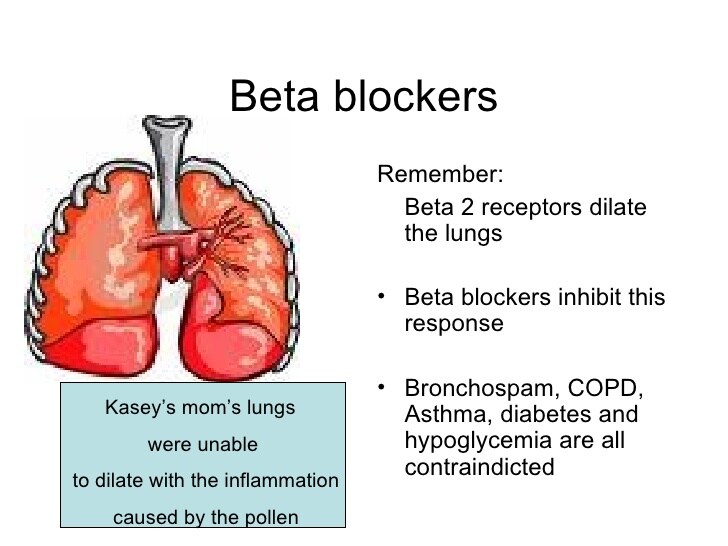
Beta Blockers For Asthma Patients
Our body contains three different types of beta-receptors known as 1, 2, and 3 receptors. The 1 receptors are located in the heart and the kidneys, followed by the 2 receptors which are located in the liver, lungs, skeletal muscles, uterus, gastrointestinal tract, and the vascular smooth muscle. The 3 receptors are found in the fat cells of the body. Now, there are two types of beta blockers that are available, the non-selective beta blockers and the selective beta blockers. As the name signifies, the non-selective beta blockers can block multiple types of beta receptors in the body. On the other hand, the selective beta blockers are designed to block only selective types of beta receptors in the body.
When a person is suffering from a condition like asthma, other signs and symptoms like anxiety and sleeplessness can occur. Both these conditions result from the shortness of breath and discomfort that occurs in asthma patients during attacks. In this condition, sleeping pills and tranquilizers are something that the patient may ask for, however, make sure that you dont go for them at all without medical supervision! As far as beta blockers are concerned, some people also use certain short-acting beta blockers for sleep related problems which should again be avoided. So, make sure that you completely avoid beta blockers if you have asthma. It is always best to consult with your doctor for alternate medications and remedies.
Are There Differences Among Beta Blockers
Beta blockers differ by which receptors are blocked.
First generation beta blockers such as propranolol , nadolol , timolol maleate , penbutolol sulfate , sotalol hydrochloride , and pindolol are non-selective in nature, meaning that they block both beta1 and beta2 receptors and will subsequently affect the heart, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver, uterus, vascularsmooth muscle, and skeletalmuscle and as an effect, could cause reduced cardiac output, reduced renal output amongst other actions.
Second generation beta blockers such as metoprolol , acebutolol hydrochloride , bisoprolol fumarate , esmolol hydrochloride , betaxolol hydrochloride , and acebutolol hydrochloride are selective, as they block only 1 receptors and as such will affect mostly the heart and cause reduced cardiac output.
Beta blockers such as pindolol , penbutolol sulfate , and acebutolol hydrochloride differ from other beta blockers as they possess intrinsic sympathomimetic activity , which means they mimic the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine and can cause an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. ISA’s have smaller effects in reducing resting cardiac output and resting heart rate, in comparison to drugs that do not possess ISA.
Beta blocker such as propranolol , acebutolol hydrochloride , and betaxolol hydrochloride possess a quinidine-like or anesthetic-like membrane action, which affects cardiac action potential .
