Natural Selection And Evolution
Mutations alter an organism’s genotype and occasionally this causes different phenotypes to appear. Most mutations have little effect on an organism’s phenotype, health, or reproductive . Mutations that do have an effect are usually detrimental, but occasionally some can be beneficial. Studies in the fly suggest that if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, about 70 percent of these mutations will be harmful with the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial.
studies the distribution of genetic differences within populations and how these distributions change over time. Changes in the in a population are mainly influenced by , where a given allele provides a selective or reproductive advantage to the organism, as well as other factors such as , , , and .
Over many generations, the genomes of organisms can change significantly, resulting in . In the process called , selection for beneficial mutations can cause a species to evolve into forms better able to survive in their environment. New species are formed through the process of , often caused by geographical separations that prevent populations from exchanging genes with each other.
Causes And Inciting Factors Of Asthmatic Episodes
Asthmatic episodes may begin suddenly or may take days to develop. Although an initial episode can occur at any age, about half of all cases occur in persons younger than 10 years of age, boys being affected more often than girls. Among adults, however, women are affected more often than men.
When asthma develops in childhood, it is often associated with an inherited susceptibility to allergenssubstances, such as pollen, dust mites, or animal dander, that may induce an allergic reaction. In adults, asthma may develop in response to allergens, but viral infections, aspirin, weather conditions, and exercise may cause it as well. In addition, stress may exacerbate symptoms. Adults who develop asthma may also have chronic rhinitis, nasal polyps, or sinusitis. Adult asthma is sometimes linked to exposure to certain materials in the workplace, such as chemicals, wood dusts, and grains. These substances provoke both allergic and nonallergic forms of the disease. In most of these cases, symptoms will subside if the causative agent is removed from the workplace.
Know The Early Symptoms Of Asthma
Early warning signs are changes that happen just before or at the very beginning of an asthma attack. These signs may start before the well-known symptoms of asthma and are the earliest signs that your asthma is worsening.
In general, these signs are not severe enough to stop you from going about your daily activities. But by recognizing these signs, you can stop an asthma attack or prevent one from getting worse. Early warning signs of an asthma attack include:
- Frequent cough, especially at night
- Losing your breath easily or shortness of breath
- Feeling very tired or weak when exercising
If you have these warning signs, adjust your medication, as described in your asthma action plan.
Viral Infection To Predisposition
The fact that early-in-life sensitization to multiple allergens carries the greatest risk for developing asthma brings the question of what factors result in a predisposition to this phenotype. Although infection with rhinovirus is the major cause of acute exacerbation, in those genetically at risk of asthma, rhinovirus-induced wheezing in the first three years in the life is also the greatest risk factor for developing asthma at 6 years of age . Impaired TLR3-mediated IFN- and – production by asthmatic epithelial cells would make susceptible to both viral infection and allergic sensitization . Reduced primary IFN production by lower-airway epithelial cells enables some viruses to replicate, leading to cytotoxic cell, release of inflammatory products and enhanced viral shedding. Such events provide a strong stimulus for recruitment of immature DCs and their priming for allergen sensitization . When asthmatic epithelial cells are received to damage by rhinovirus infection, the cells generate increased amounts of the pro-Th2 cytokine thymic stromal lympoietin , which stimulates DCs and increases allergic inflammation, whereas exogenous IFN-b applied to asthmatic epithelium exerts anti-Th2 as well as antiviral properties .
What Should Be Done During The Attack
People with asthma should have an action plan for dealing with an acute attack. In general, it is important to stay calm and take prescribed medications. Quick-relief medications, including, rapid-onset inhaled beta2-agonist bronchodilators, such as albuterol, are used to treat asthma attacks and are taken on an as-needed bases. They relieve symptoms rapidly by relaxing the muscles surrounding the airways, helping to open the bronchial tubes. More severe attacks may require systemic corticosteroids to reduce airway mucus and swelling.
Global Alliance Against Chronic Respiratory Diseases
The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases contributes to WHOs work to prevent and control chronic respiratory diseases. GARD is a voluntary alliance of national and international organizations and agencies from many countries committed to the vision of a world where all people breathe freely.
