Whats An Asthma Attack
When you breathe normally, muscles around your airways are relaxed, letting air move easily. During an asthma attack, three things can happen:
- Bronchospasm: The muscles around the airways constrict . When they tighten, it makes the airways narrow. Air cannot flow freely through constricted airways.
- Inflammation: The airway linings become swollen. Swollen airways dont let as much air in or out of the lungs.
- Mucus production: During the attack, your body creates more mucus. This thick mucus clogs airways.
What Is The Normal Oxygen Level For Someone With Copd
Health Line Anything between 92% and 88%, is still considered safe and average for someone with moderate to severe COPD. Below 88% becomes dangerous, and when it dips to 84% or below, its time to go to the hospital. Around 80% and lower is dangerous for your vital organs, so you should be treated right away.
Knowing The Differences Between Copd And Asthma Is Vital To Good Practice
This content was published in 2011. We do not recommend that you take any clinical decisions based on this information without first ensuring you have checked the latest guidance.
The Outcomes strategy for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma was launched in July 2011 by the Department of Health, with the overall aim to drive improvements in outcomes for patients.1 Once implemented, it is expected to help people to avoid lung disease and lead longer and healthier lives. The strategy recognises the role of community pharmacy in supporting the management of people with respiratory disease through medicines use reviews and new pharmacy services.
In addition, the introduction of national target groups for MURs in England, under amendments to the NHS Community Pharmacy Contractual Framework, aims to ensure the service is provided to those who will benefit most. One of the target groups is patients with asthma or COPD.2 Both diseases have a major impact in the UK in terms of mortality and morbidity3 and the aim of MURs with these patients is to support them to take their medicines as intended, increase their engagement with their condition and medicines, and promote healthy lifestyles, in particular stopping smoking.
Don’t Miss: Does Albuterol Cause Weight Gain
Evaluating Asthma And Copd Symptoms And Causes
Because they are both lung diseases that inhibit regular breathing, asthma and COPD share many similarities in both symptoms and causes. The inflammatory immune reactions that cause an asthma attack are often triggered by airborne substances like smoke, dust, pollen, pet dander, mites and mold spores. COPD is caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants, such as cigarette smoke, toxic fumes and chemicals, which results in damaged lung cells.
While there are many external factors like tobacco smoke and secondhand smoke that can cause COPD or asthma, inherited genetic factors can also play a role in susceptibility to either of the diseases. For instance, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is also referred to as inherited emphysema. Because of their similar causes and the way they affect the lungs, COPD symptoms can oftentimes look like an asthma attack and vice versa.
Here are the symptoms that may be found in both those with asthma and those with COPD:
Although the symptoms of COPD and asthma have a great amount of overlap and similarities, there are some subtle differences among them. For example, the chronic cough often experienced by those with COPD tends to produce far more phlegm and mucus than the amount produced by asthma. For this reason, a chronic cough is much more common in those with COPD than with asthma.
Symptoms Of Asthma Vs Bronchitis
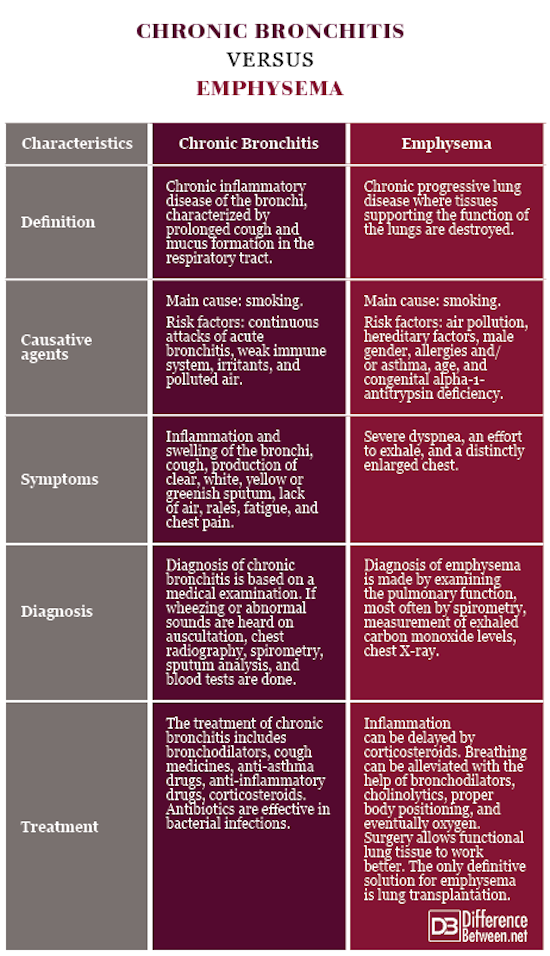
Cough is the main symptom of bronchitis and is also a typical asthma symptom. In fact, acute bronchitis and asthma are the first and second most common causes of cough, respectively.1,4 Unlike a cold or pneumonia, acute bronchitis does not usually cause a runny and stuffy nose or fever.1
People with asthma often have other breathing symptoms as well, such as wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. However, cough can be the only asthma symptom for some people.
