Causes And Triggers Of Asthma
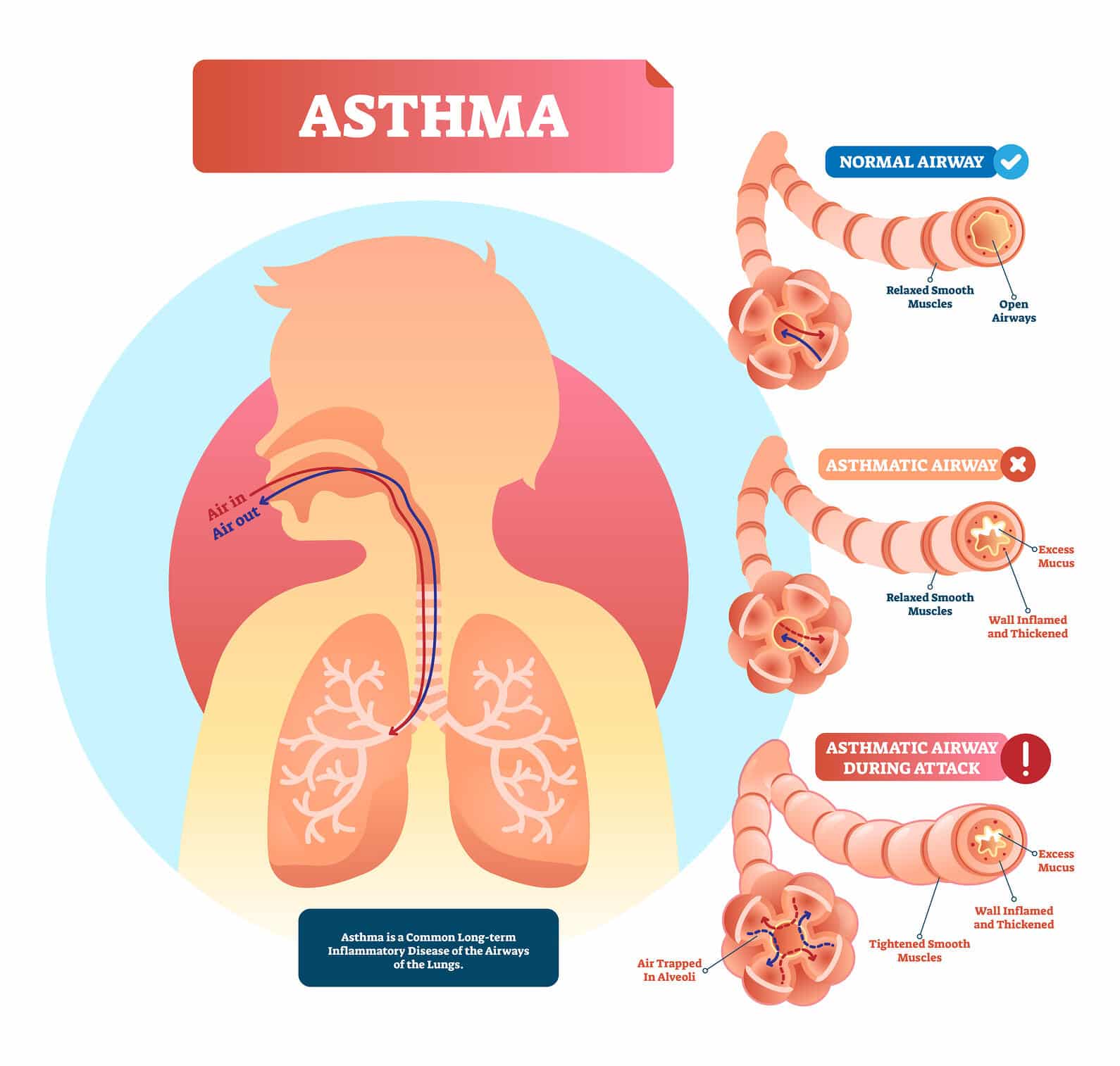
Asthma is caused by swelling of the breathing tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs. This makes the tubes highly sensitive, so they temporarily narrow.
