Patients At Risk For Severe Asthma Exacerbations
Careful consideration should be carried out in patients with risk factors for severe asthma exacerbations. Patients with exacerbations that led to endotracheal intubation, previous admissions to the ICU, a history of multiple hospitalizations in the past year or multiple emergency department visits in the past month, the need of chronic oral corticosteroids use, poor access to health care, and frequent use of rescue inhalers are considered to have increased risk of severe asthma exacerbations and death. Patients with asthma and with these characteristics should be evaluated promptly and treated expeditiously. In addition, a minority of patients with asthma may experience a significant decline in lung function without a change in symptoms. These under-perceivers are at higher risk for near-fatal exacerbations. This article focuses on the approach to manage exacerbations of asthma.
Treatment Of Acute Asthma Exacerbations
, DO, Wake Forest Baptist Health
The goal of asthma exacerbation treatment is to relieve symptoms and return patients to their best lung function. Treatment includes
Corticosteroids Leukotriene modifiers Mast cell… read more .)
Patients having an asthma exacerbation are instructed to self-administer 2 to 4 puffs of inhaled albuterol or a similar short-acting beta agonist up to 3 times spaced 20 minutes apart for an acute exacerbation and to measure peak expiratory flow if possible. When these short-acting rescue drugs are effective , the acute exacerbation may be managed in the outpatient setting. Patients who do not respond, have severe symptoms, or have a PEF persistently & lt 80% should follow a treatment management program outlined by the physician or should go to the emergency department .
Allergies And Bronchial Asthma
Allergies are a major trigger of bronchial asthma. Inhaling certain substances called allergens can trigger an allergic reaction, causing your airways to become irritated, inflamed, and swollen.
Swelling and inflammation narrow the opening that air passes through, making it more difficult to breathe. Wheezing sounds and coughing are common symptoms that can develop with an allergic asthma attack.
Many allergens can lead to an asthma attack. Food allergies and allergic skin reactions are linked to a higher risk of asthma.
Read Also: Do Essential Oils Trigger Asthma
What Causes Asthmatic Bronchitis
There are many triggers that may initiate the release of inflammatory substances. Common asthmatic bronchitis triggers include:
- Chest tightness
- Excess mucus production
You might wonder, is asthmatic bronchitis contagious? Bronchitis itself can be caused by a virus or bacteria, which are contagious. However, chronic asthmatic bronchitis typically is not contagious.
Bronchial Asthma: Symptoms Triggers And More
Reza Samad, MD, is a board-certified pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine in New Jersey.
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects your breathing. All types of asthma impact the tubes that move air in and out of your lungs, called bronchial tubes or bronchi. These tubes become swollen and inflamed in people with asthma, earning this condition its name.
This article will explore the different asthma types, what sets them apart, and how to manage them.
Westend61 / Getty Images
You May Like: How Do Hospitals Treat Asthma Attacks
Mild To Moderate Attack
- Reassure the patient place him in a 1/2 sitting position.
- salbutamol : 2 to 4 puffs every 20 to 30 minutes, up to 10 puffs if necessary during the first hour. In children, use a spaceraCitation a.If a conventional spacer is not available, use a 500 ml plastic bottle: insert the mouthpiece of the inhaler into a hole made in the bottom of the bottle . The child breathes from the mouth of the bottle in the same way as he would with a spacer. The use of a plastic cup instead of a spacer is not recommended .to ease administration . Single puffs should be given one at a time, let the child breathe 4 to 5 times from the spacer before repeating the procedure.
- prednisolone PO: one dose of 1 to 2 mg/kg
Management And Treatment Of Acute Asthma
While chronic asthma has no cure, it can be controlled. With proper management and treatment, the occurrence of acute asthma attacks can be minimized.
An asthma treatment plan will be two-pronged: control of chronic asthma and treatment of acute asthma symptoms. Together, these two paths will help minimize the chances of attacks and make them easier to deal with when they do occur.