Study Design And Outcomes
The primary analysis was a nested case-control design used to more efficiently account for time-varying confounders and drug exposure . The nested case-control design assesses the risk of exposure versus non-exposure among cases and controls and it is normal for cases to appear sicker than controls . Two nested case-control studies were performed evaluating moderate asthma exacerbations and severe asthma exacerbations. Severe asthma exacerbations were defined as a hospitalisation for asthma or death from asthma. Moderate asthma exacerbations were identified by receipt of rescue oral steroids in primary care, defined as oral prednisolone prescriptions of less than 2 weeks duration using5 mg strength tablets. People with non-rescue oral steroids were excluded from this analysis to prevent outcome misclassification bias. For each outcome, the date of the first asthma event was the index date for case subjects.
Read Also: Is Asthma A Small Airway Disease
Beta Blockers Are Not Approved For Anxiety Reduction
Maybe the most important reason to avoid beta blockers is that they’re not technically approved for anxiolytic use. Doctors prescribe these medicines “off-label” – meaning that they aren’t approved for use but are used anyway.
Off-label use is not uncommon for medications – not even medications for anxiety. What makes beta-blockers unique is that not only are they used off-label but doctors aren’t even sure why beta blockers reduce anxiety. Their mechanism is only partially known. Beta blockers lower heart rate and reduce norepinephrine, which can spike when a person has anxiety. This then controls the symptoms of anxiety. What is not entirely clear is whether or not beta blockers control any mental symptoms of anxiety. Doctors and patients sometimes find that people taking beta blockers seem to experience reduced anxiety, but it is not clear if any emotional symptoms are due to the beta blockers themselves, or just a reaction to weaker physical symptoms.
Do Beta Blockers Work
In theory, beta blockers may help reduce anxiety. But they don’t reduce anxiety for everyone, and they can’t cure anxiety altogether. Beta blockers are taken as needed. to reduce anxiety in the moment, but the anxiety will still come back if not properly managed.
If you’re willing to commit to medication, then you’re willing to commit to something better and safer, and thus it is highly recommended that – no matter your success with beta blockers – you consider a supplementary non-medicinal treatment to learn how to manage your stress and anxiety.
Read Also: Asthmatic Reaction
Can You Take Propranolol With Inhaler
propranolol albuterol Using propranolol together with albuterol may reduce the benefits of both medications, since they have opposing effects in the body. In addition, propranolol can sometimes cause narrowing of the airways, which may worsen your breathing problems or trigger severe asthmatic attacks.
Learn More About Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are some of the most widely used medications in the world, prescribed for heart conditions, anxiety and more. Safe, easy to use and effective, they provide fast and noticeable results that make them ideal for preventing chronic anxiety and panic attacks.
Our guide to propranolol goes into more detail on how one of the most widely used beta blocker medications works, from its history to major benefits, potential side effects, drug interactions and more.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
Get updates from hims
You May Like: Does Ibuprofen Make Asthma Worse
What Are Alternatives To Using Ace Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors do not cause lung function to decrease.1 Therefore, people with asthma may be able to take these medications if they are necessary. If one ACE inhibitor causes cough, others probably will too.1 Your health care provider may be able to recommend a different type of medication to treat your condition. You may also be able to take medications that reduce coughing.
Is It Safe To Stop Using Beta
Its dangerous to stop taking beta-blockers suddenly, even if youre experiencing side effects.
When you take beta-blockers, your body gets used to your hearts slower speed. If you stop taking them suddenly, you could increase your risk of a serious heart problem, such as a heart attack.
Contact your doctor if you experience unpleasant side effects with beta-blockers that last for more than a day or two. Your doctor might suggest another type of medication, but youll still need to slowly taper your beta-blocker dose.
Recommended Reading: Nsaid Induced Asthma
Why Does Beta Blockers Cause Hypoglycemia
4.6/5blockerhypoglycemiablockerscause hypoglycemia
Furthermore, why do beta blockers mask hypoglycemia?
Beta blockersThese medicines are designed to blunt the -effect of adrenalin and related substances. As noted above, beta blockers will also prevent adrenalin from stimulating the liver to make glucose, and therefore may make the hypoglycemia more severe and/or more protracted.
One may also ask, why do beta blockers cause hyperglycemia? In people with diabetes, –blockers such as propranolol, metoprolol, and atenolol can result in consistently elevated fasting blood glucose levels. –blockers are thought to contribute to the development of hyperglycemia by impairing the release of insulin from the pancreatic -cell.