It may happen randomly or after exposure to a trigger.
Common asthma triggers include:
- infections like colds or flu
Identifying and avoiding your asthma triggers can help you keep your symptoms under control.
Tests Of Bronchial Hyperreactivity
When spirometry is normal, but symptoms and the clinical history are suggestive of asthma, measurement of airway responsiveness using direct airway challenges to inhaled bronchoconstrictor stimuli or indirect challenges may help confirm a diagnosis of asthma.
Tests of bronchial hyperreactivity should be conducted in accordance with standardized protocols in a pulmonary function laboratory or other facility equipped to manage acute bronchospasm. Bronchopovocation testing involves the patient inhaling increasing doses or concentrations of an inert stimulus until a given level of bronchoconstriction is achieved, typically a 20% fall in FEV1. An inhaled rapid-acting bronchodilator is then provided to reverse the obstruction. Test results are usually expressed as the provocative dose or provocative concentration of the provoking agent that causes the FEV1 to drop by 20% . For methacholine, most pulmonary function laboratories use a PC20 value less than 4-8 mg/mL as the threshold for a positive result indicative of airway hyperreactivity, supporting a diagnosis of asthma. However, positive challenge tests are not specific to asthma and may occur with other conditions such as allergic rhinitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . Therefore, tests of bronchial hyperreactivity may be most useful for ruling out asthma among individuals who are symptomatic. A negative test result in a symptomatic patient not receiving anti-inflammatory therapy is highly sensitive .
Acute Asthma Prognosis And Treatment
Most recent update: July 2021Originally Posted: September 2004
Division of Allergy and Immunology,University of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL 33612
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector, Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair in Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalEmail: rlockey@health.usf.edu
Michael A. Kaliner, MD FAAAAIMedical Director, Institute for Asthma and AllergyChevy Chase and Wheaton, MarylandProfessor of Medicine, George Washington University School of MedicineWashington, DC
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector of the Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair of Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida College of Medicine and the James A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL
Abstract
Key words: Asthma flare Acute asthma Asthma attack Wheezing Acute asthma diagnosis Acute asthma management
Abbreviations
EPR-3 – The Expert Panel Report 3EPR-4 The Expert Panel Report 4FeNO Fractional Exhaled Nitric OxideOCS – Oral corticosteroidsCOPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseasePEF – Peak expiratory flowSABA – Short acting beta agonistAE Adverse eventsFVC- Forced vital capacity
Introduction
1. Recognition of patients who are at a greater risk for near-fatal or fatal asthma.
Physical Examination
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Asthma
Also Check: Non Pharmacological Management Of Asthma
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider will contact you a few days after spirometry testing to discuss your results. Reach out to your healthcare provider if you dont hear from them with your results after a few days.
You may have to schedule lung function tests every year if you have a chronic lung disease.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
See your healthcare provider if you notice any changes in your breathing. The changes might not be serious, or they might be a symptom of a lung condition. Your healthcare provider can use spirometry to help diagnose any possible lung conditions. Spirometry isnt painful. A proper diagnosis can help you and your healthcare provider determine a healthcare plan that enables you to improve or maintain your quality of life.
When To See A Gp
See a GP if you think you or your child may have asthma.
Several conditions can cause similar symptoms, so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis and correct treatment.
The GP will usually be able to diagnose asthma by asking about symptoms and carrying out some simple tests.
Find out more about how asthma is diagnosed.
Also Check: How Does Asthma Affect The Respiratory System
Why Is Severe Asthma Different From Mild
If you receive a severe asthma diagnosis, this means your asthma requires high doses of medication such as inhaled corticosteroids and others to control symptoms and prevent flare ups .
Even with proper medication and addressing all modifying factors that can influence your severe asthma it is still poorly controlled.
