What Are Asthma Symptoms
Asthma symptoms can differ for each person, but here are some of the most common:
- Wheezing. You may notice a whistling sound when you breathe. Sometimes this happens only when you exercise or have a cold.
- Frequent cough. This may be more common at night. You may or may not cough up mucus.
- Shortness of breath. This is the feeling that you can’t get enough air into your lungs. It may occur only once in a while, or often.
- Chest tightness. Your chest may feel tight, especially during cold weather or exercise. This can also be the first sign of a flare-up.
Treatment Of Asthma In Children
-
For acute attacks, bronchodilators and sometimes corticosteroids
-
For chronic asthma, inhaled corticosteroids and possibly leukotriene modifiers and/or cromolyn
Treatment is given to resolve sudden attacks and sometimes to prevent attacks.
Children who have mild, very infrequent attacks usually take drugs only during an attack. Children who have more frequent or severe attacks also need to take drugs even when they are not having attacks. Different drugs are used depending on the frequency and severity of the attacks. Children with infrequent attacks that are not very severe usually take a low dose of an inhaled corticosteroid or a leukotriene modifier every day to help prevent attacks. These drugs reduce inflammation by blocking the release of the chemical substances that inflame the airways.
Prognosis For Asthma In Children
Many children outgrow asthma. However, as many as 1 in 4 children either continue to have asthma attacks or the asthma symptoms resolve only to return when children are older. Children who have severe asthma are more likely to have asthma as adults. Other risk factors for persistence and relapse include female sex, smoking, development of asthma at a younger age, and sensitivity to household dust mites.
Although asthma causes a significant number of deaths each year, most of these are preventable with treatment. Thus, the prognosis is good for children who have access to treatment and who are able to follow their treatment plan.
Don’t Miss: What To Do If My Child Has An Asthma Attack
Risk Factors For Asthma
Doctors do not completely understand why some children develop asthma, but a number of risk factors are recognized:
-
Inherited and prenatal factors
-
Viral infections
Most children who are having an asthma attack and 90% of children who have been hospitalized for asthma have a viral infection . Children who have bronchiolitis Bronchiolitis Bronchiolitis is a viral infection that affects the lower respiratory tract of infants and young children under 24 months of age. Bronchiolitis usually is caused by viruses. Symptoms include… read more at an early age often wheeze with subsequent viral infections. The wheezing may at first be interpreted as asthma, but these children are no more likely than others to have asthma during adolescence.
Diet may be a risk factor. Children who do not consume enough of vitamins C and E and omega-3 fatty acids or who are obese may be at higher risk of asthma.
Reducing The Burden Of Asthma
Asthma cannot be cured, but good management with inhaled medications can control the disease and enable people with asthma to enjoy a normal, active life.
There are two main types of inhaler:
- bronchodilators , that open the air passages and relieve symptoms and
- steroids , that reduce inflammation in the air passages. This improves asthma symptoms and reduces the risk of severe asthma attacks and death.
People with asthma may need to use their inhaler every day. Their treatment will depend on the frequency of symptoms and the different types of inhalers available.
It can be difficult to coordinate breathing using an inhaler, especially for children and during emergency situations. Using a spacer device makes it easier to use an aerosol inhaler and helps the medicine to reach the lungs more effectively. A spacer is a plastic container with a mouthpiece or mask at one end and a hole for the inhaler in the other. A homemade spacer, made from a 500ml plastic bottle, can be as effective as a commercially manufactured inhaler.
Access to inhalers is a problem in many countries. In 2021, bronchodilators were available in public primary health care facilities in half of low- and low-middle income countries, and steroid inhalers available in one third.
You May Like: How To Sleep With Asthma Attack
Natural History Of Asthma
Describing the natural history of asthma poses the same challenges as defining asthma. This is due to the heterogeneity of the airway diseases unified under the asthma label . Thus, the natural history may follow different paths of disease progression, including lung function decline, remission, reoccurrence, morbidity and mortality.
Asthma Prognosis During Childhood
The course of asthma varies in childhood, although the disease is considered chronic in the early stages of life. Around 60%³ of asthmatic children at seven years of age wont grow up to be asthmatics.
Additionally, around 5% of the general population has persistent symptoms from childhood to adulthood.
Symptoms of the clinical syndrome of asthma in children include:
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest tightness
In addition to these symptoms, asthmatic children might experience bronchial hyperresponsiveness and variable expiratory flow limitation.
