What You Need To Know About Your Childs Asthma
There are many things to think about and plan for when your child has asthma. It is important to learn as much as you can about the condition. Your doctor and pharmacist are there to help you. Talk to them about any concerns you may have about your childs asthma. To manage your childs asthma effectively, it is important to know:
- the pattern of their asthma
- their asthma medications what they do and how to help your child take them properly
- what to do if they have an asthma attack know and follow asthma first aid.
Make sure you have an updated written asthma action plan and understand how to use it.
Donât Miss: What To Do When Someone Has An Asthma Attack
How Often Does Acute Asthma Occur In The United States
Asthma exacerbations can be prevented with appropriate and regular therapy and patient education. Despite this, in the United States alone, approximately 12 million people experience an acute exacerbation of their asthma each year, a quarter of which require hospitalization. .
What happens to your airways during an asthma attack?
During an asthma attack, also called an asthma exacerbation, your airways become swollen and inflamed. The muscles around the airways tighten, and the airways also produce extra mucus, causing your breathing tubes to narrow.
Testing For Severe Asthma
Before you can be tested for severe asthma, you will need a referral from your primary healthcare asthma provider to either an asthma specialist or allergy specialist . The specialist will review your medical history, your current asthma treatment plan and do a physical exam to assess your symptoms. If the specialist thinks you may have severe asthma, they will discuss additional testing with you to determine your specific type. This often starts with testing to identify a biomarker.
Biomarkers help determine what is causing the inflammation in your airways. Taking a blood sample, analyzing a mucus sample or taking a breathing test that measure substances in your breath droplets are all common tests doctors use. These tests are performed in a doctors office or an outpatient clinic setting. Your specialist will recommend one or more of these tests based on your medical history and current symptoms. Once the biomarkers are identified, your doctor can determine the type of severe asthma and the different treatment options that are available to treat that specific type.
Don’t Miss: Can Asthma Make You Dizzy
Can Current Therapeutic Regimens Prevent Virus
There is no doubt that the reductions observed in asthma morbidity and mortality observed over the last 20 years are the result of better therapeutic management however, the real question is, are asthma therapeutics effective in virus-induced exacerbations? Large studies have shown that even low-dose inhaled corticosteroids reduce exacerbations and the risk of death from asthma . For example, in comparison to no treatment, 100 g budesonide twice daily resulted in a 60% reduced risk of having a severe exacerbation in the OPTIMA trial . The addition of a long-acting 2-agonist to ICS further reduces the frequency , severity and duration of exacerbations. Studies such as these were not designed to identify the cause of the exacerbation however, as viruses are thought to cause 50% of all exacerbations, it is reasonable to assume that some reduction in the incidence of virus-induced exacerbations would occur. None of these studies specifically identified whether improved asthma management does one or more of the following: 1) reduces the rate of respiratory viral illnesses 2) reduces the rate at which respiratory viral infections trigger a sequence of inflammatory events that will result in an exacerbation or 3) reduces the severity of symptoms or lung function such that the episode does not require exacerbation-defining medical intervention.
Summary And Next Steps
Much is already known about asthma exacerbation risk and prevention. Currently, medical history, biomarkers, environmental assessments, and technology have allowed for more personalization of asthma care for the prevention of asthma exacerbations than ever before. Further study into the underlying mechanisms for asthma exacerbations and gene-environmental interactions will provide for further personalization in the future. Future steps to further personalize asthma therapy includes the further elucidation of genetic-environmental interaction risk factors for exacerbations including the role of the human rhinovirus receptor in asthma exacerbations,114 proteomics,115 and metabolomic116 and microbiome117,118 evaluations. This expanding understanding of exacerbation risk could be harnessed into more precise, and possibly even real-time exacerbation prediction, as has been envisioned.119 However, in the meantime, providers can utilize currently available information to predict asthma exacerbations, including demographic information, asthma history , markers of lung function, biomarkers including allergen sensitization, FeNO and eosinophils, and indoor and outdoor environmental exposures.
