Assessment And Diagnostic Findings
To determine the diagnosis of asthma, the clinician must determine that episodic symptoms of airway obstruction are present.
- Positive family history. Asthma is a hereditary disease, and can be possibly acquired by any member of the family who has asthma within their clan.
- Environmental factors. Seasonal changes, high pollen counts, mold, pet dander, climate changes, and air pollution are primarily associated with asthma.
- Comorbid conditions. Comorbid conditions that may accompany asthma may include gastroeasophageal reflux, drug-induced asthma, and allergic broncopulmonary aspergillosis.
Sample Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care Plans
Here we have formulated a sample nursing care plan for Acute Exacerbation of Bronchial Asthma based on a hypothetical case scenario.
It will include three sample nursing care plans with NANDA nursing diagnoses, nursing assessment, expected outcome, and nursing interventions with rationales.
Nursing Interventions For A Client In Status Asthmaticus With Tachycardia That Stems From His Underlying Heart Disease And Anxiety Regarding His Underlying Asthma:
Educate the client about breathing techniques, monitor his vital signs, and implement the immediate interventions listed above. Because he is likely to be anxious, it will be necessary for the nurse to maintain a calm demeanour and keep him informed of his status regarding treatment measures or procedures that are being initiated. The nurse also should frequently monitor the patients pulse oximetry readings, blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and capillary refill time. If the pulse oximeter is unstable and exceeds 90%, then a clinician should be notified immediately.
You May Like: Why Does Asthma Get Worse At Night
Nursing Care Plans Concept Map Bronhial Asthma
Recommended Reading: College Of Dupage Nursing School
Cystic Fibrosis Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
Cystic fibrosis is a rare, genetic, and progressive disease that damages the lungs, digestive system, and causes further complications to other organs. Cystic fibrosis is normally diagnosed as a newborn. There is no cure for CF and patients usually do not live past their 50s. Mutations to the CFTR Read more
Also Check: How Can You Treat Asthma
Nursing Interventions With Rationales For Bronchial Asthma Anxiety
| Nursing Interventions | |
| Stay with the patient and encourage slow, deep breaths. | Consistent presence and coaching can help lessen feelings of anxiety during an asthma exacerbation. |
| Provide a calm environment and decrease stimuli. | A calm environment will decrease anxiety, thus decreasing oxygen consumption. |
| Educate the patient on pursed-lip breathing. | Pursed lip breathing is an intentional breathing technique that encourages slow, deep, effective breaths. |
| Help the patient develop an emergency plan for asthma attacks. | The patient should always have their rescue inhaler on hand. During an asthma exacerbation, the patient should sit upright and administer their rescue inhaler. If no relief is felt within 4 minutes, the patient should seek immediate medical attention, and continue administering the rescue inhaler every 4 minutes. |
Nursing interventions with rationales for Asthma Anxiety
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Severe Very Severe Asthma
Severe signs and symptoms include rapid and labored breathing, anxiety, or restlessness, leading to panic attacks. You also may have a hoarse voice from excessive mucus production, cough with frothy sputum , dyspnea with wheezing even during rest, and increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Difficulty in speaking or walking and feeling very tired,
-Dyspnea while talking
Nursing Diagnosis: Airway Clearance Disorder Acute and Chronic
Defining Characteristics:
Lack of airway obstruction because the respiratory passages that carry air to and from the lungs are open. However, there may be a productive cough or wheezing while breathing. This indicates a respiratory infection in progress.
Breathing is labored rapid breathing is common with asthma, and it may not get enough oxygen to the body tissues.
Nursing diagnosis of asthma: Impaired gas exchange related to effects of bronchoconstriction and cellular infiltration. It is caused by thick, sticky mucus that can plug up the airways. Impaired gas exchange is the primary problem, and it causes all the other issues.
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements
Impaired Skin Integrity: related to retention of sputum, thick or excessive mucus
Nursing Diagnosis: Alteration in Breathing Pattern Caused by Asthma Attack
Asthma Symptoms diagnosis: Allergic reaction or asthma attack usually begins with a series of symptoms including
1) Rapid, shallow breathing
2) Labored breathing
4) Cough
8) Fatigue
You May Like: Why Does Asthma Cause Coughing At Night
Nursing Care Plan For Copd 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to COPD and pneumonia as evidenced by shortness of breath, SpO2 level of 85%, productive cough, and greenish phlegm
Desired Outcome: The patient will achieve effective breathing pattern as evidenced by respiratory rates between 12 to 20 breaths per minutes, oxygen saturation between 88 to 92%, and verbalize ease of breathing.
