Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
The CCDSS is a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in the health insurance registries thus, the CCDSS coverage is near-universal with the exception of some small populations. Case definitions are applied to these linked databases and data are then aggregated at the provincial and territorial level before being submitted to PHAC for reporting at the provincial, territorial and national levels.
The CCDSS has expanded from its initial mandate of diabetes surveillance to include data on several additional chronic diseases and conditions including: hypertension, mental illness, mood and/or anxiety disorders, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, osteoporosis, arthritis and neurological conditions. Asthma and COPD were added to the CCDSS in 2012.
The data presented in this report and subsequent updates can be accessed on the Public Health Agency of Canada’s Public Health Infobase.
Asthma Treatment Options& copd Treatment Options
In many cases, both lung diseases treatments are the same, such as Bronchodilators and inhalable steroids, but there are also a few treatment options that are specific to each condition.People with asthma may be encouraged to stay away from triggers or avoid going outdoors when pollen levels are high. In cases of people with severe asthma, a bronchial thermoplasty may be recommended. The procedure burns off some of the muscles in the airway, reducing their ability to constrict.
On the other hand, people with COPD may be encouraged to alter lifestyle habits, such as quitting smoking, to help prevent any further damage. They may also be prescribed oxygen or pulmonary rehabilitation. In severe cases of COPD, procedures like lung volume reduction surgeries and lung transplants may be suggested.
Both Asthma and COPD are treatable diseases that will require some lifestyle changes. Staying informed on your options and taking care of your health is very important in managing lung diseases. For any further questions about these conditions and their treatments, click the link below!
Therapeutic Responses In Asthma Copd And Overlap Syndrome
A comprehensive review of the available treatments for obstructive airway diseases is beyond the scope of this article however, it is important to appreciate that the nature of the underlying inflammation differs between asthma and COPD, as does the response to different classes of medications. Although specific interventions vary by disease, the treatment goals of asthma and COPD are similar and driven primarily by patient-centered outcomes such as controlling symptoms, optimizing health status and quality of life, and preventing exacerbations .
In general, therapies for COPD have a much more limited effect compared with those for asthma. While inhaled corticosteroids are the cornerstone of the pharmacologic management of patients with persistent asthma, inhaled bronchodilators are the therapeutic mainstay for patients with COPD. There are no disease-modifying medications currently available that can alter the progression of AO in either asthma or COPD. Smoking cessation, however, is an essential component of the successful management of any obstructive airway disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Allergies Cause Asthma Attacks
Staging And Treatment Of Asthma
The goals of long-term management of asthma should include the following: 1) achievement and maintenance of control of symptoms 2) prevention of asthma exacerbations 3) maintenance of pulmonary function as close to normal levels as possible 4) maintenance of normal activity levels, including exercise 5) avoidance of adverse effects from asthma medications 6) prevention of the development of irreversible airflow limitation and 7) prevention of asthma mortality.
The recommended GINA treatment algorithm, together with the clinical features and staging of severity of asthma, are available on the GINA website . It is important to note that the forced expiratory volume in one second levels are before treatment, i.e. in the unmedicated state.
Until the advent of anti-inflammatory drugs, asthma was treated on an as-needed basis and treated as an acute disease rather than a chronic disease. With the recognition that asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease, there has been a gradual move towards treating it more aggressively and earlier in the hope that this may change the natural history of asthma and prevent some of the remodelling that sometimes occurs.
