What Is An Asthma Flare Up
An asthma flare-up is when asthma symptoms start up or get worse compared to usual. The symptoms wont go away by themselves and need treatment.
These flare-ups can happen quite quickly but they can also come on gradually over hours or days .
The term asthma attack is confusing because it means different things to different people from a bout of wheezing after running for the bus through to being admitted to hospital for asthma.
An asthma flare-up can become serious if not treated properly, even in someone whose asthma is usually mild or well controlled. A severe flare-up needs urgent treatment by a doctor or hospital emergency department.
Signs Symptoms And Complications
How often signs and symptoms of asthma occur may depend on how severe, or intense, the asthma is and whether you are exposed to allergens. Some people have symptoms every day, while others have symptoms only a few days of the year. For some people, asthma may cause discomfort but does not interfere with daily activities. If you have more severe asthma, however, your asthma may limit what you are able to do.
When asthma is well controlled, a person shows few symptoms. When symptoms worsen, a person can have what is called an asthma attack, or an exacerbation. Over time, uncontrolled asthma can damage the airways in the lungs.
What Are The Treatments For Asthma
If you have asthma, you will work with your health care provider to create a treatment plan. The plan will include ways to manage your asthma symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. It will include
- Strategies to avoid triggers. For example, if tobacco smoke is a trigger for you, you should not smoke or allow other people to smoke in your home or car.
- Short-term relief medicines, also called quick-relief medicines. They help prevent symptoms or relieve symptoms during an asthma attack. They include an inhaler to carry with you all the time. It may also include other types of medicines which work quickly to help open your airways.
- Control medicines. You take them every day to help prevent symptoms. They work by reducing airway inflammation and preventing narrowing of the airways.
If you have a severe attack and the short-term relief medicines do not work, you will need emergency care.
Your provider may adjust your treatment until asthma symptoms are controlled.
Sometimes asthma is severe and cannot be controlled with other treatments. If you are an adult with uncontrolled asthma, in some cases your provider might suggest bronchial thermoplasty. This is a procedure that uses heat to shrink the smooth muscle in the lungs. Shrinking the muscle reduces your airway’s ability to tighten and allows you to breathe more easily. The procedure has some risks, so it’s important to discuss them with your provider.
Also Check: Does Weight Gain Make Asthma Worse
How Many People Have Asthma
One in every nine Australians have asthma around 2.7 million of us .
Its more common in males younger than 14 years. However, for people aged 15 years and over, it is more common in females .
The rate of asthma among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders is almost twice as high as that of non-Aboriginal Australians. This is even more marked in the older adult age group .
Asthma is more common in people living in socioeconomically disadvantaged areas .
The prevalence is significantly higher in people living in outer regional and remote areas compared to people living in major cities .
More than one in every two children who are younger than 15 years have a written Asthma Action Plan .
But fewer than one in every five people who are aged over 15 years have a written Asthma Action Plan . This is lowest for people aged 25-44 .
REFERENCES
Asthma Expert Professor John Price On The Questions To Ask
John Price, professor of paediatric respiratory medicine at Kings College London, answers the questions often asked by parents of children with asthma.
What do you think triggers my childs asthma?The triggers vary from child to child. In some children, colds trigger their attacks. In others, it can be exercise. Allergies may also be a big factor, and excitement, e.g. laughing and crying, may be another factor. Unfortunately, excitement at birthday parties is a well-known trigger of attacks.
Which treatments are available and how should my child take them? Some children should only take treatment when they wheeze. Others need to take treatment more regularly as a preventative measure, as well as when they wheeze. Children with persistent symptoms tend to need regular treatment to prevent asthma.
Where possible, your childs asthma should be treated with an inhaler. There are a couple of very good treatments that can be taken by mouth, but generally, the best treatments are taken with an inhaler. There are different inhalers for different ages, so ask your doctor or nurse which type of inhaler is most appropriate for your child.
Are the treatments safe? Largely, the treatments taken to relieve wheezing are very safe. The most commonly taken treatment is an inhaled steroid. If this is taken in a large dose, it can have side effects. If you’re worried about the dose your child is taking, talk to your doctor or nurse.