Asthma Nursing Care Plan For A Client With Stable Well
1) Review all environmental exposures that may irritate or aggravate asthma, such as cold air drafts from windows, allergens, cigarette smoke, high pollen count, and pets.
2) Have the client use a peak flow meter daily to monitor his rate of airflow.
3) Use a spacer when administering medications for the treatment of asthma or have the patient take deep breaths using short puffs of air from their inhaler through pursed lips.
4) Educate patients regarding the importance of good nutrition in maintaining overall health and wellness and its effect on asthma symptoms.
5) Assess the patients current health care provider and medication regimen, including dosage schedule, to determine if changes are needed.
You May Like: Is Asthma An Autoimmune Disease
Causes Of Copd Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Asthma Nursing Care Plan For A Client In Status Asthmaticus:
1) Maintain patent airway, and frequently assess for change in mental status.
2) Administer Albuterol 2.5mg every 12 hours by nebulizer through a spacer. If wheezing persists, administer Albuterol every 5 minutes by nebulizer with the client sitting position on bed rest.
3) Administer oxygen by nasal cannula at 8-10L/min or via facemask at 15L/ min.
4) Place an IV and infuse fluids at a rate of 50mL/kg/hr.
5) If the client is hypotensive, administer IV epinephrine 0.1 to 0.5 mcg/kg every 5 minutes as needed for systolic BP less than 90mmHg or diastolic less than 60mmHg.
6) Administer Diphenhydramine HCl every 4 to 6 hours PRN.
7) Consider IV magnesium sulphate with at least two additional drugs if significant tachycardia persists despite other interventions or if hypotension is present.
8. Auscultate breath sounds every 4 hours and report dyspnea, rales, or crackles to a physician.
9) Assess vital signs hourly for changes and notify the physician if necessary.
Don’t Miss: When To Go To Urgent Care For Asthma
Shortness Of Breath Nursing Care Plan 2
Ineffective Airway Clearance
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Airway Clearance related to copious and persistent bronchial secretions secondary to pertussis, as evidenced by dyspnea, increased mucus secretions, and productive cough.
Desired Outcome:
- The patient will be able to maintain clear and open airways as evidenced by normal breath sounds, normal depth, and rate of respirations.
- The patient will demonstrate the ability to effectively cough up secretions after treatments and deep breathing exercises.
- The patient will demonstrate increased air exchange.
- The patient will be able to classify methods to improve the removal of secretions.
- The patient will recognize the significance in changes of sputum such as the color, characteristics, and amount.
- The patient will be able to identify and avoid necessary factors that limit effective airway clearance.
Focused Exam: Asthma Exacerbation Results
Pediatrics – Spring 2022, NUR 113
Return to Assignment
Sales Tax Notification: Elsevier Inc. DBA Shadow Health charges applicable sales tax as required by state and local regulations.
If you are using Safari and have issues with audio in your assignment, please click here for assistance. Click here for more information
Don’t Miss: Pulmonologist Or Allergist For Asthma
Role Of Primary Care In The Administration Of Biological Therapies For Asthma
Until recently, the primary choice of therapy for recurrent exacerbations was repeated or long term use of corticosteroids. New treatments such as omalizumab , mepolizumab and benralizumab dramatically improve symptom control and reduce exacerbations and oral corticosteroid use in patients with severe refractory asthma.10
How Do You Test For Asthma
There are many ways to test asthma, but the most accurate way is with spirometry or peak flow. Spirometry assesses how much air is inhaled and exhaled in a specific amount of time, while peak flow monitors lung function by measuring the speed at which air leaves your lungs during a forced breath. The two methods work together to provide information about how well your lungs are functioning and can be used as part of an overall treatment plan for asthma.
To accurately monitor lung function with either method, you must follow all instructions carefully and use your best effort when taking the measurement.
Spirometry or peak flow will help identify asthma because it measures how well you can move air through your lungs by measuring the volume and the speed with which you exhale . There are many reasons for wheezing that may not be related to asthma, so if your doctor suspects asthma, they will need more tests such as a lung function test called spirometry or peak flow test.
Spirometry measures the amount of air you can exhale in one second, while peak flow measurement records how much air you can blow out in one breath. Peak flow readings are typically assessed by blowing into an asthma-management device called a peak flow meter which usually displays your reading as millimetres of mercury . The higher the number on the meter reading, the better your airflow is likely to be.