What Is An Asthma Attack
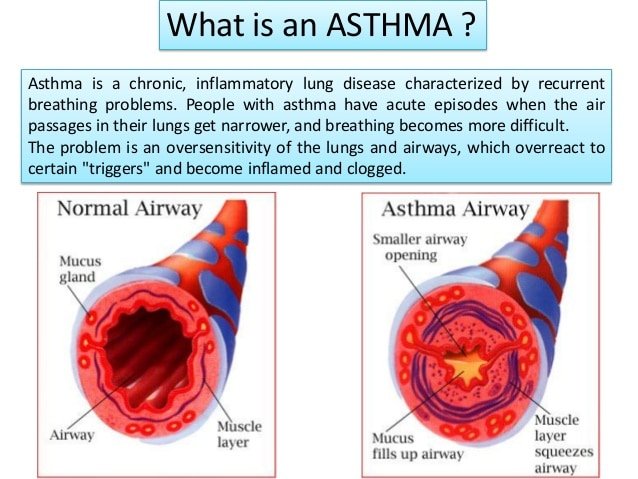
An asthma attack is the episode in which bands of muscle around the airways are triggered to tighten. This tightening is called bronchospasm. During the attack, the lining of the airways becomes swollen or inflamed, and the cells lining the airways make more and thicker mucus than normal.
All of these things — bronchospasm, inflammation, and mucus production — cause symptoms such as trouble breathing, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and trouble with normal daily activities.
Other symptoms of an asthma attack include:
- Severe wheezing when breathing both in and out
- Coughing that won’t stop
- Feelings of anxiety or panic
- Pale, sweaty face
- Blue lips or fingernails
An asthma attack can get worse quickly, so it’s important to treat these symptoms right away.
Without immediate treatment, such as with your asthma inhaler or bronchodilator, it will become harder to breathe. If you use a peak flow meter at this time, the reading will probably be less than 50% of your usual or normal peak flow reading.. Many asthma action plans suggest interventions starting at 80% of normal.
As your lungs continue to tighten, you wonât be able to use the peak flow meter at all. Your lungs will tighten so there is not enough air movement to make wheezing. You need to go to a hospital right away. Unfortunately, some people think that the disappearance of wheezing is a sign of improvement and donât get emergency care.
What Can Be Done About It
Asthma can be controlled. Moreover, it can be controlled by those who have asthma. The role of the physician is to provide the means for the patient to control asthma and to teach the patient to use provided measures .
Since asthma varies greatly in pattern of symptoms and severity, the treatment plan needs to be individualized. This should be done in a systematic manner. Goals of therapy must be realistically attainable and explicitly defined for you. The plan for attaining the treatment goals must be understood. Once the measures needed for control of asthma are identified, they can be placed in the hands of the patient with appropriate instructions for usage. Parental supervision is needed for young children, but progressive responsibility for self-management is given with advancing maturity.
Treatment may consist of medication, environmental changes, and life-style changes. The more the patient understands the disease and its treatment, the better the outcome is likely to be. The patient should therefore be an active partner in making decisions about treatment. Be wary, however, of superstitions and misinformation regarding asthma. More than almost any other medical problem, asthma is associated with a wide diversity of medical and nonmedical opinion. Both the physician and the patient therefore need to exercise judgment. Four common sense measures to remember are:
Reducing The Burden Of Asthma
Asthma cannot be cured, but good management with inhaled medications can control the disease and enable people with asthma to enjoy a normal, active life.
There are two main types of inhaler:
- bronchodilators , that open the air passages and relieve symptoms; and
- steroids , that reduce inflammation in the air passages. This improves asthma symptoms and reduces the risk of severe asthma attacks and death.
People with asthma may need to use their inhaler every day. Their treatment will depend on the frequency of symptoms and the different types of inhalers available.
It can be difficult to coordinate breathing using an inhaler especially for children and during emergency situations. Using a spacer device makes it easier to use an aerosol inhaler and helps the medicine to reach the lungs more effectively. A spacer is a plastic container with a mouthpiece or mask at one end, and a hole for the inhaler in the other. A homemade spacer, made from a 500-ml plastic bottle, can be as effective as a commercially-manufactured inhaler.
Access to inhalers is a problem in many countries. In 2019, only half of people with asthma had access to a bronchodilator and less than one in five had access to a steroid inhaler in public primary health-care facilities in low-income countries .
