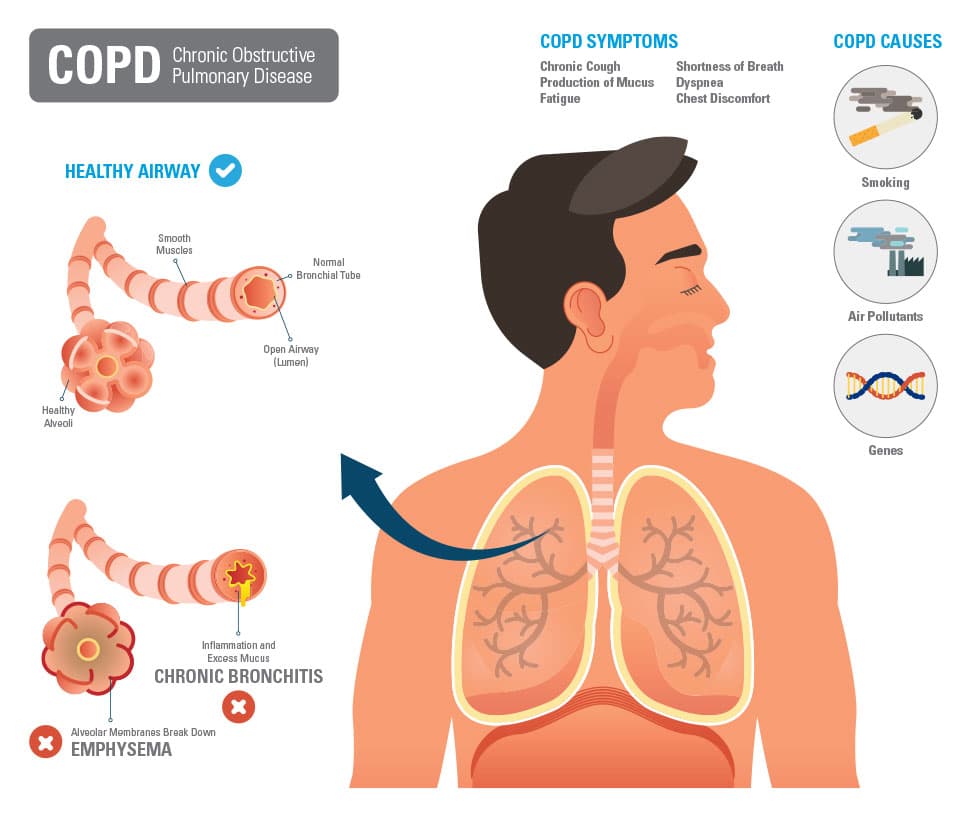
How Is Emphysema Diagnosed
The diagnosis of emphysema cannot be made solely on symptoms. Several tests are used to make the diagnosis. One simple test is to tap on your chest and listen with a stethoscope for a hollow sound. This means that air is being trapped in your lungs. Other tests include:
You might also talk to your doctor about whether testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is appropriate for you.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Asthma To Go Away
Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
The CCDSS is a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in the health insurance registries thus, the CCDSS coverage is near-universal with the exception of some small populations. Case definitions are applied to these linked databases and data are then aggregated at the provincial and territorial level before being submitted to PHAC for reporting at the provincial, territorial and national levels.
The CCDSS has expanded from its initial mandate of diabetes surveillance to include data on several additional chronic diseases and conditions including: hypertension, mental illness, mood and/or anxiety disorders, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, osteoporosis, arthritis and neurological conditions. Asthma and COPD were added to the CCDSS in 2012.
The data presented in this report and subsequent updates can be accessed on the Public Health Agency of Canada’s Public Health Infobase.