Jennifer Dunnick MD, MPH, … Jerri A. Rose MD, in, 2018
Recommended Reading: How Is Severe Asthma Treated
Allergies Can Cause Asthma
Allergies with asthma is a common problem. Eighty percent of people with asthma have allergies to things in the air, like tree, grass, and weed pollens mold animal dander dust mites and cockroach droppings. In one study, children with high levels of cockroach droppings in their homes were four times more likely to have childhood asthma than children with low levels. An allergy to dust mites is another common asthma trigger.
If you have asthma thatâs hard to control, see an allergist to find out if you have allergies. Treating your allergies with medication and avoiding your triggers can help lower the odds of a severe asthma attack.
Can You Prevent An Asthma Exacerbation
If you have asthma, you can prevent many asthma exacerbation episodes by following the treatment plan that you developed with your healthcare provider. That means you’ll need to take your prescribed medication daily and use your quick-acting medicine as soon as you begin to notice symptoms of an asthma exacerbation.
It’s also crucial to learn your triggers and avoid them as often as possible. That way, you can prevent your body from reacting to them in the first place. With help from your healthcare provider and an allergist, you can learn to avoid triggers and decrease the instances in which you’ll need to use a quick-acting medicine.
Most people with asthma can lead normal lives, especially if they’ve got an effective treatment plan in place.
Recommended Reading: Can Cold Air Cause An Asthma Attack
What Is An Asthma Exacerbation
When exposed to certain triggers like allergens or chemicals, a person with asthma can have an asthma exacerbation, also known as an asthma attack. When this happens, the muscles around the bronchial tubes begin to constrict, and this causes the air passages to become narrow, making it very difficult to breathe. This can feel like a heavy weight on your chest or a tightening sensation in your lungs.
Episodes can vary in severity and last from a few minutes to hours or even days. This experience can be scary, but there are fast-acting treatment options that can help to stop an episode quickly and effectively.
When To See A Doctor
If you’ve been diagnosed with asthma, it’s important to see your healthcare provider at least once each year. That way, you can effectively manage your condition and maintain a treatment plan that keeps asthma exacerbations at a minimum.
If you have any of the following symptoms, it’s important to call your doctor immediately:
-
Feeling faint, dizzy, or weak
-
Trouble doing normal activities like cleaning or walking
-
A persistent cough
-
Wheezing when you breathe, especially if it persists after using your quick-acting inhaler
If you have the following symptoms, it’s a medical emergency.
-
Blue nails or lips
-
Flaring nostrils when you inhale
-
The skin between your ribs or near your collarbone stretches each time you breathe
-
Breathing more than 30 times each minute
-
Talking or walking becomes difficult
Working closely with your healthcare provider will allow you to live a normal life that eliminates the most severe symptoms of asthma. Make sure you meet with your doctor at least once a year to maintain a treatment plan that’s effective and up to date.
You May Like: What To Do If Someone Has An Asthma Attack
What You Should Know About Asthma Exacerbation
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects a person’s airways and makes breathing difficult. More than 25 million Americans¹ suffer from asthma, and there is currently no cure for this condition. People with asthma need to work closely with their doctors to manage the symptoms and keep asthma exacerbations to a minimum.
Let’s look at what it means to have an asthma exacerbation and what treatment options are available for relief.
Have you considered clinical trials for Asthma?
We make it easy for you to participate in a clinical trial for Asthma, and get access to the latest treatments not yet widely available – and be a part of finding a cure.
First Area: Diagnosis And Elements Of The Diagnosis
For patients with asthma exacerbation, what severity criteria in medical history and at initial physical examination are associated with an increased risk of mortality and/or intensive care admission?
R1.1 adultFrom first contact with patients with asthma exacerbation, the following severity criteria should be sought: history of hospital admission for asthma or need for mechanical ventilation, recent use of oral corticosteroids, considerable or increasing use of beta-2 adrenergic agonists, age> 70 years, difficulty speaking, altered consciousness, shock, respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min, arguments in favor of an underlying pneumonia.