Recommended Reading: Join Military With Asthma
Is It Asthma Or Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is an ongoing condition characterized by a cough that occurs on most days of the month, at least three months out of the year, and lasts for at least two years. It is considered a diagnosis of exclusion meaning that your healthcare provider needs to make sure that your coughing symptoms are not being caused by another condition like asthma. Symptoms are caused by inflammation and irritation of the airways in the lung.
Causes And Triggers Of Asthma
Asthma is caused by swelling of the breathing tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs. This makes the tubes highly sensitive, so they temporarily narrow.
It may happen randomly or after exposure to a trigger.
Common asthma triggers include:
- allergies
- smoke, pollution and cold air
- exercise
- infections like colds or flu
Identifying and avoiding your asthma triggers can help you keep your symptoms under control.
Recommended Reading: How To Smoke Weed With Asthma
The Differences Between Copd And Asthma
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are both respiratory diseases involving chronic inflammation that leads to airflow obstruction. While they share similar symptoms, their causes and treatments differ. In some cases, asthma and COPD may overlap in what is termed asthma-COPD overlap syndrome, or ACOS.
However, the frequency and predominating symptoms in asthma and COPD are different. With COPD, you are more likely to experience a morning cough, increased amounts of sputum, and persistent symptoms. If you have asthma, you are more likely to experience episodic symptoms during and/or at night.
Another difference between asthma and COPD is the intermittent symptoms seen with asthma versus the chronic, progressive symptoms seen in COPD. Asthma symptoms are likely to occur after exposure to specific triggers, whereas COPD symptoms occur more regularly.
How Are Copd And Asthma Similar And Different
Asthma and COPD are similar in many ways. They are also different in many ways. Here is a list of the differences between asthma and COPD. Years ago, asthma was an umbrella term under which all lung diseases fell, including COPD. Today, asthma is no longer considered an umbrella term. Today, asthma is a disease entity on its own.
Also Check: Marijuana Effects On Asthma
What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
It is yet another respiratory condition characterized by chronic interference with the lung airflow that impairs breathing. The respiratory disease is not fully reversible as seen in asthma.
Examples of COPD symptoms are shortness of breath, recurrent coughing that yields mucus, clearing throat, and progressive exercise tolerance.
The main cause of COPD is smoking. It is further divided into chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The recurrent symptoms are progressively worsening with time.
Other people susceptible to COPD are former smokers, passive smokers, and those suffering from asthma. Exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes might also cause COPD.
There is no cure for COPD. But patients are given treatment in form of oxygen therapy, medicine, lung transplant and advised to cease smoking.
Implications For Research And Practice
This study suggests that overdiagnosis of asthma in patients with COPD is more likely than overdiagnosis of COPD in patients with asthma. COPD is possibly more conservatively diagnosed as it is considered a more severe disease, whereas asthma can be more liberally diagnosed. In addition, a patient with COPD can be diagnosed with asthma in the years before first COPD diagnosis, after which no further recording of asthma is made, suggesting that the asthma diagnosis was likely to be false. In patients with presumed concomitant diagnosis of asthma and COPD, reversibility testing can be used to verify the asthma diagnosis.
The findings from the present study have implications for further research into concomitant asthma and COPD. Identifying potential concomitant asthma and COPD using electronic health records should be done cautiously. If only a single code for both diseases is required for the identification algorithm, the prevalence of concomitant diagnosis of asthma and COPD is likely to be overestimated.
Also Check: An Inhaler Used To Treat Airway Constriction In Asthma Or Allergy Might Contain A Drug That
Additional Medication For Severe Asthma
In addition to a reliever and preventer inhaler, severe asthmatics may be prescribed other treatments. You may need to try several options before your healthcare provider finds the right choice for your needs.
