Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
SYSTEMS PHYSIOLOGY EXAM 3 CASE STUDIES
Pacific Union College Preparator
Week 6_ Signature Assignment_ Case Study .pdf
West Coast University, Ontario
2 pages
Pacific Union College Preparator BIOL 348
SYSTEMS PHYSIOLOGY EXAM 3 CASE STUDIES
test_prep
Southwest Tennessee Community College NUR 330
4Respiratory Case Study
West Coast University, Ontario PATH 370
Week 6_ Signature Assignment_ Case Study .pdf
West Coast University PATHOPHYSI 261
Path week4
Shoreline Community College BIOL 242
AP3.doc
West Coast University PATHOPHYSI 261
casestudy week6
Asthma Symptoms In Children
- Coughing, especially at night
- A wheezing or whistling sound when breathing, especially when exhaling
- Trouble breathing or fast breathing that causes the skin around the ribs or neck to pull in tightly
- Frequent colds that settle in the chest
This page was reviewed for accuracy 4/17/2018.
How The Treatment Goals Are Attained
Unfortunately, there is no magic bullet for asthma. While treatment can control symptoms safely and effectively for most patients most of the time, it is not a simple matter of the doctor writing a prescription and the patient taking the medication. Successful treatment of asthma is likely to require several steps on the part of physician. These include:
- Confirmation of the diagnosis
- Characterization of the asthma with regard to:
- Chronicity
- Severity
- Identification of triggers
- Identification of the components of airway obstruction
The diagnosis of asthma is suspected when a patient has a history of recurrent or chronic shortness of breath, labored breathing, or cough in the absence of any other obvious reason. The diagnosis is confirmed by obtaining evidence that there is airway obstruction that reverses either spontaneously or as a result of treatment with anti-asthmatic measures. The procedures used to make the diagnosis include a careful history, measurement of pulmonary function , and therapeutic trials of medication.
Triggers of asthma, those identifiable factors that commonly worsen symptoms include:
- Viral respiratory infections ;
- Airborne allergens ;
- Inhaled irritants ;
- Cold air
- Exertion
Patients with an intermittent pattern of asthma require only intervention measures.
You May Like: How To Deal With Asthma Without Inhaler
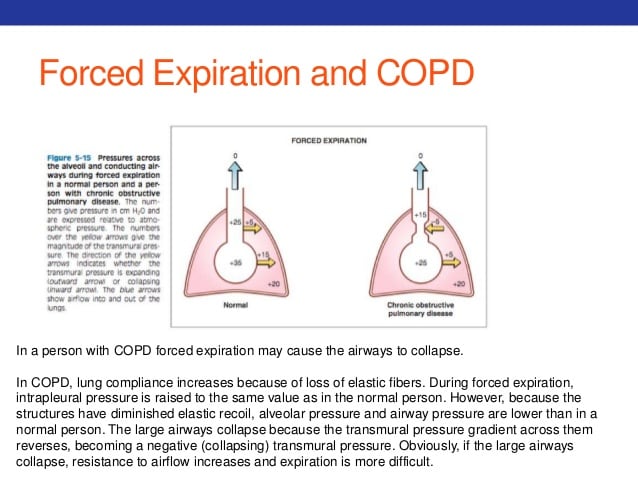
What Force Is Responsible For Normal Expiration
force responsible for normal expiration
People Also Asked, What forces are responsible for normal and forced expiration?
Considering this, what forces are responsible for normal and forced expiration?In forced expiration, when it is necessary to empty the lungs of more air than normal, the abdominal muscles contract and force the diaphragm upwards and contraction of the internal intercostal muscles actively pulls the ribs downwards.
Also know, what occurs during resting expiration?During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. As a result, the lungs contract and air is forced out.
Contents
Reactive Airways Dysfunction Syndrome And Irritant
-
Airway hyperreactivity
-
Airway remodeling
In patients with asthma, TH2 cells and other cell typesnotably, eosinophils and mast cells, but also other CD4+ subtypes and neutrophilsform an extensive inflammatory infiltrate in the airway epithelium and smooth muscle, leading to airway remodeling . Hypertrophy of smooth muscle narrows the airways and increases reactivity to allergens, infections, irritants, parasympathetic stimulation , and other triggers of bronchoconstriction.