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Asthma
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including information about your parents and siblings. Your provider will also ask you about your symptoms. Your provider will need to know any history of allergies, eczema and other lung diseases.
Your healthcare provider may order a chest X-ray, blood test or skin test. Your provider may order spirometry. This test measures airflow through your lungs.
Environmental Remediation For Asthma
The medical management of asthma and treatment of acute attacks has improved substantially, but the prevalence of asthma continues to rise in urban settings in industrialized Western countries. There is still controversy about the hygiene hypothesis, and it is not yet clear that early exposure to certain antigens could be exploited as a preventive measure. Given what is known about asthma, avoidance of asthma trigger factors would be expected to at least reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. EPA recommendations for an “Asthma Friendly House” are shown in the iFrame below.
EPA Recommendations Asthma Friendly House
For additional measures, also see the EPA Home Environment Checklist.
There is some evidence that interventions to reduce dust, animal dander, mold, and exposure to cockroaches are effective, but the literature indicates that allergen reduction is difficult to achieve and the effectiveness is not as great as expected. The four articles cited below suggest that environmental remediation interventions that target one or two potential targets are of limited, if any value. However, they suggest that multifaceted interventions can reduce symptoms, school absences, and hospital visits for acute asthma care.
From the Abstract:
Results
Summary:
From the Abstract:
“Evidence synthesis
Summary
How Is Asthma Diagnosed
Asthma is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical examination, and lung function tests.14 Your health care provider will ask about the type and frequency of symptoms and what you were doing when the symptoms started. Additionally, your provider may do a test called spirometry. This test checks how much and how quickly you can exhale air.
It is possible for a person with a history of asthma symptoms to have normal spirometry results.1 In this case, your health care provider may suggest a methacholine challenge. Methacholine is an inhalable spray that is especially irritating to people with asthma. It triggers airway narrowing and allows your provider to measure how sensitive your airways are.
The methacholine challenge is best for ruling out asthma, although the results are not always conclusive. The test also helps to differentiate asthma from other lung conditions. People whose airways do not narrow after inhaling methacholine are very unlikely to have asthma.
Finally, other tests may be used to figure out what subtype you have.
