What Does A High Eosinophil Count Mean
An eosinophil count can help diagnose a few conditions. You might have a high count with the following:
- Acute hypereosinophilic syndrome, a rare condition thatâs similar to leukemia and can be life-threatening
- An allergic disorder like asthma or hay fever
- Autoimmune conditions
- An infection caused by a parasite or fungus
- A reaction to certain medications
- Leukemia and other blood disorders
Discussion And Next Steps
The high clinical need in severe asthma and the introduction of effective biological therapies for severe asthma related to eosinophilia make the development of a consensus to support clinicians treating these patients an important undertaking. The ERS has expressed an interest in taking this subject forward, potentially through an ERS research seminar and through discussion in sessions at national and international congresses. The intention is to develop a position statement supported by evidence to reflect a broader expert opinion around the management of patients with severe corticosteroid-refractory asthma, and to ensure that the fast-moving scientific developments in this field are applied to clinical practice for the benefit of patients.
Cytokine And Growth Factor Receptors
The heterodimeric receptor for IL-5 is thought to be the most important cytokine receptor expressed by eosinophils. The beta-subunit is identical to the beta-subunit of the receptors for granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-3 . The alpha-subunit, IL-5R, is specific to IL-5 and has been identified as a therapeutic target for severe eosinophilic asthma and other eosinophil-mediated conditions. The IL-5 receptor is also expressed by basophils.
Eosinophils also express receptors for multiple other cytokines and growth factors, including for IL-4, IL-13, IL-33, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and transforming growth factor- .
Read Also: How To Treat Bronchial Asthma At Home
Treatment: How Do We Treat Patients With Sea
Patients with severe asthma who have an eosinophilic-driven phenotype may benefit from newly developed precision medicines. One group clearly eligible for treatment with biologics is those patients with severe asthma adherent to high-dose inhaled corticosteroids who nevertheless have frequent exacerbations with or without symptoms, and who have persistently elevated levels of circulating blood eosinophils.
