Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Given that most patients will be on lifetime treatment for COPD and severe asthma, managing the treatment with beta-2 agonists in the context of the National Asthma Education and Prevention and GOLD guidelines, respectively, require a patient-centered approach involving coordination between interprofessional team members. In primary care, studies have shown improvement in the quality of diagnostic and guideline-oriented therapy approaches in settings with a designated respiratory care specialist. Patient outcomes improved under more focused care in terms of overall decreases in symptoms and decreases in the usage of rescue inhalers. Patients also demonstrated proper inhaler technique more frequently compared to facilities without a respiratory care specialist, and the use of spirometry as a means of diagnosis was greater. Pharmacists can verify dosing, teach proper inhalation and spacer technique, and perform medication reconciliation, altering the prescriber to any concerns. Nursing can monitor care and also reinforce administration counseling, as well as assessing therapeutic effectiveness.
Beta-2 agonist therapy requires an interprofessional team approach, including physicians, specialists, specialty-trained nurses, respiratory therapists, and pharmacists, all collaborating across disciplines to achieve optimal patient results.
Can You Take Long
Using long-acting beta agonists during pregnancy or breastfeeding may be advisable due to the risks of uncontrolled bronchospasm, but the uncertainties of LABA use in these circumstances should be recognized. There is not much clinical study data on use of LABA in pregnancy and breastfeeding, and there is a concern about uterine contractions being altered during labor.
When Are Sabas Used
New updates to asthma guidelines were published in 2020, known as the 2020 Asthma Guideline Update From the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Although changes were made from the previous guidelines, SABAs are still recommended as first-line treatment for people with intermittent asthma.3
People with intermittent asthma have symptoms like wheezing, shortness of breath, and cough that occur fewer than 2 days a week and do not interfere with daily activities. People with intermittent asthma may also experience symptoms at night fewer than 2 days per month.4
The new guidelines kept the previous recommendation of using the SABA albuterol as the first step if needed as a rescue treatment in people ages 12 years or older with intermittent asthma.3
People with mild, moderate, or severe persistent asthma often use a SABA as needed, along with another inhaled drug, such as an inhaled steroid and/or other drugs.3
Read Also: Is Jogging Good For Asthma
When Are Labas Used For Asthma
New updates to asthma guidelines were published in 2020. These updates are known as the 2020 Asthma Guideline Update From the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. These guidelines help doctors decide which drugs are right for asthma.3
The guidelines recommend major changes to the way doctors use LABAs treat asthma. They also make asthma treatment much simpler for most people with the condition. Now, in general:3
- Most people with asthma can be prescribed just 1 inhaler an ICS-LABA combination product. This should be used as both a maintenance and rescue inhaler.
- Most people, even those with mild asthma, should start with an ICS-LABA combination. Before, doctors recommended people start with an ICS alone.
- For people with mild intermittent asthma, an ICS-LABA should include low-dose ICS and be used as needed for symptoms. When asthma symptoms are under control, people can go without any inhalers. The ICS-LABA replaces albuterol as a rescue inhaler.
What Is A Beta Blocker
Beta blockers are a type of medicine developed in the 1960s that interfere with the body’s “fight or flight” response to stress.1 In response to stress or danger, your sympathetic nervous system releases adrenaline and noradrenaline. These are hormones that act as chemical messengers. Tiny proteins on the outer surface of many different types of cells called beta receptors sit and wait to latch on to these hormones. They then direct the body to respond in these ways:1,2
- The heart starts to beat faster
- Your blood vessels narrow and tighten
- The airways relax
- You sweat excessively
- Your blood pressure rises
All of those reactions can be useful in people who are in danger or who are responding to stress. But, in those with certain health conditions, such as angina or high blood pressure, those responses can be harmful. That’s where beta blocker medicines come in. They latch on to the beta receptors so that adrenaline and noradrenaline can’t bind to them.