Flare-ups can be severe and life threatening. Quality of life is significantly impacted, and daily symptoms can be debilitating.
Being diagnosed with mild-moderate asthma on the other hand will not require such high doses of medications to control symptoms. Asthma does not present daily symptoms or prevent you from accomplishing everyday tasks and being physically active. Flare-ups and the risk of death are greatly reduced.
Read Also: How Do You Get Asthma As An Adult
Why Are Asthma Cases Rising
The total number of asthma cases is on the risethe American Thoracic Society estimates the number of Americans with asthma will grow 10% by 2039. That means asthma is also a serious public health issue, and one study projects that uncontrolled asthma could cost the U.S. health system around $300 billion in that timeframe5.
Scientists dont know for sure why asthma rates are increasing, but its thought that increased urbanization, lifestyle changes, and even growing rates of obesity could play a role.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If My Kid Has Asthma
Conditions Related To Asthma
Certain health conditions are more common in people with asthma than in the general population. Health problems may be related to asthma in different ways. Some conditions may share risk factors with asthma. Other conditions may contribute to the development of asthma. Still others may make asthma harder to diagnose or treat. Its important to understand conditions related to asthma to get proper treatment and better manage your overall health.
When someone has more than one health condition at the same time, the conditions are known as comorbidities. When an additional medical condition occurs as a result of a primary disease, it is known as a complication.
You May Like: Can Asthma Symptoms Last For Weeks
How Common Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Most children get RSV before two years of age. Infection is easily spread in young children because of their close contact with other children who may be infected, through the sharing of their toys and constant touching of objects that may be contaminated with the virus. Some 57,000 children under age five require hospital care due to RSV each year in the U.S.
Among adults, about 177,000 older adults are hospitalized each year for RSV. Some 14,000 adults die due to this infection each year.
You May Like: What Does A Nebulizer Do For Asthma
Whats Different About Severe Asthma
Severe asthma is the most serious and life-threatening form of asthma. Most people with asthma can manage their symptoms well with the usual medicines like a preventer inhaler and a reliever inhaler.
But someone with severe asthma struggles to manage their symptoms even with high doses of medicines.
And sometimes it can take a while to find a combination of medicines and doses that works best for you.
Even if your asthma is difficult to control, its not the same as severe asthma. If you have difficult to control asthma you should be able to get on top of your symptoms with support from your GP or asthma nurse, with an action plan, regular reviews and a good routine of taking your asthma medicines.
What We Know About Asthma And Covid
Asthma is a pre-existing lung condition affecting 1 in 13 people in the U.S. It can cause wheezing, chest tightness, coughing, and shortness of breath. Asthma can be controlled by taking medications and avoiding triggers.
COVID-19 is a respiratory disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The virus affects cells in the airways, from the nose and throat down to the deepest parts of the lungs. In the nose and throat it might cause symptoms of a cold. In the upper airways, it might cause some breathlessness and cough. When the coronavirus lodges itself deep in the lungs, this is when things can start to get serious. Here, the coronavirus commonly causes a double lung infection, or bilateral pneumonia.
Interestingly, research so far does not suggest any link between having asthma and getting a more severe COVID-19 illness, or between asthma and coronavirus deaths.
Whether this is because the SARS-CoV-2 virus doesnt affect people with asthma in the same way as other respiratory viruses, or because there simply isnt enough data yet, remains to be seen.
Also Check: Can Cs Gas Cause Asthma
Asthma Causes And Triggers
When you have asthma, your airways react to things in the world around you. Doctors call these asthma triggers. They might cause symptoms or make them worse. Common asthma triggers include:
- Infections like sinusitis, colds, and the flu
- Allergens such as pollens, mold, pet dander, and dust mites
- Irritants like strong odors from perfumes or cleaning solutions
- Strong emotions such as anxiety, laughter, sadness, or stress
- Medications such as aspirin
- Food preservatives called sulfites, found in things like shrimp, pickles, beer and wine, dried fruits, and bottled lemon and lime juices
What Are The Complications Of Asthma

Poorly-controlled asthma can have a negative effect on your quality of life. Complications may include:
- being less productive at work or while studying
- an inability to exercise and be physically active
- reduced lung function
- poor mental health
Taking your medications exactly as prescribed is important. If you feel that your asthma is affecting your quality of life, contact your doctor for a medicines review.