There are number of targeted therapies, both licensed and in development, that are appropriate for consideration in this patient population. Three biologic therapies are now licensed for severe asthma: omalizumab ), mepolizumab ) and reslizumab . Four more are currently in the development process: benralizumab has recently reported successful phase 3 results tralokinumab and dupilumab are in phase 3 trials and pitrakinra has completed phase 2 trials . Guidance is needed to understand how best to use these different treatments in practice, tailoring treatment choice to the clinical picture and selecting patients likely to benefit.
What Do The Results Mean
Eosinophils make up 0.0 to 6.0 percent of your blood. The absolute count is the percentage of eosinophils multiplied by your white blood cell count. The count may range a bit between different laboratories, but a normal range is usually between 30 and 350.
A count of more than 500 cells per microliter of blood is considered eosinophilia.
You May Like: Will An Epipen Help With An Asthma Attack
Clinical Characteristics Of Ea And Nea
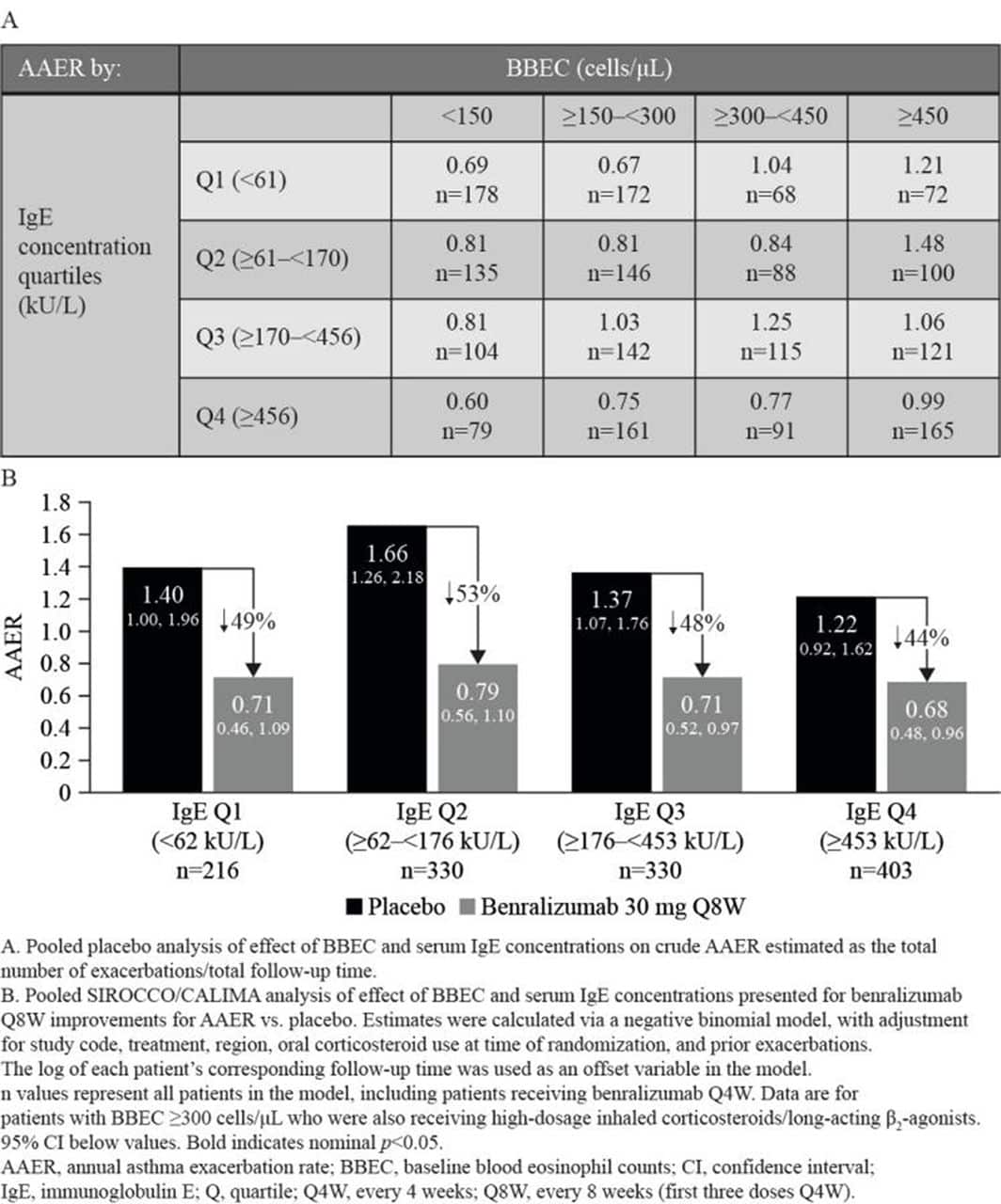
Although stratification by blood eosinophils is relatively easy, this does not create robust clinical phenotypes. Therefore, cluster analysis has been used to identify groups of patients with asthma who share specific clinical characteristics. For example, using unsupervised cluster analysis, which used clinical characteristics of age of asthma onset, lung function, bronchodilator reversibility, and demographics, the Severe Asthma Research Program cohort identified five clinical clusters of adult asthma, in which four demonstrated eosinophilia of varying degrees , and four clusters of pediatric asthma, all of which included eosinophilia . A recent investigation evaluating the ADEPT cohort identified four phenotypes, which were also present in the UBIOPRED cohort . Three of the four asthma clusters were associated with eosinophilia. A representative comparison of the clinical clusters from the three mentioned cohorts as examples of the cluster analysis approach to defining clinical characteristics in asthma is presented in Table 1. Although cluster analysis can define groups of patients with asthma with specific shared clinical characteristics, it does not define specific endotypes, as it is likely that several endotypes drive the phenotypes present in each cluster.
Eosinophil Differentiation Maturation Migration Activation And Degranulation
Eosinophils develop from pluripotent CD34+ granulocyte progenitor cells.
