What About Nonprescription Products
From the above discussion, it should be apparent that thebest medical advice for asthma treatment is to use only those drugs thatare prescribed by your physician. However, you have probably seenadvertisements for nonprescription asthma medications such as Primatene,Bronkaid, and Asthmanefrin. What is their role?
Those caring for asthma patients can consult awell-accepted set of guidelines for asthma treatment written by theNational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute . The expert panel thatcreated these guidelines recommends safer and more effectiveprescription products for asthma and does not believe thatnonprescription products have any role in asthma treatment.
If you are using your prescription asthma medications asrecommended, you should never add OTC products to the regimen withoutchecking with your physician first. This will prevent unwanted sideeffects and will also ensure that the more effective prescriptionmedications work as directed.
If you decline to get your prescriptions filled and electto use the nonprescription products instead, you have made a riskydecision. They do not work as well, so your asthma may not becontrolled. They are less safe to use, and may cause unwanted sideeffects. Overall, it is far better to follow your physicians advice anduse your prescribed medications as directed.
Remember, if you have questions, Consult Your Pharmacist.
A New Nonprescription Asthma Product
Asthmanefrin Inhalation Solution is a new asthma product that contains the FDA-approved ingredient racepinephrine 2.25%.18,19The product consists of a bottle of liquid medication and a separatebattery-powered atomizer . Until HFA-pressurizedinhalers containing epinephrine return to the market, this is the onlynonprescription inhalation option for asthma treatment.
Racepinephrine acts in the same manner as othernonprescription bronchodilators, through relaxation of airway musclespasm, relieving shortness of breath. Nonprescription bronchodilatorsmay cause increased rate and force of the heart beat, hypertension,nervousness, sleepless-ness, and nausea or vomiting.20
What To Do If You Miss A Dose Of Bronkaid
-
Take a dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, wait until then and take a regular dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose.
-
Ask your pharmacist, doctor, or health caregiver about the best way to dispose of any outdated medicine or medicine no longer needed.
-
Keep all medicine out of the reach of children. Never share your medicine with anyone.
Also Check: Which Of The Following Are Associated With Extrinsic Asthma
Role Of The Pharmacist
As accessible health care professionals, pharmacists have an important role in increasing awareness of the chronic burden of intermittent asthma and the public health need for OTC treatment options that are available in the pharmacy.4
Bronkaid® Max and Primatene® Tablets are located behind the pharmacy counter, which ideally positions pharmacists to answer questions, provide education, and offer support to patients who are interested in treatment options for the temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma.4 Refer to the TABLE for information that can be used to discuss the available options.6-12
Pharmacists should be aware of the directions, warnings, and precautions in the Drug Facts labels. Several safety considerations can be reviewed on the Drug Facts label for each of the products. All 3 OTC asthma medications should not be taken with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor or if MAOIs were taken in the past 2 weeks.6-8 They should not be taken with food or beverages that contain caffeine or with supplements that have a stimulant effect.6-8
Importantly, pharmacists can ensure that these OTC options for asthma management are regularly stocked at the pharmacy to support populations with the self-management option.4
The Effect Of Other Drugs On Bronkaid Serum Concentration Measurements
Most serum Bronkaid assays in clinical use are immunoassays which are specific for Bronkaid . Other xanthines such as caffeine, dyphylline, and pentoxifylline are not detected by these assays. Some drugs , however, may interfere with certain HPLC techniques. Caffeine and xanthine metabolites in neonates or patients with renal dysfunction may cause the reading from some dry reagent office methods to be higher than the actual serum Bronkaid concentration.
Also Check: Asthma Social Determinants Of Health
Which One Should I Choose
Everyones body reacts differently to medications. It might be that your body responds better to Primatene or Bronkaid. Your doctor will recommend the drug that is likely to be better for you based on your own medical history and severity of asthma symptoms.
Since one Primatene tablet contains half the amount of active ingredients as Bronkaid, this gives you a bit more flexibility in taking less amount of the drug in situations where your symptoms may not be too severe. However, you should always check with your doctor on the dosage that is right for you and whether you should take one or two tablets of Primatene per dose.