What Are The Different Types Of Copd
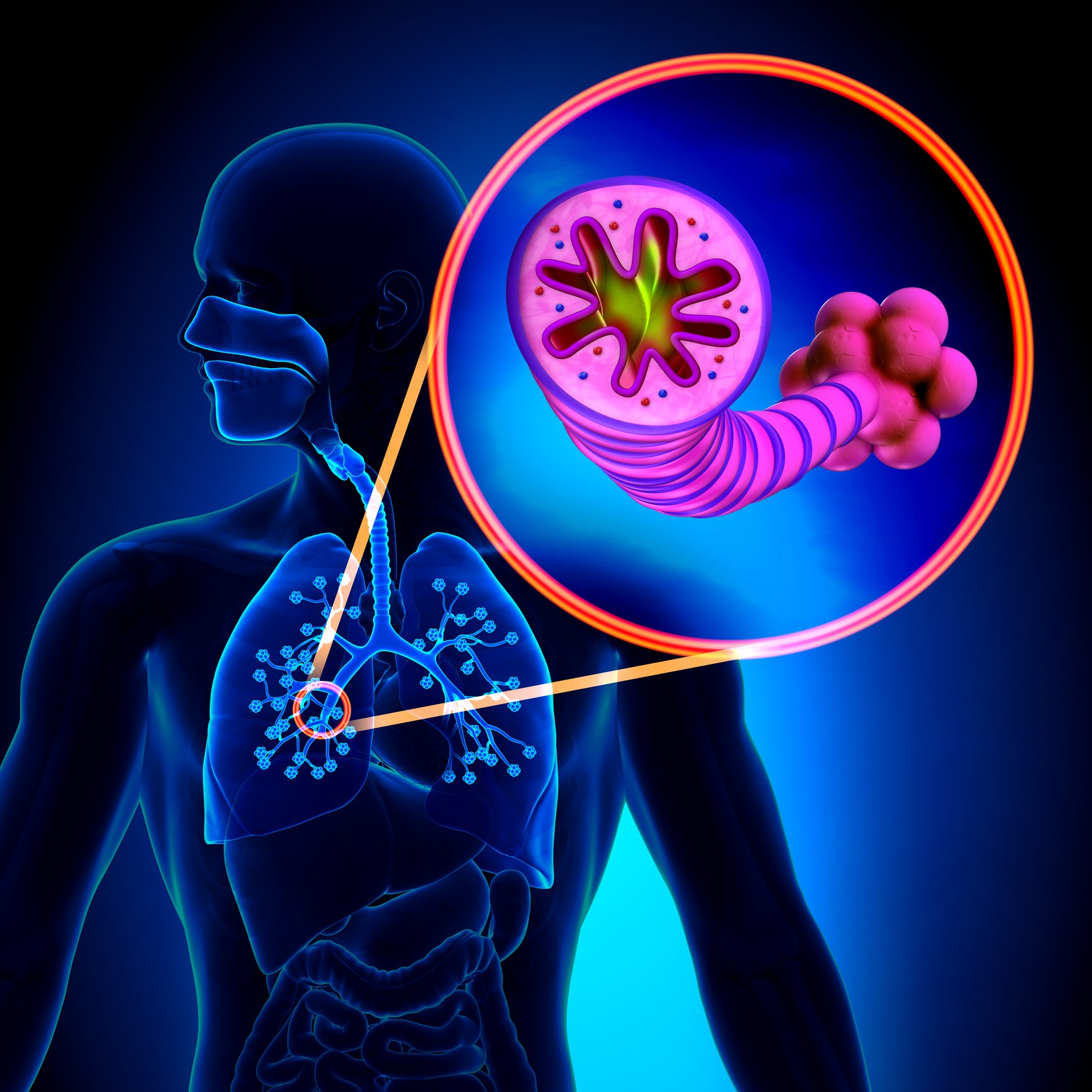
The two most common conditions of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Some physicians agree that asthma should be classified as a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, while others do not. A brief description of asthma, is included below:
| 1
What is chronic bronchitis?Chronic bronchitis is a long-term inflammation of the bronchi , which results in increased production of mucus, as well as other changes. These changes may result in breathing problems, frequent infections, cough, and disability. |
1
What is pulmonary emphysema?Emphysema is a chronic lung condition in which alveoli may be:
This can cause a decrease in respiratory function and breathlessness. Damage to the air sacs is irreversible and results in permanent “holes” in the lung tissue. |
1
What is asthma?Asthma is a chronic, inflammatory lung disease involving recurrent breathing problems. The characteristics of asthma include the following:
|
Recommended Reading: Breathing Treatments Side Effects
Asthma And Copd: What’s The Difference And Is There A Link
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are lung diseases. Both cause swelling in your airways that makes it hard to breathe.
With asthma, the swelling is often triggered by something youâre allergic to, like pollen or mold, or by physical activity. COPD is the name given to a group of lung diseases that include emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Emphysema happens when the tiny sacs in your lungs are damaged. Chronic bronchitis is when the tubes that carry air to your lungs get inflamed. Smoking is the most common cause of those conditions .
Asthma gets better. Symptoms can come and go, and you may be symptom-free for a long time. With COPD, symptoms are constant and get worse over time, even with treatment.
Q: Whats The Difference Between Asthma And Copd
Asthma occurs frequently in people with a family history of the disease and often begins in childhood. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, and these symptoms flare up during an asthma attack. At other times, symptoms may fade or become minimal.
COPD is different and usually strikes later in life. Most people diagnosed with COPD either used to smoke, or still do. Some symptomssuch as chest tightness and coughingare similar to asthma. Other symptoms, such as mucus production, are distinct to COPD. Unlike asthma, symptoms rarely ever fade completely.
