How Do I Know If My Infant Or Child Has Severe Asthma
If you are concerned that your infant or childs asthma may be severe, observe their behavior for the indicators below and speak to your healthcare provider right away.
Observe your infant for any of the following indicators of Severe Asthma:
- Sits up, refuses to lie down
- Stops feeding
- Pale or bluish-looking skin anywhere
- Irritable
- Rapid breathing
- Using accessory muscles of breathing-in, drawing of muscles at the neck when breathing it may look like the skin is being tugged in. If you see this, your child must be assessed by a healthcare provider.
Observe your child for any of the following indicators of Severe Asthma:
- Pale looking or bluish looking skin- anywhere
- Breathless
- Irritable
- Peak flow less than 50% of personal best
- Using accessory muscles of breathing-in, drawing of muscles at the neck when breathing it may look like the skin is being tugged in. If you see this, your child must be assessed by a healthcare provider.
With Proper Treatment A Child With Eia Does Not Need To Limit Overall Physical Activity
Weather changes. Cold air, wind, rain, and sudden changes in the weather can sometimes trigger asthma. Each case of asthma is unique. It is important for parents to keep track of the factors or triggers that seem to provoke a childs asthma. Because symptoms do not always occur during or immediately after exposure, this effort may take a bit of detective work. Once you know those triggers, you can take steps to manage your childs exposure to them.
Side Effects Of Asthma Medication
If you are worried about possible side effects from asthma medication, speak to your doctor. Do not stop or reduce doses of medication for your child without speaking with your doctor. Common side effects from inhaled asthma medication:
Preventers
- sore mouth and throat
- fungal throat infections.
Using a spacer reduces the risk of these side effects. as does rinsing the mouth with water after using an inhaler.
Relievers
- fast heart beat.
Recommended Reading: Does Weight Affect Asthma
How Is Asthma Treatment Different For Older Children
Sometimes when asthma is suspected, the doctor will put your child on a trial of asthma medication to see if it helps. If your child gets better while taking the medicine, it can be a signal that your childs symptoms are due to asthma. The medication will depend on how severe your childs symptoms are and how often they occur.
The goal of treatment for children include:
- Managing the childs environment to avoid triggers
- Treating the airway inflammation and bronchospasm with medication
- Keeping asthma in control so activity does not need to be limited
- Teaching the child about asthma, their medications and how to be as healthy as possible in a way they can understand
When administering medication to your child, make sure to follow the instructions given to you by your doctor and on the package insert.
Recommended Reading:
Youre Not Alone Get The Information And Support You Need
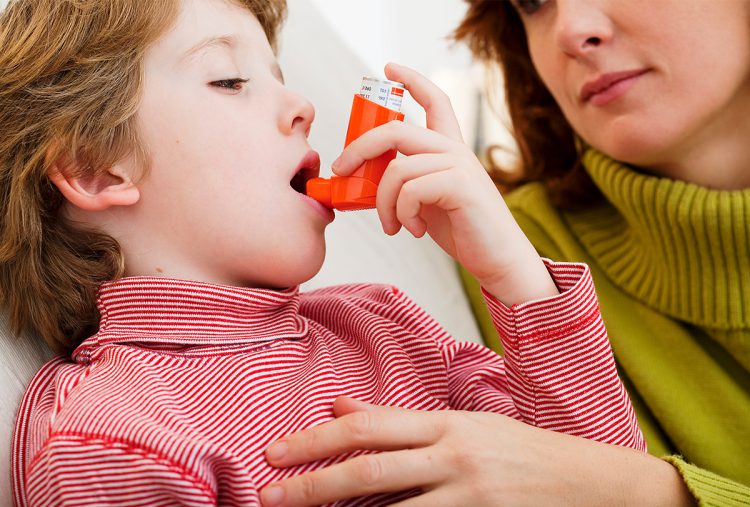

We know that getting a diagnosis of asthma can bring a mix of emotions. You may feel relieved to have it confirmed after a few years. But you may also feel scared or sad because your child has a long-term condition.