As a result, this happens:2
- Your heart beats more slowly
- Electrical signals in the heart communicate better
- Your blood vessels throughout the body relax
- Blood pressure lowers
Recommended Reading: Can Essential Oils Help Asthma
Interactions With Other Medicines
Bronchodilators may interact with other medicines, which could affect the way they work or increase your risk of side effects.
Some of the medicines that can interact with bronchodilators include:
- some diuretics, a type of medication that helps remove fluid from the body
- some antidepressants, including monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants
- digoxin, a medication used to treat arrhythmias
- benzodiazepines, a type of sedative that may sometimes be used as a short-term treatment for anxiety or sleeping problems
- lithium, a medication used to treat severe depression and bipolar disorder
- quinolones, a type of antibiotic medication
This is not a complete list of all the medications that can interact with bronchodilators, and not all of these interactions apply to each type of bronchodilator.
Always carefully read the patient information leaflet that comes with your medication.
You may be able to find a specific leaflet on the medicines A to Z on the MHRA website.
If in doubt, speak to a pharmacist or GP.
Page last reviewed: 26 April 2019 Next review due: 26 April 2022
What Are The Side Effects Of Sabas
The most common side effects of SABAs include:1,5
More severe side effects include:1,5
- Paradoxical bronchospasm
- Low potassium levels
If you experience paradoxical bronchospasm, stop using your SABA medicine and contact your doctor as soon as possible.5
If you have ever had an allergic reaction to a medicine that contains albuterol or levalbuterol, notify your doctor. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have occurred. Symptoms may include itching, rash, swelling around the mouth/face/tongue, and/or trouble breathing. If you experience any of these serious symptoms, seek emergency medical care.5
These are not all the possible side effects of SABAs. Talk to your doctor about what to expect or if you experience any changes that concern you during treatment with SABAs
Read Also: What Is The Spiritual Root Cause Of Asthma
What Are The Possible Side Effects
The most common side effects of LABAs include:4
- Fast heart rate
More severe side effects include:4
- Hives, rash, or swelling of the mouth, face, or tongue
- Unexpected difficulty breathing
If you experience any side effects that may be life-threatening, contact 911 right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of LABAs. Talk to your doctor about what to expect or if you experience any changes that concern you during treatment with LABAs.
Factors Associated With Saba Overuse
Males, adolescents and older patients were more likely to overuse SABA compared to females and those in the 1824-year age group . Compared to patients in treatment step 3, patients in the other treatment steps had greater risk of overusing SABA, with a 50% and 90% increased risk for patients in treatment steps 1 and 5, respectively. In addition, use of hypnotics and sedative drugs and increasing comorbidity burden were associated with increased risk of SABA overuse.
Association between baseline short-acting 2-agonist use and risk of mortality. a) Overall mortality b) asthma-related mortality c) respiratory-related mortality. Adjusted for treatment step, Charlson Comorbidity Index, sex and age. 2 canisters: patients collecting two or fewer SABA canisters during the baseline year 3 canisters: patients collecting three or more SABA canisters during the baseline year HR: hazard ratio.
Recommended Reading: Arizona Asthma And Allergy Scottsdale
Asthma And Copd Drugs Market Size Share Growth Newest Industry Data Future Trends And Forecast 2027
Digital Specialist at Market Research
Global Asthma and COPD Drugs Market are expected to register a CAGR of 7.90% during the forecast period with a market value of USD 43,444.72 Million till 2027. Asthma is a type of inflammatory disease that affects the lungs and makes breathing difficult. It is one of the common chronic condition affecting many people across the globe. COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is an umbrella term used for a group of respiratory diseases such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Segment Analysis
The Global Asthma and COPD Drugs Market have been segmented by disease, product, route of administration, and distribution channel. The market, based on disease, has been bifurcated into asthma and COPD.
