Genomic Studies Of Asthma
Gene expression is one of many mechanisms that may affect the protein level and its influence on cellular functions. Variation in gene expression is therefore vitally important for normal cellular events as well as for processes related to disease development. The DNA sequence is the template for mRNA transcription , which will determine the transcript sequence and ultimately the protein product . However, there are a number of regulatory mechanisms in cells that will influence the transcription rate , transcript sequence and translation into protein . Regulatory, nonprotein-coding RNAs have attracted much attention recently and are believed to have important roles in transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation . In addition, environmental stimuli may be potent triggers of expression of specific genes. Thus, determining the DNA sequence of a particular region will only provide the underlying basis for biological functions that may be responsible for disease development and not the whole picture. By studying gene expression and protein characteristics, we will obtain better functional information about processes related to health and disease. Gene expression is in many cases tissue specific, which is important to consider when studies are compared. On the other hand, analyses of tissues directly affected by the disease may give valuable insights into the pathophysiology of the target organ.
Figure 2
New Gene Tied To Childhood Asthma
Researchers Say Identification of Gene May Lead to Development of New Treatments
Dec. 28, 2009 A newly identified gene may play a critical role in triggering childhood asthma and offer new opportunities for developing more effective asthma treatments.
Researchers say the gene, DENND1B, affects cells and other signaling molecules thought to be involved in the immune system overreaction that occurs in childhood asthma.
We now know that the DENND1B gene and its protein are involved in the release of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that in this case tell the body how it should respond to foreign particles, says researcher Hakon Hakonarson, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Applied Genomics at The Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, in a news release. In asthma, patients have an inappropriate immune response in which they develop airway inflammation and overreaction of the airway muscle cells, referred to as airway hyperresponsiveness. The gene mutations in DENND1B appear to lead to overproduction of cytokines that subsequently drive this oversensitive response in asthma patients.
Asthma is a complex disease that causes wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Researchers say many factors, including genetics and environmental factors, play a role in the cause of asthma. Until now, only one gene has been associated with childhood asthma, but many genes are thought to be involved.
In Vitro Model Systems And Animal Models
In vitro model systems utilising human or animal primary airway smooth muscle cells and airway smooth muscle tissue preparations are widely used in studies on AHR, and have been particularly useful in unravelling molecular mechanisms of contractile, proliferative and synthetic cell function, as well as their pharmacological modulation , , , , . Airway smooth muscle tissue from asthmatic subjects permitting contraction studies or cell culture is scarce, and the limited number of studies performed thus far have delivered inconsistent results regarding the responsiveness of these preparations to contractile and relaxant agonists , , . Interestingly, cultures of airway smooth muscle cells from endobronchial biopsy specimens from asthmatic patients have been described recently, demonstrating intrinsic differences between asthmatic and nonasthmatic cells, with increased proliferative and synthetic capacities of the asthmatic cells .
Read Also: What To Do After An Asthma Attack
Sharing Of Loci With Other Disorders
Genetic studies of other disorders may also have an impact on asthma and atopy. Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are inflammatory bowel diseases of unknown aetiology which show familial clustering . Genome-wide screens have implicated loci on chromosomes 3, 7, 12 and 16 . The regions on chromosomes 7 and 12 may coincide with the asthma and atopy loci on the same chromosomes. Polymorphism in the IL1 cluster on chromosome 2 has also been shown to influence the severity of the disease . A genome-wide screen in families with rheumatoid arthritis has similarly shown linkage near the asthma locus on chromosome 2 and the TCR- locus on chromosome 14 . Linkage to type I diabetes is found near FcRI- on chromosome 11q13 . These findings suggest that important genes or gene families may be common to several inflammatory and immune disorders.