We have lots of information to support you, from helping your child to use their inhalers, to keeping them safe at school and when doing sports. We also have advice on explaining asthma to your child.
You can get advice and support about managing your childs asthma by calling a respiratory nurse specialist on our Helpline, 0300 222 5800 . Or you can WhatsApp them on 07378 606 728.
Recommended Reading: Can Allergies Cause Asthma Attacks
When Will I Get A Confirmed Diagnosis For My Child After Tests
How soon your child will get a confirmed diagnosis depends on how well your child has been able to perform the tests, and how well they have got on with any asthma treatments tried.
Diagnosis of asthma will be confirmed once your childs GP has all the pieces of the puzzle they need:
- Your child has asthma symptoms that come and go.
- Tests showed blocked airways, but reliever medicines helped them.
- Tests for allergic asthma came back positive
- Peak flow measurements showed lung function varied over time.
If tests still do not clearly confirm an asthma diagnosis, but your child is still having symptoms, their GP should review symptoms and re-test in six weeks.
Depending on their results, if asthma is not confirmed, your child may be referred to a specialist for more assessments, or to consider different diagnoses.
Its important to confirm a diagnosis with tests
Even if your child is getting on well with asthma treatments, its important to take them for tests once they are old enough to confirm they have asthma to make sure theyre not taking asthma medicines unnecessarily, or taking more medicines than they need. Its also important to make sure other things have not been missed.
You can get advice and support about asthma tests by calling a respiratory nurse specialist on our Helpline, 0300 222 5800 . Or you can WhatsApp them on 07378 606 728.
New In Long Term Management Of Asthma
Asthma treatment goals in children and adolescents are to minimize the short term effects and the risk of adverse asthma outcomes . It is imperative to optimize maintenance therapies, assess for the independent significant risk predictors at least once a year, like short acting 2-agonist overuse, not receiving inhaled corticosteroids , tobacco exposure, ongoing allergen exposure, psychosocial issues, comorbidities 2) and poor lung function. Ensuring good quality, consistent parental education is vital.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Homemade Inhaler For Asthma
What Causes Asthma In Children
The exact cause of asthma is unknown. Genetics and environment likely play a role in which children get asthma.
An asthma attack can happen when your child is exposed to an asthma trigger. An asthma trigger is something that can set off or worsen asthma symptoms. Different triggers can cause different types of asthma:
- Allergic asthma is caused by allergens. Allergens are substances that cause an allergic reaction. They can include
- Dust mites
Asthma triggers may be different for each child and can change over time.
When To See A Doctor
If you believe your child may be showing symptoms of childhood asthma, its time to visit a doctor. The longer you wait to address their symptoms, the higher your childs risk is of having an asthma attack if they do, in fact, have asthma.
If your child has been diagnosed with asthma, you can begin a treatment protocol that will improve both the asthma symptoms and your childs quality of life.
