How Can Diet Affect Samters Triad
Drinking alcohol can affect those with AERD. Some people, for example, have been found to experience reactions when they consume alcohol such as red wine or beer, and so reducing alcohol consumption could be beneficial.
Immunologist Max Samter originally thought that AERD symptoms might be ongoing due to the consumption of salicylates in the diet. Some studies have explored the benefits of a low salicylate diet and found that it may improve nasal symptoms for those with AERD. However, the evidence is not conclusive and more research is needed to support this theory, especially as a low salicylate diet involves cutting out a lot of healthy and nutritious foods, such as fruits and vegetables, which is restrictive and not ideal for your general health.
Instead, some experts suggest that a diet low in omega-6 fatty acids and high in omega-3 fatty acids may be more appropriate for AERD. Research into the benefits of decreasing consumption of omega-6 fatty acids has seen positive results. As people with AERD often have high levels of cysteinyl leukotrienes and prostaglandin D2 , which are derived from the metabolism of omega-6 fatty acids, decreasing these acids can be helpful. Study results showed that this reduction has improved sinus symptoms and asthma control. However, you should always consult a doctor before changing your diet they can offer the best advice and approach on how to do so and recommend if its a good idea for you.
Management Of A Patient With Aspirin Triad
Management of asthma and rhinosinusitis in an NSAIDs-hypersensitive patient is similar to treatment of other forms of asthma and rhinosinusitis. However, there are several important additional treatment modalities to be considered when N-ERD is diagnosed3.
Avoidance of NSAIDs and use of alternative analgesics
Patient education and careful avoidance of ASA and other NSAIDs which are strong COX-1 inhibitors is important because COX-1 inhibitors can cause severe asthma leading to hospitalization in an intensive care unit and even intubation. Therefore, ideally, the aspirin-hypersensitivity should be confirmed by a challenge test.
In general three groups of NSAIDs can be distinguished based on their capacity to induce hypersensitivity reactions in N-ERD patients24, Table 1.
Alternative antipyretic or analgesic drugs, such as acetaminophen are preferred. Preferential COX-2 inhibitors, such as nimesulide and meloxicam, are tolerated by most, but not all, NSAIDs-intolerant subjects. Selective preferential COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib or valdecoxib, are tolerated by almost all aspirin-intolerant subjects. However, oral challenge in the office is recommended to ensure that patients are able to tolerate COX-2 inhibitors.
Mangement of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis
Management of asthma
Desensitization toaspirin and Aspirin Treatment after Desensitization
Can Asthma Be Prevented
While theres no way to prevent asthma completely, you and your healthcare practitioner can design a detailed plan for reducing the severity and frequency of your attacks. Lets take a look at some of the top things you can do to prevent future asthma attacks:
- Follow your treatment plan. Asthma is a chronic condition that requires consistent monitoring and treatment. Just because youre asymptomatic one day doesnt mean you can forgo your treatment plan.
- Get vaccinated for the flu and pneumonia. Staying up-to-date with vaccinations can reduce the chances of asthma flares caused by respiratory illnesses.
- Identify and avoid your triggers. Keep a journal to determine what causes or worsens your symptoms and take steps to avoid those triggers.
- Identify and treat attacks early. If you act at the first sign of an attack, your symptoms are less likely to become severe.
- Manage stress. Because stress is a common trigger of asthma symptoms, its important to learn how to manage it.
Recommended Reading: How Does Montelukast Differ From Other Asthma Medications
What Treatments Are Available
There is currently no cure for asthma. However, there are many treatment options, which fall into four primary categories:
- Quick-relief medications: These medications, called bronchodilators, work within minutes to relax the tightened muscles around your airway, rapidly decreasing symptoms. Bronchodilators are most commonly taken with an inhaler and can be used to treat sudden symptoms or before exercise to prevent a flare-up.