Is It Possible To Outgrow It
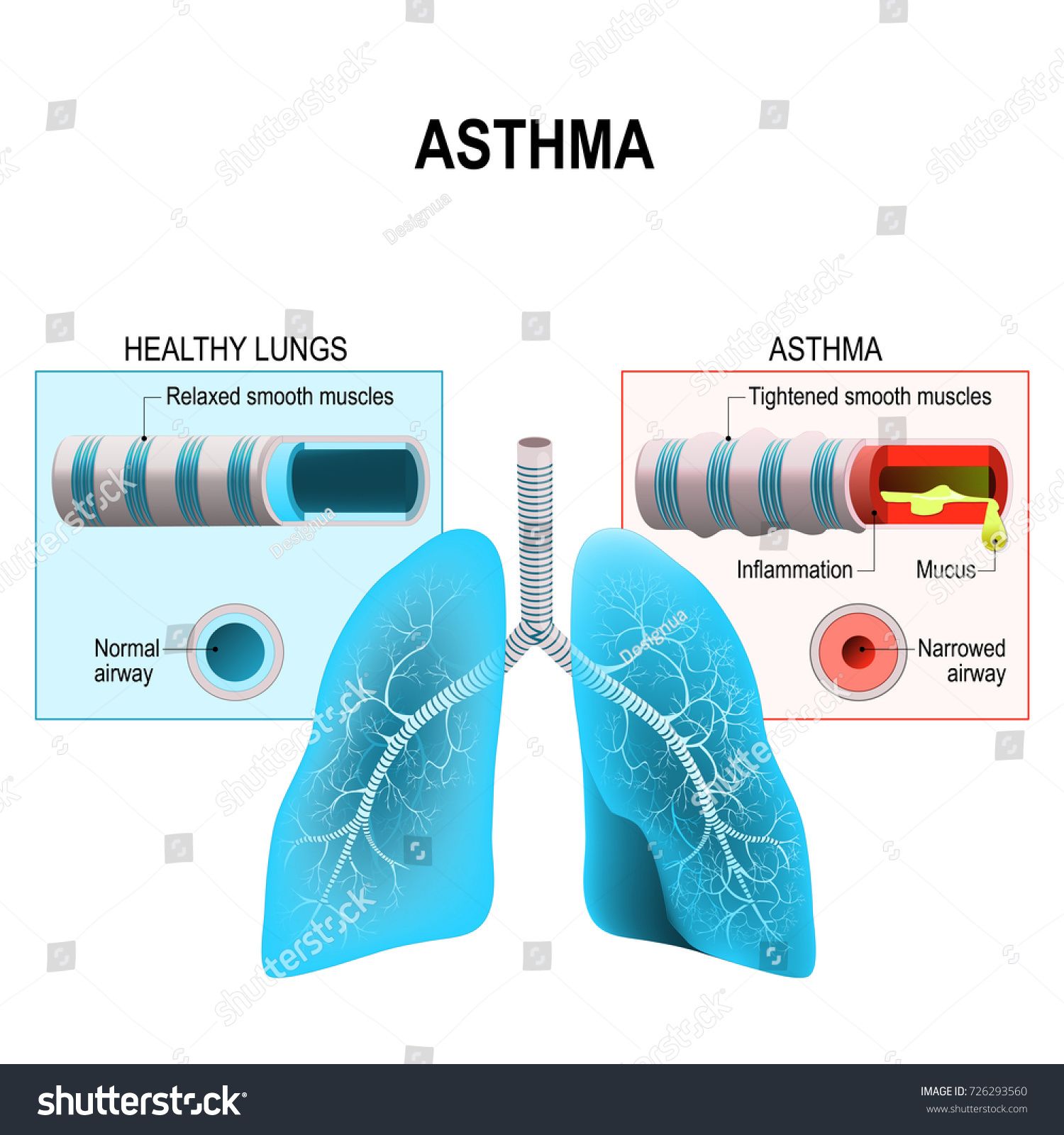
Asthma is a long-term disease. You may feel better for months, but generally, the airways remain inflamed and sensitive.
Some children do seem to “outgrow” their symptoms.1 However, other children need to continue taking medications to control their asthma. In one study, 64% of people with mild childhood asthma symptoms did not have symptoms as adults.6 However, only 15% of people with severe childhood asthma were symptom-free in adulthood. It is not possible to predict who will outgrow their symptoms.
What Is Asthma Characterized By
4.9/5AsthmaAsthmacharacterized
There are many different types of asthma, brought on by many different triggers.
- Adult-Onset Asthma. Can you get asthma as an adult?
- Allergic Asthma.
- Nonallergic Asthma.
- Occupational Asthma.
Similarly, what causes a person to develop asthma? Asthma triggersExposure to various irritants and substances that trigger allergies can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Airborne substances, such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander or particles of cockroach waste. Respiratory infections, such as the common cold.
In this regard, what are the hallmarks of asthma?
The classic signs and symptoms of asthma are shortness of breath, cough , and wheezing . Many patients also report chest tightness.
What are the 4 types of asthma?
Medical professionals rank asthma into four types from mild to severe.These types include:
What Is Type 2 Inflammation In Asthma
As many as 50-70 percent of asthma patients have a form of asthma characterized by Type 2 inflammation. Type 2 inflammation is a type of systemic allergic response that can result in increased asthma exacerbations and decreased lung function.
Cytokines, which are proteins that signal the bodys cells and begin an immune response, are major contributors to Type 2 inflammation.
Common asthma biomarkers are also present in Type 2 inflammation. These include:
- eosinophils
- Immunoglobulin E
- fractional exhaled nitric oxide
When there are too many eosinophils in the blood, there is an increased risk of severe asthma flares. Learn more about eosinophilic asthma at eosasthma.org.
Genetics also appear to play a role in Type 2. Studies show that if one or both parents have Type 2 inflammation related to asthma, their child is four times more likely to have asthma or an allergic disease.
Regulation Of The Pulmonary Circulation Helps Restore The Ventilation/perfusion Ratio
Pulmonary circulation depends on the pulmonary vascular resistance , gravity, alveolar pressure, and the hydrostatic pressure gradient provided by the right heart. The PVR, in turn, is influenced mainly by two factors: the inflation of the lung and the reaction of the arterioles to the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood.