Typical acute asthma treatments include:
Also Check: Does Ibuprofen Cause Asthma Attacks
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Asthma
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including information about your parents and siblings. Your provider will also ask you about your symptoms. Your provider will need to know any history of allergies, eczema and other lung diseases.
Your provider may order spirometry. This test measures airflow through your lungs and is used to diagnose and monitor your progress with treatment. Your healthcare provider may order a chest X-ray, blood test or skin test.
Clenbuterol For Treatment Of Acute Bronchial Asthma
Clenbuterol is a steroid-like drug used as a bronchodilator and decongestant by those suffering from breathing disorders. It relaxes the smooth muscle tissue in the airways to allow for freer breathing. Clenbuterol relaxes and widens the smooth muscles in the airways to improve breathing. It also increases the volume of oxygen in the blood.
You May Like: How To Control Your Asthma
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
In many countries, including the US, asthma kills one out of every 100,000 persons. The worse the lung function, the higher the mortality. In addition, mortality has also been linked to poor management and lack of medication compliance, especially in young people. Other factors that increase the risk of death include smoking and use of illicit drugs.
Asthma also results in millions of school and workdays lost. In the US alone, close to 2 million asthmatics seek regular care in the emergency department, which also increases the costs of healthcare.
Even though asthma is a reversible disorder, poor lifestyle and lack of management can lead to airway remodeling that leads to chronic symptoms, which are disabling.
The disorder has no cure, and thus life long monitoring is necessary. For best outcomes, an interprofessional approach is recommended.
Evidence-based Medicine
Many evidence-based asthma plans are available for the management of asthma and should be handed out to patients. Finally, nurses also play a vital role in school-based asthma education programs that can help improve self-esteem, knowledge, and self-management behaviors.
Outcomes
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Asthma
People with asthma usually have obvious symptoms. These signs and symptoms resemble many respiratory infections:
- Chest tightness, pain or pressure.
With asthma, you may not have all of these symptoms with every flare. You can have different symptoms and signs at different times with chronic asthma. Also, symptoms can change between asthma attacks.
Read Also: What To Do When Someone Is Having An Asthma Attack
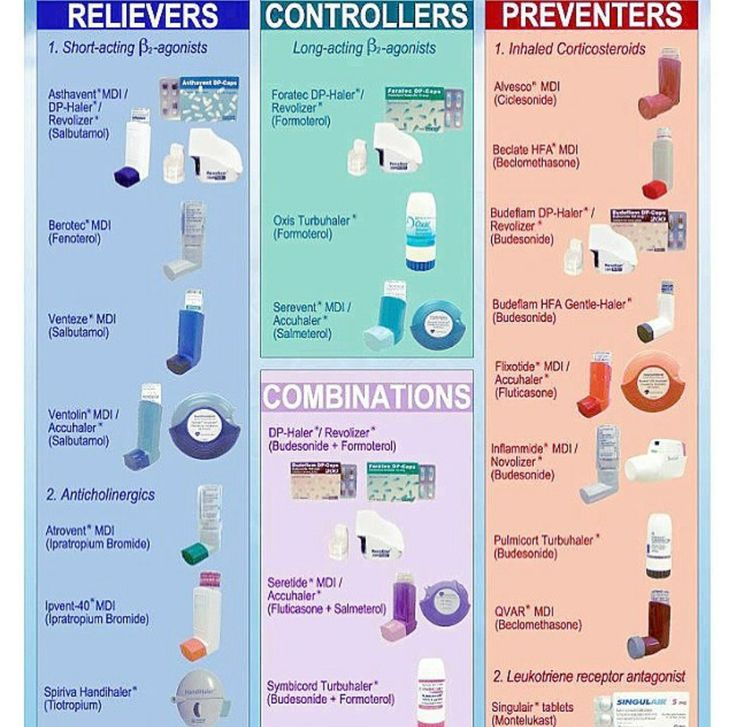
What Asthma Treatment Options Are There
You have options to help manage your asthma. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to control symptoms. These include:
- Bronchodilators: These medicines relax the muscles around your airways. The relaxed muscles let the airways move air. They also let mucus move more easily through the airways. These medicines relieve your symptoms when they happen and are used for intermittent and chronic asthma.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines: These medicines reduce swelling and mucus production in your airways. They make it easier for air to enter and exit your lungs. Your healthcare provider may prescribe them to take every day to control or prevent your symptoms of chronic asthma.
