continue to be held and managed by the Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden. Relevant anonymised data are available on reasonable request from the authors. The questionnaire can be downloaded from the study website: www.rhine.nu
Read Also: Can Fire Smoke Trigger Asthma
Is Pneumonia Treated Any Differently In Children
Essentially no. Just like adults, bacterial causes of pneumonia in children may be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are not used to treat pneumonia caused by viruses. Flu-related pneumonia may be treated with antiviral medicine if caught early in the course of illness. Most cases of pneumonia are treated with comfort care measures that ease symptoms. These may include:
- Drinking more fluids.
- Getting more rest.
- Taking over-the-counter medicines for cough and acetaminophen for fever. Be sure to check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns about giving medicines to your child.
- Using a cool mist humidifier in your childs room.
How Is The Condition Diagnosed

To diagnose asthma, your physician will question you about your symptoms, perform a physical exam, and conduct lung function tests. You also may be tested for allergies.
Your internist or family physician may refer you to an allergist or pulmonologist for specialized testing or treatment.
After middle age, most adults experience a decrease in their lung capacity. These changes in lung function may lead some physicians to overlook asthma as a possible diagnosis.
Untreated asthma can contribute to even greater permanent loss of lung function. If you have any asthma symptoms, dont ignore them, and dont try to treat them yourself. Get a definitive diagnosis from your health care provider.
Also Check: How Do You Prevent Getting Asthma
Having An Asthma Action Plan
You and your doctor will also put together an asthma action plan. This is a personalised set of instructions that includes a list of your usual asthma medications and doses, guidance on what to do in different situations , and your doctors contact details.
Treatment: Effect Of Macrolides
Macrolides are well known for their antibacterial properties. However, data confirm that macrolides also possess antiinflammatory properties that may contribute to clinical benefits observed in patients with airways inflammation.32,33,34,35 Macrolides seems to modulate inflammatory activity by inhibiting inflammatory cell chemotaxis, cytokine synthesis, adhesion molecule expression and reactive oxygen species production.33 The effectiveness of these drugs seems to be limited to 14membered and 15membered macrolides. The relative ineffectiveness of 16membered ring macrolides compared with that of 14membered ring molecules, despite relatively comparable antimicrobial activity, also suggest a mechanism that is unrelated to antimicrobial activity.36
Interest in the immunomodulatory effect of macrolides began with the observation that the use of troleandomycin as adjunctive treatment in patients with steroiddependent asthma improved asthma symptoms, and the patients were able to discontinue concomitant treatment with oral steroids.32 This spurred interest in the potential benefits of their longterm application in a variety of chronic pulmonary diseasescystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, sinusitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and diffuse panbronchiolitis.34,35,37,38 Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia may be another disease that can benefit from such treatment.39
Recommended Reading: How To Help Asthma Attack