GRADE 1+, STRONG AGREEMENT
Rationale
The criteria of clinical severity on admission of patients with SAE have mainly been investigated in observational studies . The criteria of poor prognosis used in these studies were death or the need for mechanical ventilation. In patients admitted to intensive care, advanced age, neurological disorders, and tachycardia were clinical features associated with a poor prognosis . Data concerning hospitalized patients were reported by a 2017 Japanese publication . Age , shock, altered consciousness, and infectious lung disease were associated with increased risk of death. Peak expiratory flow measured at admission was seldomly studied, but was not associated with a poor prognosis .
GRADE 2+, STRONG AGREEMENT
Rationale
You May Like: How To Use Kalonji For Asthma
What Is An Asthma Action Plan
Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop an asthma action plan. This plan tells you how and when to use your medicines. It also tells you what to do if your asthma gets worse and when to seek emergency care. Understand the plan and ask your healthcare provider about anything you dont understand.
What Causes Asthma To Flare Up
Your asthma can flare up for different reasons. If youre allergic to dust mites, pollens or molds, they can make your asthma symptoms get worse. Cold air, exercise, fumes from chemicals or perfume, tobacco or wood smoke, and weather changes can also make asthma symptoms worse. So can common colds and sinus infections.
Read Also: Non Pharmacological Management Of Asthma
How Is An Acute Asthma Exacerbation Treated
Short-acting inhaled beta2-agonists are the mainstay of treatment for acute asthma. A spacer inhaler is equivalent to nebulized short-acting beta2-agonist treatment in children and adults. Continuous administration of beta2 agonists reduces hospitalizations in patients with severe acute asthma.
Strictly Follow Your Medication As Prescribed By Doctor
Either you feel your asthma symptoms or not, you have to strictly follow your asthma medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Many of us make this mistake by stopping the medications when we dont feel any symptoms.
Its a very bad practice that will worsen your asthma symptoms anytime when they get a trigger and youll have a sudden asthma attack. You should always remember that asthma is a chronic disease. Once you have asthma means youll have it all the time.
Also Check: Medical Marijuana And Asthma
Don’t Miss: Can Acid Reflux Cause Asthma
Why Are Corticosteroids Used To Treat Severe Asthma Exacerbations
-Agonists and other bronchodilators target bronchospasm while corticosteroids reduce the inflammatory response by inhibiting the activation of inflammatory cells and by reducing mediator production, microvascular leakage, and mucus formation. Corticosteroids have been used to treat asthma for approximately 50 years.
Study Design And Population
This is a longitudinal population-based cohort study where motherbaby pairs were identified from health administrative databases and their health outcomes studied from April 1, 2003 to March 31, 2012
Mother cohort
The mother cohort included women aged between 13 and 45years with prevalent asthma during pregnancy who had at least one pregnancy resulting in a live or still birth between fiscal year 2006 and FY2012. Women with multiple births, without OHIP coverage for a period of 14months prior to pregnancy, who were missing data on age, residence postal code and non-identifiable in the MOMBABY database were excluded.
Baby cohort
Babies born to women with prevalent asthma during pregnancy were identified from the MOMBABY database and were followed from birth to 5years of age. Stillborn babies and those who died before age 5years were excluded from the cohort. We excluded multiple births, as the intrauterine physiology underlying maternalfetal transmission differs between multiples and singletons and multiple pregnancies have significant risk complications .
You May Like: Is Warm Moist Air Good For Asthma
Second Area: Pharmacological Treatment
What are the methods of administration of beta-2 adrenergic agonists in patients with SAE?
R2.1Beta-2 adrenergic agonists should not be administered intravenously first line in adult or pediatric patients with SAE even in mechanically ventilated patients.