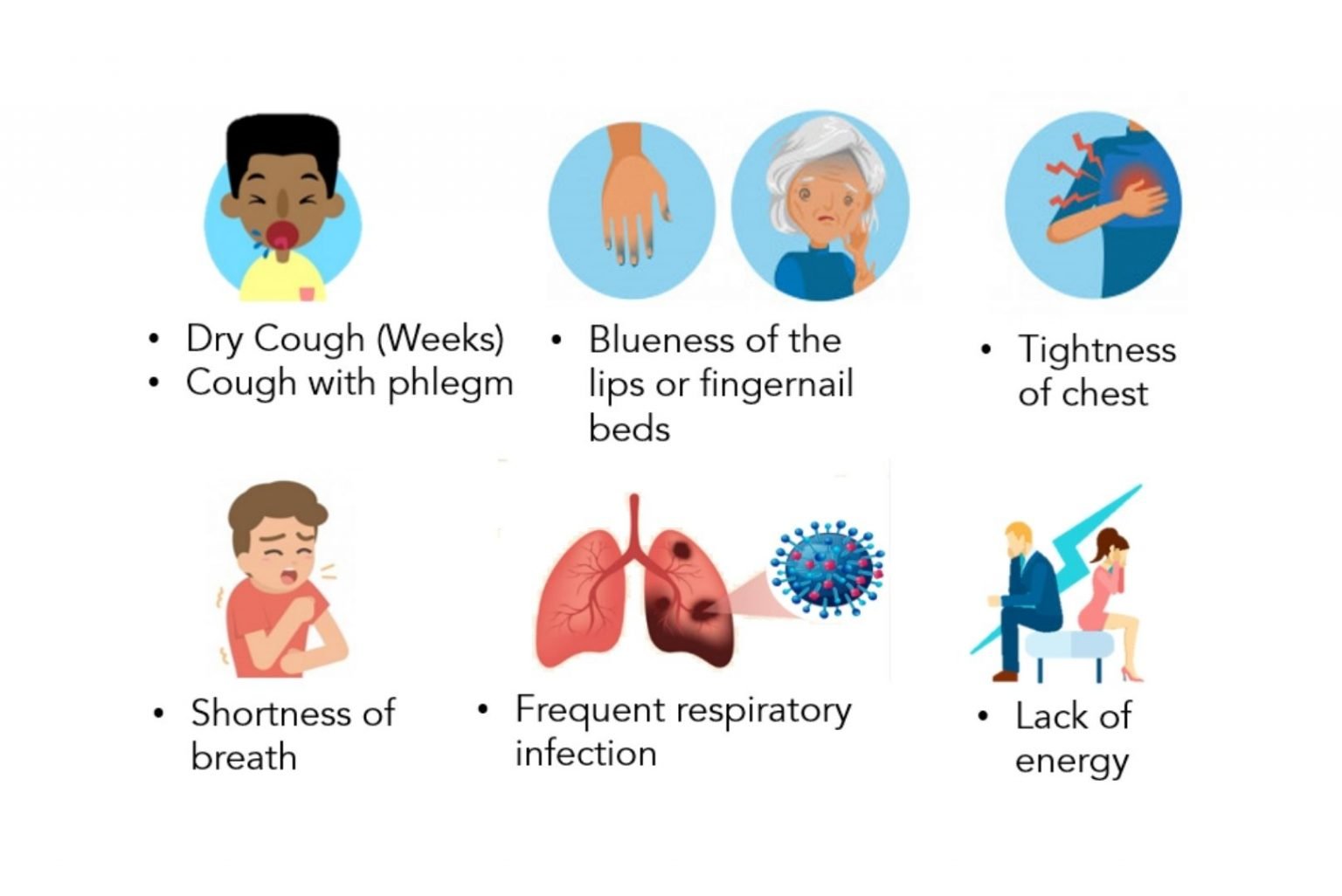
Childhood asthma is one of the most common lung conditions worldwide. Symptoms of asthma in children may include:
- coughing
Also Check: What Can Cause Asthma Like Symptoms
New In The Management Of Acute Asthma Improving Treatment Of Acute Asthma Attacks
An asthma attack should not be viewed as a temporary inconvenience but rather an event that may be associated with permanent damage to the lung . It is important to understand the impact of terminology and asthma specialists recommend replacing the term exacerbation or flare up with attack as this will convey severity, future risk, and potential for death . The presence of previous severe asthma attacks, psychological factors, and non-adherence to maintenance therapy are known factors contributing to high risk patients with asthma .
What Are The Symptoms Of Pediatric Asthma
In children, asthma symptoms can include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness and shortness of breath. Often, kids cant describe themselves what theyre feeling, but they may say they feel pain in their chest when they run, for example, says Alia Bazzy-Asaad, MD, director of the Asthma Program at Yale Medicine.
Some children with asthma have a chronic cough that doesnt go away. This is known as cough variant asthma. In young children, breathing louder or faster than normal may also be a sign of asthma.
