People With Eosinophilic Asthma Are Prone To Sinus Infections Nasal Polyps And Ear Infections
Eosinophilic asthma causes swelling along the entire respiratory tract from the sinuses to the lower airways, obstructing airflow and increasing mucus production. This can lead to chronic sinus and ear infections. Patients may report stuffy or runny nose, drainage from the ears, and decreased sense of smell and hearing. Nasal polyps, which are small, painless tear-drop shaped skin growths, are often present.
What Is Different About Eosinophilic Asthma
Everyone has eosinophils . Theyre white blood cells, a normal part of your immune system. But for some people, too many can cause airway inflammation and lead to asthma attacks.
Nearly 7 out of 10 adults with asthma may have elevated eosinophils.* Elevated eosinophils may indicate eosinophilic asthma.
*While not well defined for severe asthma, elevated blood eosinophils were considered 150 cells/µL or more in this analysis of registry data.
Eosinophilic Asthma: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Healthcare professionals have typically thought of asthma as a single condition. But medical science reveals there is more to the narrative.
Asthma is now known as a collection of conditions with differences in age of onset, symptoms, and treatment strategies. Among these conditions is eosinophilic asthma.
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the lung’s airways. It often results from allergic triggers such as dust mites, pet dander, etc. But when a person has eosinophilic asthma, the inflammation in the respiratory system is caused by eosinophils.
These are types of white blood cells that help fight disease but may also cause swelling. Therefore, you may suffer eosinophilic asthma even if you don’t have a history of allergies or allergic conditions such as eczema, food allergy, hay fever, etc.
Have you considered clinical trials for Asthma?
We make it easy for you to participate in a clinical trial for Asthma, and get access to the latest treatments not yet widely available – and be a part of finding a cure.
Also Check: How Can We Prevent Asthma
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Recovery from eosinophilic pneumonia depends on the type and severity. Many people with acute eosinophilic pneumonia recover quickly, sometimes within 48 hours after steroid treatment. Most people take one to two weeks to fully heal.
If you have chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, youll likely receive an oral steroid that you take for an extended period for months or even years. You’ll also receive treatment for any underlying conditions like asthma.
How Do Eosinophils Impact Asthma

Eosinophils can become active due to common asthma triggers. As a result, activated eosinophils can cause inflammation in the lungs. This inflammation may lead to increased asthma symptoms and asthma attacks.
Identifying your asthma as uncontrolled may be one of the first steps.
The following may be signs of uncontrolled asthma driven by eosinophils:
Waking up at night more than twice a month due to asthma
You often use a rescue inhaler to control your asthma symptoms
Often need oral steroids like prednisone for your asthma
Also Check: Does Singulair Help With Asthma
How Are Eosinophilic Lung Conditions Diagnosed In Children
Your child will need to have tests to diagnose an eosinophilic lung condition. These may include:
- blood tests to find out how many eosinophils are in the blood
- lung biopsy – this may be needed if the other tests do not give a definite diagnosis. A sample of tissue is taken from the lungs, and the eosinophils are counted
- chest X-ray or CT scan – damage because of eosinophils can show up as shadows on the lung
- bronchoalveolar lavage – a tube called a bronchoscope is inserted into the airways and saline solution is passed through this tube to wash out the cells. This fluid is collected, and the tubing is removed. The cells in the fluid are then looked at and counted under a microscope.
What Do Doctors Know About It
Eosinophilic asthma is a rare type of asthma. Itâs often severe and usually comes on in adults. The main treatment for asthma — drugs called inhaled corticosteroids — donât have much of an effect on it, even in high doses. That means it’s harder to manage and youâre more likely to have asthma attacks. Usually, you need to take corticosteroid pills, which can have more side effects than an inhaler. Several biologics are approved to reduce the frequency of eosinophilic asthma attacks. These include:
Your respiratory system is your bodyâs system for breathing. It goes from your nose and mouth down to the tiniest airways in your lungs. When you have eosinophilic asthma, you have inflammation in your respiratory system caused by cells called eosinophils.
Eosinophils are white blood cells. Theyâre part of your bodyâs immune system, and normally, they help you fight disease. One of their jobs is to help cause swelling. That may sound odd, but swelling is one of your bodyâs key tools in fighting germs. But too much swelling can cause problems.