Asthma is considered a syndrome, not a single disease because the symptoms stem from different subtypes. Therefore, a variation exists both in the course and subtypes of asthma.
Read Also: How Many People Have Asthma
Eosinophilic Asthma Like Regular Asthma Can Be Managed For A Long Healthy Life
A subtype of asthma, eosinophilic asthma is more severe than regular asthma because it involves the entire respiratory tract in airflow obstruction. In addition, mucus coughed up contains more eosinophils that could lead to more severe asthma attacks. However, like asthma, eosinophilic asthma can be managed with treatment so you can live a long, healthy life. Minimizing triggers and seeing your doctor regularly are key components in treatment and management to help prevent or reduce the severity of asthma attacks.
How Do You Monitor Asthma Symptoms
You should keep track of your asthma symptom. Its an important piece of managing the disease. Your healthcare provider may ask to use a peak flow meter. This device measures how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It can help your provider make adjustments to your medication. It also tells you if your symptoms are getting worse.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Asthma Wheezing Without Inhaler
Acute Asthma Prognosis And Treatment
Most recent update: July 2021Originally Posted: September 2004
Division of Allergy and Immunology,University of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL 33612
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector, Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair in Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalEmail: rlockey@health.usf.edu
Michael A. Kaliner, MD FAAAAIMedical Director, Institute for Asthma and AllergyChevy Chase and Wheaton, MarylandProfessor of Medicine, George Washington University School of MedicineWashington, DC
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector of the Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair of Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida College of Medicine and the James A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL
Abstract
Key words: Asthma flare Acute asthma Asthma attack Wheezing Acute asthma diagnosis Acute asthma management
Abbreviations
EPR-3 – The Expert Panel Report 3EPR-4 The Expert Panel Report 4FeNO Fractional Exhaled Nitric OxideOCS – Oral corticosteroidsCOPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseasePEF – Peak expiratory flowSABA – Short acting beta agonistAE Adverse eventsFVC- Forced vital capacity
Introduction
1. Recognition of patients who are at a greater risk for near-fatal or fatal asthma.
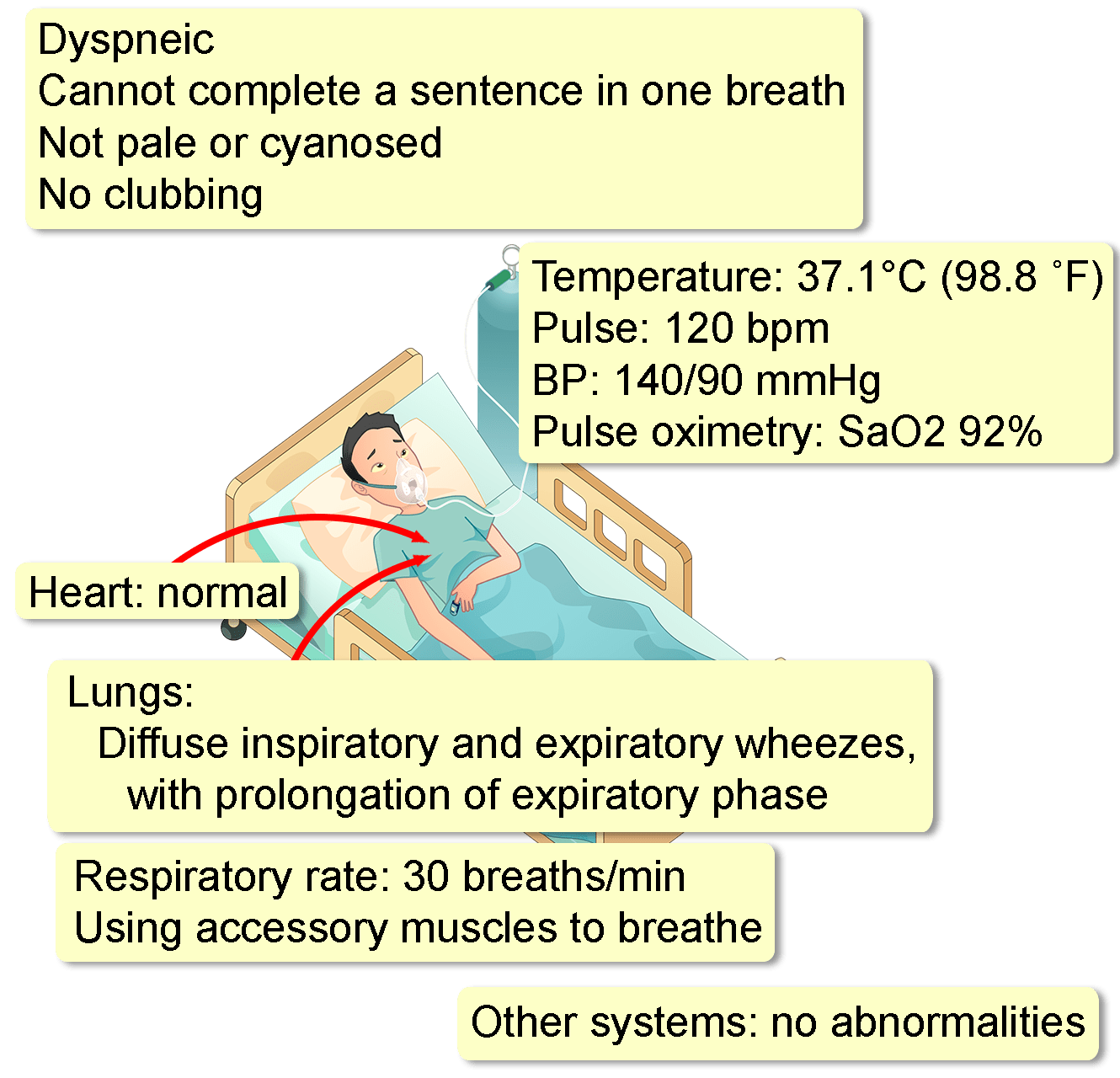
Physical Examination
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Asthma
What Are The Different Types Of Asthma
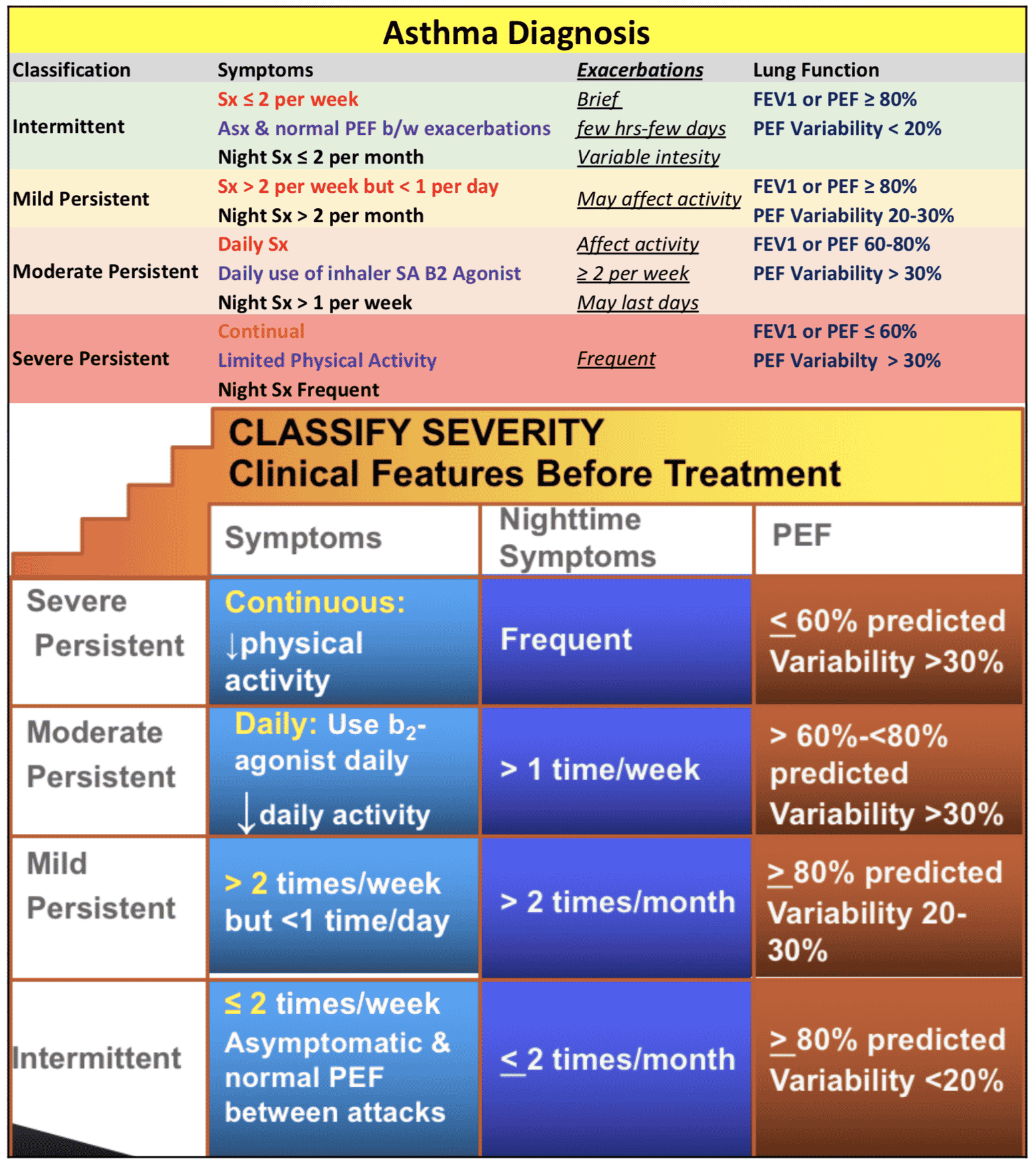
There are four levels of asthma, based on the severity of your asthma. How often you have symptoms, and your lung function determines your asthma level. Your doctor will ask you questions such as:
The answers to these questions help figure out the severity of your asthma. There are different treatment options if your asthma is intermittent or persistent .