You May Like: Does Qvar Cause Weight Gain
A Delay In Identification Of Asthma In Children And Adolescents Is Common And Why It Happens
A delay in identification of childhood asthma, especially in young children is still common . We previously reported that almost two thirds of children under 18 years of age had a delay in asthma diagnosis, and the delay was as long as 3 years after one met Predetermined Asthma Criteria . Bisgaard et al. revealed that 32% of children, ages 15 years in the US and Europe , reported recurrent respiratory symptoms , and 28% of children reported weekly asthma symptoms of whom only 20% had an asthma diagnosis and only 9.5% were receiving ICS . Also, the Lung Health Survey showed that 7.5 % of high school students with recurrent and significant asthma symptoms were not diagnosed with asthma . Consequently, a delayed asthma diagnosis was associated with increased urgent care visits suggesting suboptimal care and limited access to proper asthma therapy .
Table 1. Operational diagnostic criteria for asthma in children 15 years of age, a Canadian Thoracic Society and Canadian Pediatric Society.
Table 2. Two asthma ascertainment criteria which were used for developing NLP algorithms.
Asthma Symptoms In Infants And Young Children

In young children, cough is often the only symptom of asthma.
Asthma symptoms generally include coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, but asthma symptoms vary widely among children. Some cough all night but are symptom-free during the day, while others seem to get frequent chest colds that just wont go away.
Children have very small, narrow airways, and can wheeze when they have a viral infections. First episodes of cough, runny nose and fever that happen in cold and flu season is likely not asthma. If your child has several more episodes of wheeze and cough, it is more likely to be asthma. The most common cause of asthma in infants and children under three years of age is a cold. Even after the cold is gone, asthma symptoms and airway swelling can last for several weeks.
Don’t Miss: Anaphylaxis Military Waiver
Which Children Are Most Likely To Develop Asthma
Certain risk factors make some children more likely to develop asthma.
Heredity. To some extent, asthma seems to run in families. Children whose brothers, sisters, or parents have asthma are more likely to develop the illness themselves. If both parents have asthma, the risk is greater than if only one parent has it. For some reason, the risk appears to be greater if the mother has asthma than if the father does.
Atopy. A child is said to have atopy when he or she is prone to developing allergies. Being atopic causes the body to respond to allergens by producing an antibody known as immunoglobulin E antibodies. Substances in the environment that cause an allergic reactionsuch as pollen, mold, or animal danderare known as allergens. When the body of an atopic child is stimulated by an allergen, IgE molecules are made that recognize and bind to the allergen. Once IgE molecules are made, they bind to the surface of cells capable of releasing the chemicals that cause allergic reactions. At this point, the child is sensitized to the allergen. Encountering the allergen again leads to binding of the allergen to IgE molecules on the cell surface and this interaction triggers the cells to release the chemicals that cause an allergic reaction.
Keeping Your Childs Asthma Action Plan Up To Date
Your childs asthma action plan helps you control your childs asthma symptoms. It tells you what medicines your child needs to take and how often, as well as what to do if their symptoms get worse.
If your child was using one before they were diagnosed, nows the time to ask your childs GP or asthma nurse to update it if they need to.
If your child has not started using an action plan yet, you can find out more about them and download one here. Book an appointment with your childs GP or asthma nurse so you can get their action plan filled in.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Asthma Inhalers For Free
What We Know About Asthma And Covid
Asthma is a pre-existing lung condition affecting 1 in 13 people in the U.S. It can cause wheezing, chest tightness, coughing, and shortness of breath. Asthma can be controlled by taking medications and avoiding triggers.
COVID-19 is a respiratory disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The virus affects cells in the airways, from the nose and throat down to the deepest parts of the lungs. In the nose and throat it might cause symptoms of a cold. In the upper airways, it might cause some breathlessness and cough. When the coronavirus lodges itself deep in the lungs, this is when things can start to get serious. Here, the coronavirus commonly causes a double lung infection, or bilateral pneumonia.
Interestingly, research so far does not suggest any link between having asthma and getting a more severe COVID-19 illness, or between asthma and coronavirus deaths.