Other factors on which medication you should choose will depend on other medications that you currently take, and whether you have a history of high blood pressure or heart problems.
Recent Otc Developments In Asthma
W. Steven Pray, PhD, DPhBernhardt Professor, Nonprescription Products and DevicesCollege of Pharmacy
Gabriel E. Pray, PharmD CandidateCollege of PharmacyWeatherford, Oklahoma
US Pharm
Pharmacists fill numerous prescriptions for asthmaproducts in a typical week. Occasionally, patients also ask aboutnonprescription products. It is vital for the pharmacist to understand the role of OTC asthma products in order to render proper advice.
Don’t Miss: Nursing Interventions For Asthma Exacerbation
The Status Of Combination Ephedrine Tablets
Patients may ask the pharmacist whether nonprescriptionephedrine combination products are appropriate for their asthma. It isimportant to stress that the bronchodilators ephedrine, epinephrine, andracepinephrine are all FDA approved for self-treatment of asthma as ofthis writing.4 Despite the FDA approval of these products,there are issues with their use. First, federal law made ephedrine aSchedule V controlled substance to limit its availability and to helpstop production of methamphetamine. Second, currently available products include guaifenesin, whichis not FDA approved for any use in asthma.4
On the Primatene Tablets Web site, under a Frequently Asked Questions page, the question What is an expectorant? appears.5The answer fails to provide any asthma-related justification for itsinclusion, only providing a narrow description of the use ofexpectorants in facilitating removal of sputum from the respiratorytract.
A further issue with ephedrine-guaifenesin combination tablets involves the widely accepted Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma developed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute , last updated in 2007.6,7In its treatment section, there were no circumstances in which eitherephedrine or guaifenesin is recommended for patients with asthma.
Labels Of Nonprescription Asthma Products
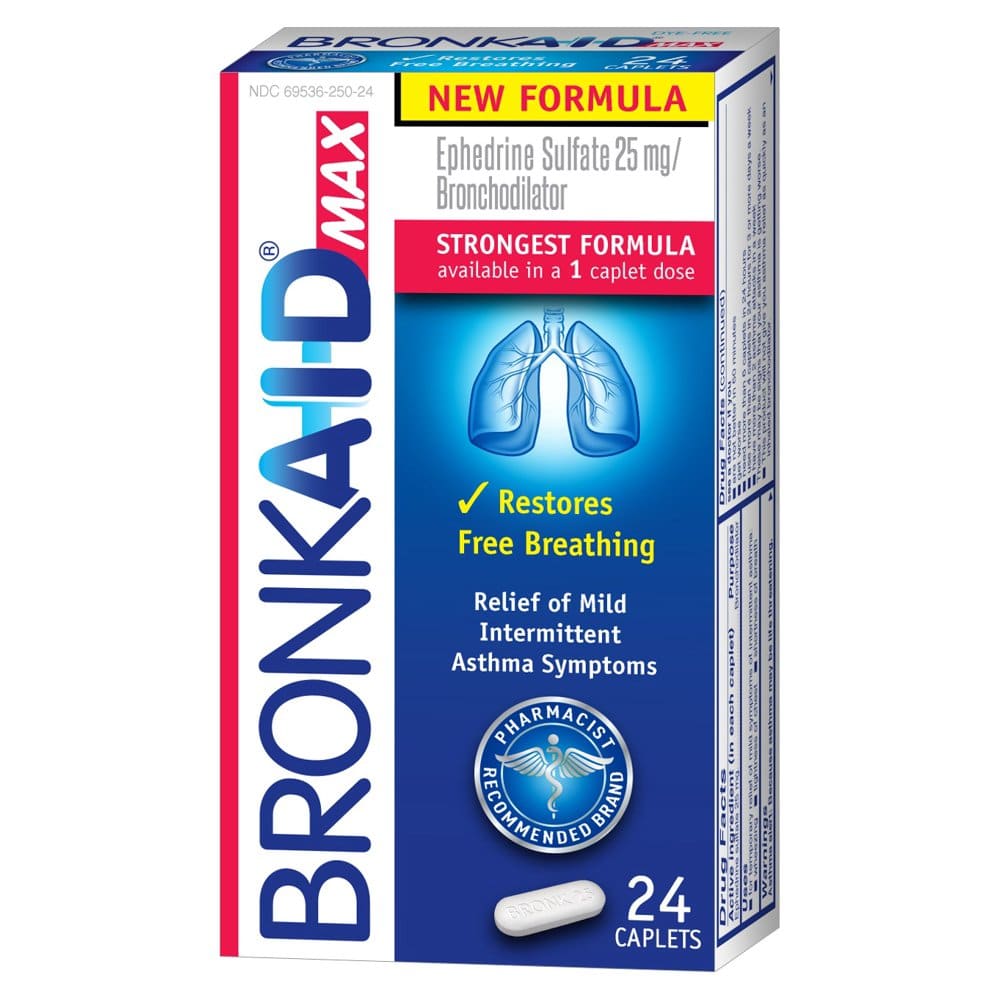
The labels of Primatene Tablets, Bronkaid Caplets, andAsthmanefrin Inhalation Solution carry important instructions that thepharmacist should be thoroughly familiar with when patients attempt topurchase these products.19,21,22