- Biologic therapies for asthma: These are used for severe asthma when symptoms persist despite proper inhaler therapy.
You can take asthma medicines in several different ways. You may breathe in the medicines using a metered-dose inhaler, nebulizer or another type of asthma inhaler. Your healthcare provider may prescribe oral medications that you swallow.
Working On A Manuscript

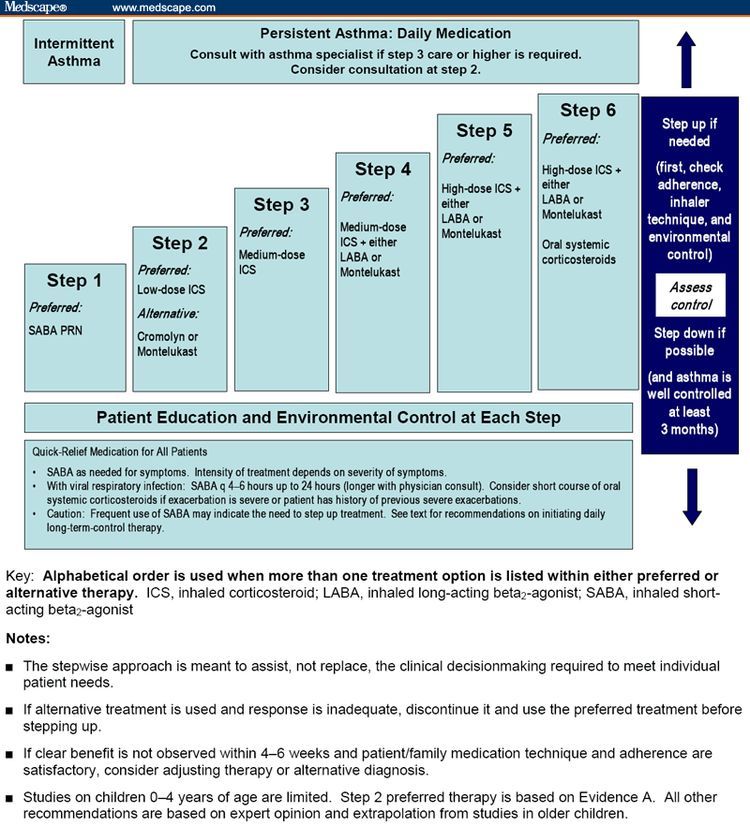
Advances in the knowledge of clinical pharmacology and pulmonary physiology have significantly improved the management of asthma in children and adolescents. However, asthma prevalence, morbidity and mortality continue to increase in most countries .
Fig. 1
In the US, children with asthma incur an average yearly healthcare expenditure of $1128 ± $5310 compared with $468 ± $2960 for children without asthma. The purpose of this review is to examine the multiple alternatives available to treat the hospitalised child with acute severe asthma, and approaches to reduce the medical, economic and emotional burdens of this condition by the immediate use of aggressive and reliable pharmacological treatments.
Prior to a discussion of drug therapies, it is necessary to understand the indications for hospitalisation, intensive care unit admission, and the institution of mechanical ventilation so as to triage the asthmatic child to an appropriate treatment facility .
Table I
Also Check: How Does Asthma Affect The Lungs And Stomach
When To Visit A Doctor
Any unexplained or severe difficulty in breathing could be a potentially serious issue. Weve discussed a number of conditions that can result in such difficulties, and consulting with a doctor as soon as possible after it happens will help determine the underlying cause.