The PVR, which determines blood flow, is affected by three separate variables: the alveolar gas pressure that compresses the capillaries, the resistance of alveolar vessels , and resistance of extraalveolar vessels. Unlike the systemic circulation, the capillaries in the lungs accounts for about 40% of the PVR. At lung volumes greater than the FRC, capillaries are stretched and compressed, and the resistance of the alveolar vessels increases. At lower lung volumes, the extraalveolar vessels are not held open by their tethers to the alveolar tissues, and their resistance increases. These effects contribute to a biphasic relationship between PVR and lung volume. The PVR is minimum around the functional residual capacity, FRC.
When To See A Doctor
If asthma is well controlled and you follow your treatment plan, you may be able to postpone worsening symptoms.
However, asthma can get worse over time. Thats why its important to maintain regular check-ups with your doctor.
If you think your asthma symptoms are occurring more frequently before youre scheduled for your next appointment, go ahead and make a new appointment. Its important to stay on top of changes in asthma symptoms so you can control them.
Asthma Causes And Triggers
When you have asthma, your airways react to things in the world around you. Doctors call these asthma triggers. They might cause symptoms or make them worse. Common asthma triggers include:
- Infections like sinusitis, colds, and the
- Allergens such as pollens, mold, pet dander, and dust mites
- Irritants like strong odors from perfumes or cleaning solutions
- Air pollution
- Strong emotions such as anxiety, laughter, sadness, or stress
- Medications such as aspirin
- Food preservatives called sulfites, found in things like shrimp, pickles, beer and wine, dried fruits, and bottled lemon and lime juices
When Asthma Is Not Just Asthma: Type 2 Inflammation
News, Asthma, Severe Asthma News & Updates
Asthma was once considered a single, though complex, disease. Now its recognized as a spectrum of diseases. Genetic and environmental factors play a role in airway inflammation and hyper-reactivity. This leads to common asthma symptoms: coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath.
Severe asthma is one form of the disease. Its estimated that 5-10 percent of people with asthma have severe asthma.
Severe asthma is the diagnosis when
- symptoms are not well-controlled by high-dose inhaled controller medications
- the patient experiences two or more asthma flares in a 12-month span requiring oral corticosteroids
Recent medical breakthroughs involving severe asthma are transforming how its diagnosed and treated. Airway inflammation is a particular focus.
Effect Of Interventions On Natural History Of Asthma
Two recent studies addressed the possibility that ICSs may prevent the putative declines in lung function believed to occur shortly after the beginning of the disease in adults who have late-onset asthma. A retrospective study reported the results of an observational study of adults who had mild-to-moderate asthma and were treated for 5 years with an ICS. One group, treated early in the disease , had better outcomes in terms of lung function than those who started treatment more than 2 years after diagnosis. The group in which treatment was started more than 2 years after diagnosis, however, had lower levels of lung function at the beginning of the trial. Therefore, it is not possible to determine from these data what the results would have been in a randomized trial. Two recent long-term observational studies report an association between ICS therapy and reduced decline in FEV1 in adults who have asthma . However, long-term RCTs will be necessary to confirm a causal relationship.
Who Strategy For Prevention And Control Of Asthma
Asthma is included in the WHO Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs and the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
WHO is taking action to extend diagnosis of and treatment for asthma in a number of ways.
The WHO Package of Essential Noncommunicable Disease Interventions was developed to help improve NCD management in primary health care in low-resource settings. PEN includes protocols for the assessment, diagnosis, and management of chronic respiratory diseases , and modules on healthy lifestyle counselling, including tobacco cessation, and self-care.
Reducing tobacco smoke exposure is important for both primary prevention of asthma and disease management. The Framework Convention on Tobacco Control is enabling progress in this area as are WHO initiatives such as MPOWER and mTobacco Cessation.
Know The Symptoms Of An Asthma Attack
An asthma attack is the episode in which bands of muscle surrounding the airways are triggered to tighten. This tightening is called bronchospasm. During the attack, the lining of the airways becomes swollen or inflamed and the cells lining the airways produce more and thicker mucus than normal.