Moreover, do beta blockers cause hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia?
In insulin-dependent diabetics, beta–blockers can prolong, enhance, or alter the symptoms of hypoglycemia, while hyperglycemia appears to be the major risk in noninsulin-dependent diabetics. beta–blockers can potentially increase blood glucose concentrations and antagonize the action of oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Does propranolol cause low blood sugar?
Stopping propranolol suddenly can cause changes in your heart rhythm and blood pressure, worsened chest pain, or a heart attack. Diabetes warning: Propranolol can cause low blood sugar . It may also mask the signs of low blood sugar, such as a heart rate that’s higher than normal, sweating, and shakiness.
Side Effects Of Beta Blockers
Yet the main reason to avoid beta blockers is the side effects. What’s unique about beta blockers is that no one knows how they’ll affect any given person. Everyone responds to beta blockers differently. So while some may find temporary relief from their anxiety, others may find their anxiety to be much worse, while others may see no effect.
The most common side effects of beta blockers for anxiety include:
- Nausea
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Asthma Symptoms Last
How The Conditions Intersect
Blood pressure is a major part of asthma.
You can have high blood pressure with asthma. But it usually isnât because of a severe asthma attack. When you have less intense episodes, your blood pressure might go up because your lungs wonât pull in enough air. Your heart will pump faster to get enough oxygen to the rest of your body, so your blood pressure will go up, as a result.
Who Can Take Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are not suitable for everyone. To make sure they are safe for you, tell your doctor before starting a beta blocker if you have:
- had an allergic reaction to a beta blocker or any other medicine in the past
- low blood pressure or a slow heart rate
- serious blood circulation problems in your limbs
- metabolic acidosis when there’s too much acid in your blood
- lung disease or asthma
Tell your doctor if you’re trying to get pregnant, are already pregnant or breastfeeding.
It’s important not to stop taking beta blockers without seeking your doctor’s advice. In some cases suddenly stopping the medicine may make your health condition worse.
Read Also: Marijuana Helping Asthma
What Are Alternatives To Aspirin And Nsaids
People with aspirin-induced asthma can either avoid these medications or undergo aspirin desensitization. If you chose to avoid the medications, your health care provider can recommend safe alternatives to take for pain and inflammation.3
Aspirin desensitization leads to improvements in about 60% of people.5 The process takes two to four days and is done in a specialized facility.4 You are given a very low starting dose of aspirin. The next dose you are given is slightly higher. Increasing doses are given until all the reactions disappear.1 After aspirin desensitization, you will need to take aspirin daily to maintain the effect.
Beta Blockers And Asthma
The interrelationship between beta blockers and asthma is something that has been a concern for various healthcare specialists. On one hand, where beta blockers can help in treating some serious health conditions, they can also cause some chronic ones, including asthma. This article discusses the uses of beta blockers and how it can cause asthma.
The interrelationship between beta blockers and asthma is something that has been a concern for various healthcare specialists. On one hand, where beta blockers can help in treating some serious health conditions, they can also cause some chronic ones, including asthma. This article discusses the uses of beta blockers and how it can cause asthma.
Beta blockers are a group of medications that are used to treat various forms of illnesses and ailments including blood pressure, heart problems, glaucoma, hypertension and migraines. They are also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents because they tend to block the effects of the adrenaline hormone in the body.
Don’t Miss: Can Cold Weather Affect Asthma
Cautions With Other Medicines
There are some medicines that may interfere with the way that beta blockers, including beta blocker eyedrops, work.