- Long-term control medications: These medications are taken daily to help reduce the number and severity of asthma symptoms. These medications include anti-inflammatories, anticholinergics, and long-acting bronchodilators. Its important to note that these medications dont manage the immediate symptoms of an attack.
- A combination of quick-relief and long-term control medications: Often, people with asthma use a combination of the above two treatment options.
- Biologics: Reserved for severe cases of asthma that dont respond to other medications, biologics work by targeting specific antibodies, disrupting the pathway that leads to inflammation of the airway.
The content and/or opinions voiced in this Triad Clinical Trials resources page are for general information only and are not intended to provide specific healthcare advice or recommendations for any individual.
Mechanisms Of Aspirin Desensitization
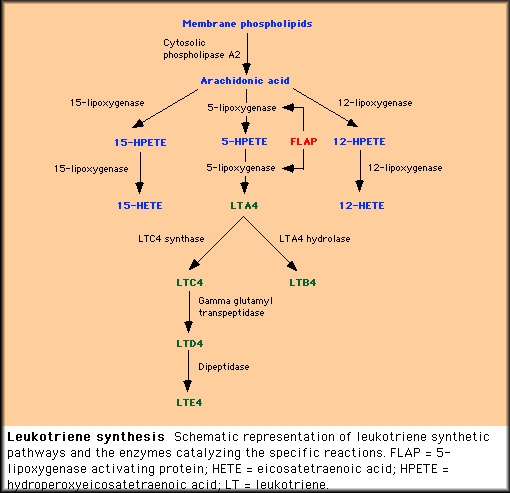
The pathophysiologic mechanisms of desensitization remain unclear. However, aspirin desensitization leads to decreased LT production, down-regulation of Cys-LTR, and decreased tryptase and histamine release acutely within 3 hours of exposition . After prolonged daily aspirin treatment, the number of nasal inflammatory cells expressing Cys-LTR1 was decreased . A reduction in urinary LTE4 excretion after 2 weeks and LTB4 synthesis in peripheral monocytes after desensitization has been shown in another study .
Direct modulation of intracellular biochemical pathways in key inflammatory cells was reported to another possible mechanism. Daily aspirin therapy inhibited IL-4- and IL-13-induced activation of STAT6 and activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-B . Another studies have shown that long-term aspirin desensitization involves IL-4 inhibition, downregulation of proinflammatory matrix metallopeptidase 9, an increase in the Th1 marker FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand, and a decrease in the IL-10 and interferon- expression of CD4 T lymphocytes .
Also Check: Does Asthma Qualify For 1b Covid Vaccine
Loss Of Smell In Patients With Aspirin
A common problem for AERD patients is loss of sense of smell, or anosmia, but its impact on patients quality of life, mental health, and physical wellbeing has been poorly studied. We developed a new questionnaire about the consequences of anosmia, which, along with several other quality-of-life questionnaires was sent to all our Registry patients. Eighty-five percent of the 853 patients who answered the questionnaires reported diminished sense of smell and/or taste, and we learned that their loss of smell severely impacts their physical, emotional, and mental health. Many patients with diminished smell responded that they could not identify spoiled food , did not enjoy food , felt unsafe , and had encountered dangerous situations because of their poor smell.We think that the importance of sense of smell and the relevance of anosmia to patients lives should be acknowledged and evaluated by clinicians caring for these patients. Read more here.
Type 2 Inflammation In Asthma
More specific to asthma, IL-13 has effects on goblet and airway smooth muscle cells, which impact mucus secretion, smooth muscle contractility and basement membrane thickening . Moreover, in asthma, along with the production of mucus, IL-13 facilitates airway obstruction by tethering to mucus-producing cells in the epithelium and impairing mucociliary transport, identified by the expression of the mucin 5AC protein, which is considered to be a marker of airway goblet cells and mucus hypersecretion , leading to the development of mucosal plugs. Nitric oxide production is also upregulated by IL-13 in asthma .