All of these factors — bronchospasm, inflammation, and mucus production — cause symptoms such as difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and difficulty performing normal daily activities. Other symptoms of an asthma attack include:
- Severe wheezing when breathing both in and out
- Coughing that won’t stop
- Feelings of anxiety or panic
- Pale, sweaty face
- Blue lips or fingernails
The severity of an asthma attack can escalate rapidly, so it’s important to treat these asthma symptoms immediately once you recognize them.
Without immediate treatment, such as with your asthma inhaler or bronchodilator, your breathing will become more labored. If you use a peak flow meter at this time, the reading will probably be less than 50%. Many asthma action plans suggest interventions starting at 80% of normal.
As your lungs continue to tighten, you will be unable to use the peak flow meter at all. Gradually, your lungs will tighten so there is not enough air movement to produce wheezing. You need to be transported to a hospital immediately. Unfortunately, some people interpret the disappearance of wheezing as a sign of improvement and fail to get prompt emergency care.
Diagnostic Criteria And Therapeutic Interventions In The Elderly With Asthma
Existing pharmacological therapies that are frequently utilized to treat and manage asthma include inhaled corticosteroids, -agonists, and anti-IgE antibodies . Non-allergic asthma, which is more frequent in the elderly population, is less responsive to corticosteroids . Total serum IgE measurement was initially thought to be a reliable indicator of asthma since many asthmatic patients are allergic and it might distinguish asthma from COPD during the diagnostic work-up . However, it has been recognized that not all asthmatic patients are allergic. Furthermore, elderly patients tend to have lower IgE levels due to immunosenescence thus making the clinical diagnosis difficult using this method . Much of the research that has investigated asthmatic biomarkers has excluded the elderly population. Thus, further studies are necessary in order to understand the effect of aging and immunosenescence on the expression of biomarkers that may be utilized in the clinical diagnosis of asthma .
How Do You Monitor Asthma Symptoms
Monitoring your asthma symptoms is an essential piece of managing the disease. Your healthcare provider may have you use a peak flow meter. This device measures how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It can help your provider make adjustments to your medication. It also tells you if your symptoms are getting worse.
Key Points: Definition Pathophysiology And Pathogenesis Of Asthma And Natural History Of Asthma
- Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. This feature of asthma has implications for the diagnosis, management, and potential prevention of the disease.
- The immunohistopathologic features of asthma include inflammatory cell infiltration:
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Epithelial cell injury
Recombination And Genetic Linkage
Chromosomal crossoverGenetic linkageThomas Hunt Morgan
The diploid nature of chromosomes allows for genes on different chromosomes to or be separated from their homologous pair during sexual reproduction wherein haploid gametes are formed. In this way new combinations of genes can occur in the offspring of a mating pair. Genes on the same chromosome would theoretically never recombine. However, they do, via the cellular process of . During crossover, chromosomes exchange stretches of DNA, effectively shuffling the gene alleles between the chromosomes. This process of chromosomal crossover generally occurs during , a series of cell divisions that creates haploid cells. , particularly in microbial , appears to serve the adaptive function of repair of DNA damages.
The first cytological demonstration of crossing over was performed by Harriet Creighton and in 1931. Their research and experiments on corn provided cytological evidence for the genetic theory that linked genes on paired chromosomes do in fact exchange places from one homolog to the other.
Some DNA sequences are transcribed into RNA but are not translated into protein productsâsuch RNA molecules are called . In some cases, these products fold into structures which are involved in critical cell functions . RNA can also have regulatory effects through hybridization interactions with other RNA molecules .
What Does Control Of Asthma Mean
- The ability to deal with acute exacerbations of asthma so that the need for urgent medical care is prevented
- Prevention of hospitalization for asthma
- Tolerating all normal activities up to and including competitive athletics if otherwise able
- The avoidance of symptoms that interfere with sleep.
- Normal pulmonary physiology .
- These goals should be reached safely and with the least interference with a normal life-style. The risks and bother of the treatment must be carefully weighed against the risk and bother of the asthma. The benefit obtained from the treatment must be worth any inconvenience and potential medication risks imposed by the treatment.
In other words, it is the goal of treatment to determine the simplest, safest therapeutic measures that minimize disability, normalize lung function, avoid the need for acute medical care of asthma, and permit a normal life.
