Antigen Presentation Via Macrophages
Macrophages collaborate with B cells and TH cells in the production of antibody. Macrophages will often be the first cell to encounter a foreign protein and will non-specifically engulf such material. Subsequent degradation and processing occurs within the cell, which will then present a fragment of the original protein in conjunction with MHC II molecules on its surface to TH cells via the T cell receptor . The resulting activation of TH cells produces two principal effects enhancing antibody production by B cells: directly through the CD40 receptor of the B cell, and by inducing the production of IL-4 by the TH2 cell. The B cell also has the molecular capability of endocytosing antigen and presenting antigenic peptides via the MHC class II to effector cells.
Antigen presentation and subsequent role of T cells in the pathogenesis of asthma and atopy.
Cellular Mechanisms Of Asthma21415
Many cell types are involved in the pathophysiology of asthma. A summary of the interactions between these cells is shown in Figure 27.2, which also shows the principal cytokines that facilitate communication between the cells.
Mast cells are plentiful in the walls of airways and alveoli and also lie free in the lumen of the airways where they may be recovered by bronchial lavage. Mast cell activation is the main cause of the immediate bronchospasm seen in allergen-provoked asthma. The surface of the mast cell contains a large number of binding sites for the immunoglobulin IgE. Activation of the cell results from antigen bridging of only a small number of these receptors, and may also be initiated by complement fractions C3a, C4a and C5a, substance P; physical stimulation and many drugs and other organic molecules.
The second major event after mast cell activation is the initiation of synthesis of arachidonic acid derivatives . The most important derivative of the cyclooxygenase pathway is prostaglandin PGD2, which is a bronchoconstrictor, although its clinical significance is still not clear. The lipoxygenase pathway results in the formation of leukotriene C4, from which two further peptide leukotrienes, LTD4 and LTE4, are formed .
Susana Marinho, Adnan Custovic, in, 2008
Study Designs In Analyses Of Complex Genetic Traits
Most studies on the genetics of asthma are based on allele sharing methods, transmission disequilibrium test analysis, or tests for associations. The allele sharing methods approach involves testing how often a genetic marker is shared by affected pedigree members. If allele sharing occurs significantly more often than expected by chance, linkage of the particular marker and disease can be assumed, indicating that the chromosomal region containing the genetic marker also contains a gene that contributes to disease expression.
The TDT approach is based on genotype analysis of affected subjects and their parents. The TDT tests whether genetic marker alleles from heterozygous parents are transmitted as frequently as expected by chance . Overtransmission of a particular marker allele indicates linkage of this allele with the respective ‘disease’ allele.
Association studies are usually applied once polymorphisms in candidate genes for asthma/atopy have been identified.
Also Check: Triggers For Asthma Attack
Sharing Of Loci With Other Disorders
Genetic studies of other disorders may also have an impact on asthma and atopy. Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are inflammatory bowel diseases of unknown aetiology which show familial clustering . Genome-wide screens have implicated loci on chromosomes 3, 7, 12 and 16 . The regions on chromosomes 7 and 12 may coincide with the asthma and atopy loci on the same chromosomes. Polymorphism in the IL1 cluster on chromosome 2 has also been shown to influence the severity of the disease . A genome-wide screen in families with rheumatoid arthritis has similarly shown linkage near the asthma locus on chromosome 2 and the TCR- locus on chromosome 14 . Linkage to type I diabetes is found near FcRI- on chromosome 11q13 . These findings suggest that important genes or gene families may be common to several inflammatory and immune disorders.
Chromosome 5q Gene Variants And Asthma
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : November 21, 2000Last Update Posted : February 18, 2016 |
- Study Details
BACKGROUND:
The study is in response to a Request for Applications on “Positional Candidate Approaches in Asthma Gene Discovery” released in October 1999.
DESIGN NARRATIVE:
The study completion date listed in this record was obtained from the “End Date” entered in the Protocol Registration and Results System record.
Read Also: How To Recover From Asthma Attack
Genetics Of Childhood And Adult Onset Asthma
We first examine evidence from: multivariate family based studies, where two traits e.g., childhood-onset asthma and adult-onset asthma are measured in the same family and the correlations between family members across traits are interpreted; the counting of overlapping genome-wide significant simple nucleotide polymorphism regression results from genome-wide association studies of each trait; the accuracy of a genetic risk score generated from a GWAS of one trait in predicting the second trait in a second GWAS; methods combining all SNPs from two GWAS to estimate the genetic correlation between traits; and Mendelian Randomization studies of asthma risk factors, where genetic variants affecting the risk factor are tested for an association for asthma, thus increasing evidence of causation between the risk factor and asthma.