You May Like: Can You Die In Your Sleep From Asthma
Table : Indications For Treatment With Aspirin After Desensitization In N
Adapted from Kowalski ML, Agache I, Bavbek S, et al. Diagnosis and management of NSAID-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease -a EAACI position paper. Allergy. 2019 74:28-393.
|
Asthma Plus Three: Aspirin
Pharmacy Times
This potentially serious condition is only partially understood, and its triad of symptoms often goes unrecognized.
This potentially serious condition is only partially understood, and its triad of symptoms often goes unrecognized.
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease occurs in adults and is somewhat of a misnomer since aspirin sensitivity is not its only component, nor is aspirin the only aggravating analgesic. The Centers for Disease Control indicates that 8.2% of the US population has asthma, and up to 9% of adult asthmatics have this nonallergic hypersensitivity reaction. Patients experience 3 annoying and potentially life-threatening symptoms, dubbed the Samter triadsevere chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal polyposis , and aspirin sensitivity. Onset usually occurs between the ages of 30 and 40 years, although a small number of children develop this condition, and it is more common in women.1
Patients frequently report having had a never-ending cold, causing researchers to think that a viral infection may start the inflammatory cascade. AERD patients react to even small doses of aspirin and other COX-1 inhibiting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with nasal congestion and bronchospasm within 30 minutes to 3 hours. Of note, patients can and do react to NSAIDs on the first dose, unlike the situation when an allergy is present and reaction occurs only after a sensitizing dose.2 Most patients are allergy freeand within 2 years, they develop asthma.
Read Also: Does Medicare Cover Asthma Inhalers
The Symptoms You Feel In Asthma
As the airways narrow, breathing gets more challenging. There is less space for air to move in and out of the lungs, and breathing becomes difficult. Moving the air out of the lungs is especially stressful.4
Anytime something disturbs your airways, it can give you trouble with breathing. This is because the small muscles around the airways are squeezing tightly, and they are swelling inside. The excess mucus makes it hard to breathe. Besides having trouble breathing, a person with asthma experiences coughing and shortness of breath. You can feel as if something is tightening around your chest. You may make a whistling sound called wheezing as you inhale and exhale.4
Hows Samters Triad Treated
People with Samters Triad will need to take medications daily to control their symptoms. An inhaler is used to control asthma symptoms. Intranasal steroid sprays or steroid sinus rinses can be used to treat sinus inflammation. Nasal polyps can be treated with steroid injections.
Treatment for Samters Triad can also involve sinus surgery to remove the nasal polyps. But theres a high likelihood that the nasal polyps will reappear after surgery.
There are several other treatment approaches for Samters Triad:
Also Check: Can Asthma Cause A High Heart Rate
Asthma And Associated Type 2 Inflammatory Airway Diseases
Type 2 inflammatory airway diseases, such as asthma, CRSwNP, NSAID-ERD/AERD, eosinophilic COPD and allergic rhinitis often coexist in the same patient, and are driven by a similar underlying type 2 pathophysiology . The risk of asthma symptoms increases with increasing presence of CRSwNP along with the increased likelihood of poor asthma control . Likewise, the presence of a comorbid type 2 inflammatory disease increases the severity and clinical burden of CRSwNP, with disease severity being significantly greater in patients with CRSwNP and asthma versus those with CRSwNP alone . The presence of a comorbid type 2 inflammatory disease has also been associated with an increased risk of recurrence of nasal polyps post-surgery in patients with CRSwNP .
The coexistence of type 2 inflammatory diseases is associated with greater decline in lung function and clinical outcomes in patients with asthma. A 5-year study of patients with recently diagnosed adult-onset asthma showed that the presence of comorbid nasal polyps was significantly associated with a greater decline in post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1s per year . Moreover, comorbid disease has been shown to increase disease burden in patients whose asthma is driven by type 2 inflammation, with the presence of rhinitis, nasal polyps or atopic dermatitis as independent predictors for future asthma exacerbations .