Don’t Miss: Frequent Asthma Attacks
Why Is It Important
There are several reasons why the overlap syndrome is important. First, patients with overlapping asthma and COPD are excluded from clinical trials of treatment. This means that for an increasing proportion of older patients with obstructive lung disease, the data on efficacy of treatment may not be relevant. The clearest example of this comes from the studies on the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. These studies typically exclude smokers with asthma because of the difficulty in separating asthma from COPD in smokers with obstructive lung disease. However, up to 30% of people with asthma are smokers, and this means a substantial proportion of the population are excluded from randomised controlled trials. Extrapolation of the efficacy results for corticosteroids in non-smokers to smokers with asthma is flawed. Smokers with asthma have a relative corticosteroid resistance such that corticosteroids are much less efficacious in smokers with asthma than in non-smokers with asthma. This emphasises the need to study drug efficacy in relevant clinical populations, and the necessity to include overlap syndrome in drug evaluation programmes.
What Are The Stages Of Copd
Doctors generally use the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Program to stage COPD. These staging guidelines have been proven to be consistent and accurate by doctors and scientists. Other methods can be used to stage COPD, but they may be influenced by other factors.
There are many treatment options and ways to manage COPD. The newest 2017 guidelines emphasize the use of combined bronchodilators as first-line therapy for COPD. Doctors recommend vaccinations for people with the condition to decrease the risk of lower respiratory tract infections. Alterations in health-related behaviors is emphasized. Spirometry measurements can help determine the extent of obstructive lung disease. As COPD progresses, oxygen therapy, especially if you have obstructive sleep apnea, may help improve your survival.
Like COPD, there are many treatment options and ways to manage asthma. Your primary care doctor and/or an allergist will discuss and suggest the best choice of treatment and management drugs for you. Medications used include corticosteroids, short acting beta agonists , and occasionally anticholinergic medications for severe exacerbations.
Emergency treatment of life-threatening asthma or COPD may involve intravenous corticosteroids, intubation, mechanical ventilation, and oxygen treatment until the crisis is resolved.
Recommended Reading: Albuterol And Weight Gain
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
In the recent Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Guidelines , COPD is defined as follows: a disease state characterised by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. The airflow limitation is usually progressive and associated with an abnormal response of the lungs to noxious particles or gases.
Key Differences Between Asthma And Copd
The following points will target on the fundamental differences between both kinds of reparatory diseases:
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Homemade Inhaler For Asthma
Symptoms And Signs: 6 Similarities Between Copd Vs Asthma
COPD is caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants that damage lung cells. The main cause of COPD in the United States is cigarette smoke followed by other tobacco smoke . Other possible causes of COPD include chemical or toxic fumes, and inherited factors, like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, but these causes are far less common than cigarette smoking.
Although cigarette smoke may trigger asthma in some patients, asthma triggers are different from person to person, and most commonly include airborne substances such as pollen, dust, mites, mold spores, pet dander, and/or many other substances. Inflammatory immune reactions to asthma triggers in the airways is the main cause of asthma.
Inflammatory Cells In Copd
Neutrophils are present in sputum of smokers but increased in COPD and related to disease severity. They may be important in mucus hypersecretion and through release of proteases. Macrophages: big numbers are in airway lumen, lung parenchyma, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. They produce increased inflammatory mediators and proteases and may show defective phagocytosis. T lymphocytes: both CD4+ and CD8+ cells are increased in the airway wall and lung parenchyma, with big CD8+/CD4+ ratio. Increased is the number of CD8+ T cells and Th1 cells which secrete interferon- and express the chemokine receptor CXCR3. CD8+ cells may be cytotoxic to alveolar cells. B lymphocytes: are increased in peripheral airways and within lymphoid follicles, possibly as a response to colonization and infection. Eosinophils: increased eosinophil proteins in sputum and eosinophils in airway wall during exacerbations. Epithelial cells: May be activated by cigarette smoke to produce inflammatory mediators .
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Nebulizer Treatment
Strengths And Limitations Of The Systematic Review
One significant strength of this systematic review is being the first review to offer comprehensive information about the extent of availability and affordability of medicines and diagnostic tests of asthma and COPD in SSA. Despite this, some of the limitations are heterogeneity of the study findings and health facilities surveyed and the low methodological quality of the eligible original studies.