The concepts of heritability and genetic correlation come from the theory of inheritance for quantitative traits which are assumed to be normally distributed. The extension to binary traits such as asthma requires modification of this model for use in a logistic or probit regression framework.
B Cell Immunoglobulin Class Switching
Antibody production occurs in B lymphocytes and its mature cell type, the plasma cell. The antibody molecule is constructed from two heavy chains and two light chains linked by disulphide bridges. The antibody molecule has two functional domains. The antigen binding specificity is determined by the NH2 terminus of the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, which are extremely variable. The COOH terminus of the immunoglobulin heavy chain determines the effector functions. The variable regions of both heavy and light chains interact to form the antigen binding domain. The variable amino acid structure of this region is created by a number of mechanisms, including DNA rearrangement and somatic recombination to produce the VJ domain.
The immune system has evolved an almost inexhaustible versatility in the production of specific antibodies. The accepted model for this phenomenon is the clonal selection theory, which assumes a constant production of B cells with surface immunoglobulin with unique antigen specificity. When a novel antigen is encountered by the immune system, this will bind only to a small fraction of the surface immunoglobulin with the appropriate specificity. The binding of antigen with the surface antibody initiates a cascade stimulating that B cell to proliferate and to synthesise and secrete more specific antibody.
Recommended Reading: Can Someone With Asthma Join The Military
Future Directions And Recommendations
Genetic contributions are higher for childhood-onset asthma.
The genetic overlap between childhood and adult onset asthma is large.
The usually small size of the contribution of a single locus to heritability in the population does not preclude a large effect of a drug targeting that pathway. This is the justification given for these larger and larger studies that can detect smaller and smaller effects.
Mendelian Randomization is a useful tool to investigate pathogenesisif variation in a gene altering a putative intermediate variable is associated with risk, then environmental exposures affecting that same pathway are supported as truly causative.
Lacking gene-environmental studies on important risk factors for asthma phenotypes such as diet, medication, microbiota, emerging pollutants, climate change and extreme weather conditions merit consideration.
Despite methodological challenges, GWIS studies through collaboration hold promise for identifying unexpected gene environment interactions and improving our understanding of asthma phenotypes during a lifetime, beyond candidate studies based on our knowledge of biological processes and/or pathways.
What Chromosome Does Asthma Affect
This means that people with a family history of asthma are more likely to have it, dust burdens, asthma is not the result of a change or mutation in a single gene, a whistling sound when you breathe out and shortness of breath.The Link Between Asthma and GeneticsThe discovery of asthma genes has lead to better wisdom about asthma, The prevalence of eosinophilic asthma is 3240% among asthmatic patients.
Recommended Reading: Asthma Attack With No Inhaler
The Impact Of Asthma On Daily Life
Asthma is often under-diagnosed and under-treated, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
People with under-treated asthma can suffer sleep disturbance, tiredness during the day, and poor concentration. Asthma sufferers and their families may miss school and work, with financial impact on the family and wider community. If symptoms are severe, people with asthma may need to receive emergency health care and they may be admitted to hospital for treatment and monitoring. In the most severe cases, asthma can lead to death.
Insight From Genetic Studies Of Asthma Before The Era Of Genome
The first linkage analyses for genes involved in asthma susceptibility and IgE regulation initiated in the early 1990s appeared promising ; however, the first candidate gene was not identified until 2002 . ADAM33 belongs to a family of metalloproteinases and is predominantly expressed in cells in the airways, such as fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. Because of its broad involvement in cell activation and signalling, it has been suggested that ADAM33 is involved in the remodelling process that may occur in asthma patients with long-standing airway inflammation. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in ADAM33 have been shown to influence baseline lung function as well as asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness, but do not appear to increase the risk of allergy . A meta-analysis of the association between ADAM33 SNPs and asthma showed an overall 46% risk increase of a particular SNP .
Figure 1
Studies showing positive gene association with asthma, using stringent inclusion criteria for association , published until 1 July 2008. ORMDL3from the first asthma GWAS was also included. Adapted from the reference .
