Diagnosing Asthma In Older People
Older people are more likely to have other lung diseases that also cause shortness of breath , so doctors have to determine how much of the person’s breathing difficulty is related to asthma and reversible with the appropriate anti-asthma therapy. Often, in these people diagnosis involves a brief trial of drugs that are used to treat asthma to see whether the person’s condition improves.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Asthma
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including information about your parents and siblings. Your provider will also ask you about your symptoms. Your provider will need to know any history of allergies, and other lung diseases.
Your healthcare provider may order a chest X-ray, blood test or skin test. Your provider may order . This test measures airflow through your lungs.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
includes several lung diseases that can make it harder to breathe, including chronic bronchitis and . Chronic bronchitis causes of the bronchial tubes and more mucus, both of which make it harder for your lungs to work. is generally caused by long-term exposure to things that irritate the lungs, such as cigarette smoke, but people with can also develop it.
Continued
Airway Disease And Sputum
Sputum production is associated with many lung disease processes and sputum may become infected, stained with blood or contain abnormal cells.
Smoking – Smoking has many effects on the airways. Inhaled smoke destroys the cilia that are important for moving mucus to the throat for swallowing. As a result, mucus accumulates in the bronchioles and irritates the sensitive tissues there, causing a cough. Coughing is vital as it is the only way smokers can remove mucus from their lungs and keep the airways clean . This is characterised by the smokers cough.
Constant coughing to clear the sputum has an effect on the smooth muscle of the bronchioles which becomes hypertrophied . This in turn causes more mucus glands to develop.
Smoking also causes hyperplasia of the mucus-producing goblet cells . Because of the constant irritation, more mucus is produced and collects in the alveoli, which can become overburdened and collapse.
Another effect of smoking is the development of emphysema when the alveoli expand, the capillary blood supply deteriorates and gaseous exchange is reduced. Smoking makes other lung diseases worse and is a major cause of lung, and many other, cancers.
Smoking cessation improves lung health – bronchial tubes relax and the work of breathing becomes easier, and cilia begin to regrow within a few months, so mucus and debris can be cleared without the need for constant coughing. Also, the risk of cancers reduces over time.
– The production of sputum;
Assessment Of Mast Cell Degranulation
The amount of mast cell degranulation was assessed by counting all discrete areas of mast cell tryptase staining in which a nucleus was present. Mast cells seen under high power were classified as intact if they were dense, compact, with unbroken cytoplasmic boundaries and no surrounding positively stained granules . All other mast cells were classified as degranulated . The number of intact cells was expressed as a percentage of the total number of positively stained cells. The percentage of degranulated cells was assessed in two ways. Firstly, in two airways from each case 10 random high powered fields around the airway perimeter were chosen so that one border of the high powered field abutted the epithelial surface. All cells falling within that high powered field, regardless of which airway compartment they fell into, were counted. Secondly, to examine the degree to which degranulation of mast cells was affected by which airway wall compartment it was in, the percentage degranulation was calculated for all mast cells across the airway wall, assessed separately for each compartment .
Figure 1
High powered photomicrograph of a submucosal mucous gland from a non-asthmatic subject stained with AA1 and counterstained with haematoxylin showing a tryptase positive mast cell in which the staining of the individual cell is dense and uniform without obvious signs of free granules. These cells were counted as intact mast cells. Magnification ×1000, bar = 50 m.
Figure 2
What Are The Long Term Health Prospects For Asthma Sufferers
Although asthma cannot be cured it can usually be well treated so that the symptoms give little trouble. Around half of the children who get asthma ‘grow out of it’ with their asthma settling as they become adults.
It is vital to stop smoking to avoid developing long-term lung damage , which severely reduces lung function.
Severe attacks of asthma can be fatal but only if they are treated inadequately or not soon enough.
Medicines for asthma are generally thought of in two main groups:
Relievers
These are quick-acting that relax the muscles of the airways. This opens the airways and makes it easier to breathe. They are used to relieve or ease symptoms and can be used by themselves if you only have symptoms now and then. However, if you are using them more than 3 times a week to ease asthma symptoms then a preventer inhaler should also be used.
Preventers
These act over a longer time and work by reducing the inflammation within the airways. They should be used regularly for maximum benefit. When the dosage and type of preventive medicine is correct, there will be little need for reliever medicines.
