The Impact Of Asthma On Daily Life
Asthma is often under-diagnosed and under-treated, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
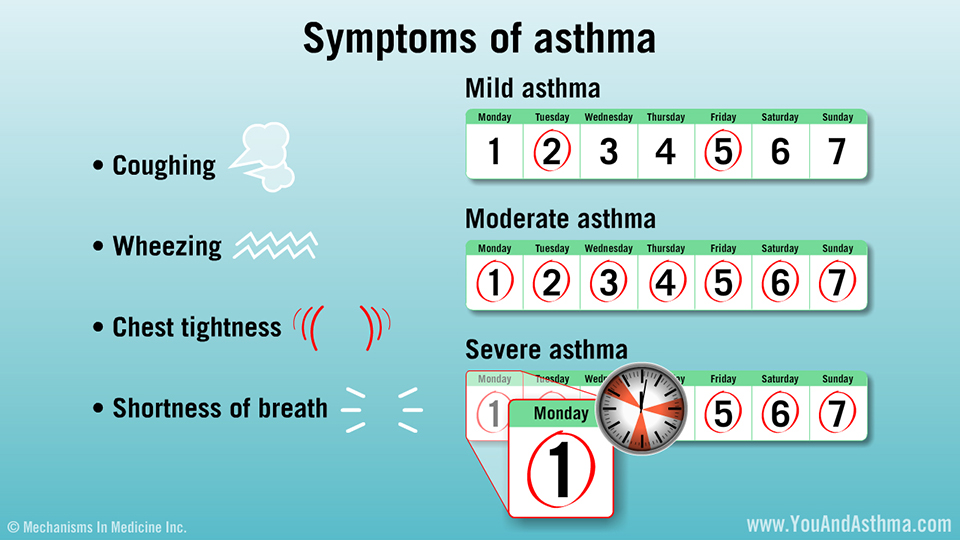
People with under-treated asthma can suffer sleep disturbance, tiredness during the day, and poor concentration. Asthma sufferers and their families may miss school and work, with financial impact on the family and wider community. If symptoms are severe, people with asthma may need to receive emergency health care and they may be admitted to hospital for treatment and monitoring. In the most severe cases, asthma can lead to death.
Clinical And Laboratory Assessment
Patients with acute, severe asthma appear seriously dyspneic at rest, are unable to talk with sentences or phrases, are agitated and sit upright 2) . Drowsiness or confusion are always ominous signs and denote imminent respiratory arrest. Vital signs in acute, severe asthma are: respiratory rate usually > 30 breaths/min heart rate > 120 beats/min wheezing throughout both the inspiration and the expiration use of accessory respiratory muscles evidence of suprasternal retractions and pulsus paradoxus > 12 mmHg.
Additional Medication For Severe Asthma
In addition to a reliever and preventer inhaler, severe asthmatics may be prescribed other treatments. You may need to try several options before your healthcare provider finds the right choice for your needs.
In addition to inhalers, treatment options include:
- Long-acting bronchodilators these can be added to a preventer inhaler and help keep the airways open for at least 12 hours.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists a non-steroid tablet that helps to calm inflamed airways, block the effects of leukotrienes and help with allergies.
- Long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists a form of long-acting bronchodilator that can work for 12-24 hours.
- Long-acting beta-agonists another form of long-acting bronchodilator that is used to relax the muscles in the airways.
- Slow-release theophylline a non-steroid tablet that helps to relax the smooth muscles in the airways, enabling air to more easily flow through.
- Short-acting beta 2-agonists a form of quick relief medication that can be used when asthma symptoms occur.
- Daily steroids these are prescribed in tablet or liquid form and are a type of anti-inflammatory medicine. They work by helping to reduce the sensitivity in the airways.
- Monoclonal antibodies a newer form of medication for severe uncontrolled asthma. They work by blocking the activity of immune system chemicals that trigger airway inflammation.
You May Like: Does Ibuprofen Make Asthma Worse
Living With Severe Asthma
Healthtalk Australia recently conducted qualitative research on living with severe asthma. They interviewed 35 people about their experience with severe asthma from all around Australia, including regional areas.
In their video interviews available on the Healthtalk Australia Severe Asthma section they talk to each person about how severe asthma affects them the emotional burden, challenges of everyday life, personal relationships, what they value out of their interactions with healthcare providers and how the medication affects them.
Additional therapies such as Monoclonal Antibodies Biologicals
More people living with severe asthma will be able to access life-changing, injectable asthma drugs called Biologics Therapies following an announcement under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme . For people with diagnosed severe asthma, they can ask their GP about accessing Biologics Therapies. They will need to be referred to a specialist to be considered for Biologics.