GRADE 1, STRONG AGREEMENT
R2.2Beta-2 adrenergic agonists should probably be administered by continuous rather than discontinuous nebulization during the first hour in adult and pediatric patients with SAE.
GRADE 2+, STRONG AGREEMENT
Rationale
There is no pediatric study that has rigorously compared the efficacy of continuous and intermittent nebulization of short-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonists in children with SAE. Several cohort studies have demonstrated that there is no increase in adverse effects with continuous versus intermittent nebulization .
What Is The Most Common Cause Of Asthma Exacerbation
Asthma exacerbations are most commonly triggered by viral respiratory infections, particularly with human rhinovirus. Given the importance of these events to asthma morbidity and health care costs, we will review common inciting factors for asthma exacerbations and approaches to prevent and treat these events.
Recommended Reading: A National Survey Of Asthma Conducted On May 1 2012
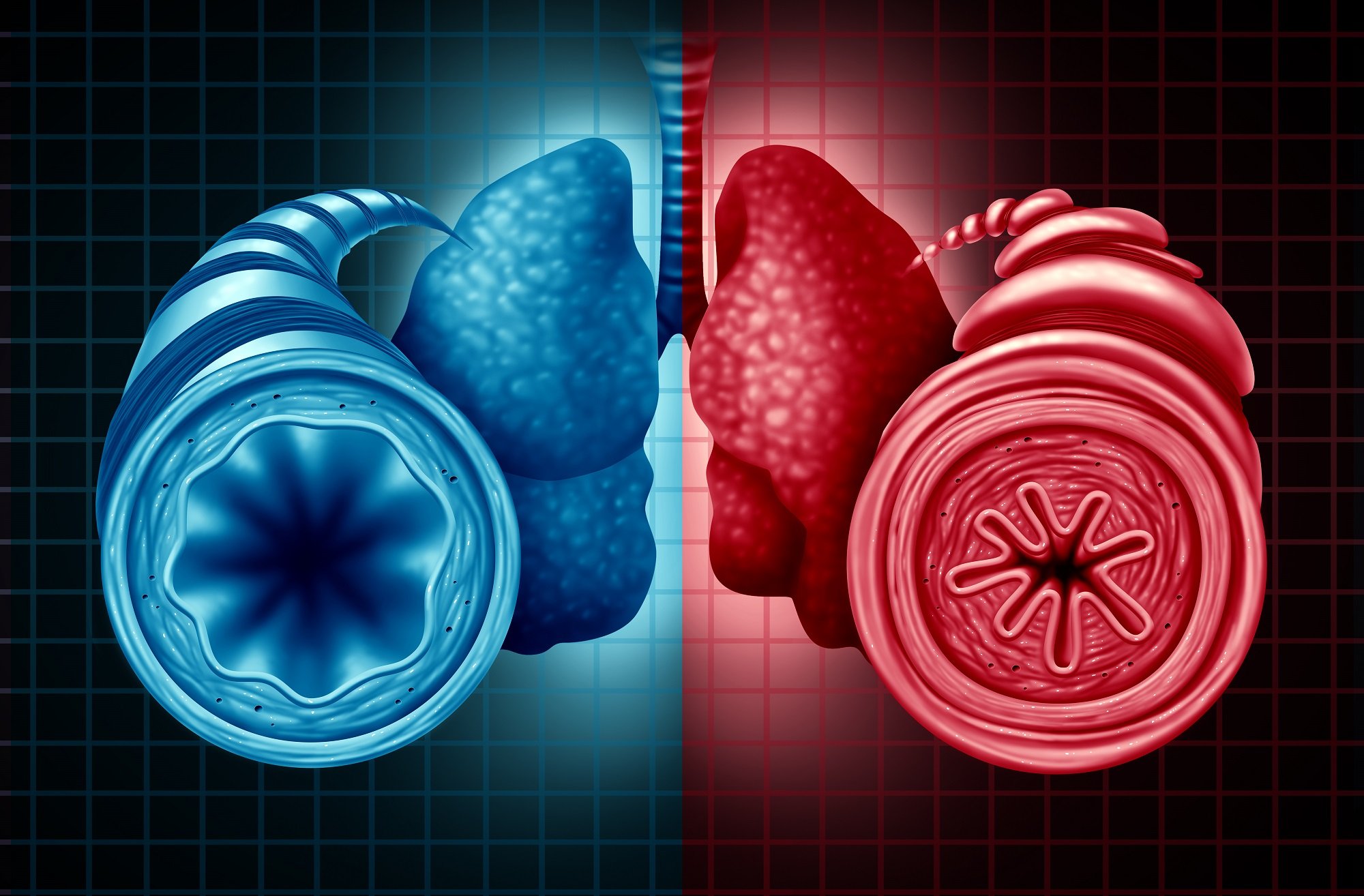
Breathing: Normal Airways Vs Asthma Airways
Normal: In someone with optimal lung function, air is inhaled through the nose and mouth, passing through the trachea before moving into the bronchi . The bronchi branch into smaller tubes, ending in many small sacs called alveoli. Its in the alveoli that oxygen is passed to the blood and carbon dioxide is removed.
Asthma: In someone with asthma, the airways are inflamed, and when triggered, can constrict even more, obstructing airflow to the lungs.
Will My Wheezing Or Coughing Be Worse
Not necessarily. You might be surprised to learn that you may not have more of these than usual during a severe asthma attack. So donât judge how bad your asthma attack is based on how much you wheeze or cough.