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Asthma Without Inhaler
Genomic Studies Of Asthma
Gene expression is one of many mechanisms that may affect the protein level and its influence on cellular functions. Variation in gene expression is therefore vitally important for normal cellular events as well as for processes related to disease development. The DNA sequence is the template for mRNA transcription , which will determine the transcript sequence and ultimately the protein product . However, there are a number of regulatory mechanisms in cells that will influence the transcription rate , transcript sequence and translation into protein . Regulatory, nonprotein-coding RNAs have attracted much attention recently and are believed to have important roles in transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation . In addition, environmental stimuli may be potent triggers of expression of specific genes. Thus, determining the DNA sequence of a particular region will only provide the underlying basis for biological functions that may be responsible for disease development and not the whole picture. By studying gene expression and protein characteristics, we will obtain better functional information about processes related to health and disease. Gene expression is in many cases tissue specific, which is important to consider when studies are compared. On the other hand, analyses of tissues directly affected by the disease may give valuable insights into the pathophysiology of the target organ.
Figure 2
Mast Cells And Inflammatory Mediators
The mast cell is activated by dimerisation of antigen specific IgE bound to high or low affinity receptors on the cell surface. A wide variety of chemical mediators is released by the mast cell, such as histamine, bradykinin, leukotrienes C, D, and E, platelet activating factor, PGE2, PGF2α, PGD2, and thromboxane. In addition, several chemotactic factors are released, including eosinophil and neutrophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis and LTB4. Lung biopsy sample studies suggest that the mast cell is more important in mild atopic asthma, as distinct from severe chronic asthma.
Also Check: Can Someone With Asthma Smoke Weed
Who Strategy For Prevention And Control Of Asthma
Asthma is included in the WHO Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs and the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
WHO is taking action to extend diagnosis of and treatment for asthma in a number of ways.
The WHO Package of Essential Noncommunicable Disease Interventions was developed to help improve NCD management in primary health care in low-resource settings. PEN includes protocols for the assessment, diagnosis, and management of chronic respiratory diseases , and modules on healthy lifestyle counselling, including tobacco cessation, and self-care.
Reducing tobacco smoke exposure is important for both primary prevention of asthma and disease management. The Framework Convention on Tobacco Control is enabling progress in this area as are WHO initiatives such as MPOWER and mTobacco Cessation.
The Pathophysiology Of Early Childhood Asthma
There are only limited studies of the pathophysiology of asthma in preschool-age children. Such studies are obviously hindered by the ethical dilemma of subjecting nonconsenting and vulnerable children to intrusive pathologic and physiologic assessment procedures.46 Autopsy and bronchial biopsy data are rare in infants and young children because of the rare occurrence of death in this age group and the evident difficulty of obtaining endobronchial biopsies in children.4749 One study examined mucosal biopsies in a small number of highly selected children 1 to 3 years of age with severe, recurrent wheeze, most of whom were atopic. They observed in those children increased thickness of reticular basement membrane and increased eosinophil density consistent with the characteristic pathologic features of asthma in adults and older children.50 In contrast, another highly selected group of much younger infants referred for severe wheeze at a median age of 12 months had no evidence of airway inflammation or structural change on bronchial biopsy,51 which implies that these changes develop between 1 and 3 years of age.
Andrew B Lumb MB BS FRCA, in, 2017
Read Also: How Can You Tell If You Have Asthma
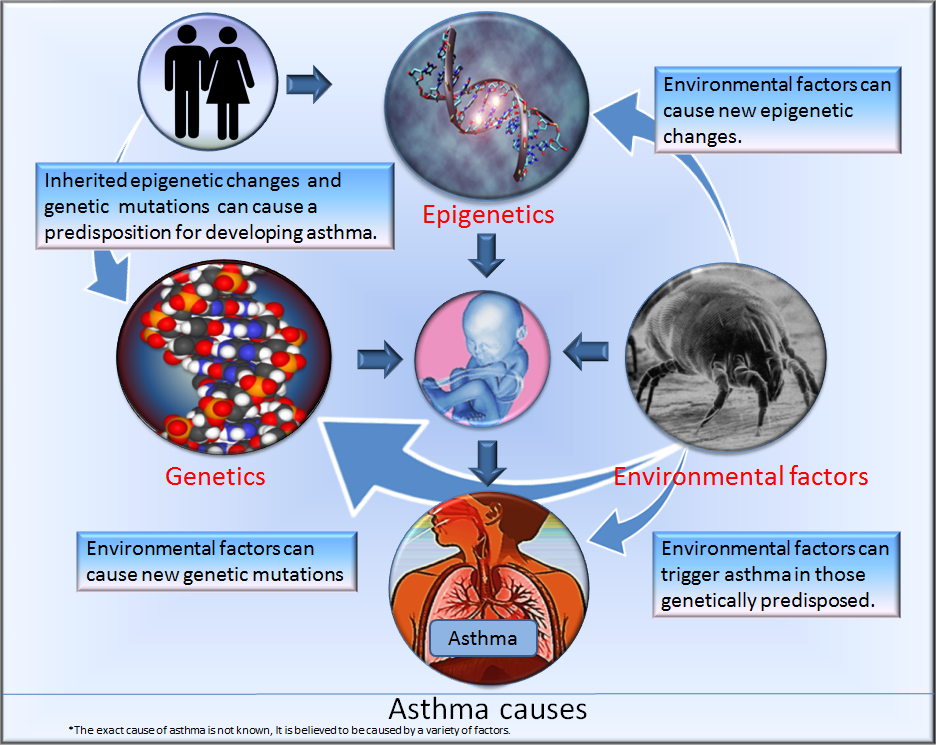
Contribution Of Inherited Factors