Learn more about Biologics here.
Access the new Severe Asthma and COVID-19 resource on MAb based care for consumers, pharmacists, and health professionals here.
Complications Of Acute Severe Asthma
Pneumothorax eventually associated with pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema ,2), pneumopericardium and tracheoesofageal fistula 3) are rare but potentially severe complications of acute, severe asthma. Myocardial ischemia should be considered in older patients with coronary artery disease. Mucus plugging and atelectasis are not rare and usually respond to effective treatment. Other complications to consider include theophylline toxicity, lactic acidosis, electrolyte disturbances , myopathy and ultimately anoxemic brain injury .
Pneumomediastinum-bilateral pneumothorax in an intubated patient in status asthmaticus. Radiolucent stripes along the soft tissues of the mediastinum, and the continuous diaphragm sign indicate the presence of pneumomediastinum. Bilateral pneumothorax is also seen . Subcutaneous emphysema is also seen on the left of the figure.
You May Like: Can You Enlist With Asthma
Confirmation Of The Diagnosis
If severe asthma is suspected, differential diagnoses that may mimic asthma should first be ruled out. This requires a detailed clinical history . Because up to 40% of asthma patients in Europe smoke , subacute reversibility testing using systemic steroid therapy should be performed in addition to acute reversibility testing to rule out chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . If prednisolone therapy largely or completely restores lung function, COPD is unlikely.
Ongoing Management Of Asthma
Ongoing management centers on controller medications. These include inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists. Theophylline and cromolyn are still listed, but these are not preferred agents, and they do not work as well as inhaled corticosteroids or leukotriene receptor antagonists. Inhaled corticosteroids are the fundamental and first-line therapy in ongoing management because of their proven effectiveness and, in recommended doses, few systemic adverse effects. Well-designed studies demonstrate that inhaled corticosteroids improve asthma control more effectively in children and adults than any other single long-term controller medication.15,16
Written action plans detailing medications and environmental control strategies tailored for each patient are recommended for all patients with asthma, and especially for patients with persistent asthma.1723 Examples of action plans are available at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Web site .24
Planned asthma-care visits are one of the key recommendations of the new guidelines. These visits are essential for adequate teaching and asthma control. Strategies for planned visits have been published.25 Patients with intermittent asthma may need to be evaluated only once yearly. Those on controller agents should be seen at least twice yearly, and as often as every four months.
Also Check: Can Allergies Cause Asthma Attacks
What Should I Do If I Have A Severe Asthma Attack
A severe asthma attack needs immediate medical care. The first step is your rescue inhaler. A rescue inhaler uses fast-acting medicines to open up your airways. Its different than your normal maintenance inhaler, which you use every day. You should only use the rescue inhaler in an emergency.
If your rescue inhaler doesnt help or you dont have it with you, go to the emergency department if you have:
- Anxiety or panic.
- Bluish fingernails, bluish lips or gray or whitish lips or gums .
- Chest pain or pressure.
How Do You Monitor Asthma Symptoms
Monitoring your asthma symptoms is an essential piece of managing the disease. Your healthcare provider may have you use a peak flow meter. This device measures how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It can help your provider make adjustments to your medication. It also tells you if your symptoms are getting worse.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Homemade Inhaler For Asthma
Requirements For Treatment Optimization
The treatment of patients with severe asthma requires experience, is time-consuming, and often necessitates off-label drug use. As a result, severe asthma is sometimes inadequately diagnosed and treated . In our view, this situation makes the following desirable:
-
Inclusion of as many patients as possible in severe asthma registries such as www.german-asthma-net.de
-
Better coverage of the diagnosis and treatment of severe asthma in physicians training
-
Assessment of patients with severe asthma in specialized asthma centers, in order to give them the opportunity to participate in clinical trials.
What Is Severe Asthma
Someone with severe asthma has a specific type of asthma which doesnt get better with the usual medicines.
Even if someone takes those medicines exactly as prescribed, a different approach is needed to control symptoms and reduce frequent asthma attacks.
Other causes and triggers for the symptoms have also been ruled out as much as possible.
Around 4 out of 100 people with asthma have severe asthma, which is about 200,000 people in the UK.
If your GP or asthma nurse suspects you have severe asthma they may refer you to an asthma specialist clinic for an in depth assessment.
Your GP or asthma nurse will continue to look after your asthma while you are waiting to see the specialist team and will continue to share responsibility for your care even when you are seeing them.
We dont understand yet why some people get asthma and some people get severe asthma, says Dr Andy Whittamore, Asthma UK’s in-house GP.