Also Check: Juicing Recipes For Asthma And Allergies
Impact On Asthma Treatment
While there is no cure for asthma, treatment can control its symptoms and slowif not entirely stopits progression.
With the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of asthma in mind, healthcare providers can recommend strategies to either minimize or normalize the response, or prevent it from happening altogether. Given the variety of elements involved in these processes, your asthma management plan will very likely be multi-pronged.
Visit your healthcare provider regularly so they can monitor your respiratory health and alter your treatment plan over time, as needed.
What Is It Like To Have Severe Asthma
Severe asthma is an unpredictable condition and its different for everyone. So, its hard to describe exactly what its like to have severe asthma.
But people with severe asthma have more asthma attacks than people with mild or moderate asthma, they are more likely to have to stay in hospital and they are more likely to be on long term steroid tablets.
The symptoms, triggers, responses to medicines, energy levels and impact on daily life are unique to each individual, plus they can change over time.
Having severe asthma can be tough. But with the right support and treatment you can hopefully feel more confident about managing your symptoms and getting on with your life.
Read real life stories of people living with severe asthma.
You May Like: How To Treat Seasonal Asthma
Treatment Of Severe Asthma
There is no single treatment or medication solution. Everyone is affected differently and what works well for one person may have no effect on another. The same medications may be prescribed as someone who has a milder asthma, but at a much higher dose.
Treatment of severe asthma focuses on trying to control the symptoms. Youll be prescribed medication and treatment to manage the inflammation in your airways and prevent lung damage. Youll also be advised to reduce the risk of coming into contact with asthma triggers as much as possible, as this will reduce your risk of having a severe asthma attack.
As a starting point, everyone with asthma is prescribed:
- A reliever inhaler usually blue, this inhaler is used to provide relief when you need it and should be carried with you at all times.
- A preventer inhaler often brown, contains corticosteroids that help to reduce swelling and inflammation in the airways. This needs to be taken every day, as prescribed by your doctor.
If youre diagnosed with severe asthma, you should speak to your doctor about a referral to a specialist clinic. While some primary care surgeries have dedicated asthma nurses that can offer specialist support.
Why Is My Asthma Worse At Night
Asthma that gets worse at night is sometimes called nighttime asthma or nocturnal asthma. There are no definite reasons that this happens, but there are some educated guesses. These include:
- The way you sleep: Sleeping on your back can result in mucus dripping into your throat or acid reflux coming back up from your stomach. Also, sleeping on your back puts pressure on your chest and lungs, which makes breathing more difficult. However, lying face down or on your side can put pressure on your lungs.
- Triggers in your bedroom and triggers that happen in the evening: You may find your blankets, sheets and pillows have dust mites, mold or pet hair on them. If youve been outside in the early evening, you may have brought pollen in with you.
- Medication side effects: Some drugs that treat asthma, such as steroids and montelukast, can affect your sleep.
- Air thats too hot or too cold: Hot air can cause airways to narrow when you breathe in. Cold air is an asthma trigger for some people.
- Lung function changes: Lung function lessens at night as a natural process.
- Asthma is poorly controlled during the day: Symptoms that arent controlled during the day wont be better at night. Its important to work with your provider to make sure your asthma symptoms are controlled both day and night. Treating nighttime symptoms is very important. Serious asthma attacks, and sometimes deaths, can happen at night.