Whether this is because the SARS-CoV-2 virus doesnt affect people with asthma in the same way as other respiratory viruses, or because there simply isnt enough data yet, remains to be seen.
Recommended Reading: Is Asthma Worse In Cold Weather
Will Your Child Outgrow Asthma
Once a person’s airways become sensitive, they remain that way for life. About half of the children who have asthma have a noticeable decrease in symptoms by the time they become adolescentsâtherefore, appearing to have “outgrown” their asthma. However, about half of these children will develop asthma symptoms again in their 30s or 40s. Unfortunately, there is no way to predict whose symptoms will decrease during adolescence and whose will return later in life.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/01/2019.
References
Recommended Reading: Treatment For High Eosinophils
Which Children Are At Risk For Asthma
Certain factors raise the risk of asthma in children:
- Being exposed to secondhand smoke when their mother is pregnant with them or when they are small children
- Genetics and family history. Children are more likely to have asthma if one of their parents has it, especially if its the mother.
- Race or ethnicity. Black and African Americans and Puerto Ricans are at higher risk of asthma than people of other races or ethnicities.
- Having other medical conditions such as allergies and obesity
- Often having viral respiratory infections as young children
- Sex. In children, asthma is more common in boys. In teens, it is more common in girls.
Signs And Symptoms Of Childhood Asthma
Not all children have the same asthma symptoms. A child may even have different symptoms from one episode to the next. Signs and symptoms of asthma in children include:
- A cough that doesnât go away
- Coughing spells that happen often, especially during play or exercise, at night, in cold air, or while laughing or crying
- A cough that gets worse after a viral infection
- Less energy during play, and stopping to catch their breath during activities
- Avoiding sports or social activities
- Tight neck and chest muscles
- Feeling weak or tired
- Trouble eating, or grunting while eating
Your child’s doctor should check out any illness that makes it hard for them to breathe.
Experts sometimes use the terms âreactive airways diseaseâ and âbronchiolitisâ when talking about wheezing with shortness of breath or coughing in infants and toddlers. Tests may not be able to confirm asthma in children younger than 5.
When to get emergency care
A severe asthma attack needs medical care right away. Watch for these signs:
- Stopping in the middle of a sentence to catch a breath
- Using stomach muscles to breathe
- A belly that sinks in under their ribs when they try to get air
- Chest and sides that pull in as they breathe
- Severe wheezing
Read Also: What To Do If You Have Asthma And A Cold
The Burden Of Childhood Asthma
Childhood asthma is common in the Western world and underdiagnosed in minority populations in Europe and the United states. Minority populations are significantly burdened by asthma morbidity and suffer higher rates of emergency department visits, hospitalization, and even death . Quality of life in childhood asthma is affected by asthma control. The better the asthma control, the better the QoL is. Uncontrolled asthma is associated with a reduced lung function, impaired performance in physical exercise, and impaired QoL .
Most asthma symptoms occur at night. Almost half of asthmatic children presenting at a university hospital outpatient clinic suffered from nocturnal symptoms . Nocturnal symptoms cause loss of sleep . Even in children with stable asthma, quality of sleep is diminished . Sleep disruption influences daily activities, such as school attendance and performance. Nocturnal awakening may also cause parental work absenteeism, and may disrupt family life . More severe asthma leads to more frequent school absenteeism which may negatively affect an individual’s level of education and, possibly, choice of career. Furthermore, frequent nocturnal awakenings may cause depression, aggressive behaviour, and attention problems in adulthood .
What To Expect When You Visit The Doctor
Your doctor may ask whether you have any family history of asthma, eczema or hay fever.
In children, doctors assess the severity of the asthma based on the pattern and frequency of the symptoms.
Lung function tests are difficult to perform in children younger than 5 years and so are usually only used to diagnose and assess severity in children 5 years and older.
It is recommended that a paediatrician or paediatric respiratory specialist diagnose and manage asthma in infants under 12 months. If your infant is wheezing your doctor should refer to you one of these specialists.
Don’t Miss: Asthma Sputum