The indications for nonpre-scription asthma products arefor temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma, such aswheezing, tightness of the chest, and shortness of breath. Since thetablets/caplets contain guaifenesin as well, the products also carrylabeling that they help loosen phlegm and thin bronchialsecretions to rid the bronchial passageways of bothersome mucus and makecoughs more productive.21,22 Bronkaid labels add that guaifenesin acts to drain the bronchial tubes.21
The maximum-use point for Asthmanefrin Inhalation Solutionbeyond which a physician should be consulted is more than 12inhalations in 24 hours or more than 9 inhalations in 24 hours for 3 ormore days a week.19
Patients are cautioned not to use OTC bronchodilatorsunless a physician has diagnosed asthma. There is also a notificationnot to use them if the patient is currently taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor or has stopped taking it within the past 2 weeks. TheAsthmanefrin labels warn against use if the solution is brown or cloudy.Bronkaid Tablets warn against use if the patient is allergic to any ofthe ingredients. All labels request that female patients ask a healthprofessional before use if they are pregnant or breastfeeding.19,21,22
Don’t Miss: A Hunter May Have Allergies Asthma A Heart Condition
Truth Behind Primatene And Bronkaid
- Thread starter123rock
Bronkaid contains 63.24% of pure ephedrine and 36.76% sulfate ions.Primatene contains 81.92% of pure ephedrine and 18.08% hydrogen chloride ions.
Think you may be a little off on your math, I just did it myself:asthmaHowever, has483mg has around 615mg EphedrineFor me, I’ll definitely stick with Bronkaid because I like saving some money!
Conditions That Reduce Bronkaid Clearance
There are several readily identifiable causes of reduced Bronkaid clearance. If the total daily dose is not appropriately reduced in the presence of these risk factors, severe and potentially fatal Bronkaid toxicity can occur. Careful consideration must be given to the benefits and risks of Bronkaid use and the need for more intensive monitoring of serum Bronkaid concentrations in patients with the following risk factors:
- Fever 102° for 24 hours or more or lesser temperature elevations for longer periods
- Liver disease cirrhosis, acute hepatitis
- Reduced renal function in infants < 3 months of age
Cessation of Smoking
Also Check: How To Treat Asthma Wheezing
Role Of Otc Asthma Medications In The Community Pharmacy
This article was sponsored by Foundation Consumer Healthcare.