Read Also: What Happens If You Have Asthma And Smoke Weed
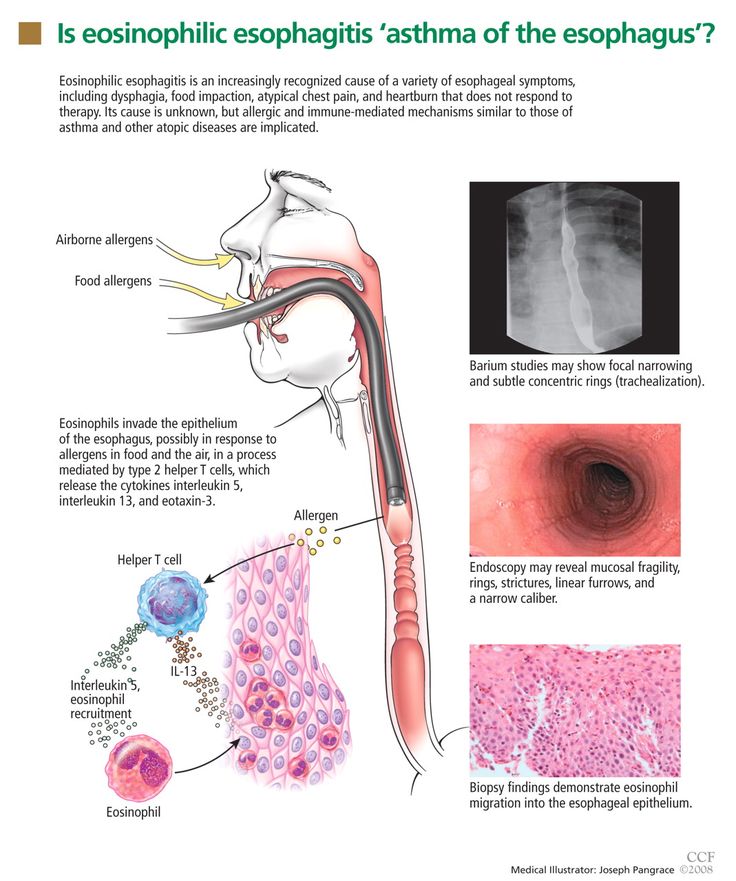
How Is Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnosed
If someone has symptoms like trouble swallowing or eating, belly pain, or heartburn, a gastroenterologist will do tests, which can include:
- an endoscopy. The doctor puts a thin tube with a light and camera down the throat and into the esophagus, then takes a biopsy .
- blood tests to check for a high eosinophil level
- skin testing and/or blood testing for allergies
When Eosinophilic Asthma Gets In The Way Of Daily Life
Sometimes people with eosinophilic asthma have this misconception that they are just getting old, Parikh says. They think theyre out of shape, and its actually dangerous because they downplay their symptoms. Nobody wants to be labelled with a chronic disease, so theyll say its not that bad, and then we find out their symptoms are really limiting their life.
In terms of lung function, experts still dont know what the decline for people with this type of asthma will be over time, says Peters. Its been presumed that happens, he says, and that may be the case but it actually has never been shown or proven.
If your asthma symptoms are severe or persistent, or in any way feel out of control to you, be sure to contact your doctor. New medications, such as biologics that target eosinophils directly, may be able to make a big difference in how you feel and function, according to the APED.
Recommended Reading: A National Survey Of Asthma Conducted On May 1 2012
What Causes Eosinophilic Lung Conditions
Occasionally the body produces too many eosinophils, particularly in the lungs. These eosinophils release harmful chemicals and proteins that can damage the tissues in the lungs. The air sacs in the lungs then become inflamed and can stop oxygen from getting into the bloodstream.
Its not always possible to work out the cause of an eosinophilic lung condition. But causes can include:
- an allergic reaction, especially to a specific type of mould called aspergillus read more about how to stop mould like aspergillus growing in your home
- a reaction to drugs, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin, ibuprofen or antibiotics
- a parasite infection, this is not a common cause in the UK where parasite infections are rare.
Eosinophilic Asthma Life Expectancy And Prognosis
People who have asthma may experience a decline in lung function faster than people who do not have asthma. This is particularly true for people who smoke and those who have asthma that is not well managed.
Death from asthma is rare, especially if a person is receiving proper treatment. Most deaths from asthma are preventable.
Asthma can be debilitating and asthma-related episodes can be frightening. Uncontrolled asthma may interfere with daily activities, such as school and work.
Many patients with eos asthma are able to manage their symptoms with inhaled or oral steroids. However, some patients experience persistent asthma attacks that are relatively resistant to typical treatments. New and emerging biologictreatments that target eosinophils may help these patients control their asthma.