Recommended Reading: Best Allergy Medicine For Seasonal Asthma
Long Term Control Medication Anti
Long-term control medications are recommended for patients with persistent asthma. These drugs reduce inflammation in the airways, keeping your lungs open and reducing asthma symptoms.
Example: Salmeterol and Fluticasone : It helps open lung airways and helps relieve breathing problems by reducing inflammation in the lungs.
Anti-inflammatory drugs include inhaled steroids or leukotriene modifiers such as Singulair.
How Specialist Services Work
Specialist asthma services provide detailed, complex evaluations of patients with severe asthma using a systematic approach, thereby ensuring patients receive an appropriate diagnosis, support and access to specialist treatments . Although each specialist service has its own locally defined pathway, all services are commissioned under a standard NHS contract to ensure comparable patient care, and all adopt a multidisciplinary approach.
Teams are composed of at least two severe asthma respiratory consultants, severe asthma nurse specialists, dietitians, physiotherapists, allergy specialists and clinical psychologists , and may include pharmacists and speech therapists. The multidisciplinary team evaluates newly referred patients to define their asthma phenotype , as well as the most appropriate individualised treatment plan.
Patients managed by specialist severe asthma services show improved outcomes, including a decreased steroid burden, fewer hospital admissions and improved QoL . The benefits for patients cannot be overestimated to see the life-changing impact of this care on one patient.
Respiratory nurse specialists play a central role in specialist asthma services, carrying out initial and follow-up assessments, acting as patient advocates, providing continuity of care and ensuring a holistic approach to management.
You May Like: Can Hay Fever Cause Asthma Like Symptoms
Diagnostic Tests For Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Medical history taking especially tobacco use, family history, occupation, and exposure to lung irritants