Dupilumab As An Adjunct To Surgery In Patients With Aspirin
We report a series of eight patients with AERD who had experienced a rapid recurrence of nasal polyps after a prior endoscopic sinus surgery, and who subsequently went on to have a revision endoscopic sinus surgery with perioperative initiation of dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin 4Ra. We found that dupilumab led to no or slower nasal polyp recurrence after surgery compared to the prior sinus surgery, and perioperative initiation of dupilumab therapy also improved upper airway symptoms. This study provides evidence for the use of dupilumab as an adjunct to surgery to prevent polyp regrowth for patients with AERD and insufficient response to standard-of-care therapies. Read more here.
Read Also: How To Run With Asthma In Cold Weather
Table : Nsaids Tolerance In Patients With Cross
Adapted from Kowalski ML, Makowska JS, Blanca M et al.. Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – classification, diagnosis and management: review of the EAACI/ENDA and GA2LEN/HANNA*. Allergy. 2011 66:818-2924.
|
Group A: NSAIDs cross-reacting in majority of hypersensitive patients |
|
Diclofenac, Fenoprofen, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Meclofenamate Nabumetone, Flurbiprofen, Indomethacin, Ketorolac, Mefenamic acid, Naproxen |
|
Group B: NSAIDs cross-reacting in minority of hypersensitive patients |
|
Rhinitis/asthma type |
|
new selective COX-2 inhibitors *Single cases of hypersensitivity have been reported |
Why Come To Michigan For Triad Asthma Treatment
- We treat more than 200 patients with this condition every year.
- We take a multidisciplinary, step-by-step approach that takes you as a whole person into account.
- Our aspirin desensitization treatment program provides relief for more than 70% of patients involved in treatment.
- If you need us for surgery, trust the experts who perform more than 500 surgeries every year. And, when it comes to surgery, experience counts.
Also Check: What To Do When You Have Asthma But No Inhaler
Control Of Triggering Factors
Triggering factors in some patients may be controlled with use of synthetic fiber pillows and impermeable mattress covers and frequent washing of bed sheets, pillowcases, and blankets in hot water. Ideally, upholstered furniture, soft toys, carpets, curtains, and pets should be removed, at least from the bedroom, to reduce dust mites and animal dander. Dehumidifiers should be used in basements and in other poorly aerated, damp rooms to reduce mold. Steam treatment of homes diminishes dust mite allergens. House cleaning and extermination to eliminate cockroach exposure are especially important. Although control of triggering factors is more difficult in urban environments, the importance of these measures is not diminished.
High-efficiency particulate air vacuums and filters may relieve symptoms, but no beneficial effects on pulmonary function and on the need for drugs have been observed.
Sulfite-sensitive patients should avoid sulfite-containing food .
Patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma can use acetaminophen, choline magnesium salicylate, or highly selective NSAIDs like celecoxib when they need a pain reliever.
Asthma is a relative contraindication to the use of nonselective beta-blockers , including topical formulations, but cardioselective drugs probably have no adverse effects.
Biomarkers For Type 2 Inflammation
The heterogeneous nature of asthma and its comorbidities requires identification of biomarkers and timely introduction of early and effective personalised medicine for those not being adequately managed by ICS and LABA alone. Inflammatory cytokines and their receptors, among others, are important targets for treating type 2 asthma, since they promote an increase in inflammation. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide , thymus and activation-regulated chemokine , eotaxin, periostin, IgE and blood eosinophil counts have all emerged as predominant biomarkers for type 2 inflammatory airway diseases, providing opportunities for better disease targeting, improving patients health-related QoL, and reducing direct and indirect cost burdens associated with ineffective management of asthma in the long term. FeNO and blood eosinophil count are produced through the action of cytokine mediators . Chemotactic biomarkers of type 2 inflammation include eotaxin-3 and TARC, which are chemoattractants stimulated by IL-4 and IL-13 however, no single biomarker pathway is solely responsible for type 2 inflammation in airway diseases.