Inflammatory Cells In Asthmatic Airways
Mast cells -activated mucosal mast cells release bronchoconstrictor mediatorshistamine, cysteinyl leukotriens, prostaglandin D2. They are activated by allergens through IgE receptors or by osmotic stimuli . Eosinophils are in increased number in airways, release basic proteins that may damage epithelial cells, and have a role in releasing a growth factors and airway remodeling , T lymphocytes are in increased number and release specific cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 that orchestrate eosinophilic inflammation and IgE production by B lymphocytes . There may also be an increase in inKT cells which release large amounts of T helper: Th1 and Th2 cytokines . Dendritic cells,Macrophages are in increased number, and release inflammatory mediators and cytokines that amplify the inflammatory response . Nutrophils are in increased number in airways and sputum of patients with severe asthma and in smoking asthmatics, but the role of these cells is uncertain and their increase may even be due to steroid therapy .
Don’t Miss: Is Yogurt Good For Asthma
Diagnosing Asthma And Copd With Pft
I explained how a PFT can help diagnose asthma in my post at Asthma.net: What Are PFTs? I explained how a PFT can hep diagnose COPD in my post on this site, What Are PFTs?
So, if you read those, you know what an FEV1 is. You know how this can be used to determine if you have COPD. Still, heres a quick review. You do a PFT. You do a pre and post FVC. A computer determines your FEV1. This is the best indicator of airflow limitation.
You then use a bronchodilator. This can be either an inhaler or breathing treatment. Then you do a second FVC. Heres how you determine if its asthma or COPD.
- COPD. By its basic definition, its persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. Your pre and post bronchodilator FEV1 is less than 80%. Your post bronchodilator FEV1 is not much different than your pre bronchodilator FEV1. This shows that airflow limitation is persistent. It is not reversed with time or treatment. This confirms a diagnosis of COPD.1
- Asthma. By its basic definition, respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation are intermittent and vary in intensity. Asthma attacks are reversible with time or treatment. Your post bronchodilator FEV1 improves by 12% or more. This shows airflow limitation is reversible. This can help make a diagnosis of asthma. 2
- Asthma and COPD. This is when you have both. Your airflow limitation is reversible. But, your FEV1 remains under 80% despite treatment.
How Are They Diagnosed
Diagnosing COPD or asthma starts with a comprehensive evaluation of your history. A provider will take into account factors such as:
- Your symptoms and what triggers them
- Whether you smoke
- The health of your family members
- Your exposure to substances at home or the workplace
Your doctor will also perform a physical exam, which includes:
- Checking your vital signs, including your oxygen level
- Listening to your lungs with a stethoscope to detect wheezing or other signs of lung disease
- Looking for physical signs of other potential causes of symptoms
However, the history and physical exam are often not enough to diagnose you with COPD or asthma. Your provider will probably want to do a few more tests before they make a diagnosis.
The most useful to test to figure out if you have asthma or COPD is called spirometry. This test measures how much air you can breathe in and out of your lungs and how fast you can do it. You may be asked to do the test before and after taking an inhaled medication to see how your lungs respond. Your results are then compared to normal ranges based on your age, height, and sex.
Chest X-ray or computed tomography scans are also common tests if you have trouble breathing. While the tests can show signs of pneumonia and other lung problems, they cant determine for certain whether you have COPD or asthma.