Of the approximately 25 million Americans with asthma, 20 million are adults aged 18 years and older.1 Asthma severity is classified into 4 groups: intermittent, persistent-mild, persistent-moderate, and persistent-severe.2 In the United States, nearly 65% of adults have persistent asthma and 35% have intermittent asthma.3 Intermittent asthma is defined as acute or subacute bouts of gradually intensifying cough, chest tightness, wheezing, and shortness of breath for 2 or fewer days per week and awakening from these symptoms 2 or fewer times per month as recalled by the patient or caregiver.2
Although it is the least severe asthma classification, adults with intermittent asthma with mild symptoms are still at risk of asthma exacerbations .2 Intermittent asthma is a chronic illness that usually requires ongoing management throughout adulthood for those who may have been diagnosed during childhood.2
As accessible health care professionals, pharmacists can recognize potential challenges and barriers to asthma care as well as provide counseling and access to OTC medications that are available for the management of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma.
Barriers To Ongoing Asthma Care In Specific Populations
Patients with well-managed intermittent asthma typically receive an asthma management plan from their care team and appropriate prescription medicines. The goals of asthma management are to reduce asthma symptoms , reduce the number of asthma episodes or attacks, prevent emergency health care visits, and reduce the need for quick relief therapy.2
However, not all patients who receive a diagnosis of intermittent asthma have access to ongoing medical care or prescription medications that are needed for the management of their condition.4 This population may not have adequate medical insurance coverage for regular visits to a pulmonologist or prescription drug coverage for needed prescription medications.4 Also, patients may not take their condition seriously, may not follow their treatment plan, or may forget to carry their rescue inhaler at all times.4
Intermittent asthma that is undertreated or not well-managed is associated with potentially serious health risks and substantial health care and financial burdens that impact those with asthma, their families, and the public health care system overall.4 Undertreated asthma can cause sleep disturbance, tiredness during the day, and poor concentration. Moreover, this can lead to missed days of school and work.5 The clinical and economic implications associated with asthma attacks can include increased patient morbidity and health care resource utilization , which drive the total costs of asthma care.4
Read Also: Which Child Is More Likely To Develop Asthma
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects: Category C
In studies in which pregnant mice, rats and rabbits were dosed during the period of organogenesis, Bronkaid produced teratogenic effects.
In studies with mice, a single intraperitoneal dose at and above 100 mg/kg during organogenesis produced cleft palate and digital abnormalities. Micromelia, micrognathia, clubfoot, subcutaneous hematoma, open eyelids, and embryolethality were observed at doses that are approximately 2 times the maximum recommended oral dose for adults on a mg/m2 basis.
In a study with rats dosed from conception through organogenesis, an oral dose of 150 mg/kg/day produced digital abnormalities. Embryolethality was observed with a subcutaneous dose of 200 mg/kg/day .
In a study in which pregnant rabbits were dosed throughout organogenesis, an intravenous dose of 60 mg/kg/day , which caused the death of one doe and clinical signs in others, produced cleft palate and was embryolethal. Doses at and above 15 mg/kg/day increased the incidence of skeletal variations.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Bronkaid should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Drug Facts And Warnings
Due to the fact that the caplets take time to be absorbed into the body, they provide relief much more slowly as compared to an inhaled bronchodilator. Since asthma can be a life-threatening disorder, there are several warnings. If you take a caplet and you do not feel better within one hour or you get even worse, seeing a doctor is highly recommended. If you need more than 6 tablets in 24 hours, are you need to use more than 4 tablets in 24 hours for 3 or more days a week your asthma may be getting worse. Apart from this, if you are taking prescription drugs for asthma, obesity, weight control, depression or psychiatric or emotional conditions, using this medicine is not recommended.
When using this product, your blood pressure or heart rate may rise. This could possibly increase your risk of heart attack or stroke. Your risk of suffering a heart attack or stroke increases if you have a history of high blood pressure, if you take this product more frequently or take more than the recommended dose. It is recommended that anybody who takes this medicine reference from consuming foods and beverages that contain caffeine and avoid dietary supplements containing ingredients that may have a stimulant effect.
Also Check: How Does Asthma Affect The Kidneys
Monitoring Serum Bronkaid Concentrations
Serum Bronkaid concentration measurements are readily available and should be used to determine whether the dosage is appropriate. Specifically, the serum Bronkaid concentration should be measured as follows:
- When initiating therapy to guide final dosage adjustment after titration.