Read Also: How Long Does Viral Induced Asthma Last
Is Samters Triad Autoimmune
While research into AERD is ongoing, it is currently not regarded as an autoimmune condition. With autoimmune diseases, antibodies attack the tissues in the body this is not believed to occur with Samters Triad.
Instead, Samters Triad is regarded as being a disease based on chronic immune dysregulation.
Studies have shown that people who have AERD often have high levels of eosinophils in their nasal polyps and high levels of eosinophils in their blood. Eosinophils are immune cells that are connected to inflammation and could lead to chronic inflammation in the airways.
Its also been found that people with AERD have impaired cyclooxygenase enzyme pathways and produce high levels of leukotrienes or inflammatory molecules. Levels of leukotrienes increase further when aspirin is taken, suggesting AERD has an element of inflammatory disease.
Treatment Of Acute Asthma Exacerbation
The goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function. Treatment includes
-
Inhaled bronchodilators
-
Usually systemic corticosteroids
Details of the treatment of acute asthma exacerbations Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations The goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function. Treatment includes Inhaled bronchodilators … read more , including of severe attacks requiring hospitalization Hospitalization The goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function. Treatment includes Inhaled bronchodilators … read more , are discussed elsewhere.
Recommended Reading: Is Ginger Good For Asthma
What Causes Samters Triad
Theres no clear cause of Samters Triad. According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, about 9 percent of adults with asthma and 30 percent of adults with both asthma and nasal polyps also have Samters Triad.
The condition develops in adulthood, typically in people between 20 and 50 years old. The average age of onset is 34 years of age.
Is A Cannabinoid Nasal Wash The Answer Using Biomarkers To Detect Respiratory Disease
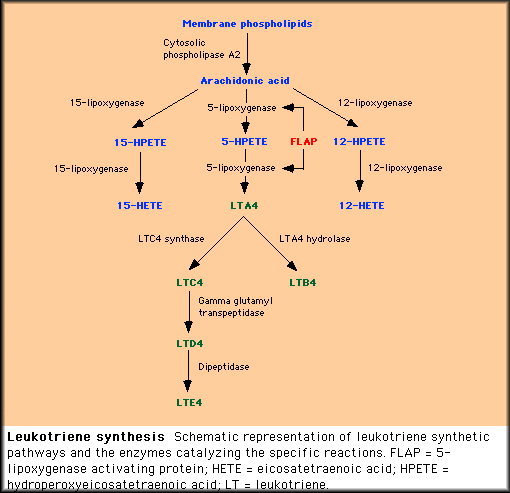
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease ” rel=”nofollow”> AERD), also known as Samter’s Triad, is a chronic medical condition with three main features: asthma, sinus disease with recurrent nasal polyps, and a sensitivity to aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs . It affects about one million peopleabout 30% of patients with asthma and nasal polyps have AERD. It can develop suddenly in adulthood, and symptoms include repeated sinus infections and the loss of one’s sense of smell.
“People may not realize they have this disease,” says otolaryngologist Joshua Levy, assistant professor of otolaryngology at Emory, who specializes in rhinology and sinus surgery at Emory Sinus, Nasal & Allergy Center and is director of resident research. “It’s progressive, which is another reason it’s difficult to diagnose. You can wind up in the hospital after taking one aspirin. It can be quite dramatic, causing life-threatening airway issues.”
The reaction can be stimulated by aspirin, NSAIDs “basically any over the counter pain killer that is not Tylenol,” says Levy. “The reaction tends to occur quickly and is severe enough that it’s unlikely you would not be aware of it.”
The cannabinoid compound used to diagnose, and perhaps to treat, AERD would be similar to CBD oil in that it would activate the receptor but would not produce a psychogenic response, or a “high.”
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Asthma Triggers