We know that each individual with asthma can have different triggers and a different chemical reaction in their airways.
Thats why Asthma UK is supporting research looking into what goes on in the body to cause severe asthma, and what makes it so much harder to control with the usual asthma medicines.
Don’t Miss: Can You Join The Army If You Have Asthma
Types Of Severe Asthma
There are two main categories of severe asthma Type-2 inflammation and Non-Type-2 inflammation. These categories are based on a persons response to treatment. Type-2 inflammation includes allergic asthma and eosinophilic asthma and Non-Type-2 inflammation includes non-eosinophilic asthma. For example, allergic asthma and e-asthma respond to treatment with inhaled corticosteroids and IgE -directed therapy or other biologics listed in the above table. Patients with Non-Type-2 inflammation, including non-eosinophilic asthma, generally do not respond well to inhaled corticosteroids. Allergic asthma and e-asthma have distinct biomarkers and treatment options available today. Treatments for non-eosinophilic asthma are currently being development.
Allergic asthma is caused by exposure to allergens such as pollen, pet dander, molds, etc. Most people diagnosed with allergic asthma will also have a diagnosis of hay fever or rhinitis. For these patients, exposure to allergens causes the bodys immune system to produce immunoglobulin E, an antibody that attaches to certain cells and causes them to release chemicals creating an allergic reaction. When this happens, common symptoms are sneezing, itchy/watery eyes, severe allergic reactions , and increased airway sensitivity.
Non-eosinophilic asthma includes neutrophilic, smooth-muscle mediated and mixed cells. People in this subgroup have few to no eosinophils in test results, and do not respond well to inhaled corticosteroids.
Subcutaneous Epinephrine And Terbutaline
Subcutaneous administration of epinephrine or terbutaline should be considered, in patients not responding adequately to continuous nebulised salbutamol, and in those patients unable to cooperate It should also be attempted in intubated patients not responding to inhaled therapy. Epinephrine may also be delivered effectively down the endotracheal tube in extreme situations . Subcutaneously, 0.30.4 ml of epinephrine can be administered every 20 min for three doses .3). Terbutaline can be administered subcutaneously or as intravenous infusion starting at 0.050.10 g/kg per min .3). When administered subcutaneously, however, terbutaline loses its -selectivity and offers no advantages over epinephrine . Terbutaline administered subcutaneously should be preferred only in pregnancy because it appears safer . Subcutaneous administration of epinephrine or terbutaline should not be avoided or delayed since it is well tolerated even in patients older than 4050 years with no history of cardiovascular disease . Intravenous administration of -agonists is also an option in extreme situations and should be considered in the treatment of patients who have not responded to inhaled or subcutaneous treatment, and in whom respiratory arrest is imminent, or in patients not adequately ventilated and severely hyperinflated, despite optimal setting of the ventilator.
Also Check: What Happens If You Smoke Weed With Asthma
Is There A Difference Between Severe Asthma And Uncontrolled Asthma
Not all uncontrolled asthma is severe and not all severe asthma is uncontrolled. A person with mild or moderate asthma can have uncontrolled asthma. Lack of control is defined using Baylor Universitys Rules of Two ®. Your asthma is considered uncontrolled if you experience any or all of the following:
- You use your quick relief inhaler each week
- You need oral steroids
- You have asthma symptoms at night
- You have to refill your quick-relief inhaler often
Severe asthma is not always uncontrolled. Severe asthma is asthma that requires a higher level of daily treatment. The measure of severe asthma is based upon:
- How often you need your controller medication
- The frequency and duration of your asthma symptoms
- The impact of asthma on your daily life
Do you or your teenage child have asthma? We are recruiting patients for the PRECISION asthma study. By participating in the study, you’ll attend 6 virtual asthma coaching sessions for free and help advance asthma care.
There are several asthma assessment tools you can use to determine if your asthma is in control or not:
How Do I Monitor My Daily Asthma Symptoms
National asthma guidelines suggest using a daily symptom diary such as Allergy & Asthma Networks AsthmaTracker to keep track of symptoms, peak expiratory flow rates and medications used.
What is an AsthmaTracker?
The AsthmaTracker can help your track how well your symptoms respond to your treatment plan. By writing down your symptoms, peak expiratory flow rate and medication use each day, youll notice a pattern to your symptoms and develop strategies to stop the symptoms before they can stop you.
What is a peak flow meter?
A peak flow meter is a handheld device that measures the peak expiratory flow rate , or how much air you can forcibly push out of your lungs at a particular time.