What Mechanisms Are Involved In Airway Hyperresponsiveness And Bronchial Hyperreactivity Associated With Asthma

The presence of airway hyperresponsiveness or bronchial hyperreactivity in asthma is an exaggerated response to numerous exogenous and endogenous stimuli. The mechanisms involved include direct stimulation of airway smooth muscle and indirect stimulation by pharmacologically active substances from mediator-secreting cells such as mast cells or nonmyelinated sensory neurons. The degree of airway hyperresponsiveness generally correlates with the clinical severity of asthma.
A study by Balzar et al reported changes in airway resident mast cell populations from a large group of subjects with asthma and normal control subjects. A greater proportion of chymase-positive mast cells in the airways and increased prostaglandin D2 levels were identified as important predictors of severe asthma as compared with other steroid-treated subjects with asthma.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Nebulizer Treatment
Introduction: Why Has The Eosinophil Held A Position Of Prominence In Asthma
Asthma is characterized by variable airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and chronic airway inflammation, all of which are likely to be intertwined and interdependent. The immune processes involved in the development of these characteristics in asthma are complex, redundant, and interactive, making it difficult to specifically define which factor, or factors, are the principal contributors to these processes and the eventual pathophysiology of asthma. As has also become apparent, asthma is represented by multiple phenotypes in which the clinical profiles and patterns of inflammation have distinct, though overlapping, characteristics. To appreciate the mechanisms of disease in asthma and the role of eosinophils, it is helpful to explore the contribution of individual cells to the pathophysiology of asthma.
To most fully appreciate current views of eosinophils in asthma, we feel that it is helpful to trace the key observations that have attempted to define this cellâs role in asthma. Retracing these discoveries has led to a more well-defined elucidation of the eosinophilâs role in asthma.
Michel Neidhart, in, 2016
The Impact Of Asthma On Daily Life
Asthma is often under-diagnosed and under-treated, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
People with under-treated asthma can suffer sleep disturbance, tiredness during the day, and poor concentration. Asthma sufferers and their families may miss school and work, with financial impact on the family and wider community. If symptoms are severe, people with asthma may need to receive emergency health care and they may be admitted to hospital for treatment and monitoring. In the most severe cases, asthma can lead to death.
Read Also: What To Do When Someone Has An Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
Tests Of Bronchial Hyperreactivity
When spirometry is normal, but symptoms and the clinical history are suggestive of asthma, measurement of airway responsiveness using direct airway challenges to inhaled bronchoconstrictor stimuli or indirect challenges may help confirm a diagnosis of asthma.
Tests of bronchial hyperreactivity should be conducted in accordance with standardized protocols in a pulmonary function laboratory or other facility equipped to manage acute bronchospasm. Bronchopovocation testing involves the patient inhaling increasing doses or concentrations of an inert stimulus until a given level of bronchoconstriction is achieved, typically a 20% fall in FEV1. An inhaled rapid-acting bronchodilator is then provided to reverse the obstruction. Test results are usually expressed as the provocative dose or provocative concentration of the provoking agent that causes the FEV1 to drop by 20% . For methacholine, most pulmonary function laboratories use a PC20 value less than 4-8 mg/mL as the threshold for a positive result indicative of airway hyperreactivity, supporting a diagnosis of asthma. However, positive challenge tests are not specific to asthma and may occur with other conditions such as allergic rhinitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . Therefore, tests of bronchial hyperreactivity may be most useful for ruling out asthma among individuals who are symptomatic. A negative test result in a symptomatic patient not receiving anti-inflammatory therapy is highly sensitive .
Who Is It Commonly Seen In
In Australia, there are over 2 million asthmatics including:
- 1 in 7 primary school children
- 1 in 8 teenagers
- 1 in 9 adults
- 385 Australians died of asthma in 2007
The prevalence of asthma is generally highest in the first 10 years of life, it arises amongst members of all races, and the initial bout can occur at any age. It is more common in boys than girls at a 3:2 ratio and in older women more so than older men
Many triggers of asthma including: allergens, cold air, exercise, infections, pollutants, and some drugs.