Don’t Miss: How To Calm Down Asthma Symptoms
What You Can Do
There is no one way to deal with your asthma, but there are some things you can do to improve how you live with asthma:
- Acknowledge and accept the feelings your asthma brings up. Facing your feelings head on can help you identify problems and ways to cope. Talk to your kids about how theyre feeling about their asthma, both in their daily lives and during an attack.
- Take an active role in taking care of yourself. Learn about your asthma and ask questions. Help your kids understand what asthma does. Just knowing whats happening can help you feel more in control.
- Teach others. Helping others understand asthma and how it works can help them better support you, help you feel included, and help you become an expert on your asthma.
- Ask for help.In 2011, 1 in 12 people suffered from asthma. Youre not alone. Your family and friends can be a wonderful team to support you and help you tackle stressful situations.
- Find a care provider you trust and feel comfortable with. Trusting your doctor and his treatment is an important part of overcoming stress caused by your asthma.
- Try relaxation exercises. Yoga, Pilates, meditation, deep breathing, muscle relaxation, and clearing negative thoughts can all help you reduce stress.
- Live a healthy lifestyle. Eating right, exercising, and getting a good nights sleep can help you recharge physically and emotionally, which can reduce stress and asthma attacks.
How Is Asthma Classified
Doctors rank how bad asthma is by its symptoms:
Your asthma may be getting worse if:
- You have symptoms more often and they interfere more with your daily life.
- You have a hard time breathing. You can measure this with a device called a peak flow meter.
- You need to use a quick-relief inhaler more often.
You May Like: Can A Humidifier Help With Asthma
Pollen And Its Effect On The Body
Part of a plants reproductive system, pollen consists of microscopic particles that must be transferred to various areas of a plants reproductive parts to produce viable seeds. Bees and other insects cross-pollinate plants, as well as wind. Pollen counts are based on how much pollen is in a cubic meter of air measured over 24 hours.
What does pollen do to your body? Pollen is responsible for many seasonal allergy symptoms, as well as asthma. Common sources of pollen-producing asthma come from plants such as ragweed, lambs quarters, Russian thistle, Kentucky bluegrass, Bermuda grass, Johnson and Timothy grasses, and various wind-pollinated trees like ash, elm, oak, hickory, box elder, pecan, and mountain cedar.
Research For Your Health
The NHLBI is part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health the Nations biomedical research agency that makes important scientific discovery to improve health and save lives. We are committed to advancing science and translating discoveries into clinical practice to promote the prevention and treatment of heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders, including asthma. Learn about the current and future NHLBI efforts to improve health through research and scientific discovery.
Also Check: How To Make A Homemade Inhaler For Asthma
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Asthma Attack
What Body Systems Are Affected By Asthma
Fact Checked
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects your ability to breathe. Wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and coughing are common asthma symptoms. According to the Centers for Disease Control, an asthma attack or episode can affect your respiratory system, immune system and nervous system 1.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
How Asthma Affects Your Body
Asthma is a disease that affects the airways of your lungs. With asthma, your airways’ lining tends to always be in a hypersensitive state characterized by redness and swelling . It’s similar to how your skin becomes red, irritated and sensitive after a sunburn. This hypersensitive state makes the airways react to things that you are exposed to every day, or asthma “triggers.” A trigger could be the common cold, stress, changes in the weather, or things in the environment, such as dust, chemicals, smoke and pet dander. Learn more about how the air we breathe plays a role in our health.
You May Like: Mast Cell Asthma
How Long Asthma Lasts For
Asthma is a long-term condition for many people, particularly if it first develops when you’re an adult.
In children, it sometimes goes away or improves during the teenage years, but can come back later in life.
The symptoms can usually be controlled with treatment. Most people will have normal, active lives, although some people with more severe asthma may have ongoing problems.