Also Check: How To Test For Asthma
Explaining Your Symptoms To Your Gp
Its a good idea to start a diary of your symptoms before speaking to your GP. Taking note of when symptoms flare-up may help you to understand your triggers. This diary will then help your GP to understand and properly assess your condition. You could also try filming your symptoms if they are hard to describe.
There are several different tests for asthma â so your GP wont be able to diagnose you straightaway. Our advice on diagnosing asthma explains this process in more detail.
Contact Us Today If You Are Having Problems With Asthma In The Los Angeles Area
Asthma can be a real problem regardless of whether it is an acute or chronic issue. Contact Dr. Avi Ishaaya at Dr. Avi Ishaaya Centers in Los Angeles, CA to learn more about how asthma testing and treatment can work for you. You can visit us on West Olympic Boulevard in the Carthay Square neighborhood, or you can schedule an appointment with us online.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Asthma And Not Know It
What Is Chronic Asthma
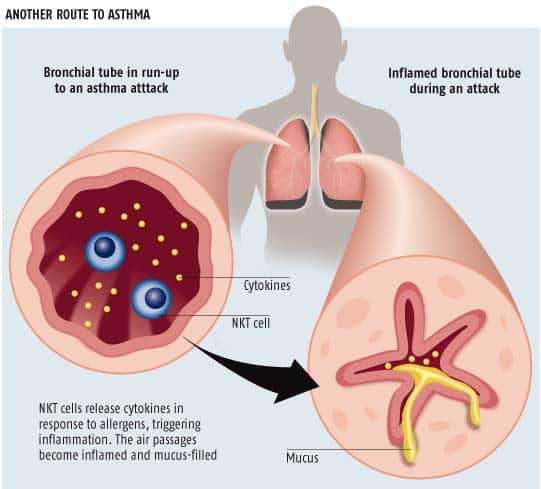
Chronic asthma is a condition that involves persistent inflammation and irritation of the airways. When external triggers such as cold air or allergens are present, asthma sufferers experience acute attacks of wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. Asthma attacks can last anywhere from a few minutes to over 24 hours, and mild breathing difficulties can linger in between episodes. Chronic asthma is most often an inherited disorder that tends to clear up in late childhood or adolescence, though many people have lifelong symptoms. Doctors can prescribe medications to expand the airways during an acute attack to help prevent future episodes.
Lungs and air passages afflicted with chronic asthma are always irritated to some degree. Some people with the condition cannot take deep breaths due to limited lung capacity and mucous buildup. During an attack, inflammation worsens and the airways constrict severely. The bodys natural response to inflammation is increased mucous production, which further obstructs air passages. Sufferers experience chest pain and tightness, wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. Pain and respiratory problems can lead to a rapid pulse and a loss of consciousness in the most serious cases.
Control As A Guide To Medication Adjustment
After targeted, step-based initiation of pharmacologic therapy, the classification of asthma control is used to adjust medication, stepping up or down depending on the level of control. Patients whose asthma can be classified as well controlled can be maintained on their current medications and, if stable for at least three months, a step down in therapy can be considered . Patients whose asthma is classified as not well controlled on their initial therapy are advised to step up one step and be reevaluated in two to six weeks for patients with very poorly controlled asthma, consider short-term oral systemic corticosteroid use and stepping up one or two steps, then reassessing in another two to four weeks.
| Components of control |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Is Olbas Oil Good For Asthma
Who Gets Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection
RSV infects almost all children at least once before they are two years old. Most of the time, this virus only causes minor cold-like symptoms. However, for some babies and certain adults, the infection can be more dangerous.
Infants and adults at highest risk of severe or life-threatening RSV infection are:
- Premature infants .
- Infants under 6 months of age.
- Infants born with heart or lung disease.
- Children and adults with weakened immune systems, including those who have received an organ transplant or those undergoing chemotherapy.
- Children who have difficulty swallowing or cant clear mucous.
- Adults 65 years of age and older.
- Adults with heart and lung diseases, such as congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma.