As with other subsets of asthma, patients who have eos asthma should receive ongoing medical care to maintain their health.
You May Like: Where Does Asthma Occur In The Lungs
Difficult To Treat Asthma
People whose asthma remains uncontrolled despite using high dose controller medicines are described as having difficult to treat asthma. Factors that may make an asthma patient more difficult to treat are having another chronic health condition, incorrect inhaler technique, and/or inconsistent use of prescription medicine.
How Do You Treat Eosinophilic Asthma

Your doctor may do several tests to confirm your type of asthma. This may include checking your mucus or saliva for eosinophils, checking your blood eosinophil count, or doing a test that checks your breath for a nitric oxide gas. Your doctor will also ask you about your current and past symptoms, as well as any current and/or history of allergies If your doctor diagnoses you with e-asthma, understanding this unique type of asthma is important to help you manage symptoms and have better quality of life.
Current management of e-asthma begins with standard guideline-based therapy. For example, most people with asthma are prescribed two medicines:
- A controller medicine that treats airway swelling usually an inhaled corticosteroid
- A quick-relief medicine to help relieve symptoms when they occur by relaxing bronchospasms when muscles tighten and squeeze around the airways
Depending on how often and how severe your symptoms are, you may take these medicines every day or as needed. Your health care provider should develop a clear, written, and understandable action plan for effective management of asthma symptoms.
Biologics target specific cells to block swelling and reduce symptoms. You get these therapies as a shot or by IV every few weeks or two months, depending on the treatment.
Current biologic options for e-asthma include:
- Tezepelumab-ekko
Read Also: Why Do Adults Get Asthma
Who Is Affected By Eosinophilic Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma usually affects adults aged 35 to 50, even if they have previously been asthma and allergy-free. It may also present in older adults and pediatric cases. This subset of asthma affects men and women at about the same rate.
Although the exact prevalence is unknown, some studies² show that it affects about 5% of adults with asthma. Other studies³ suggest that severe eosinophilic asthma could have a higher prevalence than experts have previously known.
What Is Eosinophilic Asthma And What Makes It Different
For many people living with asthma, identifying triggers and getting the right treatment can make managing their condition easier on a day-to-day basis. But for people with eosinophilic asthma, symptoms and onset can be more unusual and harder to treat – and that in turn may make diagnosis and management more difficult.
Reviewed byDr Colin Tidy
12-Jul-22·6 mins read
AstraZeneca, creators of www.giveyourlungsavoice.co.uk provided input into the article content and reviewed for medical accuracy and compliance with industry codes of practice.GB-36411 DOP 06.2022
Asthma is a common condition which affects the airways. Many of us can identify the hallmark signs of asthma: wheezing, breathlessness, coughing and chest tightness, to name a few. These symptoms may be triggered by any number of factors including exercise, allergy and air quality.
Getting to know triggers, if any, is essential to prevent symptoms from happening in the first place and to get on the right treatment regime.
Read Also: Atlanta Asthma And Allergy Clinic
How Are Eosinophilic Lung Conditions Treated
If your child is having difficulty breathing, they may need:
- steroid medicines to reduce the inflammation in their lungs. This is usually very effective, and the dosage can be lowered as the condition improves
- non-steroidal medicines to improve the outlook and avoid steroid side effects
- oxygen therapy to help their breathing
- full intensive care support in hospital if the condition is life-threatening. This may be needed until the steroid treatment starts to work.
Treating the underlying cause of the eosinophilic lung condition is important. For example, if a parasite is causing the body to produce too many eosinophils, your child will be given anti-parasitic medicines.
A Personalized Treatment Plan May Include:
Macrolide antibiotics are used to help the body fight infection. These medicines control the number of white blood cells found in your airways. One study showed positive results using macrolide antibiotics in people with high counts of neutrophils in blood or sputum samples. Doctors dont suggest these medications be used long term though because side effects, such as antibiotic resistance, can be very serious.