In fact, very severe asthma attacks may affect your airways so much that you donât get enough air in and out of your lungs to make a wheezing sound or cough.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Asthma If You Never Had It
Susceptibility To Viral Infection
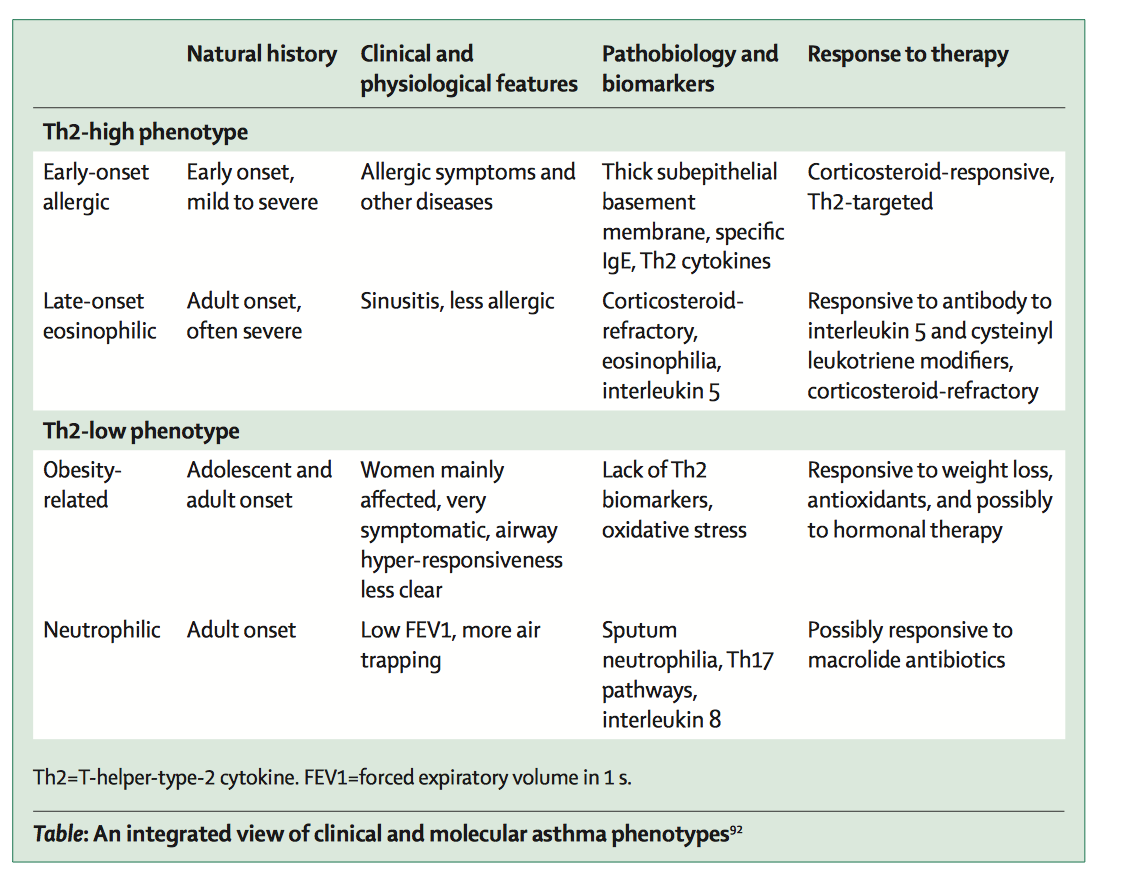
People with asthma do not appear to be more likely to develop symptomatic colds than nonasthmatic individuals, but they are more likely to develop lower respiratory tract symptoms and these symptoms are more prolonged. While this may represent the effect of virus infection on asthmatic inflammation, it may also indicate an increased susceptibility to virus infection in asthmatics. Traditionally, antiviral responses have been characterised by a Th1 phenotypic response with raised levels of IFN and recruitment of CD8 cells. This is in contrast to the Th2 response thought to be dominant in asthma, with increased levels of IL4, IL5 and IL13. Subjects infected with RV who have a Th2 characteristic response, as seen by a lower ratio of IFN to IL5 in sputum, were less efficient at clearing the virus. Infection of peripheral blood monocytes from subjects with atopic asthma and nonatopic controls with RV also showed differential responses. Nonasthmatic PBMCs responded with vigorous release of IFN and IL12, while this response was lower in asthmatic PBMCs which had higher levels of the antiinflammatory cytokine IL10 and a small increase in IL4 levels .
Concluding Remarks: At Least Two Synergistic Inflammatory Processes Are Required To Induce Asthma Exacerbations
Asthma exacerbations result from the activation of BEC and DCs, These cells then produce cytokines and chemokines attracting and activating T cells, eosinophils and neutrophils which in turn injure the epithelium and amplify the inflammatory process .