Additional contributors to airway hyperreactivity include loss of inhibitors of bronchoconstriction and loss of other substances called endopeptidases that metabolize endogenous bronchoconstrictors. Mucus plugging and peripheral blood eosinophilia are additional classic findings in asthma and may be epiphenomena of airway inflammation. However, not all patients with asthma have eosinophilia.
Also Check: What Does A Nebulizer Do For Asthma
Inspiratory Vs Expiratory Wheezing
There are two main types of wheezing inspiratory and expiratory .
Its easier to hear expiratory wheezing because your airways narrow more during this breathing phase. Sometimes, expiratory wheezing is loud enough to hear on its own. Expiratory wheezing alone often indicates a mild airway obstruction.
Inspiratory wheezing occurs when you inhale. In some people with asthma, you can only hear wheezing during the inspiratory phase.
If youre wheezing when you exhale and inhale, you could have a more severe breathing issue. To diagnose what type of wheezing you have, your doctor will use a stethoscope to hear if its loudest over your lungs or neck.
Inspiratory wheezing often accompanies expiratory wheezing when heard over the lungs, specifically in acute asthma. However, if inspiratory wheezing or stridor is heard over the neck, that could be an indication of a serious upper airway obstruction.
What Does Control Of Asthma Mean
- The ability to deal with acute exacerbations of asthma so that the need for urgent medical care is prevented
- Prevention of hospitalization for asthma
- Tolerating all normal activities up to and including competitive athletics if otherwise able
- The avoidance of symptoms that interfere with sleep.
- Normal pulmonary physiology .
- These goals should be reached safely and with the least interference with a normal life-style. The risks and bother of the treatment must be carefully weighed against the risk and bother of the asthma. The benefit obtained from the treatment must be worth any inconvenience and potential medication risks imposed by the treatment.
In other words, it is the goal of treatment to determine the simplest, safest therapeutic measures that minimize disability, normalize lung function, avoid the need for acute medical care of asthma, and permit a normal life.
Recommended Reading: How To Take Care Of Asthma Without An Inhaler
How Is Ventilation Controlled
4.4/5ventilationcontrolled
Ventilation Control CentersNeurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group .
Furthermore, how is the breathing rate controlled? The parasympathetic nervous system tells the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to tighten and relax more quickly or more slowly to adjust your breathing rate in response to carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the brain. This system also causes your bronchial tubes to narrow and the pulmonary blood vessels to widen.
In this manner, what does pulmonary ventilation mean and how it is controlled?
Pulmonary ventilationIt is the process of air flowing into the lungs during inspiration and out of the lungs during expiration . Air flows because of pressure differences between the atmosphere and the gases inside the lungs.
What affects pulmonary ventilation?
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation: Surface Tension of Alveolar Fluid. The surface tension of alveolar fluid is regulated by pulmonary surfactant, allowing efficient respiration.
Other Ethnic Groups And Other Factors
The size of the lungs relative to body size varies with age . It also varies with ethnic group . Some of the variability is due to ethnic differences in trunk length relative to standing height. This factor provides part of the explanation for black people having smaller lungs with lower values for FEV1 and FVC compared with white people. But trunk length does not account for all of the difference, nor does it explain why many Asian Indian, Polynesian and Mongoloid people also have relatively small lungs; differences in fat free mass, chest dimensions and the pressure that can be generated by respiratory muscles may all contribute, whilst ethnic differences in alveolar size or airway dimensions are less likely. The differences can be allowed for by taking ethnic group into account. Either reference values for the appropriate ethnic group can be consulted or a correction factor can be applied to the corresponding reference values for white people. Some correction factors in current use are given in .
Difficulty can arise on account of:
1. Differences in methodology; not all studies meet present day criteria.
2. Migration. This does not of itself affect the lung function, so the reference values need not be based on information in the country of residence.
You May Like: Help Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
What Can Be Done About It
Asthma can be controlled. Moreover, it can be controlled by those who have asthma. The role of the physician is to provide the means for the patient to control asthma and to teach the patient to use provided measures .