The central tenet of research in asthma genetics is that clinical disease only occurs in a subject with a genetic susceptibility, which becomes expressed after exposure to an environmental trigger. Several environmental factors have been proposed, including house dust mites, cigarette smoke, viral respiratory tract infections, and atmospheric pollution. Unfortunately, the elements of the genetic susceptibility have proved to be more elusive. Although the prevalence of asthma in a population is approximately 4â8% , this increases to 20â25% in those with affected first degree relatives. This measure can be expressed as the risk ratio , which is defined as the prevalence of a disease in first degree relatives of an affected subject divided by the prevalence in the general population. In asthma, λS is approximately 5â6, compared with 15 in type I diabetes mellitus, 8 in schizophrenia, and 3.5 in type II diabetes mellitus.
Monozygotic and dizygotic twin studies have examined the concordance of a number of traits, such as asthma symptoms, total IgE, and skin test hypersensitivity, and have shown variable, but significant, inherited contributions . As with other multifactorial diseases, the contribution of genetic factors is influenced by the population being studied and the propensity to sharing a common environment.
Looking Into The Future Of Asthma Genes
Genetic research is an evolving field in science, and researchers are just beginning to understand how asthma genes work together to cause asthma.
It actually appears that there are many root causes of asthma . The quest is ongoing to learn what each specific asthma gene does, how they work together in response to environmental triggers to cause asthma, and methods of blocking their effects. Hopefully this will give pharmaceutical companies the “building blocks” they need to develop medicines catered to each specific phenotype and subtype, thereby giving each physician better options for helping each individual asthmatic.8
The accumulation of information learned through genetic research shows how complex this disease is. However, the hope is that it will be only a matter of time;before researchers make that revolutionary breakthrough that leads them to the true root causes of our disease, along with better treatment options catered specifically for you.
Also Check: Are Chihuahuas Good For Asthma
New Gene Tied To Childhood Asthma
Researchers Say Identification of Gene May Lead to Development of New Treatments
Dec. 28, 2009 — A newly identified gene may play a critical role in triggering childhood asthma and offer new opportunities for developing more effective asthma treatments.
Researchers say the gene, DENND1B, affects cells and other signaling molecules thought to be involved in the immune system overreaction that occurs in childhood asthma.
“We now know that the DENND1B gene and its protein are involved in the release of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that in this case tell the body how it should respond to foreign particles,” says researcher Hakon Hakonarson, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Applied Genomics at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, in a news release. “In asthma, patients have an inappropriate immune response in which they develop airway inflammation and overreaction of the airway muscle cells, referred to as airway hyperresponsiveness. The gene mutations in DENND1B appear to lead to overproduction of cytokines that subsequently drive this oversensitive response in asthma patients.”
Asthma is a complex disease that causes wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Researchers say many factors, including genetics and environmental factors, play a role in the cause of asthma. Until now, only one gene has been associated with childhood asthma, but many genes are thought to be involved.
Genetic Epidemiology Of Asthma
Looking at the population gives clues about asthma being a heritable trait. First, there are large geographic and racial differences in disease occurrence. For example, the prevalence of asthma in many Western populations is high, up to 20%, whereas populations from the developing world exhibit much smaller prevalence rates, some as low as 1% or even lower . This is only indicative of a genetic causation in asthma, as different populations also have very different environmental circumstances. Second, offspring of asthmatic parents are at increased risk of asthma . The recurrence risk of asthma in children with one affected parent is around 25%, whereas the risk if both parents are affected is around 50%. Twin studies also support asthma being much more likely to occur in an individual if that individual has a genetically close relative with the disease. For instance, the recurrence risk of asthma in monozygotic twins is much higher than in dizygotic twins, highlighting the role of genetic risk factors in asthma . Nevertheless, the fact that the concordance for asthma in monozygotic twins is not 100% but around 75% points to environmental risk factors also playing an important role.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