Figure 4.3. Immunopathology of asthma exacerbations. Upon allergen, virus or pollutant stimulation, bronchial epithelial cells and dendritic cells are activated via pattern recognition receptors to produce cytokines and chemokines and express membrane molecules that will attract and activate T cells, eosinophils, mast cells and neutrophils.
We have largely developed above the theory that asthma exacerbations are related to a proper inflammatory response, differing from the ongoing chronic inflammation related to asthma itself. It is nevertheless clear that this first chronic inflammatory step is necessary, as neither viruses, pollutants nor allergens induce exacerbation in non-asthmatic patients, and as exacerbations are efficiently prevented by inhaled corticosteroids in most patients. Indeed, inhaled steroids clear this chronic inflammation. In atopics, allergens are considered as responsible for this first chronic inflammatory step. In non-atopic asthma, the chronic inflammation is similar but the trigger is unknown. However, whatever the atopic status, an intrinsic chronic inflammation is found in asthmatic patients.
Leonard B. Bacharier, Robert C. Strunk, in, 2016
Read Also: Is Lavender Oil Good For Asthma
What Can Cause Asthma Exacerbation
Of these, rhinoviruses account for 60% to 70% of all viral-induced asthma cases, with the majority of remaining cases linked to influenza viruses and RSV. However, it is unclear how these different viral infections trigger asthma.
Most scientists agree that there is not a simple cause-and-effect relationship. What follows are a few hypotheses as to why viral-induced asthma occurs.