- Arterial blood gas analysis to measure the gas exchange in the lungs
- Pulmonary function tests to measure the level of air during inhalation and exhalation. The most common one is spirometry. Other tests include pulse oximetry and six-minute walk test.
- Imaging chest x-ray and/or CT scan
- Genetic testing for AAt deficiency if the patient has a family history of COPD
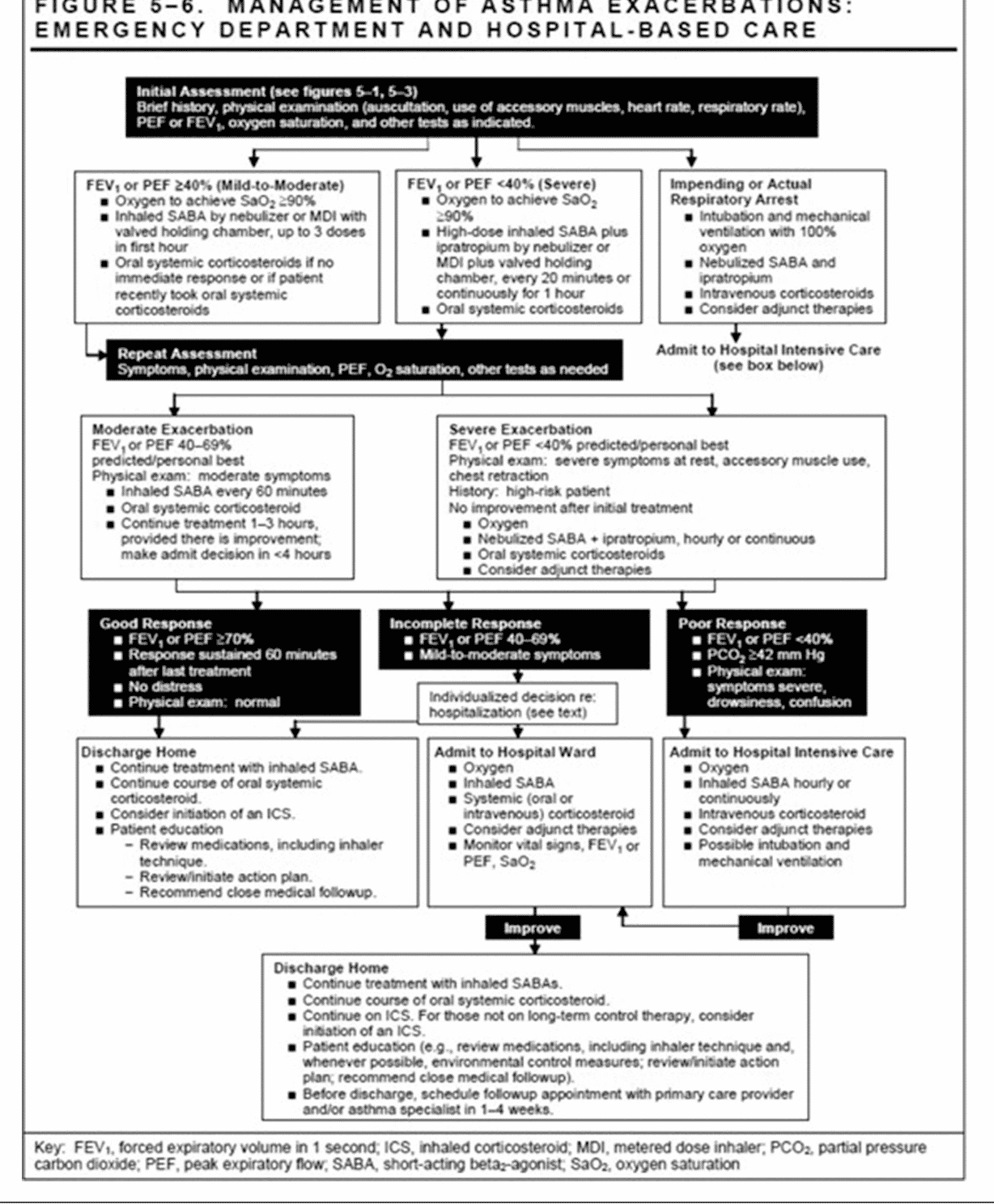
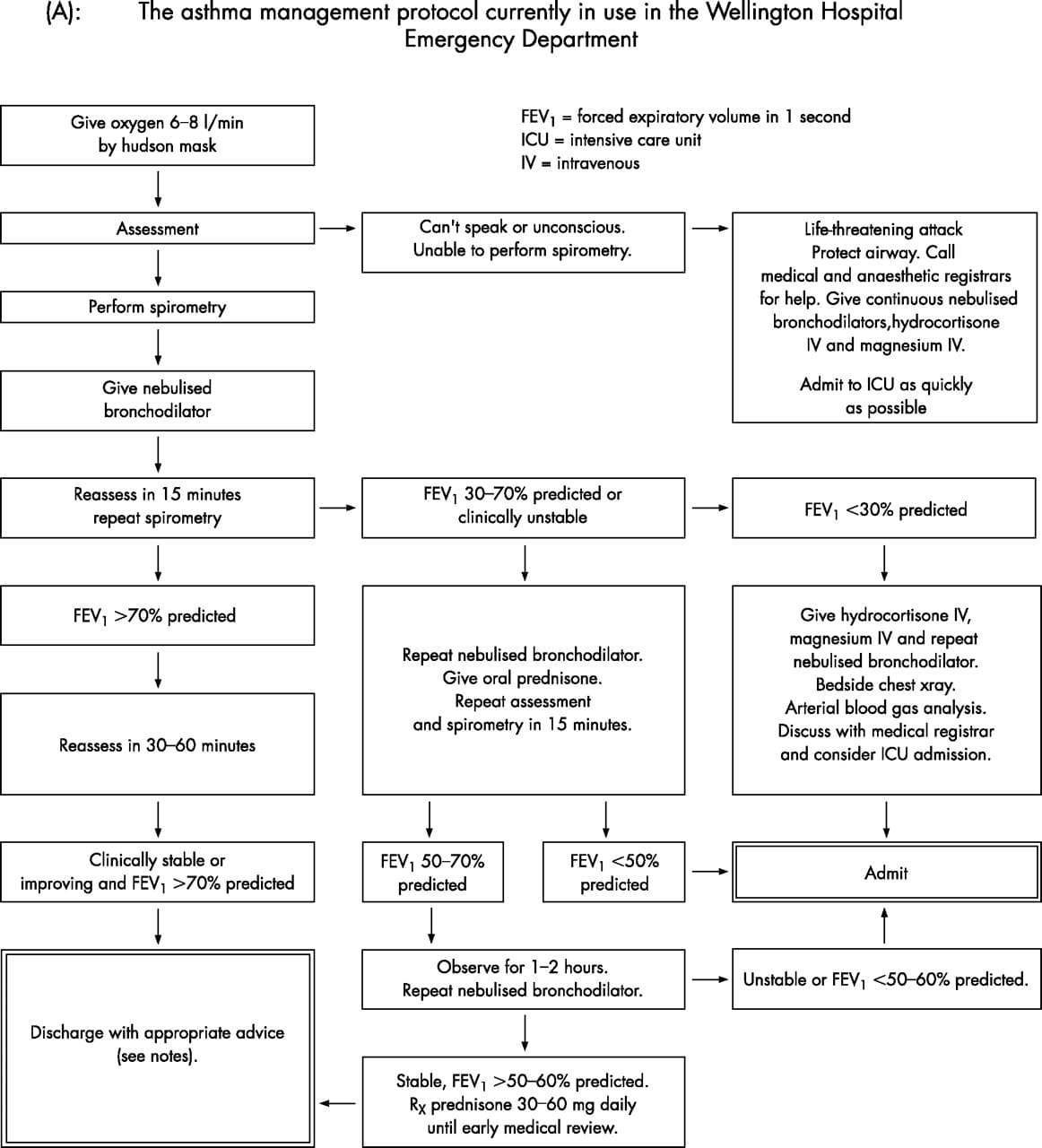
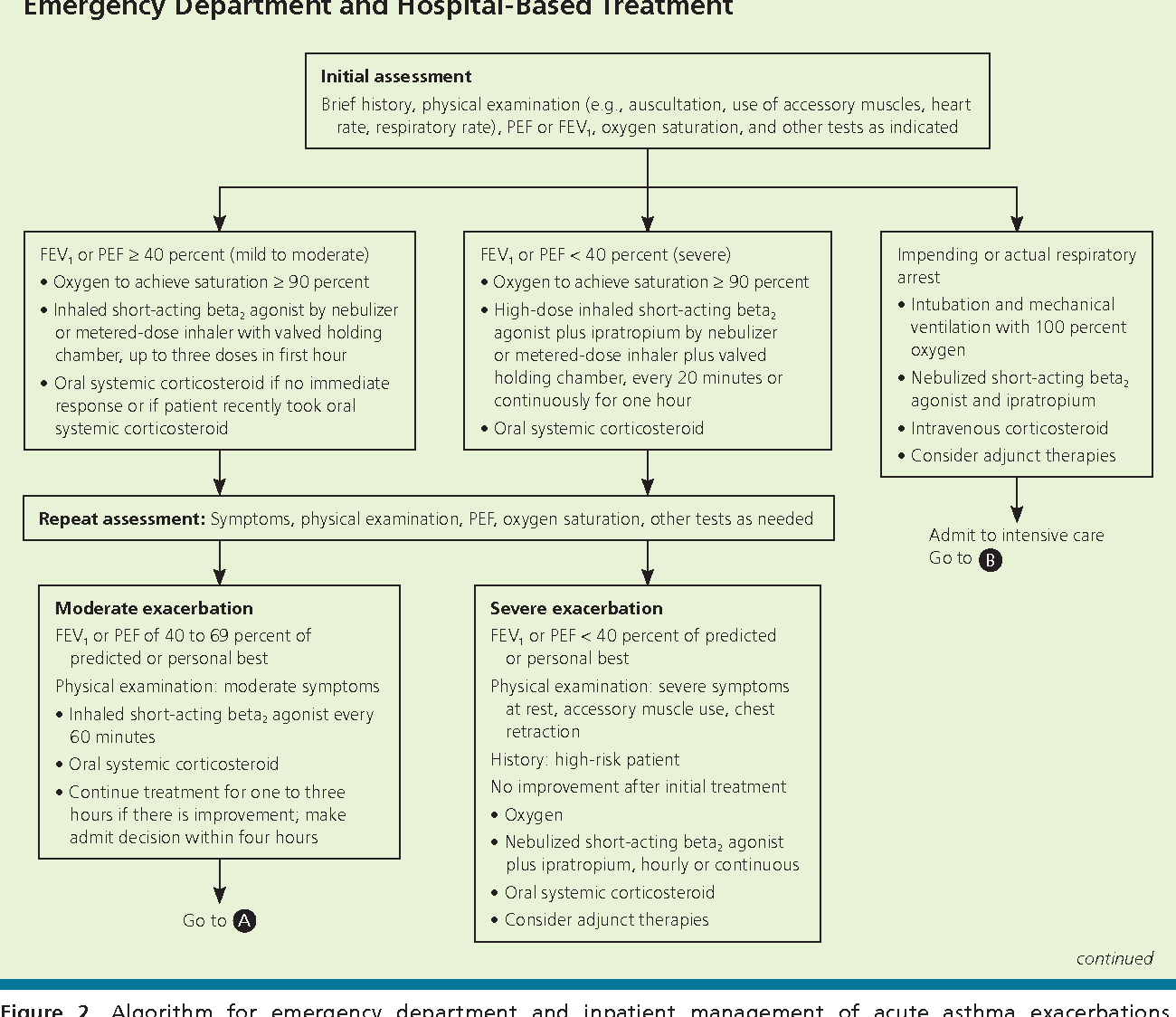
Nursing Interventions For Asthma
Presenting with an asthma attack:
- Baseline vital signs
- Keep patient calm and comfort the patient
- Position in high Fowlers to help with ease of breathing
- Administer bronchodilators as ordered by MD
- Administer oxygen
- Assess peak flow meter reading
- Auscultate lung sounds throughout:
- Monitor skin color and for any retractions of the chest, can they talk to you with ease now or is it still difficult for them to talk?)