You may also hear about different types of asthma from your doctor or others. These names may describe what is causing the asthma. Here are some types of asthma:
Read Also: What Can You Do For Asthma
What Causes Asthma Symptoms
For people with asthma, respiratory infections, allergens, chemicals, odors, physical activity, emotions, seasonal changes and smoking can irritate the lungs. We call these triggers because they cause changes in the airways. Understanding what triggers your asthma will help you manage your disease. Work with your healthcare provider to identify the triggers that cause your asthma symptoms. Once you have identified your triggers, work on ways to avoid the trigger entirely or to limit your exposure to it.
Talk To Your Healthcare Provider If You Are Experiencing Any Of These Symptoms
The sooner you begin treating your asthma and maintaining control, the less damage you will cause your lungs in the long run.
There are many resources available for people living with asthma and their loved ones. To learn more about your asthma, visit one of the links below:
Also Check: Does 2nd Hand Smoke Cause Asthma
A Personalized Treatment Plan May Include:
Macrolide antibiotics are used to help the body fight infection. These medicines control the number of white blood cells found in your airways. One study showed positive results using macrolide antibiotics in people with high counts of neutrophils in blood or sputum samples. Doctors dont suggest these medications be used long term though because side effects, such as antibiotic resistance, can be very serious.
Oral corticosteroids are medicines that help to control inflammation. While experts recommend these medicines only for short-term use, doctors may prescribe them long-term for people with more frequent asthma flare-ups. Severe asthma patients use these medications in combination with quick-relief medicine, high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators. Side effects from using oral corticosteroids can pose a risk to the function of other bodily organs, but the benefits may at times outweigh the risk. The hope is that by using these powerful drugs for a short period of time, patients can gain better control and will eventually not need them at all. This treatment option is approved for adults and children, although long-term use in children is not recommended due to the higher risk side effects. If symptoms are still not controlled with long-term use of an oral corticosteroid, another treatment option should be considered.
|
Type of severe asthma |
Cardiac Asthma Is Not The Same As Asthma
Although they share a name, cardiac asthma is not a type of asthma. Asthma is caused by the narrowing and inflammation of the airways in the lungs, while cardiac asthma is coughing or wheezing that occurs due to left-sided heart failure. Treatments for cardiac asthma typically are the same as those for heart failure. Cardiac asthma prognosis depends on several factors, including what stage your heart failure is in, your diet, and lifestyle elements, such as exercise routine and tobacco and alcohol use. The mortality rate for heart failure at one year is 22% and at five years is 43%.
You May Like: How To Treat Asthma Without Inhaler
Role Of Ics Alone Or In Combination In Different Asthma Phenotypes
The understanding of the biology and pathophysiology of asthma has progressed, with the identification of a number of distinct phenotypes . However, current international guidelines recommend initiating ICS treatment to almost all patients . ICSs work through both positive gene regulation and gene repression, with the result of this dual action being potent anti-inflammatory action in the airways .