In addition to inhalers, treatment options include:
- Long-acting bronchodilators these can be added to a preventer inhaler and help keep the airways open for at least 12 hours.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists a non-steroid tablet that helps to calm inflamed airways, block the effects of leukotrienes and help with allergies.
- Long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists a form of long-acting bronchodilator that can work for 12-24 hours.
- Long-acting beta-agonists another form of long-acting bronchodilator that is used to relax the muscles in the airways.
- Slow-release theophylline a non-steroid tablet that helps to relax the smooth muscles in the airways, enabling air to more easily flow through.
- Short-acting beta 2-agonists a form of quick relief medication that can be used when asthma symptoms occur.
- Daily steroids these are prescribed in tablet or liquid form and are a type of anti-inflammatory medicine. They work by helping to reduce the sensitivity in the airways.
- Monoclonal antibodies a newer form of medication for severe uncontrolled asthma. They work by blocking the activity of immune system chemicals that trigger airway inflammation.
Contact Post Acute Medical Today
If you have asthma or COPD, learn more about the cardiopulmonary health services available to you by contacting Post Acute Medical today. At Post Acute Medical, we concentrate on quality care, patient satisfaction and long-term positive outcomes. Providing high-quality care to our patients is our top priority.
Find out how Post Acute Medical can help you manage your COPD or asthma by locating the facility nearest you and calling for more information.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Tell If You Have Asthma
Airway Inflammation In Asthma
The airway inflammation in asthma is persistent even though symptoms are episodic, and the relationship between the severity of asthma and the intensity of inflammation is not clearly established .The inflammation affects all airways including in most patients the upper respiratory tract and nose but its physiological effects are most pronounced in medium sized bronchi . The pattern of inflammation in the airways appears to be similar in all clinical form of asthma, whether allergic, non-allergic, or aspirin-induced and at all ages .
Is It Asthma Or Copd
A spirometry test, or pulmonary function test, can measure how well the lungs work. Individuals blow into the device as hard and as long as they can, providing information about how much air the lungs take in and expel. Many doctors use spirometry tests to measure airway problems associated with COPD and asthma.
Factors doctors look at when weighing a diagnosis with COPD or asthma include:
- A history of smoking: Most people with COPD are or were smokers.
- Age: Asthma often appears in childhood. If breathing difficulties occur after the age of 40, doctors are more likely to diagnose COPD.
- Symptoms: Coughing in the morning, heavy phlegm, and progressively getting worse suggest COPD. Recurring attacks, particularly if accompanied by allergies or eczema, suggest asthma.
- Family history: Asthma is more likely to run in families.
- Symptom triggers: People with COPD may have symptoms when they are active or at rest, without a known trigger. Asthma attacks may be caused by physical activity or something in the environment.
- Onset of symptoms: COPD tends to get worse over time, while asthma attacks come on suddenly.
- Responsiveness to treatment: Asthma tends to respond better to quick acting rescue inhalers than COPD does.
Diagnosis with either condition doesnt rule out developing another breathing disorder, so patients should report all symptoms to their doctor.
Recommended Reading: Treat Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
Inflammatory Cells In Asthmatic Airways
Mast cells -activated mucosal mast cells release bronchoconstrictor mediatorshistamine, cysteinyl leukotriens, prostaglandin D2. They are activated by allergens through IgE receptors or by osmotic stimuli . Eosinophils are in increased number in airways, release basic proteins that may damage epithelial cells, and have a role in releasing a growth factors and airway remodeling , T lymphocytes are in increased number and release specific cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 that orchestrate eosinophilic inflammation and IgE production by B lymphocytes . There may also be an increase in inKT cells which release large amounts of T helper: Th1 and Th2 cytokines . Dendritic cells,Macrophages are in increased number, and release inflammatory mediators and cytokines that amplify the inflammatory response . Nutrophils are in increased number in airways and sputum of patients with severe asthma and in smoking asthmatics, but the role of these cells is uncertain and their increase may even be due to steroid therapy .
Is It Really Copd The Difference Between Asthma And Copd
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is an ongoing lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. Its also a disease thats often misdiagnosed as asthma. Although most patients are correctly diagnosed by their doctors as having either asthma or COPD, up to 20% of patients with respiratory symptoms are difficult to accurately diagnose.