Tell your doctor if you’re taking:
- other medicines for high blood pressure. The combination with beta blockers can sometimes lower your blood pressure too much. This may make you feel dizzy or faint
- other medicines for an irregular heartbeat such as amiodarone or flecainide
- other medicines that can lower your blood pressure. These include some antidepressants, nitrates , baclofen , medicines for an enlarged prostate gland like tamsulosin, or Parkinson’s disease medicines such as levodopa
- medicines for asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- medicines for diabetes, particularly insulin beta blockers may make it more difficult to recognise the warning signs of low blood sugar
- medicines to treat nose or sinus congestion, or other cold remedies
- medicines for allergies, such as ephedrine, noradrenaline or adrenaline
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines , such as ibuprofen. These medicines may increase your blood pressure, so it’s best to keep them to a minimum
How Do Beta Blockers Work
Beta blockers block the effects of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine. Beta blockers slow the heartbeat and cause it to beat with less force, which lowers blood pressure. They also help to open up veins and arteries to boost blood flow.
There are different types of beta blockers some mainly affect the heart, while others impact both the heart and blood vessels. You and your healthcare provider will work together to choose the right beta blocker for your condition. Examples of oral beta blockers include:
Some people may also experience less common side effects, such as:
- Depression
- Shortness of breath
- Trouble sleeping
Often, healthcare providers will prescribe beta blockers along with one or more additional medications to lower blood pressure.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
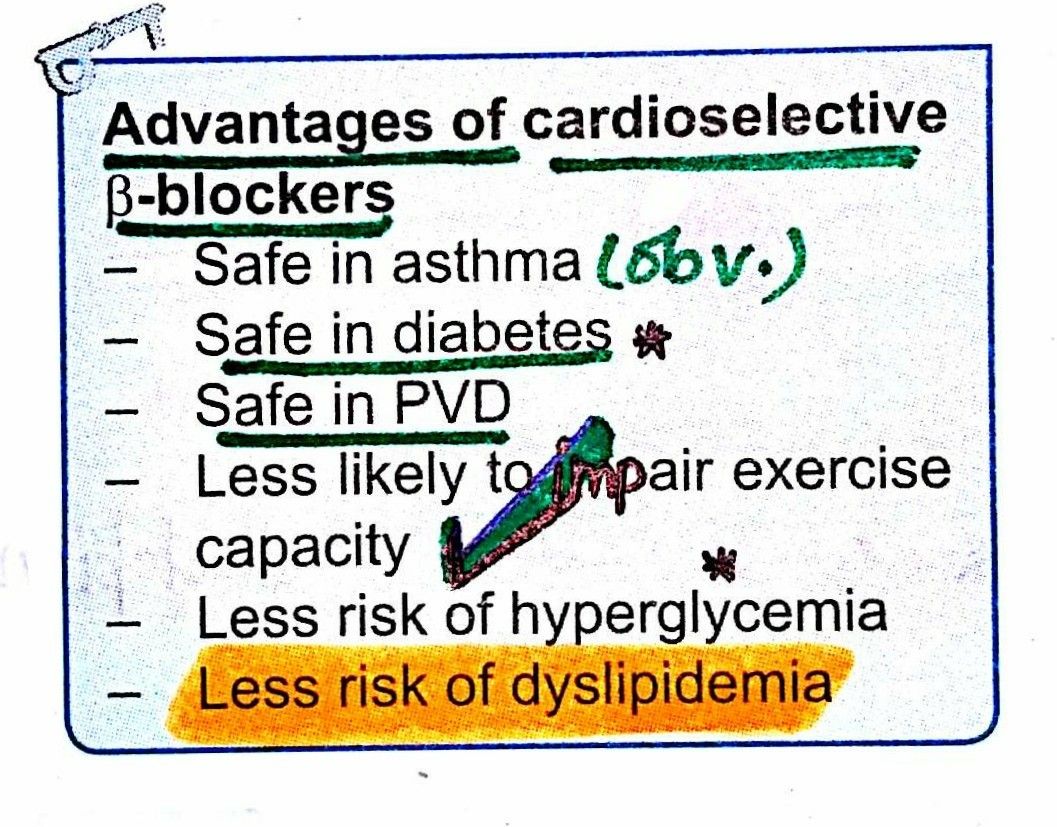
Selective Vs Nonselective Beta Blockers
There are two main types of beta blocker medications: selective beta blockers and nonselective beta blockers.