A number of other types of drugs may also be used, for example to reduce secretions.
What Should I Do If I Have A Severe Asthma Attack
A severe asthma attack needs immediate medical care. The first step is your rescue inhaler. A rescue inhaler uses fast-acting medicines to open up your airways. Its different than your normal maintenance inhaler, which you use every day. You should only use the rescue inhaler in an emergency.
If your rescue inhaler doesnt help or you dont have it with you, go to the emergency department if you have:
- Anxiety or panic.
- Bluish fingernails, bluish lips or gray or whitish lips or gums .
- Chest pain or pressure.
Does Having Phlegm Mean My Asthma Is Getting Worse
Coughing up more phlegm than usual could be a sign that your airways are inflamed. This means your airways get narrower and this can cause other asthma symptoms, like:
- coughing
- wheezing
- breathlessness.
If you have more asthma symptoms than usual, your reliever inhaler will help open up your airways. But remember, if youre using your reliever inhaler more than three times a week, you need to see your doctor.
Taking your daily preventer inhaler as prescribed should help reduce the inflammation thats causing your asthma symptoms. Find out more about how preventer inhalers help asthma.
Speak To Our Team Today
Find out if you qualify for our lung treatments.
Every day the Lung Health Institute is changing peoples lives. Our duty and obligation is to help our patients. We measure our success by our patients satisfaction and their satisfaction with our services and the care they receive from our dedicated staff.
Patient Satisfaction Focused
With over 9,000 procedures performed, each patient is assigned a dedicated Patient Care Specialist for a personalized experience.
CDC Safety and Quality Standards in Place
We have adapted and delivered comprehensive infection prevention, including COVID-19 precautions, safety innovations and processes to safeguard you during your visit.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Our patients are provided resources and exercises focused on improving their lifestyle with exercises, nutritional guidance, and counseling to assist in their long-term lung health. After treatment, patients are given access to an online portal with pulmonary therapy support and more.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to suggest diagnosis, treatment, cure or prevention of any disease. Lung Health Institute operates in compliance with CFR Title 21 Part 1271.15 Regulation.
Why Does Someone Get It
Over 10% of people have some history of asthma. It often runs in families. The heritable nature of asthma is not well understood, however, and geneticists cannot define the precise manner in which it is passed from parents to children. All we can say is that families with asthma are more likely to have children with asthma. Although there appears to be an inherited predisposition to develop asthma, severity varies considerably among asthmatics, even among members in the same family. If asthma is present in both parents, the likelihood of a child having asthma is even greater, but even then not all of the children will have asthma. Even among identical twins, both do not necessarily have asthma, although this is more likely than if they were just siblings or nonidentical twins. This suggests that there is some additional factor that we do not yet fully understand, other than inheritance, that influences the development of asthma.
When Mucus In Throat Can Become A Serious Issue
The color of your mucus in throat is a strong indicator of how severe the health problem is. Generally, thin and clear is the safest, and other colors could indicate a particular infection. Here are some guidelines to know when mucus in throat is a serious issue.
Thin and clear: Sign of cold or allergies, it could also be a sign of medication side effect or a reaction to certain food.
Thick and colored: If mucus is very thick, it could be a sign of dryness, which can be caused by heating systems. If mucus appears green, yellow, or brownish, it could indicate a bacterial infection.
Rattling sound in chest: If mucus is dripping down to your chest, it may be difficult to swallow and may cause a rattling sound, which may be pointing to .
Burning sensation: If mucus is burning, it could be a result of a heartburn or .Paying attention to your mucus can help offer insights into your overall health and give you indications on how to treat the mucus.
Study Uncovers New Clues About Overproduction Of Mucus In Asthma And Copd
In solving a 20-year mystery about the role of a protein associated with mucus production, researchers provide new insights that may lead to new treatments for asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis and other diseases.
The researchers, from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis , MO, report their findings in the journal eLife.
Thomas J. Brett, senior study author and assistant professor of medicine at WUSTL, says:
The new study lays the groundwork for developing treatments for diseases such as asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis and even certain cancers.
In diseases such as and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , the body produces too much mucus, making breathing difficult.
In cystic fibrosis, the mucus that is produced is too thick and clogs up the lungs and digestive tract.