Since asthma varies greatly in pattern of symptoms and severity, the treatment plan needs to be individualized. This should be done in a systematic manner. Goals of therapy must be realistically attainable and explicitly defined for you. The plan for attaining the treatment goals must be understood. Once the measures needed for control of asthma are identified, they can be placed in the hands of the patient with appropriate instructions for usage. Parental supervision is needed for young children, but progressive responsibility for self-management is given with advancing maturity.
Treatment may consist of medication, environmental changes, and life-style changes. The more the patient understands the disease and its treatment, the better the outcome is likely to be. The patient should therefore be an active partner in making decisions about treatment. Be wary, however, of superstitions and misinformation regarding asthma. More than almost any other medical problem, asthma is associated with a wide diversity of medical and nonmedical opinion. Both the physician and the patient therefore need to exercise judgment. Four common sense measures to remember are:
When To See A Doctor
If a person is wheezing for an unknown reason or thinks that they might have asthma or COPD, they should see a doctor.
Anyone who notices signs of pneumonia, has difficulty breathing, or sees that their skin has turned blue should seek emergency help.
People should also seek emergency medical attention if they are having an asthma attack or have started wheezing after:
- getting an insect sting or bite
- taking medication
- having an allergic reaction
If people have had an anaphylactic reaction, they should seek emergency help immediately, even if they have taken an epinephrine injection and are feeling better.
Anyone with long-lasting or repeat bronchitis infections should see their doctor for treatment.
Read Also: Army Asthma Waiver
Is All Asthma The Same
Asthma is quite variable. Symptoms can range from trivial and infrequent in some to severe, unrelenting, and dangerous in others. Even when severe, however, the airway obstruction is usually fully reversible, either spontaneously or as a result of treatment. This means that symptoms can be relieved, airway obstruction can be reversed, and pulmonary function can be made normal.
There are different patterns of asthma. Some people have only an intermittent pattern of disease. They have self-limited episodes of varying severity followed by extended symptom-free periods. The individual episodes are frequently triggered by viral respiratory infections . This is particularly common in young children in whom viral respiratory infections are frequent . Others have these intermittent symptomatic periods brought on by vigorous exertion, cold air, or specific environmental exposures. This pattern is intermittent asthma.
More prolonged periods of symptoms occur in people who have asthma from seasonal outdoor inhalant allergens. This may be from grass pollen on the West Coast or mold spores from molds that grow on decaying vegetation in the Midwest. Through a knowledge of the aerobiology in your area and allergy skin testing, your physician can attempt to identify whether the symptoms fit into this pattern of disease. This pattern is seasonal allergic asthma.
How Do Your Airways Work When You Have Asthma
When you have asthma, your airways aren’t able to function as well as they should.
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
Asthma causes inflammation, or swelling, in the lungs. It can also cause squeezing, called bronchoconstriction , and extra sensitive or twitchy airways.
When something bothers your airways, you have trouble breathing. This is;called an asthma attack or episode.;It gets harder to breathe because the tiny muscles around your airways squeeze tightly and they have swelling inside.
Your airways will make more mucus inside your airways, which makes it even harder to breathe. These changes in your airways can cause coughing and wheezing.
There is no cure for asthma. But you can take steps to manage it. If you have asthma, it’s important to see an asthma specialist, like an allergist or pulmonologist, to come up with the right asthma treatment plan. Medicines and avoiding asthma triggers can help reduce swelling and relax tight muscles in your airways.
ASTHMA Care for Adults
Don’t Miss: Eosinophilic Asthma Blood Test
Ems Assessment And Treatment Of Asthma: 5 Things To Know
December 7th, 2015CapnoAcademyArticles, Columnists, Learn
EMS1.com Columnists
Asthma, a leading cause of respiratory compromise, can be assessed with capnography and effectively treated with BLS and ALS medications
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects 24 million people in the United States and causes 5,000 to 6,000 deaths each year . Prompt recognition and treatment of asthma, a leading cause of respiratory compromise, by EMS providers can quickly relieve symptoms and improve patient outcomes. Here are five things you should know about caring for patients with asthma:
What Happens To Alveoli During Inspiration
During inspirationalveolialveolarinspirationalveolarDuringoccurs
During forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume. During forced expiration, accessory muscles of the abdomen, including the obliques, contract, forcing abdominal organs upward against the diaphragm.