Also Check: Why Do Adults Get Asthma
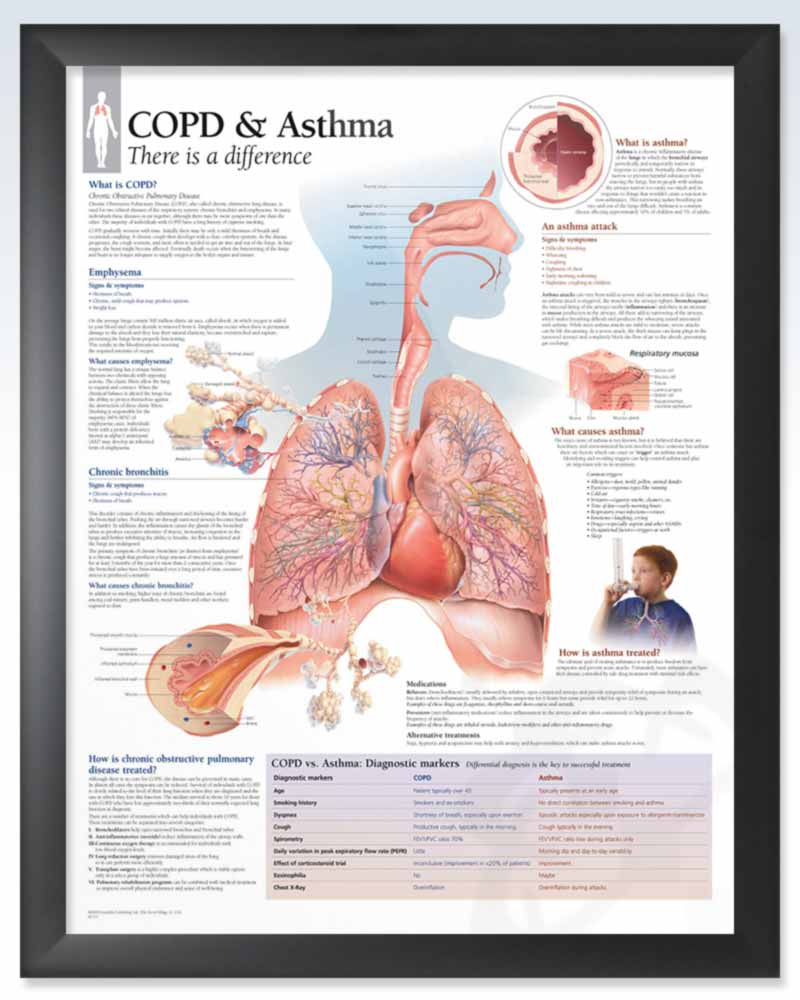
Differences Between Asthma & Copd
Its easy to get confused between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . After all, these two conditions share some of the common symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath and the inability to get air into the lungs. Not only they share the same symptoms but they also share the same medications for treatment. So, what are the differences between them?
Read Also: How To Help Wheezing Without Inhaler
Inflammatory Mediators Involved In Asthma
Chemokines are important in the recruitment of inflammatory cells into the airways and are mainly expressed in airway epithelial cells . Eotaxin is selective for eosinophils, whereas thymus and activationregulated chemokines and macrophage-derived chemokines recruit Th2 cells . Cysteinyl leukotrienes are potent bronchoconstrictors and proinflammatory mediators mainly derived from mast cells and eosinophils . Cytokines orchestrate the inflammatory response in asthma. Key cytokines include IL-1 and TNF, and GM-CSF. Th2-derived cytokines include IL-5, which is required for eosinophil differentiation and survival IL-4, which is important for Th2 cell differentiation and IL-13, needed for IgE formation . Histamine is released from mast cells and contributes to bronchoconstriction and inflammation . Nitric oxide , a potent vasodilator, is produced from syntheses in airway epithelial cells . Exhaled NO is increasingly being used to monitor the effectiveness of asthma treatment . Prostaglandin D2 is a bronchoconstrictor derived predominantly from mast cells and is involved in Th2 cell recruitment to the airways .
Airway structural cells involved in the pathogenesis of asthma are: airway epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts and airway nerves .
You May Like: How Can You Treat Asthma
Pulmonary Rehabilitation For Copd
Pulmonary rehabilitation has clear benefits for patients with COPD. Exercise increases endurance, improves shortness of breath, increases maximal oxygen consumption, and improves quality of life. Numerous studies have documented improvement in symptoms, maximum oxygen consumption, and quality-of-life measures. A decrease in the number of hospitalizations has also been shown in patients who participate in pulmonary rehabilitation programs.
Benefits do vary among individuals, however, and consistent participation in an exercise regimen is necessary to maintain improvements. In addition, it has not been shown that pulmonary rehabilitation produces any change in pulmonary function tests or overall oxygen requirements for individuals.
Recommended Reading: Can You Join The Army If You Have Asthma
Symptoms And Signs: 6 Similarities Between Copd Vs Asthma
COPD is caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants that damage lung cells. The main cause of COPD in the United States is cigarette smoke followed by other tobacco smoke . Other possible causes of COPD include chemical or toxic fumes, and inherited factors, like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, but these causes are far less common than cigarette smoking.