The significance of the new study lies in revelations about ion channels special proteins that make pores in the cell membrane and help regulate the flow of charged particles in and out of the cell.
Ion channels allow cells to send and receive electrical signals and perform roles essential to health, such as secrete substances like mucus, control heart rhythm and support brain function.
However, with diseases like cystic fibrosis and asthma, too much mucus that is too thick is produced, which makes breathing difficult and raises risk of infection.
Control Of Polymeric Mucin Production

The induction of Muc5ac in allergically inflamed mice is dependent upon two important signaling pathways: the IL-13/IL-4 receptor- complex and the epidermal growth factor receptor . The functional dominance of these signaling pathways, however, does not translate into a simple intracellular pathway for Muc5ac gene activation. The principal signaling molecule activated by IL-13 is signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 . STAT6 signaling in mouse airway Clara cells is necessary and sufficient for Muc5ac induction and airway hyperreactivity in response to IL-13 . STAT6 binds to a canonical motif, 5-TTCN4GAA-3, but this motif is not present in the conserved promoter regions of any mammalian MUC5AC orthologs . One indirect mechanism that may explain IL-13-mediated Muc5ac promoter activation is STAT6-dependent downregulation of forkhead box a2 . Foxa2 is a critical negative regulator of Muc5ac expression, and genetic deletion of Foxa2 in mice leads to constitutive Muc5ac overproduction resembling mucous metaplasia .
Transcriptional control of Muc5ac production gr2
Evaluating An Asthma Attack
Because people who are having a severe asthma attack commonly have low blood oxygen levels, doctors may check the level of oxygen by using a sensing monitor on a finger or ear . In severe attacks, doctors also need to measure levels of carbon dioxide in the blood, and this test typically requires obtaining a sample of blood from an artery or, occasionally, a vein. However, carbon dioxide levels can sometimes be monitored in the person’s breath using a sensor placed in front of the nose or mouth.
Doctors may also check lung function, usually with a spirometer or with a peak flow meter. Usually, a chest x-ray is needed only when asthma attacks are severe, in order to rule out other serious conditions .
Egfr Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Inhibition of EGFR tyrosine kinase has been a major interest as therapy for airway hypersecretory diseases. Inhibition reduces mucin synthesis and goblet cell hyperplasia . Analysis of MUC5AC in human cells pre-treated with TGF- found increased expression that was blocked by selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as BIBX1522 . These inhibitors also prevent IL-13-induced goblet cell hyperplasia and neutrophil recruitment. Furthermore, upregulation of EGFR mRNA and its induced phosphorylation are prevented by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition . BIBX1382 is a similar EGFR-TKI that inhibits the intracellular domain of EGFR but failed a Phase I trial due to low bioavailability and an undesirable benefit: risk ratio .
Gefitinib is an EGFR-TKI used as an anti-cancer drug and has shown to reduce goblet cell hyperplasia in mice, suggesting its potential use in reducing mucus synthesis in hypersecretory phenotypes . However, there are adverse effects to many EGFR-TKIs including gefitinib, such as papulopustular eruptions, as well as lack of successful trials on human asthma and COPD patients .
A safety and efficacy trial of an EGFR antagonist published in 2010 found that this EGFR-TKI had no significant efficacy in reducing mucin stores in airway epithelial cells of COPD patients, and was not well tolerated among patients. Twenty four percent of the BIBW 2948 subjects discontinued their treatment due to adverse events .
Scientists Develop Antibodies To Treat Mucus Production In Asthma Patients
Petra Wiesmayer
Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs and especially the airways. It causes the inside airways to become inflamed and swollen. As a result, the bronchial mucous membranes secrete viscous mucus, which leads to an acute narrowing of the airways a so-called bronchial obstruction and to shortness of breath and various other complaints in the affected persons.
According to figures from the German Lungeninformationsservice, the number of adults suffering from asthma in Germany has risen by 35 percent in recent years. So far, it has been assumed that children are particularly affected by the disease bronchial asthma is the most common chronic disease in childhood. About seven to ten percent of children suffer from asthma. According to the latest studies, however, the frequency of asthma in adults has significantly increased during the observation period from 2009 to 2016. From 4.3 percent in 2009 to 5.9 percent in 2016. Researchers observed that around 25 percent more people in large cities were treated for asthma than in rural areas. Fortunately, the mortality rate due to asthma is quite low. Yet, in Germany the disease still kills four to eight people per 100,000 inhabitants. The average in Central Europe is one to eight deaths per 100,000 inhabitants.