Differentiation and maturation occurs as follows:
Allergen challenge of mild asthmatics results in increased expression of IL-5R on CD34+ cells in the bone marrow, associated with blood and sputum eosinophilia . Eosinophil differentiation usually occurs in the bone marrow. However, eosinophil precursors have been isolated from the peripheral blood of atopic subjects at significantly higher concentrations compared to non-atopic controls . Increased numbers of CD34+/IL-5R+ eosinophil precursors have also been identified in bronchial biopsies of atopic asthmatics, compared to non-asthmatic control subjects . Eosinophil-lineage committed cells have also been identified in lung tissue in a mouse model of allergic airway inflammation . More recently, eosinophil progenitors isolated from the blood of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma have been shown to have an exaggerated clonogenic response to IL-5 in vitro, compared to eosinophil precursors from mild asthmatics, suggesting that in situ eosinophilopoiesis may have a clinically relevant role in severe eosinophilic asthma .
The eosinophils ability to store several preformed cytotoxic mediators ready for rapid release upon appropriate stimulation facilitates a much quicker reaction to pro-inflammatory stimuli, compared to other cells, whose responses depend on upregulating the transcription of genes coding for such proteins.
Recommended Reading: How To Use Asthma Pump
Role Of The Pharmacist
Pharmacists play a critical role in the selection of treatment for EA, as well as the education and assessment of patients with EA. Although the benefits and risks of biologic therapy for EA must be carefully weighed, other patient factors must also be carefully considered, such as affordability, access, and preference. Pharmacists should also assess adherence to ICS treatment and rule out other causes of asthma exacerbation prior to adjunctive treatment recommendations for severe EA. In addition, pharmacists can assist patients with referrals to support services as well as psychological services to manage emotional, social, and other burdens of EA and its management.
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
What Is Eosinophilic Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma is a subtype of asthma that has been recognized for more than 100 years. It usually develops in adulthood and tends to be a severe form of asthma. It can be hard to control because it does not respond to treatment with high doses of oral corticosteroids like other forms of asthma.1,2
Eosinophilic asthma impacts the whole respiratory tract, from the sinuses to the small, or distal, airways deep in the lungs. People with EA are often diagnosed with nasal polyps and chronic sinus disease too.
You May Like: Can Vicks Vapor Rub Help Asthma
Preparing For A Doctors Appointment
Patients with asthma or suspected asthma will likely be referred to an allergist or a pulmonologist. These tips may help you be more prepared for your appointment:
- Keep a log of symptoms you are having, even if they are seemingly unrelated.
- Bring a list of any prescription or over-the-counter medications you are taking. Donât forget to list vitamins and supplements, too.
- Jot down a list of questions, such as:
- What tests or procedures will be performed?
- How will my asthma be monitored?
- How should I use my medications? How should they be stored?
- What triggers might cause my asthma to flare? Is there anything I can/should do to reduce my risk of having an asthma attack?
- Will I have an asthma action plan?
- How often do I need follow-up care?
How To Prepare For Your Appointment
To get ready for your doctorâs appointment, it might help to keep a journal of all your symptoms, even ones that donât seem related to asthma. You can write down:
- Symptoms and how severe they are
- Date and time you got the symptoms
- Anything that might have triggered your symptoms
This will save you from having to recall everything on the spot at your doctorâs office. It also makes sure you donât forget any important details.
Youâll also want to make a list of any other health conditions you have, as well as any medicines, herbs, vitamins, or supplements you take regularly.
Finally, you might want to write down some questions to ask your doctor, such as:
- What tests will I need?
- How accurate are those tests?
- How will you tell for sure if I have eosinophilic asthma?
- What can I do to avoid asthma attacks?
- How will you manage my asthma?
- How do I use the medicine you gave me?
- How often will I need to see you?
- Could anything else be causing my symptoms?
- Will I need to see other types of doctors as well?
- Where can I look for more information to learn more?
Sometimes, people with eosinophilic asthma are told they have a different disease, called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , which is common in people who smoke. If youâre told you have COPD, ask how you can know itâs COPD and not asthma.