Homeostasis And Its Relation To Asthma
What is homeostasis? Like most medical terms, theres a dictionary definition, but thats not always very helpful in understanding what a concept actually looks like and how it operates in the body. Biology dictionaries define homeostasis as the tendency of an organism or a cell to regulate its internal conditions, usually by a system of feedback controls, so as to stabilize health and functioning, regardless of the outside changing conditions. In terms of asthma, homeostasis refers to your bodys respiratory system functioning correctly without increases in inflammation or other parts of the pathophysiology of asthma negatively impacting you. If that definition seems overly complicated and contrived, dont worry, we will be discussing what it means and how it relates to the body thoroughly.
Recommended Reading: Can You Join The Reserves With Asthma
Read Also: Does A Humidifier Help Asthma
How Do Your Airways Work When You Have Asthma
When you have asthma, your airways arent able to function as well as they should.
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
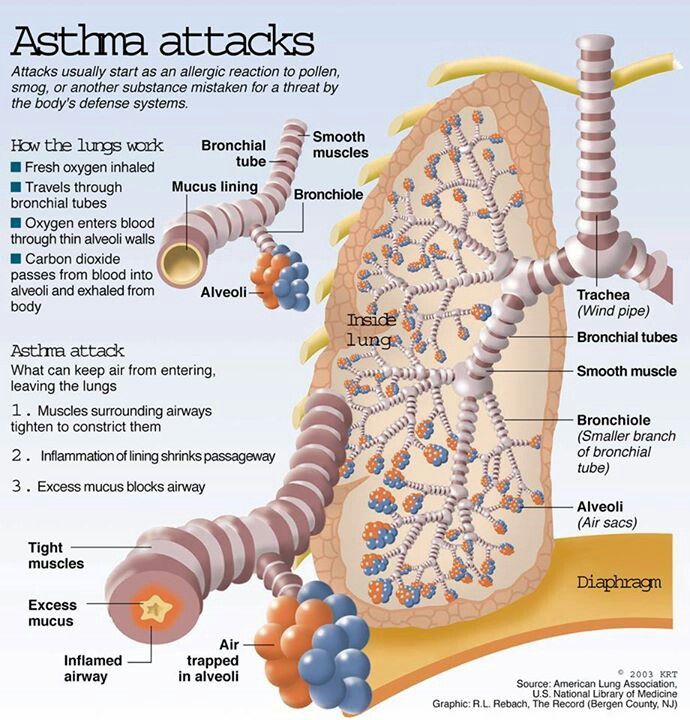
Asthma causes inflammation, or swelling, in the lungs. It can also cause squeezing, called bronchoconstriction , and extra sensitive or twitchy airways.
When something bothers your airways, you have trouble breathing. This is called an asthma attack or episode. It gets harder to breathe because the tiny muscles around your airways squeeze tightly and they have swelling inside.
Your airways will make more mucus inside your airways, which makes it even harder to breathe. These changes in your airways can cause coughing and wheezing.
There is no cure for asthma. But you can take steps to manage it. If you have asthma, its important to see an asthma specialist, like an allergist or pulmonologist, to come up with the right asthma treatment plan. Medicines and avoiding asthma triggers can help reduce swelling and relax tight muscles in your airways.
ASTHMA Care for Adults
Will I Always Have Asthma
Asthma is a lifelong condition most people who have asthma will always have asthma.
But if youve been diagnosed with asthma as a child, your asthma might improve or disappear completely as you get older, particularly if the asthma was mild.
Even if asthma goes away it can come back later in life, perhaps because youve come into contact with new triggers in your job, or youve moved to an area with more air pollution for example. Hormonal changes such as pregnancy and menopause can also bring it on again.
But the good news is that even though asthma doesnt go away there are lots of safe and effective treatments available to help you stay symptom-free.
If youve tried taking all the usual treatments in the right way, but youre still having symptoms, your GP can refer you to a specialist to see if you have severe asthma. This kind of asthma only affects around 4% of all people with asthma. An asthma specialist can help you find the right treatments for you, for example monoclonal antibodies.
You May Like: Asthma Inhalers Side Effects
What Happens During An Asthma Attack
Reviewed byDr Hayley Willacy
Asthma is a common condition that affects the smaller airways . From time to time the airways narrow in people who have asthma. The typical symptoms are wheeze, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. The extent of the narrowing, and how long each episode lasts, can vary greatly.