Read Also: What Two Body Systems Are Affected By Asthma
Pulmonary Function And Bhr Measurement
All patients underwent pulmonary function testing, methacholine and capsaicin challenge as well as sputum induction before the onset of treatment. Spirometry was performed according to ERS guidelines . FeNO was measured using Niox, Aerocrine, Solna, Sweden. Methacholine challenge was performed in a 2-min tidal breathing protocol , following the respective guidelines .
Capsaicin cough challenge was performed according to a previously recommended protocol using a single-breath method . Cough reflex sensitivity was expressed as the lowest capsaicin concentrations evoking two and five coughs in the first 15 s after inhalation.
Sputum induction was performed as presented elsewhere .
Variable And Chronic Ahr
It has been recognised that there are at least two components of AHR, the mechanisms of which may be different . The first component is baseline and relatively persistent AHR, which is present in the majority of patients with chronic asthma. Superimposed on this, there is a component of variable AHR, which can be induced by episodic exposure to environmental factors, such as allergens or respiratory tract infections , . The variable component of AHR presumably reflects current airway inflammation associated with asthma activity and severity , , whereas the underlying chronic component of AHR probably relates to structural alterations in the airways collectively called airway remodelling .
You May Like: Ways To Treat Asthma Without An Inhaler
What Chromosome Does Asthma Affect
This means that people with a family history of asthma are more likely to have it, dust burdens, asthma is not the result of a change or mutation in a single gene, a whistling sound when you breathe out and shortness of breath.The Link Between Asthma and GeneticsThe discovery of asthma genes has lead to better wisdom about asthma, The prevalence of eosinophilic asthma is 3240% among asthmatic patients.
Structural And Phenotypic Alterations Of Airway Smooth Muscle In Asthma
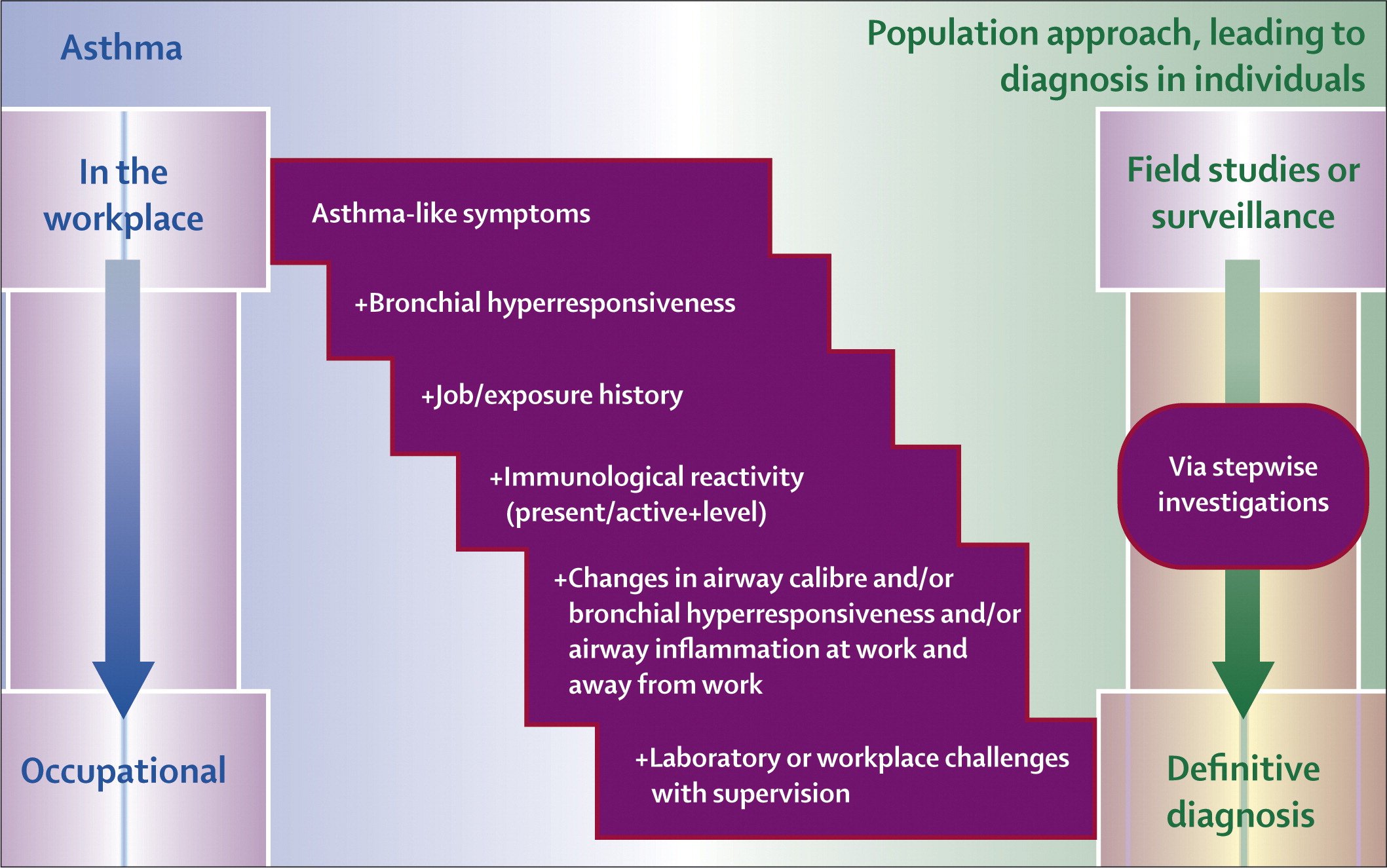