Show Sources
European Respiratory Society, ERJ Open Research: âManagement of the patient with eosinophilic asthma: a new era begins.â
Mayo Clinic: âEosinophilia.â
Read Also: How Long Does An Asthma Attack Last
Role Of Eosinophilic Inflammation In Asthma
Eosinophils, which tend to accumulate at sites of allergic inflammation, contribute to the development of bronchial asthma. They release a number of mediators, including specific granule proteins, such as major basic protein , radical oxygen species, cytokines, such as granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin -8, and lipid mediators, such as cysteinyl leukotrienes . However, previous studies investigating the effectiveness of anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody treatment for asthmatics have suggested that eosinophils may only play a small role . For example, it has been reported that anti-IL-5 mAb reduces the sputum or blood eosinophil count, but has no effect on histamine-induced AHR or allergen-induced late asthmatic response , which suggests that eosinophils do not play a role in the development of AHR or allergen-induced airflow obstruction.
Figure 1. Mechanisms of eosinophilic airway inflammation in bronchial asthma. IL-5 plays an important role in the development of eosinophilic airway inflammation. However, in the absence of IL-5, the Th2 network, which includes a cascade of VCAM-1/CC chemokines/GM-CSF, can maintain eosinophilic infiltration and activation. Yellow text indicates a cascade of VCAM-1/CC chemokines/GM-CSF.
Definition Of Eosinophilic And Noneosinophilic Asthma
Asthma can be broadly classified as eosinophilic or noneosinophilic on the basis of airway or peripheral blood cellular profiles, with approximately half of individuals with asthma falling into each category . Sputum cellular profiles are believed to directly reflect lung inflammation and therefore are the preferred method used in asthma research to determine EA . Sputum eosinophils should be reported as a percentage of total cells from either a whole expectorate or sputum plug. Sputum eosinophil levels of greater than 2 to 3% have been used to define EA . However, technical requirements for sputum processing and cell counting may limit the feasibility of using sputum eosinophil counts in all clinical centers.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Ssi For A Child With Asthma
Your Eosinophilic Test Results: What To Expect Next
If youre diagnosed with eosinophilic asthma, your doctor might prescribe one of three treatments designed to target eosinophils, says Chupp. These medications, called biologics, can help lower the levels of eosinophils and resulting inflammation in the lungs, which can reduce asthma attacks. Given as injections or infusions you receive every few weeks at your doctors office, these therapies work by targeting specific molecules involved in the action of eosinophils. Mepolizumab and reslizumab are antibodies against interleukin 5 molecules, while benralizumab is an antibody against the IL-5-receptor-alpha-chain. Studies suggest that these drugs are safe and effective in most people with eosinophilic asthma, says Chupp.
If you have severe or hard-to-treat asthma, talk to your doctor about whether you should be tested for eosinophilia. If you do have eosinophilic asthma, it can affect the type of treatment youll need.
The Eosinophils Role In Asthma Pathophysiology
Asthma pathophysiology is complex, and the relative contributions of the various cytokine networks involved vary between patients. Core features include airway hyperresponsiveness , mucus hypersecretion, tissue damage, and airway remodeling. See Figure Figure22 for an overview of the eosinophils role in asthma pathophysiology.
The role of eosinophils in asthma. An overview of the main stimuli for eosinophilic airway inflammation and the means by which eosinophils elicit the main pathophysiological changes associated with asthma . Abbreviations: MBP, major basic protein EPO, eosinophil peroxidase IL, interleukin TGF-, transforming growth factor- GM-CSF, granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor PGD2, prostaglandin-D2 5-oxo-ETE, 5-oxo 6, 8, 11, 14-eicosatetraenoic acid PAMPs, pathogen associated molecular patterns DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns Ig, immunoglobulin.
You May Like: How To Diagnose Asthma In Adults
Mechanisms Of Allergic Ea
The association between allergy and asthma is widely recognized. As a group, individuals with the allergic asthma endotype have earlier-onset disease that is triggered predominantly by exposure to aeroallergens and commonly seen with comorbid allergic rhinitis or other atopic disorders. Characteristic of atopic disease, the type 2 inflammation seen in this asthma endotype is mediated by antigen-specific Th2 cells secretion of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 from these and other cells IgE-mediated mast cell and basophil degranulation and eosinophilia . IL-5 recruits eosinophils to the site of antigen exposure, and the eotaxins establish a powerful chemotactic gradient inducing eosinophil influx into airways. Murine and ex vivo human experiments support that IL-13, also an eosinophil product , contributes to the bronchial hyperreactivity characteristic of asthma . Over time, these pathways may no longer require external stimulation and can become self-perpetuating . Airway remodeling may contribute to the persistent changes in lung function, which may be in part attributed to the presence of eosinophils through their expression of transforming growth factor- . Inhibition of IgE-mediated pathways through treatment with omalizumab can reduce the prominent viral-induced inflammation related to asthma exacerbations in atopic individuals .