Oral corticosteroids are medicines that help to control inflammation. While experts recommend these medicines only for short-term use, doctors may prescribe them long-term for people with more frequent asthma flare-ups. Severe asthma patients use these medications in combination with quick-relief medicine, high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators. Side effects from using oral corticosteroids can pose a risk to the function of other bodily organs, but the benefits may at times outweigh the risk. The hope is that by using these powerful drugs for a short period of time, patients can gain better control and will eventually not need them at all. This treatment option is approved for adults and children, although long-term use in children is not recommended due to the higher risk side effects. If symptoms are still not controlled with long-term use of an oral corticosteroid, another treatment option should be considered.
|
Type of severe asthma |
You May Like: Worst Dogs For Allergies And Asthma
What Are Eosinophils
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that plays two roles in the immune system: they destroy foreign substances and regulate inflammation. If too many eosinophils congregate in certain tissues, it can cause a host of inflammatory-based conditions, such as asthma, eczema, Crohns disease and certain types of cancer.3
With eosinophilic asthma, the number of eosinophils overpopulates the blood, lung tissue, and mucus in the respiratory tract. This causes the airways to swell and become narrow, making it hard to breathe. Research has shown that higher levels of eosinophils in the blood is linked to severe asthma attacks in the future.
How Is It Diagnosed
If youve been diagnosed with asthma but dont seem to respond well to treatment, your doctor may suspect you have a less common subtype of asthma. Theyll likely evaluate your condition and look for additional signs or symptoms that can direct them toward a diagnosis.
In the case of EA, the easiest step is to check your levels of white blood cells. For this, your doctor will collect blood, sputum, or saliva and send it to a lab. High levels of eosinophils can affirm your doctors suspected diagnosis.
In addition to the blood test, however, your doctor may conduct a physical exam. Certain physical symptoms, such as nasal polyps, can confirm the suspected diagnosis. The combination of the blood test and the physical exam may be enough for your doctor to diagnose you.
1 in 12 people has asthma. As doctors now recognize that asthma is more than one condition, they realize that the subtypes need specific treatments. Individual treatments for each subtype can help you achieve the best outcome for the condition.
Traditional asthma treatment involves inhaled corticosteroids and a rescue inhaler. However, people with EA dont always respond well to inhaled corticosteroids. Higher doses may lose their impact too, requiring a switch to an entirely new treatment.
The most common treatments for EA include the following.
Read Also: Does My Kid Have Asthma
How Is Eosinophilic Esophagitis Treated
Doctors usually treat eosinophilic esophagitis with:
- medicines that lower the amount of acid or inflammation in the esophagus
- dietary changes such as:
- avoiding foods that are common causes of allergy or inflammation
- avoiding foods that allergy testing showed a reaction to
- trying a special liquid diet that has no allergens in it
Working with a dietitian can help make sure a child gets the nutrients needed to grow and thrive.
To treat a stricture, doctors can do a procedure called dilation to widen the esophagus. This is done during an endoscopy.
Diagnostic Evaluation Of Eosinophilic Asthma
Traditional guideline-based treatment decisions in asthma target symptoms and lung function, but specific therapies targeting the underlying inflammatory process may be needed in a subset of patients. Sputum eosinophils are an accurate reflection of Th2-dominant mechanisms in uncontrolled asthma, and eosinophilic asthma is generally defined by > 1%3% of eosinophils. Induced sputum is the most reliable measure of inflammatory cell counts although quantitative sputum cell counts are difficult to obtain in routine practice and require access to specific laboratories with trained personnel. The utility of several alternative markers of eosinophilic inflammation are currently being investigated including peripheral blood eosinophil counts, fractional exhaled nitric oxide , serum IgE, and periostin levels.
Recommended Reading: How Many Kids In The Us Have Asthma
Diagnosis: What Does A Patient With Sea Look Like
Early identification of patients with SEA in clinical practice is important however, identifying these patients in day-to-day practice is not always straightforward . A key initial step, as described by the European Respiratory Society /American Thoracic Society severe asthma guidelines, is to confirm the diagnosis of asthma and address comorbidities. Secondly, adherence to therapy and inhaler technique must be assessed before a diagnosis of severe uncontrolled asthma refractory to treatment can be confirmed . This phenotype has been variously described in the literature and cluster analysis suggests a phenotype of patients with late-onset, eosinophilic, inflammation-predominant asthma .
Adult-onset asthma patients with a high blood eosinophil count have been found to have a distinct phenotype of severe asthma with frequent exacerbations and poor prognosis . Persistent airflow limitation and distal inflammation with air trapping are common in these patients, as is upper airway pathology such as chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis . The characteristics described in these and other studies are not ubiquitous in all patients . As such, classification using a set of major and minor diagnostic criteria may help to identify this pattern .
Possible diagnostic scheme for severe eosinophilic asthma