- Current peak flow meter reading numbers their personal best reading and current readings, and medications theyve taken
What is a Peak Flow Meter: it shows how controlled a patients asthma is and if it is getting worse
How does the patient use a peak flow meter? As represented in the picture above, the patient will exhale as hard as they can onto the device. The device will then measure how much air was exhaled out of the lungs.
You will be providing them with education on how to follow their prescribed asthma action plan .
Help the patient identify triggers , how to avoid and those early warning signs.
What if a trigger is exercised-induced? The patient doesnt need to quit exercising . To help decrease the chances of an attack they can:
Also Check: Allergy Shots Immunotherapy For Asthma
Nursing Care Plan For Asthma 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to inadequate pulmonary ventilation, secondary to asthma, as evidenced by shortness of breath, coughing, cyanosis, nasal flaring, changes in the depth of breathing, excessive use of accessory muscles, presence of respiratory noise, and tachypnea.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patients abnormal breathing pattern will be corrected, as evidenced by a normal respiratory pattern, with no evidence of dyspnea noted.
- The nurse will note that the use of diaphragmatic compression is evident, ABG values are within the prescribed ranges, and there is evidence of comfortable breathing, either vocally or by the patients conduct.
Also Check: Is A Dnp Required For Nurse Practitioners
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Mild And Moderate Intermittent Asthma
Asthma symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening, depending on how often you have asthma attacks, what triggers them, and your reaction to the triggers.
Mild symptoms include coughing, wheezing, breath sounds, difficulty breathing, absence of dyspnea, and no need to use the reliever inhaler.
Moderate symptoms include coughing, wheezing, difficulty in breathing with small amounts of sputum .
Signs of severe asthma are coughing, dyspnea, wheezing, blue or gray lips with feeling like you are not getting enough air in your lungs. You may also have chest tightness, trouble breathing even lying down, and an inability to speak or walk.
Also Check: Can Humidity Make Asthma Worse
Is The Asthma Controlled
Assessment of asthma control is essential for the initiation and subsequent titration of maintenance inhaler therapy and should be completed at every opportunity. In a multinational survey, 90% of patients self-rated their asthma as well controlled, but of these only 18% were indeed controlled based on the definition in the Global Initiative for Asthma guideline.2 As per these guidelines, a patient with well controlled asthma should have no limitation of activities no nocturnal, early morning or daytime symptoms and minimal use of reliever therapy . It is therefore important to ask direct and specific details of symptom frequency and severity, exacerbation episodes, oral corticosteroid use and emergency department visits. The Asthma Control Questionnaires 3 and Asthma Control Test 3 are validated questionnaires that are accessible and easy for patients to complete. They provide a valuable objective framework that can be used to assess response to treatment over time.
Read Also: La Canada Nursing Home Tucson Az
What To Do If The School Will Not Work With You
Public or private schools that get funds from the federal government have to follow Section 504 and the ADA. Public schools must provide a free and appropriate education in the least restrictive environment.6
Also, all non-religious private schools must abide by the ADA, regardless if they receive federal funding. While they do not have to provide a free and appropriate education, private schools are public accommodations under the ADA, and therefore have to take necessary steps to make sure a child is not excluded, denied services, or treated differently due to their disability .7 As a recent agreement with the Department of Justice indicated, these obligations can include the requirements to administer emergency medicine such as epinephrine auto-injectors.
If a public school is not willing to accommodate your child, contact your school districts superintendent or 504 coordinator in writing. If you continue to be unhappy with the plan as implemented by the school district, you can contact the Department of Educationâs Office for Civil Rights or file a suit in a federal court.3
Also Check: Is It Possible To Develop Asthma