If youve already been diagnosed with asthma and have an attack that does not improve with your rescue inhaler, see a doctor immediately. If you notice your symptoms worsening, make an appointment as soon as possible.
Definition Epidemiology And Background
Asthma is a common, chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by paroxysmal or persistent symptoms and is associated with airflow limitation and airway hyper-responsiveness . Canadian experts have proposed that asthma can be diagnosed in children as early as 1 year of age, if presenting with frequent asthma-like symptoms or recurrent exacerbations reversible with salbutamol with no other alternative diagnosis . Asthma is the most common chronic disease in young people. The general prevalence of asthma in Canada has been estimated at 10%, but is higher in children and youth, including their Indigenous peers -. Asthma exacerbations are a frequent cause of emergency department visits and hospitalizations in children , and asthma is the leading cause of absenteeism from school . Preschool age children with asthma represent more than 50% of consultations in the ED . In one Alberta study, nearly 10% of paediatric ED visits resulted in admission, with one death for every 25,000 ED visits .
Many health care centres, along with national and international associations, have developed practice guidelines for the assessment and management of acute asthma exacerbations -. This statement specifically addresses the management of acute asthma exacerbations in paediatric patients with a known diagnosis of asthma, including preschoolers whose pattern of symptoms suggests likelihood for asthma or suspected asthma .
You May Like: Does Black Coffee Help With Asthma
Acute Asthma: Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Asthma is a condition that results in the swelling and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. When you have an asthma attack, you will have difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing.
Asthma can be an acute condition or a chronic one. This post will discuss the former, telling you everything you need to know about what causes acute asthma, how it is diagnosed, and what you and your doctor can do about it.
Have you considered clinical trials for Asthma?
We make it easy for you to participate in a clinical trial for Asthma, and get access to the latest treatments not yet widely available – and be a part of finding a cure.
Causes And Types Of Asthma
An asthma diagnosis means you have chronic swelling and inflammation in the bronchioles. Also referred to as wheezing or bronchial asthma, this condition can run in families or be triggered by allergies and irritants.
There are different types of asthma, which are classified by the cause of the condition or what triggers symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Best Air Purifier For Asthma
Can Acute Asthma Be Prevented
With proper care, you can learn the triggers that cause your acute asthma attacks and try to avoid them.
Because it might not always be possible to avoid the triggers, your doctor will likely provide you with a rescue inhaler that can help restore you to normal breathing should you feel an asthma attack coming on.
What Should I Do If I Have A Severe Asthma Attack
If you have a severe asthma attack, you need to get immediate medical care.
The first thing you should do is use your rescue inhaler. A rescue inhaler uses fast-acting medicines to open up your airways. Its different than a maintenance inhaler, which you use every day. You should use the rescue inhaler when symptoms are bothering you and you can use it more frequently if your flare is severe.
If your rescue inhaler doesnt help or you dont have it with you, go to the emergency department if you have:
- Anxiety or panic.
- Bluish fingernails, bluish lips or gray or whitish lips or gums .
- Chest pain or pressure.
- Very quick or rapid breathing.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Flare Up
Management Of Status Asthmaticus In The Icu
Patients admitted to the ICU include individuals who require ventilator support or those with severe asthma for whom therapy failed. Most often they have refractory hypercapnia, persisting or worsening hypoxemia, deteriorating PEF/FEV1, drowsiness, confusion, or impending signs of respiratory arrest. Elective intubation by an experienced clinician is always recommended as soon as signs of deterioration are present. Intubation and mechanical ventilation may lead to hypotension and barotrauma secondary to high positive intrathoracic pressures. Care must be taken to assure that intravascular volume is adequate before intubation, and a bolus of intravenous normal saline solution is often recommended before initiation of mechanical ventilation.