Selective beta blockers are designed specifically to block the 1 receptors, which are primarily located in the heart. Because the action of these beta blockers is more specific, theyre usually safe for use if you have diabetes.
Common selective beta blockers include acebutolol, atenolol, bisoprolol, betaxolol, bevantolol, celiprolol, metoprolol, esmolol and nebivolol.
Because selective beta blockers only affect the 1 receptors, which are concentrated in heart tissue, they tend to be used to treat heart conditions and arent a popular treatment option for anxiety.
Nonselective beta blockers are designed to block the 1, 2 and 3 receptors. This means that as well as targeting beta receptors in the heart, they also affect the veins, liver, pancreas and a range of other parts of the body.
Common nonselective beta blockers include alprenolol, carteolol, oxprenolol, propranolol and sotalol. As well as being used to treat certain heart conditions, nonselective beta blockers can be used to treat some physical effects of anxiety.
Unlike selective beta blockers, nonselective beta blockers are not considered safe to use if you have diabetes.
Use With Respiratory Disease
Beta-blockers can be beneficial to those with lung disease for several reasons:
- They can help maintain optimal blood pressure and heart function, helping you avoid dyspnea .
- COPD is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, which beta-blockers can help treat.
- Heart disease is a leading cause of death among people who have pulmonary disease, and these drugs can reduce that risk.
These benefits, however, must be carefully weighed against notable risks.
Read Also: Does Humidifier Help Asthma
Availability Of Data And Materials
Clinical data, which belong to the Clinical Practice Research Datalink , cannot be made publicly available. Other researchers may extract the data from the CPRD database and replicate the analysis, provided they have appropriate governance procedures and ethical approvals. Interested researchers may contact the CPRD directly to inquire about access to the data.
What Is A Beta Agonist

Beta agonists are a type of medicine used to treat asthma .4 They are sometimes known as bronchodilators because they relax the airways. Like beta blockers, beta agonists act on the beta receptors in certain types of cells. Namely, they act on the beta receptors found in smooth muscle tissue. However, today’s beta agonists are designed to focus primarily on airway smooth muscle tissue, while minimizing the effects on smooth muscle found in the heart.5
Rather than interfering with the beta receptors, however, beta agonists enhance the action of certain enzymes that bind to the beta receptors. The result is relaxation of the lining of the airways. Overall, these are the benefits of using a beta agonist:6
- Minimize the required dose of inhaled steroids
Recommended Reading: What To Do For An Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
The Potential Risks Associated With Administration Of
In a double-blind, randomized, crossover study, Wilcox et al investigated the effect of metoprolol and bevantolol in 16 patients with asthma. Cumulative doses, ie, 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg of metoprolol or 18.75 mg, 37.5 mg, 75 mg, and 150 mg of bevantolol, were administered at 2-hour intervals. Symptoms and lung function were monitored, and treatment was stopped if significant symptoms or a 20% decline in FEV1 were observed. The cumulative dosing regimen in general proved to be a safe and effective means of assessing bronchial responsiveness to -blockers in asthma, but one patient had to be withdrawn after the first dose due to severe bronchoconstriction. Of the 15 patients exposed to both -blockers, seven patients were withdrawn prematurely. The maximum tolerated cumulative dose of metoprolol and bevantolol was 26.8 mg and 45.5 mg, respectively, doses much lower than usually required for therapeutic activity. The authors concluded that even in patients who tolerate single doses of -blockers, the response to repeated treatment is unpredictable and, therefore, that -blocker therapy should be avoided in patients with asthma.
What Is The Best Way To Take Beta Blockers
You should take your beta blocker exactly as your doctor prescribes it. Beta blockers are usually taken once or twice a day. Try to take the medicine at the same time every day. Do not stop taking your beta blocker without talking to your doctor first.
If you forget to take a dose and it has been a few hours or less since you missed the dose, take your beta blocker as soon as you remember. But if it has been four to six hours or longer since you missed the dose, don’t take the dose you missed. Instead, wait and take the next regular dose. Never take a double dose to catch up.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Recommended Reading: How To Handle An Asthma Attack Without An Inhaler