Interactions Of Neutrophils And Eosinophils In The Development Of Severe Asthma Or Asthma Exacerbation
Both neutrophilic and eosinophilic inflammation may play roles in severe asthma . Neutrophilic inflammation has been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of asthma exacerbation , which occurs frequently in severe asthma. The European Network for Understanding Mechanisms of Severe Asthma study suggested that compared with patients with mild-to-moderate asthma, those with severe asthma have both a greater sputum neutrophil count and an increased release of eosinophil-derived mediators . IL-8 plays an important role in the accumulation of neutrophils in inflammation sites, and IL-8 expression is upregulated in the airways of severe asthmatic patients . In addition, we reported that neutrophils that had migrated to IL-8 induce the transbasement membrane migration of eosinophils in vitro, even without eosinophil chemoattractants this neutrophil-induced eosinophil migration is suppressed by LTB4 antagonist or platelet-activating factor antagonist. LTB4 and PAF are potent chemotactic factors for eosinophils therefore, IL-8-stimulated neutrophils can lead to eosinophil accumulation in asthmatic airways through LTB4 or PAF .
You May Like: How Do They Diagnose Asthma
What Are Eosinophils
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that plays two roles in the immune system: they destroy foreign substances and regulate inflammation. If too many eosinophils congregate in certain tissues, it can cause a host of inflammatory-based conditions, such as asthma, eczema, Crohns disease and certain types of cancer.3
With eosinophilic asthma, the number of eosinophils overpopulates the blood, lung tissue, and mucus in the respiratory tract. This causes the airways to swell and become narrow, making it hard to breathe. Research has shown that higher levels of eosinophils in the blood is linked to severe asthma attacks in the future.
How The Test Is Done
If your doctor wants an absolute eosinophil count, youâll need a blood test. During the test, a health care worker will put a needle into one of your veins and take out some blood.
In a lab, a technician will add a special stain to your blood sample. This let them see the eosinophils and count how many you have in every 100 cells. Theyâll multiply that percentage by your white blood cell count to get your absolute eosinophil count.
Also Check: How Many People In The Us Have Asthma
Conflict Of Interest Statement
CM has attended an international conference with Boehringer Ingelheim. AMG has attended advisory boards for Glaxo SmithKline, Novartis, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Teva. He has received speaker fees from Novartis, Astra Zeneca, Vectura, Boehringer Ingelheim and Teva. He has participated in research for which his institution has been renumerated with Hoffman La Roche, Glaxo SmithKline and Boehringer Ingelheim. He has attended international conferences with Napp and Astra Zeneca and has consultancy agreements with Astra Zeneca and Vectura.
Mechanisms Of Neutrophilic Asthma
Corticosteroids are known to inhibit neutrophil apoptosis, which in turn may prolong or promote airway neutrophilia, potentially leading to the diagnosis of neutrophilic asthma . This calls into question whether the continued use of corticosteroids to treat severe neutrophilic asthma may promote or complicate diagnosis of the neutrophilic phenotype in patients using inhaled or systemic corticosteroids. Despite this, many potential molecular pathways may be implicated in the development of the neutrophilic asthma subphenotype independent of corticosteroid use . Clinically, patients with neutrophilic asthma develop asthma at an older age and demonstrate impaired lung function, less bronchodilator reversibility, and less atopy .
Mechanisms of noneosinophilic asthma. CRP=C-reactive protein CXCR2=chemokine receptor 2 DAMP=damage-associated molecular patterns dsRNA=double-stranded RNA HETE=hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid MAPK=mitogen-activated protein kinase NF-B=nuclear factor B NK=natural killer sEH=soluble epoxide hydrolase Tc1=cytotoxic T-cell subset 1 Th=T-helper cell TLR4=toll-like receptor 4 TNF=tumor necrosis factor-.
Also Check: Can You Join The Navy With Asthma