Although there are no studies that determined the optimal mode of mechanical ventilation, it seems prudent to use the mode with which one is most familiar. Most researchers have recommended an initial minute ventilation of 90130 mL/kg ideal body weight , with further adjustments based on pH and the plateau airway pressure. Based on studies by Tuxen and Lane and Peters et al, we usually use a tidal volume of 89 mL/kg with a breathing frequency of 1014 breaths/min, a flow of 100 L/s, and 0 PEEP. However, many institutions prefer to use tidal volumes of 68 mL/kg ideal body weight., We adjust the setting to maintain a plateau pressure of 30 cm H2O and judiciously adjust ventilator-applied PEEP based on its ability to lower intrinsic PEEP.
Therapy In The Emergency Department
Patients with mild-to-moderate asthma exacerbations may present to the emergency department to seek medical care. These patients should be treated as an out-patient when following the recommendation detailed above. Patients with severe or life-threatening asthma should always be managed in the emergency department. A focused, expedited history and physical examination should be carried out in all patients. It is critical to rule out other conditions that may mimic a severe asthma exacerbation, such as pneumonia, congestive heart failure, pneumothorax, and myocardial infarction. In patients with a severe exacerbation, careful attention should be placed on the level of consciousness, oxygen saturation, breathing frequency, resting pulse, and blood pressure, and on the use of accessory respiratory muscles. Patients with severe asthma may have a fast deterioration of their clinical presentation, so continuous monitoring of these patients is warranted. In the advanced stages of an asthma exacerbation, the pulmonary physical examination may reveal a silent chest, which may herald impending respiratory failure. Patients with severe asthma should also be monitored for potential complications of asthma, such as pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, and anaphylaxis.
Don’t Miss: How To Fill Out Asthma Action Plan
What Are The Symptoms Of Asthmatic Bronchitis
Symptoms of asthmatic bronchitis are related to inflammation in the lungs airways and can vary in intensity among individuals.
Asthmatic bronchitis can cause both symptoms of bronchitis and worsened symptoms of asthma.
You may experience asthmatic bronchitis symptoms daily or just once in a while. At times, any of these asthma symptoms can be severe.
Symptoms of bronchitis with asthma include:
- coughing, either with or without mucus
- chest pain or pressure
- shortness of breath or rapid breathing
Acute Asthma Prognosis And Treatment
Most recent update: July 2021Originally Posted: September 2004
Division of Allergy and Immunology,University of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL 33612
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector, Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair in Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida Morsani College of MedicineJames A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalEmail: rlockey@health.usf.edu
Michael A. Kaliner, MD FAAAAIMedical Director, Institute for Asthma and AllergyChevy Chase and Wheaton, MarylandProfessor of Medicine, George Washington University School of MedicineWashington, DC
Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Public HealthDirector of the Division of Allergy and ImmunologyJoy McCann Culverhouse Chair of Allergy and ImmunologyUniversity of South Florida College of Medicine and the James A. Haley Veterans’ HospitalTampa, FL
Abstract
Key words: Asthma flare Acute asthma Asthma attack Wheezing Acute asthma diagnosis Acute asthma management
Abbreviations
EPR-3 – The Expert Panel Report 3EPR-4 The Expert Panel Report 4FeNO Fractional Exhaled Nitric OxideOCS – Oral corticosteroidsCOPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseasePEF – Peak expiratory flowSABA – Short acting beta agonistAE Adverse eventsFVC- Forced vital capacity
Introduction
1. Recognition of patients who are at a greater risk for near-fatal or fatal asthma.
Physical Examination
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Asthma
Also Check: What Does An Asthma Attack Sound Like
What Is The Difference Between Asthma And Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an infection in the bronchial tubes. Asthma is a long-term condition that causes the airways to narrow due to swelling in the muscle and membrane.
Bronchitis is a fixed inflammatory process that will always occur following infection. Asthma is a reversible inflammatory process that causes narrowing of the airway, as you can reverse it with certain inhaled medications.
Therefore, people with asthma have bronchial tubes that are more sensitive than those of people without asthma. This means that they are more likely to get infections in their bronchial tubes, or bronchitis.
Bronchitis, in turn, can also worsen the symptoms of asthma that a person may already experience.