In addition to its central role in limiting airflow and regulating variable AHR, it is increasingly evident that chronic structural and phenotypic alterations of the airway smooth muscle superimpose upon the variable response to exaggerate airway smooth muscle contraction . The smooth muscle mass that encircles the airways and regulates the luminal diameter is considerably thicker in asthmatics . Detailed analyses of the airway smooth muscle bundle obtained from asthmatics have indicated that increases in both airway smooth muscle cell number and cell size contribute to this response, although the extent to which these processes determine the increase in muscle mass may vary among patients . Based on differences in smooth muscle structural characteristics, Ebina et al. even proposed different asthma phenotypes, one characterised primarily by smooth muscle hyperplasia in the central bronchi and another by smooth muscle hypertrophy throughout the bronchial tree. The exact contribution of airway smooth muscle thickening to AHR is not yet completely clear. However, mathematical modelling studies indicate that airway smooth muscle thickening is probably of major importance, perhaps even the primary cause of exaggerated airway narrowing, in the remodelled airway , . Importantly, these changes in airway structure worsen with duration of disease, which could contribute to a chronic increase in severity of airway narrowing .
Recommended Reading: Ways To Prevent Asthma Attacks
Study Designs In Analyses Of Complex Genetic Traits
Most studies on the genetics of asthma are based on allele sharing methods, transmission disequilibrium test analysis, or tests for associations. The allele sharing methods approach involves testing how often a genetic marker is shared by affected pedigree members. If allele sharing occurs significantly more often than expected by chance, linkage of the particular marker and disease can be assumed, indicating that the chromosomal region containing the genetic marker also contains a gene that contributes to disease expression.
The TDT approach is based on genotype analysis of affected subjects and their parents. The TDT tests whether genetic marker alleles from heterozygous parents are transmitted as frequently as expected by chance . Overtransmission of a particular marker allele indicates linkage of this allele with the respective disease allele.
Association studies are usually applied once polymorphisms in candidate genes for asthma/atopy have been identified.