One may also ask, which pressure actually keeps the lungs from collapsing? But two factors prevent the lungs from collapsing: surfactant and the intrapleural pressure. Surfactant is a surface-active lipoprotein complex formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that comprise surfactant have both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region.
Then, how does lung volume control inspiration?
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward while the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. As a result, the lungs contract and air is forced out.
Why do alveoli collapse?
Without normal surfactant, the tissue surrounding the air sacs in the lungs sticks together after exhalation, causing the alveoli to collapse.
Read Also: What To Do If Someone Is Having An Asthma Attack
Treating Inspiratory And Expiratory Wheezing
Treating wheezing ultimately depends on the underlying cause. If your wheezing is severe, your doctors may give you an oxygen mask to steady your breathing and bronchodilators to help open your airways. In this case, they may recommend you stay at the hospital overnight.
If inflammation is causing your wheezing, your doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory medications like steroids to reduce swelling and open your airways for easier breathing.
If your wheezing is caused by an infection, you may be prescribed antibiotics to treat the condition and associated symptoms.
If youre diagnosed with asthma, your doctor will prescribe you medication, usually an inhaler.
Does Asthma Cause Permanent Damage
The airway obstruction of asthma is generally completely reversible and usually does not cause permanent damage to the lungs, heart, or other organs. However, severe acute episodes of asthma can be associated with life threatening events and even fatalities. Survival of severe life threatening events can be associated with damage from lack of oxygen during the severe exacerbation, and lack of oxygen to the brain can cause loss of consciousness and brain damage.
Chronic asthma with ongoing airway inflammation may also be associated with what is called “remodeling” of the airways. This describes permanent changes occurring in the tissues surrounding the airways that results in permanent narrowing of airways. The potential for this emphasizes the importance of monitoring pulmonary function in patients with asthma at regular intervals, particularly those with a chronic pattern of asthma.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Asthma Attacks
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a global health problem that affects millions of people and is an important cause of morbidity, mortality, and extensive utilization of health care resources. COPD is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide, and the direct costs of treating COPD in the United States alone are estimated to be around $30 billion per year. COPD actually represents a spectrum of disease ranging from destruction of the alveoli and thickening of the terminal airways on one extreme to thickening of the airways with chronic inflammation and repeated bouts of infection on the other extreme. Most frequently there are elements of both of these clinical pictures.
The likelihood of COPD is heavily influenced by both environmental/behavior risk factors and by hereditary factors. In most cases, COPD is caused by chronic inhalation of harmful particles and gases , which triggers pathophysiologic changes in the small airways, in the alveoli, and in blood vessels in the lung. All smokers have inflammation in their lungs and airways, and they all have thickening of the airways, damage to ciliated cells, and hypersecretion of mucus. Immune fun
In addition, the normal processes for breakdown and repair of cellular elements and immune defense are impaired. These abnormalities produce a spectrum of largely irreversible changes ranging from mucous hypersecretion , to chronic small airway inflammation and fibrosis , and outright tissue destruction and impaired airflow .
How Does Lung Volume Control Inspiration
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward while the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. As a result, the lungs contract and air is forced out.
You may ask, Why do alveoli collapse?
Without normal surfactant, the tissue surrounding the air sacs in the lungs sticks together after exhalation, causing the alveoli to collapse.
Read Also: Can You Join The Coast Guard With Asthma
Why Is Expiration Difficult In Asthma
5/5asthmaasthma
When something bothers your airways, you have trouble breathing. This is called an asthma attack or episode. It gets harder to breathe because the tiny muscles around your airways squeeze tightly and they have swelling inside. Your airways will make more mucus inside your airways, which makes it even harder to breathe.
Subsequently, question is, how Does asthma affect your breathing? How Asthma Affects Breathing. In people with asthma, the airways are inflamed and produce lots of thick mucus. Inflamed airways are also very sensitive, and things like dust or smoke can make the muscles around them tighten up. All these things can narrow the airways and make it harder for a person to breathe
Also asked, how do you stop shortness of breath with asthma?
To try this breathing style:
Do asthma attacks cause permanent damage?
Asthma can cause permanent damage to your lungs if not treated early and well. But experts say that if you have persistent asthma and you’re only treating it during attacks, you’re not controlling it at all.