Although cigarette smoke may trigger asthma in some patients, asthma triggers are different from person to person, and most commonly include airborne substances such as pollen, dust, mites, mold spores, pet dander, and/or many other substances. Inflammatory immune reactions to asthma triggers in the airways is the main cause of asthma.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Asthma Attacks At Night
Myth : People With Copd Shouldnt Exercise
Many people with COPD are afraid to exercise for fear it is unsafe and will make them short of breath. The fact is that people with COPD need to exercise, explains Kathrin Nicolacakis, MD, a pulmonologist at the Cleveland Clinic. Exercise is important when you have COPD because it decreases your chances of having infections and being admitted to the hospital, she says. Exercise doesnt drain your energy. Rather, it energizes you and helps you feel less tired. Talk to your COPD doctor about appropriate exercises and breathing techniques in pulmonary rehabilitation, and maintain that level of exercise going forward, Dr. Nicolacakis says. Activity and exercise are encouraged in patients with COPD and formal programs, sometimes with the aid of oxygen, may benefit those with severe disease, notes Dr. Hanania. Walking in particular is strongly encouraged, but stretching the upper and lower extremities is another type of exercise that can be helpful, he adds.
RELATED: 10 Habits That Can Worsen COPD
Contact Post Acute Medical Today
If you have asthma or COPD, learn more about the cardiopulmonary health services available to you by contacting Post Acute Medical today. At Post Acute Medical, we concentrate on quality care, patient satisfaction and long-term positive outcomes. Providing high-quality care to our patients is our top priority.
Find out how Post Acute Medical can help you manage your COPD or asthma by locating the facility nearest you and calling for more information.
Read Also: How To Give Yourself An Asthma Attack On Purpose
The Type Of Inflammation May Be Different For Both
Asthma inflammation tends to be eosinophilic. This type of inflammation responds well to corticosteroids. Asthma is also reversed with medicines that dilate airways. So, bronchodilators called beta 2 adrenergics are also helpful. Often, combination inhalers provide both types of medicine. These may help asthmatics obtain good control of their disease. This means they should be symptoms free on most days.
Recommended Reading: Can You Join The Army If You Have Asthma
What Are The Symptoms Of Copd And Asthma
COPD
In the early stages of COPD, you may have no symptoms at all. Eventually, however, people with COPD tend to develop the following symptoms:
- Trouble breathing when moving around. As COPD progresses, you may become short of breath when doing very little.
- Ongoing cough that produces sputum
- Wheezing, or a whistling sound during breathing
- Chest tightness
People with COPD can also suffer from exacerbations, which is a sudden worsening of your symptoms over a few hours or days.
Asthma
Asthma symptoms are usually worse at night or in the early morning. Symptoms are usually brought on by a trigger and include:
- Sudden trouble breathing
Most people with mild or moderate asthma dont have symptoms every day. This is the main difference with COPD. The symptoms will come on suddenly, and can be triggered by things like:
- Pollen, dust, mold, pets, and cockroaches
- Viral respiratory infections
Asthma can also cause exacerbations, or an asthma attack. This is when your symptoms suddenly flare up much worse than usual.
Also Check: Is Arizona Good For Asthma
Copd In The Canadian Population
CCDSS Case Definitions
Prevalent COPD Case Definition
The case definition of diagnosed COPD is: an individual aged 35 years and older having at least one visit to a physician with a diagnosis of COPD in the first diagnostic field, or one hospital separation with a diagnosis of COPD in any diagnostic field ever, coded by ICD-9 491-492, 496 or ICD-10-CA J41-44. This case definition for COPD was validated by Gershon and colleagues.Footnote 44
Only the first diagnostic field was used in physician billing claims data as not all provinces and territories had more than one diagnostic field. All fields were included from the hospital separation file as this database allows for the recording of up to 25 diagnoses.
Based on this definition, once a case is detected, it is a prevalent case for life regardless of future contact with health services. Consequently, once someone is identified as a case, they are always included in the database as a case. All jurisdictions identified cases occurring as of 1995, with the exception of Quebec which began in 1996 and Nunavut which began in 2005.