Based on product, asthma and COPD drugs market has been segregated into long-term asthma control medications and quick-relief medications. The long-term asthma control medications are further segmented into combination drugs, anticholinergics, inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists, theophylline, and others. The combination drugs are further segregated into Seretide/Advair, Symbicort, Relvar/Breo Ellipta, Flutiform, Dulera, and others. Anticholinergics is further sub-segmented into Spiriva and others. Inhaled corticosteroids are further segmented into Pulmicort, Flovent, Qvar, and others.
Regional Analysis
Key Players
Key Findings of the Study
What Are The Forms Of Bronchodilators
There are two forms of bronchodilators:
- Short-acting bronchodilators. Short-acting bronchodilators quickly relieve or stop sudden asthma symptoms. Theyre effective for three to six hours. Another name for a short-acting bronchodilator is a rescue inhaler. Inhalers are canisters of medicine in a plastic holder with a mouthpiece. When you spray an inhaler, it gives a consistent dose of medication.
- Long-acting bronchodilators. Long-acting bronchodilators keep your airways open for 12 hours. You use these inhalers every day to prevent asthma attacks.
You May Like: How Long Does Allergic Asthma Last
Patterns Of Ics And Saba Use Over Time
Among patients collecting more than two SABA canisters per year over a 3-year period after baseline, the proportion of patients in all three SABA overuse groups was stable, and in parallel, the use of ICS was stable and did not change during the 3-year period . From a full population perspective, 85% of asthma patients overusing SABA at baseline had continuous overuse during the observation period, whereas the proportion of patients not collecting any ICS was more than doubled at the end of observation .
Considerations For Labas And Asthma

Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you need help using your LABA. For example, if you have a LABA inhaler, they can show you how to prime, use, and clean your inhaler.
Use your LABA medicine as prescribed. Do not change the dose or frequency of your LABA unless your doctor tells you to do so.
A LABA should always be used in combination with an ICS. LABAs are not a substitute for an ICS but should always be given with one, preferably as a product that contains both a LABA and an ICS. A LABA does not treat an acute asthma attack.4