The improvement with ICS in some clinical parameters, such as spirometry, is variable . As a result, different biomarkers, alone or in combination, are being used to increase the predictability of ICS response . For example, sputum eosinophil levels have been shown to predict response to ICS and to predict exacerbation risk on ICS withdrawal . In a separate study, titration of ICS treatment according to sputum eosinophil counts resulted in significantly fewer severe exacerbations compared with guideline-driven treatment . However, the analysis of induced sputum is still not widely available for routine use. Furthermore, by using multiple markers of inflammation , incremental ICS dosing in persistent asthma is associated with a plateau in symptoms and lung function, but with progressive improvement in inflammatory outcomes and AHR . Unfortunately, the use of either biomarker-based or symptom-based adjustment of ICS is not superior to physician assessment-based adjustment of ICS in terms of time to treatment failure .
What Is Status Asthmaticus
Status asthmaticus is respiratory failure that comes with the worst form of acute severe asthma, or an asthma attack. If an attack comes on quickly and it doesnât respond to regular treatment, it can lead to status asthmaticus, If it happens, you may have to go to the hospital to get it treated. If you have a bad asthma attack and your rescue inhaler or your nebulizer doesn’t help, you need medical care right away.
If you have a steroid medicine at home , you can take a dose of it on your way to the emergency room.
Many people have asthma. And there are many treatments to manage it. Itâs important to follow the asthma action plan that you made with your doctor, avoid your triggers, take your medicine, and keep up with your doctor appointments.
Still, asthma attacks can happen, and some severe ones are an emergency.
With any asthma attack, never wait to see if it goes away on its own. It could worsen so much that you need to go to a hospital.
You may hear a severe asthma attack called a âsevere asthma exacerbation.â In its most severe form, you may hear it called status asthmaticus.
Recommended Reading: Is Pollen Bad For Asthma
Childhood Asthma May Improve But Never Truly Goes Away
As children with asthma grow up, their asthma stays with them. While they may experience fewer asthma symptoms, the possibility of an asthma attack remains. Continued treatments, such as long-term control medications and rescue medications can help keep asthma under control. Lifestyle choices, such as not smoking, exercising regularly, reducing pet dander, and regular cleaning can also help prevent asthma attacks.
Smoking Could Reduce Your Asthma Life Expectancy
Because smoking harms your respiratory system, it negatively impacts asthma life expectancy. People with asthma already suffer from narrowed and inflamed airways, and tobacco smoke further irritates the airways by damaging the cilia that remove the dust and mucus from the airways. Even inhaling secondhand smoke could lead to decreased lung function and increased airway inflammation, which could spur an asthma attack. Quitting smoking or not allowing anyone to smoke in your home, car or around you helps reduce your exposure to nicotine and other substances in tobacco smoke that could trigger an asthma attack.
Recommended Reading: Asthma Symptoms When Lying Down
What Types Of Asthma Are There
Asthma is broken down into types based on the cause and the severity of symptoms. Healthcare providers identify asthma as:
- Intermittent: This type of asthma comes and goes so you can feel normal in between asthma flares.
- Persistent: Persistent asthma means you have symptoms much of the time. Symptoms can be mild, moderate or severe. Healthcare providers base asthma severity on how often you have symptoms. They also consider how well you can do things during an attack.
Asthma has multiple causes:
- Allergic: Some peoples allergies can cause an asthma attack. Allergens include things like molds, pollens and pet dander.
- Non-allergic: Outside factors can cause asthma to flare up. Exercise, stress, illness and weather may cause a flare.
Asthma can also be:
- Adult-onset: This type of asthma starts after the age of 18.
- Pediatric: Also called childhood asthma, this type of asthma often begins before the age of 5, and can occur in infants and toddlers. Children may outgrow asthma. You should make sure that you discuss it with your provider before you decide whether your child needs to have an inhaler available in case they have an asthma attack. Your childs healthcare provider can help you understand the risks.
In addition, there are these types of asthma:
Why Do Certain Racial Or Ethnic Groups Have Higher Rates Of Asthma Asthma Attacks Or Asthma Deaths
See AAFAs groundbreaking research report on Asthma Disparities in America. Racial and ethnic differences in asthma frequency, illness, and death are caused by complex factors, including:
- Structural determinants such as systemic racism, segregation, and discriminatory policies
- Social determinants such as socioeconomic status, education, neighborhood and physical environment, employment, social support networks, and access to health care
- Biological determinants such as genes and ancestry
- Behavioral determinants such as tobacco use and adherence to medicines
- Social determinants and structural inequities largely drive disparities in asthma. Factors such as genetics and individual behaviors contribute less to asthma disparities.