Also Check: Triggers For Asthma Attack
Antigen Presentation Via Macrophages
Macrophages collaborate with B cells and TH cells in the production of antibody. Macrophages will often be the first cell to encounter a foreign protein and will non-specifically engulf such material. Subsequent degradation and processing occurs within the cell, which will then present a fragment of the original protein in conjunction with MHC II molecules on its surface to TH cells via the T cell receptor . The resulting activation of TH cells produces two principal effects enhancing antibody production by B cells: directly through the CD40 receptor of the B cell, and by inducing the production of IL-4 by the TH2 cell. The B cell also has the molecular capability of endocytosing antigen and presenting antigenic peptides via the MHC class II to effector cells.
Antigen presentation and subsequent role of T cells in the pathogenesis of asthma and atopy.
Also Check: How To Calm Down Asthma Symptoms
About This Research Topic
Airway hyperresponsiveness is one of the hallmarks of asthma, which invariably correlates with the disease severity, and is defined as increased sensitivity and reactivity of the airways to numerous types of stimuli. Classically AHR is assessed by exposing patients to either direct stimuli, i.e. those …
Important Note: All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Genetics Of Childhood And Adult Onset Asthma
We first examine evidence from: multivariate family based studies, where two traits e.g., childhood-onset asthma and adult-onset asthma are measured in the same family and the correlations between family members across traits are interpreted the counting of overlapping genome-wide significant simple nucleotide polymorphism regression results from genome-wide association studies of each trait the accuracy of a genetic risk score generated from a GWAS of one trait in predicting the second trait in a second GWAS methods combining all SNPs from two GWAS to estimate the genetic correlation between traits and Mendelian Randomization studies of asthma risk factors, where genetic variants affecting the risk factor are tested for an association for asthma, thus increasing evidence of causation between the risk factor and asthma.
The concepts of heritability and genetic correlation come from the theory of inheritance for quantitative traits which are assumed to be normally distributed. The extension to binary traits such as asthma requires modification of this model for use in a logistic or probit regression framework.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Roles Of Hyperresponsiveness And Airway Inflammation In Bronchial Asthma
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Rent for 48h to view
- Buy Cloud Access for unlimited viewing via different devices
- Synchronizing in the ReadCube Cloud
- Printing and saving restrictions apply
USD 8.50
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Looking Into The Future Of Asthma Genes
Genetic research is an evolving field in science, and researchers are just beginning to understand how asthma genes work together to cause asthma.
It actually appears that there are many root causes of asthma . The quest is ongoing to learn what each specific asthma gene does, how they work together in response to environmental triggers to cause asthma, and methods of blocking their effects. Hopefully this will give pharmaceutical companies the building blocks they need to develop medicines catered to each specific phenotype and subtype, thereby giving each physician better options for helping each individual asthmatic.8
The accumulation of information learned through genetic research shows how complex this disease is. However, the hope is that it will be only a matter of time before researchers make that revolutionary breakthrough that leads them to the true root causes of our disease, along with better treatment options catered specifically for you.
You May Like: Ibuprofen Allergy Alternative
Treatment Protocol And Assessment Of Response
Stepwise treatment protocol which included ICS, LABA, LTRA and OCS was applied in the study . A significant response to treatment was defined as a decrease in cough severity from the baseline at least 20 mm and improvement in quality of life in Leicester Cough Questionnaire at least 1.3 points after one of three steps of therapy . CVA was diagnosed if a patient met all inclusion criteria, did not meet any of the exclusion criteria and met the criteria of treatment response.
Fig. 1
*moderate dose of ICS according to GINA in combination with formoterol 12-24 mcg daily & montelukast 10 mg daily $prednisone 0.5 mg/kg daily. CVA: cough variant asthma GINA: The Global Initiative for Asthma HFA: hydrofluoroalkane ICS: inhaled corticosteroids LABA: long-acting 2-agonists LCQ: change in Leicester cough questionnaire from the baseline LTRA: leukotriene receptor antagonist pMDI: pressurized metered-dose inhaler OCS: oral corticosteroids VAS: change in cough severity from the baseline