Before beginning treatment for asthma, tell your doctor about all your health conditions and any other drugs, vitamins, or supplements you are taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs.
You May Like: Does Baby Powder Cause Asthma
Case Study: Targeted Sanger Sequencing
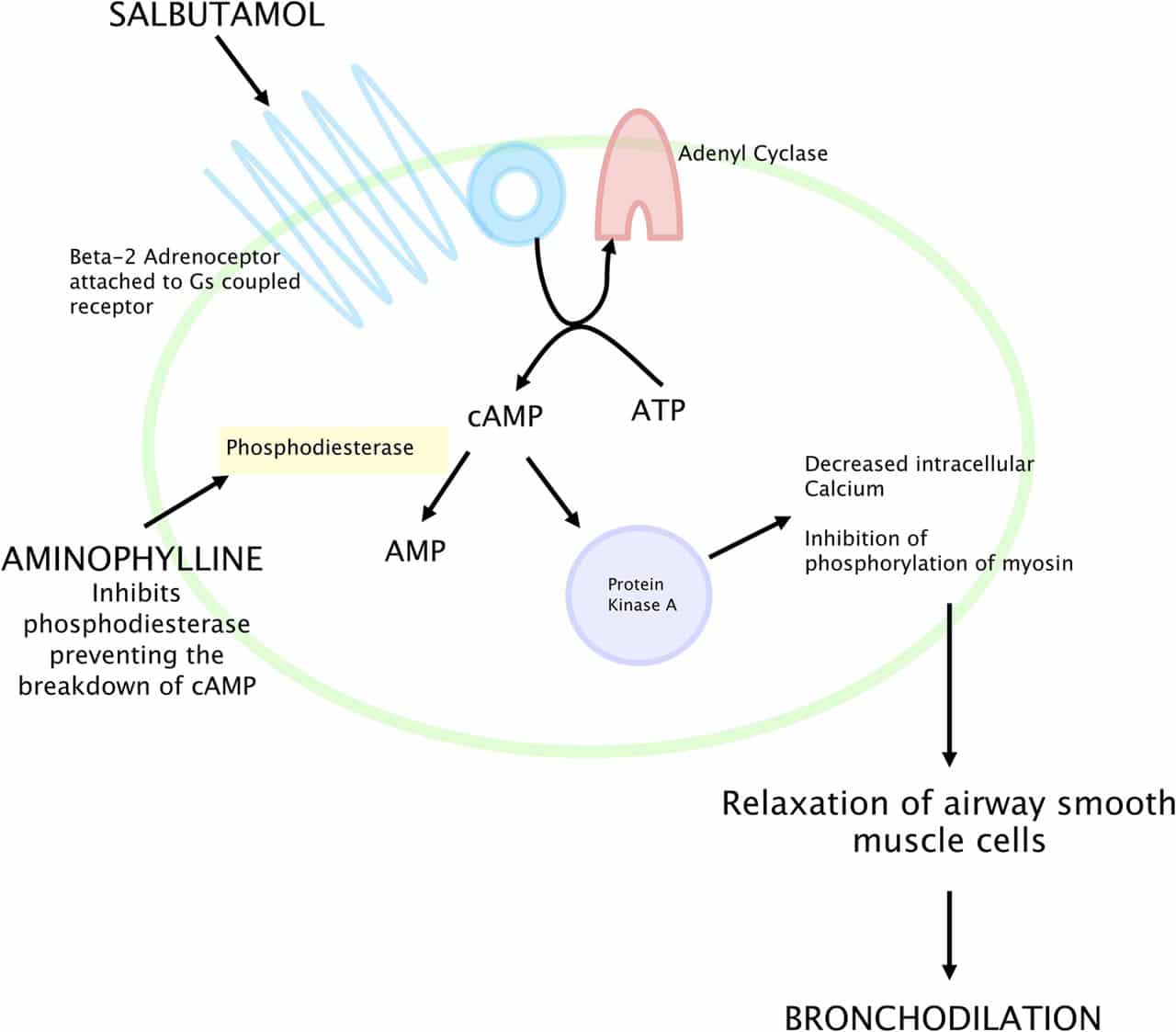
Beta-agonists are one of the most common medications used to treat airway constriction in asthma. Beta-agonists target the beta-2 adrenergic receptor, that when activated, relaxes airway smooth muscle cells. The gene for the beta-2 adrenergic receptor, ADRB2, contains only one exon and is thus small. Two common genetic variation creating the amino acid changes Gly16Arg and Gln27Glu, occur in the ADRB2 gene and have been implicated in affecting a persons responsiveness to beta-2 adrenergic agonists . In order to identify additional ADRB2 variations with potential effects on gene function, a ~5300 genomic region centered on ADRB2 was sequenced in 669 subjects . Twelve PCR products overlapping ~100150 bp were designed across the region, and each PCR product was sequenced . Fifty genetic variations were identified in the 5.3 kb region, ranging in frequency of < 1% to 45%. No new coding changes were found. However, some of the newly discovered rare variants have been further studied and implicated in increasing the risk of severe asthma exacerbations in subjects taking long-acting beta-agonists .
John A. McCoshen, … James G. Allardice, in, 1996
Additive Effects Or Synergy
It is still uncertain whether adding a LABA to an ICS results in an additive effect, because both classes of drug have effects on a common mechanism, or whether there is true synergy. In some studies it is apparent that while the LABA may have little effect on the inflammatory process alone, there is an enhancement of the corticosteroid effect when both LABA and ICS are administered suggesting that there is true synergy. This type of interaction is likely to be dependent on the cell type, the response measured and the concentrations of each drug. Whether it translates into clinical synergy has not yet been clearly established. However, even an additive interaction is likely to be clinically beneficial if the same control can be achieved with lower doses of each drug.
Read Also: Can Asthma Lead To Lung Cancer
A Word From Get Meds Info
If your asthma is not adequately managed on your current treatment plan, even if it has already been modified, speak with your healthcare provider.