- Before making a dose increase to determine whether the serum concentration is sub-therapeutic in a patient who continues to be symptomatic.
- Whenever signs or symptoms of Bronkaid toxicity are present.
- Whenever there is a new illness, worsening of a chronic illness or a change in the patients treatment regimen that may alter Bronkaid clearance .
Saliva concentrations of Bronkaid cannot be used reliably to adjust dosage without special techniques.
Bronkaid For Weight Loss
Bronkaid is a drug containing ephedrine sulfate, intended for relief of asthma symptoms. It is legal to buy it at pharmacies in the US, which makes it different from ephedrine dietary supplements which are considered illegal. Because of its ingredients, Bronkaid is used to promote weight loss, enhance energy and potentially increase athletic performance enhancement. However, oral Bronkaid tablets can also produce the same side effects as ephedrine diet pills and pose a significant risk to health when they are abused. While bodybuilders and dieters may take Bronkaid pills in an ECA stack for fat loss, this practice is strongly advised against. Due to their ingredients, these asthma tablets have a risk of harmful negative effects.
Don’t Miss: What Is Asthma Characterized By
Bronkaid Vs Primatene What’s The Difference
The bottom line is that both Bronkaid and Primatene are very similar in the way they work to relieve symptoms of asthma. Both drugs contain the same active ingredients that cause bronchodilation to open up airways that are normally constricted in asthma. They also both work to loosen up phlegm that causes chest congestion.
The combined effects of each work relatively quickly and both medications are good over the counter options for treating mild and intermittent asthma. They also have the same reported side effects, potential risks and drug interactions. Even if you consider the cost of each drug, a pack of either 24 or 60 ct. of either Primatene or Bronkaid costs exactly the same amount and they are available at the same major pharmacies, drugstores, food and mass merchandise stores.
The major difference between the two medications is in the bronchodilator active ingredient. While Bronkaid contains ephedrine sulfate as its active ingredient, Primatene contains ephedrine HCl. They also contain different amounts of each active ingredient.
Bronkaid contains 25 mg of ephedrine sulfate while Primatene has 12.5 mg of ephedrine HCl. Bronkaid also has 400 mg of guaifenesin and Primatene has 200 mg of guaifenesin as the expectorant active ingredient.
There is no evidence to show that either drug works better than the other when taken according to the instructions and as recommended by your doctor for quick relief of asthma symptoms.
Serum Concentrations At Steady
After multiple doses of Bronkaid , steady-state is reached in 30-65 hours in adults. At steady-state, on a dosage regimen with 24-hour intervals, the expected mean trough concentration is approximately 50% of the mean peak concentration, assuming a mean Bronkaid half-life of 8 hours. The difference between peak and trough concentrations is larger in patients with more rapid Bronkaid clearance. In these patients administration of Bronkaid ® may be required more frequently .
Also Check: Is Asthma A Serious Medical Condition
Bronkaid Vs Primatene: What’s The Difference
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects the airways of the lungs causing difficulty in breathing and wheezing in patients who suffer from it.
This is due to swelling of the airways that causes their narrowing, followed by mucus build-up within the narrowed airways. There is no cure for asthma. The disease is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Every asthma patient has certain triggers that can cause an asthma attack, which is a sudden onset of symptoms.
These triggers can be allergens or irritants like pollen, dust, pet dander, smoke or chemicals. A common cold can also trigger an asthma flare-up or attack. Once asthma is triggered, the airways begin to swell and become inflamed and the muscles of the airways tighten. This results in difficulty breathing because there is not enough space for air to move in and out of the narrowed airways.
Asthma can be diagnosed at any age. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , as of 2018 approximately 25 million people in the United States had asthma.
Of these, about 20 million were adults and about 5 million were children. Living with asthma can be challenging, but there are plenty of medications available on the market to help make the condition manageable. Medications used to treat asthma can help prevent asthma attacks as well as provide quick relief for symptoms of an asthma attack.