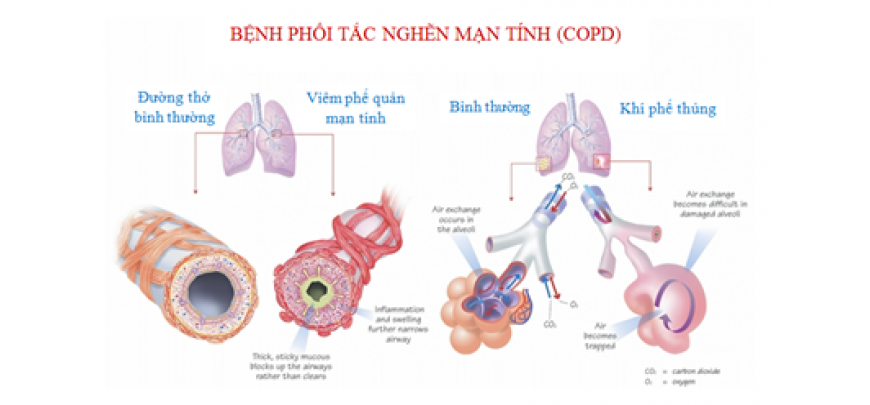
Airflow Limitation In Copd
The chronic airflow limitation of COPD is caused by a mixture of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction , the relative contributions of which vary from person to person . Chronic inflammation causes structural changes and narrowing of small airways. Destruction of the lung parenchyma, also by inflammatory processes, leads to the loss of alveolar attachments to the small airways and decreases lung elastic recoil in turn these changes diminish the ability of the airways to remain open during expiration .
So in COPD inflammation causes small airway disease and parenchymal destruction that all lead to airflow limitation .
You May Like: What Happens If You Smoke Weed With Asthma
Inflamatory And Immunological Profile
BA and COPD are characterized by chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract although the nature of the inflammation and localization are different . In both there are two groups of cells that are activated. One group is inflammatory cells recruited from peripheral blood to the lungs by chemotactic factors released locally, and the other group is airway and lung structural cells such as epithelial cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells, which also release inflammatory mediators and actively participate in the inflammatory process. In both, BA and COPD, the inflammatory response involves innate immunity and adaptive immunity .
In BA the inflammation is located from trachea to peripheral airways. In COPD the inflammatory process is located in peripheral pathways and parenchyma and is associated with systemic inflammation. Bronchial obstruction in BA occurs due to smooth muscle contraction, vascular congestion , remodeling of the airway and impaction of mucus . This inflammation also leads to bronchial hyperresponsiveness, a physiological abnormality of asthma that is characterized by variable symptoms including nocturnal worsening. In COPD, the predominantly peripheral obstruction, due to fibrosis and collapse due to loss of pulmonary elasticity , leads to gas trapping, which is an irreversible mechanism. However, there is an added cholinergic contraction that is reversible .
The Overlap Between Asthma And Copd
Asthma is traditionally described as an allergic disease that develops during childhood and is characterized by reversible AO. In contrast, COPD is typically related to smoking tobacco, develops later in life, and is characterized by incompletely reversible airflow limitation. Although both diseases share AO as a common feature, they are at opposite ends of the spectrum of obstructive airway disease that is seen in clinical practice. There is, however, a considerable pathologic and functional overlap between asthma and COPD, particularly among the elderly, who may have components of both diseases .
Airway inflammation is the central component of all different phenotypes of obstructive airway diseases that can exist in various combinations . Epidemiologic studies report an increased frequency of overlapping diagnoses with advancing age, with an estimated prevalence of < 10% in patients younger than 50 years and > 50% in patients aged 80 years or older. Patient groups that have features of asthma-COPD overlap syndrome include smokers with asthma and nonsmokers with long-standing asthma who progress to COPD.
Finally, the overlap syndrome of asthma and COPD is supported by the Dutch hypothesis, which states that asthma and AHR predispose patients to COPD later in life and that asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema are different expressions of a single airway disease. The presence of these components is influenced by host and environmental factors.
Don’t Miss: Edibles And Asthma
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For A Person Copd Vs Asthma
The prognosis for COPD ranges from fair to poor and depends on how rapidly COPD advances over time. In general, individuals with COPD have a decrease in their lifespan according to research.
If you have asthma, the prognosis for most people ranges from fair to excellent, depending upon how well you can identify what triggers your attacks, and your response to medication.
Limitations Of The Ccdss
The CCDSS may underestimate the burden of asthma and COPD as it relies partly on the physician billing claims database to identify cases. One of the limitations of this database is that physicians not paid on a fee-for-service basis are not always required to submit medical claims. Other payment schemes include salary, contract, capitation and partial fee-for-service. Alternative payment of physicians is more frequent for some specialties, in remote areas and for some primary health care centres. However, in some jurisdictions, physicians under alternative payment schemes are still expected to remit service information, otherwise known as “shadow billing”. Both fee-for-service claims and shadow billing were included where available. Services for non-fee-for-service physicians who do not shadow bill are not captured. Currently, it is not possible to establish the magnitude of this impact at the national scale further studies are required.
On the contrary, using the CCDSS, there is the potential for the accumulation of false positive cases of asthma. In other words, once someone is identified as a case, the person is always included in the database as a case, even if the person’s symptoms resolve. However, the current case definition was adopted in order minimize the number of false positives as much as possible in order to reduce their impact on the data.
Recommended Reading: Can Allergies Cause Asthma Attacks