Dont Miss: How To Help A Child Having An Asthma Attack
What Is An Asthma Attack
An asthma attack is an exacerbation of asthma symptoms, during which a patients inflamed bronchial tubes prevent them from moving air in and out of their lungs. This episode may also be referred to as an asthma flareup. Regardless of what you call it, the symptoms are the same. Asthma attacks sometimes go on for several minutes at a time. If you have a more serious case of asthma or youve been consistently exposed to an asthma trigger, then the attack can continue for hours. At worst, some attacks can endure for days.
See related: How to Help a Person Having an Asthma Attack
You may have had asthma since childhood. Symptoms typically manifest in children five or younger. Sometimes laughing or crying can lead to an asthma attack in children, while other times its playing, excessive running, cold air and other weather shifts, scents such as perfume or smoke, and allergens such as pollen, dust mites or pet dander. Even being sick with a cold can cause asthma attacks.
In other instances, your job could trigger your feelings of breathlessness. This is known as occupational asthma, in which asthma attacks occur from breathing in dust, gases, fumes or other irritants. Allergic asthma can be exacerbated by said allergen, be that pollen or pet dander.
Don’t Miss: Complications Of Asthmatic Bronchitis
Asthma: How Does It Affect The Body
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition causing a combination of variable respiratory symptoms which may include but are not limited to wheezing, shortness of breath, cough and excessive variation in lung function .
People with asthma have hypersensitivity to triggers that may set off symptoms. Triggers commonly include cigarette smoke, pollen, exercise and dust mites .
People may experience flare-ups when symptoms start or worsen. These require treatment and may become serious medical events .
Some individuals may only experience symptoms when exposed to a trigger, but others may experience symptoms all of the time .
Asthma is considered a spectrum of conditions with several recognised phenotypes that vary in severity .
It is estimated to affect 1 in 10 adults and 1 in 9 children in Australia, causing about 400 deaths annually. Over 2.7 million Australians have asthma, including children and adults .
Although it cannot be cured, if managed properly, those with asthma should be able to enjoy unhindered lives .
Can You Outgrow Asthma
Some children with asthma stop having symptoms when they mature. By adolescence, 16% to 60% of children diagnosed with asthma seem to be in remission.
However, doctors don’t usually consider asthma “cured” since, even after years of living symptom-free, you could suffer an asthma attack at any time.
The wide range of remission statistics shows that studies have been inconsistent in their design, and more research is needed to fully understand how and why some children seem to “get over” asthma.
In some studies, children who were more likely to go into remission had asthma characterized as:
- Less atopic dermatitis
Male children are also more likely to go into remission.
If your childhood asthma appears to have gone away, it may still be a good idea to avoid triggers, especially allergy triggers, as they could cause symptoms to reappear.
Little to no research has followed adults who appear to have outgrown their childhood asthma, so there’s no clear picture of whether or not this reduces the risk of long-term health effects.
You May Like: Does Weight Gain Make Asthma Worse
What Does Asthma Do To The Body
You already know that the muscles in your lungs tighten during an asthma episode. The bronchial tubes may become swollen or otherwise irritated. What else does asthma do to the body? Thats a great question.
According to American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology, asthma causes a semi-permanent inflammation in the lungs airways. That means your airways are swollen and red. Theyre characterized as being in a hypersensitive state that can be irritated by any small trigger. Some of these triggers, outlined in Asthma Attacks: Triggers and Treatments, include pet dander, smoke, chemicals, dust, cold or warm weather, pollen, stress, and illness.
Unfortunately, its very normal for someone to be scared or fatigued after suffering an asthma attack. Even seconds of this frightening breathlessness can feel like hours, and your body needs time to recover from the shock of what happened.
Thats why you will have to take care of yourself in the days following an asthma attack. Your lungs are in a weakened state, which makes you more susceptible to a second or third attack. This risk is high over several days, so keep your asthma care a high priority.