Because differentiating between asthma and COPD is essential for determining the appropriate treatment, understanding what sets these two lung diseases apart may help you decide whether or not you should further discuss your diagnosis with your doctor, or seek a second opinion.
Dont Miss: Does Weight Gain Make Asthma Worse
Read Also: How To Cure Wheezing Permanently
What Is Chronic Asthma
Chronic asthma is a condition that involves persistent inflammation and irritation of the airways. When external triggers such as cold air or allergens are present, asthma sufferers experience acute attacks of wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. Asthma attacks can last anywhere from a few minutes to over 24 hours, and mild breathing difficulties can linger in between episodes. Chronic asthma is most often an inherited disorder that tends to clear up in late childhood or adolescence, though many people have lifelong symptoms. Doctors can prescribe medications to expand the airways during an acute attack to help prevent future episodes.
Lungs and air passages afflicted with chronic asthma are always irritated to some degree. Some people with the condition cannot take deep breaths due to limited lung capacity and mucous buildup. During an attack, inflammation worsens and the airways constrict severely. The body’s natural response to inflammation is increased mucous production, which further obstructs air passages. Sufferers experience chest pain and tightness, wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. Pain and respiratory problems can lead to a rapid pulse and a loss of consciousness in the most serious cases.
Which Is Worse: Copd Or Asthma
COPD is worse than asthma. With a well-designed treatment plan, asthma symptoms can be controlled sufficiently to return lung function to normal, or very close to normal, so the condition is generally considered reversible. Though COPD symptoms can be well-managed with various treatments, the respiratory disease is irreversible, so any damage impairing lung function that has occurred cannot be restored.
Don’t Miss: Steroids For Bronchitis Side Effects
How To Prevent Bronchitis Whether You Have Asthma Or Not
Here are some steps you can take to prevent bronchitis for people who have asthma, as well as those who dont:
- Don’t smoke, and avoid being around cigarette smoke.
- Get an annual flu shot.
- Get a pneumonia shot if you are older than 65, or if you’re younger than 65 with any condition that puts you at risk, like emphysema or other breathing problems, diabetes, or heart disease.
If you do come down with acute bronchitis, remember that most cases will clear up on their own that goes for people with and without asthma. That means most people dont need treatment for acute bronchitis, but to relieve symptoms, OTC medication, such as Tylenol , can help ease pain and discomfort, and a humidifier can assist with breathing. More serious cases of bronchitis may require additional medication, such as the types of inhalers often used in asthma attacks , steroid drugs, and sometimes even oxygen.
Specifically, you should see a doctor about acute bronchitis if:
- You can’t sleep
- Your cough lasts more than a couple of weeks
- Your fever lasts more than three days or is over 101 degrees F
- The mucus you cough up is green or bloody
- You took your prescribed asthma medication but did not get any relief
- You are having difficulty breathing
- You have a heart or lung condition and suspect you have bronchitis
Although bronchitis and asthma are two different lung conditions, they’re they are closely related. Knowing the difference can help ensure you get the best treatment for the condition affecting you.
Bronchiectasis And Asthma: Similarities And Differences
Weve written many articles on the similarities and differences between COPD and bronchiectasis . But another common and well-known chronic lung condition is asthma.
Asthma affects the airways in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Its reported that 1 in 13 Americans are living with this condition, which can develop at any age. You may be more familiar with what asthma is, but did you know that asthma shares many of the same symptoms as bronchiectasis?
Read Also: Does Cold Weather Make Asthma Worse
Difference Between Asthma And Seasonal Asthma
Key difference: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways and unfortunately in todays world it is quite common. Asthma is known for causing recurring periods of wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing. In the case that a person has asthma as well as allergies, the asthma may be triggered by the allergies. This case is termed as seasonal asthma. Allergens may include plant pollen, mold, or animal hair, skin or saliva.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways and unfortunately in todays world it is quite common. Asthma is known for causing recurring periods of wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing. The coughing characteristically is worse at night or early morning. Asthma affects people of all ages, but it most often starts during childhood, due to which a number of children have to live with the disease.
The airways are tubes that carry air into and out of the lungs. Asthma causes these airways to inflame, and hence swollen and sensitive. Due to this, the airways tend to strongly react to irritants and outside substances. As the airways react, the muscles around them tighten. This causes the airways to become narrow and carry less air to the lungs that they normally would. Another way that the airways can become narrow is when the cells in the airway produce more mucus than necessary. The mucus coats the inside of the airway, thus restricting space.