Asthma Storylines an app for managing asthma
The free Asthma Storylines app is a self-care tool for managing asthma. Track symptoms, learn more about daily patterns and record topics to discuss with your healthcare team.
You May Like: Side Effects From Inhalers
What Asthma Treatment Options Are There
You have options to help manage your asthma. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to control symptoms. These include:
- Anti-inflammatory medicines: These medicines reduce swelling and mucus production in your airways. They make it easier for air to enter and exit your lungs. Your healthcare provider may prescribe them to take every day to control or prevent your symptoms.
- Bronchodilators: These medicines relax the muscles around your airways. The relaxed muscles let the airways move air. They also let mucus move more easily through the airways. These medicines relieve your symptoms when they happen.
- Biologic therapies for asthma when symptoms persist despite being on proper inhaler therapy.
You can take asthma medicines in several different ways. You may breathe in the medicines using a metered-dose inhaler, nebulizer or other inhaler. Your healthcare provider may prescribe oral medications that you swallow.
S Everyone Can Take To Lower The Risk Of Getting And Spreading Covid
- Practice social distancing/self-monitoring/self-isolation/isolation as directed by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and often with soap and warm water for at least 30 seconds.
- Wear a non-medical grade face mask when you are in public places and in situations where you are not able to maintain physical distancing, like on public transportation or the grocery store.
- Avoid closed spaces, crowded places, and close contact.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces, such as toys, phones and door handles.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, ears or mouth.
- Stay home if you are sick. Encourage those you know who are sick to stay home until they no longer have symptoms.
- Avoid contact with people who are unwell.
- Make sure that you get high-quality information about COVID-19 from reliable sources. The Public Health Agency of Canada is a reliable source of information, as are provincial and territorial public health authorities.
Recommended Reading: Can I Join The Army With Asthma
Classification Of Asthma Control
The guideline recommends that every patient with asthma be able to recognize symptoms that suggest inadequate asthma control.4,5 As with asthma severity, assessment of control is determined by current impairment and future risk. The symptoms and history used to determine current impairment are the same as those used to determine impairment in evaluating disease severity, namely daytime symptoms, nighttime awakenings, frequent use of short-acting beta agonists for symptom relief, and inability to do normal activities because of symptoms.
Several questionnaires have been validated for the evaluation of symptom control.69 The Asthma Therapy Assessment Questionnaire ,10 the Asthma Control Questionnaire ,11 and the Asthma Control Test 12 provide validated control scores that can be used to categorize asthma into three control categories: well controlled, not well controlled, and very poorly controlled.
What Is Asthma Classified As
What is asthma classified as? Asthma is often linked to other medical conditions, such as: Allergies. Asthma is usually a type of allergic reaction. People who have asthma often have other types of allergies.
Is asthma kind of allergy? Allergic asthma is a type of asthma that is triggered by an allergy . According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, many of the 25 million Americans with asthma also have allergies, and this is called allergic asthma.
What type of illness is asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that makes it harder to move air in and out of your lungs.
How do you categorize asthma? Intermittent. Mild persistent.
You May Like: Nsaid Induced Asthma
Are There Racial Disparities Among Asthma Patients
Asthma, including severe, uncontrolled asthma, disproportionately affects Black, Hispanic and Indigenous Americans. Black Americans not only have higher rates of asthma, but also significantly worse outcomes, being five times more likely to seek emergency care for asthma than white Americans, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America6.
Outlook For People With Severe Asthma
Because severe asthma is so unpredictable in the treatments it responds to, and the course it takes, the long-term outlook is different for everyone, says Dr Andy.
There are lots of treatments around for people with severe asthma and your team of healthcare professionals will work with you to find the right ones for you so you can have the best quality of life possible in the long term.
Airway remodelling
One of the possible long-term effects of severe asthma is something called airway remodelling.
This is where your airways become thicker over time, so the airway itself is narrower, making it harder to breathe.
Airway remodelling can happen if people have frequent asthma attacks. If you have severe asthma, your risk increases because youll probably have asthma attacks more often. Long-term exposure to pollutants including tobacco smoke can play a part too.
Whatever the reason, if youre continually having lots of symptoms over a long period of time then theres a risk your airways will become permanently narrowed, scarred and inflamed, which can mean your symptoms get worse.
For most people, changes to the structure of your airways can be avoided with good asthma management.
Airway remodelling can be treated with bronchial thermoplasty, but this treatment is not recommended for everyone with severe asthma.
COPD and Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome
Long term severe asthma can sometimes lead to a chronic lung condition called COPD or ACO .
Don’t Miss: Can Allergies Cause Asthma Attacks