You May Like: What Type Of Specialist Treats Asthma
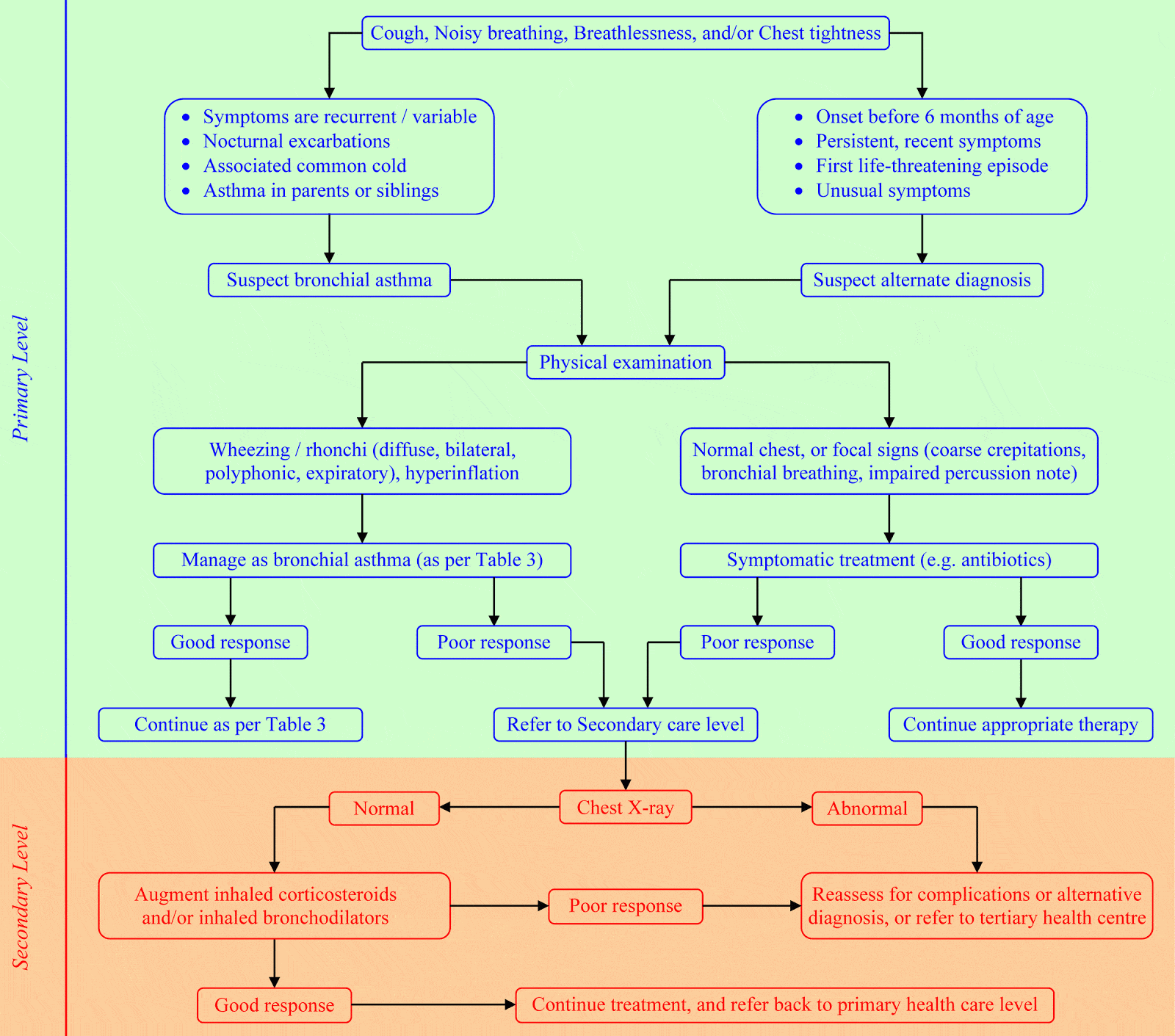
Diagnosing Asthma In Children
A child is more likely to have asthma if:
- A parent has asthma
- The child has allergies, including the allergic skin condition eczema
- Exposed to tobacco smoke during pregnancy or throughout childhood
- Exposed to indoor and outdoor air pollutants
- The child wheezes with viral infection
- The child is obese
To help your child’s healthcare provider make a correct diagnosis, be prepared to provide information about family history of asthma or allergies, the child’s overall behavior, breathing patterns and responses to foods or possible allergy triggers. Lung function tests are often used to make an asthma diagnosis, but they are very hard to do with young children. The doctor may use a 4- to 6-week trial of asthma medicines to see if they make a difference in your child’s symptoms.