Incident COPD Case Definition
Incident COPD cases were identified in the year where an individual met the case definition for the first time. A run-in period of five years, where data were collected and not reported, was employed to partially account for the prevalence pool effect i.e., to ensure that an incident case was not a pre-existing prevalent case. .
Denominator Definition
Prevalence
Incidence
Copd And Aging: Everything You Need To Know
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is one of the most prevalent lung conditions, affecting more than 328 million people around the world and an estimated 16 million people in the United States alone.
Despite how common COPD is, its often overshadowed by other chronic illnesses like lung cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. A report published by the EMBO Journal found that, while COPD results in about 300,000 deaths per year nearly double that of lung cancer it received less than a third of the funding.
While the inequity in COPD research funding can only be addressed through political and social advocacy, healthy lifestyle choices remain the best way to prevent and treat COPD. And in order to make healthy lifestyle choices, you need to stay educated about how your lungs work. There are a lot of things to consider depending on what stage of your life youre in and whether or not youve already been diagnosed with COPD.
In this post, were going to address some key facts about aging and how it affects the prognosis of people with COPD and those who are at risk of contracting COPD. In the meantime, if you are interested in getting tested for COPD, be sure to consult your doctor immediately to start discussing your symptoms.
Also Check: Can Asthma Cause Low Hemoglobin
Might I Have Both Asthma And Copd
Combined asthma plus COPD sometimes called asthma-COPD overlap is not a separate condition. However, it is possible for a person to have both asthma and COPD at the same time. It is not clear how often this happens and different studies have reported that anywhere between about one-tenth and one-half of people with either asthma or COPD might have both conditions. Rates vary widely depending on how old you are, your gender, and how the researchers set up their study.
Even though COPD is uncommon in people aged under 40 years, the combined symptoms of asthma plus COPD may appear in childhood or early adulthood.More studies are needed on people with both asthma and COPD. However, we do know that people who experience a mixture of asthma-type and COPD-type features often experience more troublesome symptoms and flare-ups. They also tend to need more healthcare support and their lung function worsens more quickly than for people who have either asthma or COPD alone.
Difference Between Asthma And Bronchitis
About 12 million people in the United States suffer from bronchitis every year. It is characterized by irritation of the mucous membranes lining the airways. Although there are similarities between asthma and bronchitis, they really arent the same disease and therefore require different treatments.
During an asthma attack you will often find that in addition to having difficulty breathing, people will also wheeze. Many sufferers have also reported tightness in the chest. In the case of bronchitis, there is also normally a hacking cough. It can be with or without phlegm. Chronic bronchitis involves a persistent phlegm-producing cough.
Chronic bronchitis can be diagnosed with a pulmonary function test. This will enable doctors to check airflow in the lungs. A chest x-ray can also be taken. Unfortunately, diagnosing asthma is more complex. It involves testing to check airway obstruction and a patients ability to exhale under various conditions.
While asthma treatment focuses on limiting exposure to triggers and controlling inflammation, bronchitis treatment includes a number of different strategies. The flu vaccine, anti-inflammation treatments, antibiotics, and bronchodilators to open airways could be applied. There are also treatments that focus on helping to clear excess mucus.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Asthma Without Inhaler
Copd Is The Same As Adult
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is comprised primarily of three related conditions: 1) chronic bronchitis, 2) chronic asthma, and 3) emphysema. With each of these three conditions there is a chronic obstruction of air flow through the airways and out of the lungs. The obstruction generally is permanent and may progress over time.Patients with COPD are often classified by the symptoms they are experiencing at the time of an increase of the symptoms of the disease. For example, if a patient is experiencing primarily shortness of breath, they may be referred to as a patient with emphysema. If the patient is primarily experiencing a cough and mucus production, he or she is referred to as having chronic bronchitis. Actually, it is preferable to refer to these patients as having COPD, since they can experience a variety of lung symptoms.
Donât Miss: Can You Develop Asthma When Pregnant