Remember that your asthma isnt well controlled if:
- You use your relief inhaler more than twice a week
- You wake up with asthma symptoms more than twice a month
- You refill your rescue inhaler more than twice a year
Discuss whether you need to add another medication to your asthma-control regimen, such as a beta2-agonist.
How To Take And Store
When using a new inhaler, or one that’s gone unused for a while, you’ll need to prime it to ensure you get the proper dosage:
If you’ve used the inhaler recently, you shouldn’t need to do this. Just follow the steps recommended for use of all bronchodilators, which include ensuring your lungs are empty before you inhale the medication, holding it in for 10 seconds before exhaling, and rinsing your mouth out with water when you’re done.
Once a week, rinse your inhaler’s plastic case and allow it to dry completely. Don’t submerge the cartridge in water or use cleaning products on your inhaler.
For safety purposes, keep your inhaler:
- At room temperature
- Away from high heat and open flames, as these situations can cause the cartridge to burst
- Where children and pets can neither see nor reach it
You May Like: What Is The Best Treatment For Asthma
What Is A Bronchodilator
A bronchodilator is a type of medication that relieves the symptoms of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other lung conditions. It quickly relaxes the muscle bands that tighten around your airways . When those muscles relax, more air comes in and out of your lungs so you can breathe comfortably.
Bronchodilators also help clear mucus from your lungs. As your airways open, mucus moves more freely, which allows you to cough mucus out of your body easily.
Bronchodilators are primarily available as inhalers and nebulizer solutions.
Beta Blockers For The Treatment Of Asthma
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : February 24, 2010Last Update Posted : April 12, 2019 |
Current asthma medicines include inhalers. A common inhaler used in asthma is called a beta-agonist . They improve asthma symptoms by stimulating areas in the human airway resulting in widening of the human airway. Although these drugs are useful after the first dose, longterm use can cause worsening asthma symptoms.
Beta-blockers are the complete opposite type of medication. Just now they are avoided in patients with asthma as after the first dose they can cause airway narrowing and cause an asthma attack.
New research has suggested that long term use of beta-blockers can reduce airway inflammation which can improve asthma control and improve symptoms.
This research was done in asthmatic patients who didn’t need inhaled steroids to control their asthma. What the investigators want to do is see if the same benefit of beta-blocker use is asthma can be seen in people who take inhaled steroids.
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Asthma In Adults
Do Bronchodilator Inhalers Damage My Lungs
Your body may fail to respond to the medicine if you use your bronchodilator too much. Overuse can also cause your body to become overly sensitive to asthma or COPD triggers. Triggers may include smoke, pollution, dust and chemical fumes.
Using steroid inhalers may also increase your risk of developing nontuberculous mycobacteria infections or pneumonia, especially if youre 65 or older.
Looking In To The Future: Ultra
Recently, new ultra-long 2-agonists with higher potency and selectivity to 2-receptors, like vilanterol, olodaterol, indacaterol and abediterol , with 24-h treatment duration and rapid onset of bronchodilation have been studied. Of these, only vilanterol, in association with inhaled corticosteroids, has been approved for treatment of asthma . The once-a-day posology might increase adherence in long-term treatment of asthma. However, superiority to twice-a-day LABA still cannot be concluded with the currently available evidence . In addition, no serious adverse effects have been observed, although the follow-up periods of the trials are short. Due to the high selectivity to 2-receptors of these drugs, it is not expected for them to have greater adverse cardiovascular effects than LABA. Conversely, this selectivity may potentially be correlated with a greater loss of adrenoreceptors but this has not been associated with functional desensitisation . Moreover, with an increasing human life expectancy, these new drugs should be shown to be safe and efficacious in an older population that may have a higher rate of cardiovascular comorbidities and use of multiple medications.
The use of ultra-long 2-agonists is increasing, prescribed in monotherapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , and frequently asthmaCOPD overlap syndrome. New data are emerging every day and will continue this story in the future.
Recommended Reading: Can You Take Aspirin With Asthma