Video: Phlegm And Asthma
Phlegm and asthma
0:07 Gross as it looksphlegm and mucus protect your body from infection.
0:11 A little bit of phlegm is totally normal but if your phlegm
0:18 changes in colour thickness or amount it could be a sign that you’re ill and your
0:20 asthma may be affected
0:23 if you find you’ve been coughing up more phlegm than
0:28 usual this could be a sign that your airways are inflamed this can cause
0:34 asthma symptoms like coughing wheezing shortness of breath or a tight chest
0:38 You should take your daily preventer inhaler as prescribed and it should help stop
0:42 these symptoms because it reduces the inflammation in your airways over time
0:47 if you’re doing this and still getting a lot of mucus on your chest you should
0:51 book an appointment with your doctor or ask the nurse
1:00 if you have yellow or green phlegm this might be a sign of an infection like a cold flu or a chest
1:04 infection these can often make asthma symptoms worse so it’s really important
1:09 to keep taking your preventer inhaler every day
1:15 if your phlegm is streaked with blood this is usually down to the pressure put on the blood vessels if
1:19 you’re coughing a lot the best thing you can do in this case is to see your
1:24 doctor to make sure it’s nothing to worry about if you have brown or black
1:28 tinged phlegm it usually occurs in smokers or if you have COPD chronic
1:34 obstructive lung disease as well as asthma when you stop smoking even just
How To Quickly Fix Anxiety And Excessive Mucus
- Mucus buildup is a common and complex symptom of anxiety
- Anxiety-breathing can cause extra mucus, and it can make some health conditions worse
- The first step should be drinking water, to make sure its not dehydration related
- Several other beverages and breathing exercises can reduce some mucus
- Eliminating all excess mucus from anxiety would require an anxiety treatment
What Are Common Asthma Attack Triggers
An asthma attack happens when someone comes in contact with substances that irritate them. Healthcare providers call these substances triggers. Knowing what triggers your asthma makes it easier to avoid asthma attacks.
For some people, a trigger can bring on an attack right away. Sometimes, an attack may start hours or days later.
Triggers can be different for each person. But some common triggers include:
- Air pollution: Many things outside can cause an asthma attack. Air pollution includes factory emissions, car exhaust, wildfire smoke and more.
- Dust mites: You cant see these bugs, but they are in many homes. If you have a dust mite allergy, they can cause an asthma attack.
- Exercise: For some people, exercising can cause an attack.
- Mold: Damp places can spawn mold. It can cause problems for people with asthma. You dont even have to be allergic to mold to have an attack.
- Pests: Cockroaches, mice and other household pests can cause asthma attacks.
- Pets: Your pets can cause asthma attacks. If youre allergic to pet dander , breathing in the dander can irritate your airways.
- Tobacco smoke: If you or someone in your home smokes, you have a higher risk of developing asthma. The best solution is to quit smoking.
- Strong chemicals or smells.
With asthma, you may not have all of these symptoms. You may have different signs at different times. And symptoms can change between asthma attacks.
How Do You Monitor Asthma Symptoms
Monitoring your asthma symptoms is an essential piece of managing the disease. Your healthcare provider may have you use a peak flow meter. This device measures how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It can help your provider make adjustments to your medication. It also tells you if your symptoms are getting worse.
Reactive Airways Dysfunction Syndrome
Reactive airways dysfunction syndrome is a rapid onset and persistent asthma-like disorder that occurs in people with no history of asthma. It is a form of environmental lung disease caused by a single large exposure to nitrogen oxide or volatile organic compounds . People have symptoms similar to those of asthma, including cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Treatment is similar to usual treatment for asthma.
Inhibition Of Mucin Synthesis
There are many aspects of mucin synthesis that have been therapeutically targeted to reduce mucin levels in the airways and to theoretically improve the symptoms of asthma and COPD. A number of inhibitors of these targets are in the process of being developed , and are discussed in this section.
Fig. 5
Potential therapeutic targets to reduce synthesis of mucins. A variety of drug classes aimed at targeting a variety of different cell-surface or intracellular molecules on/in airway epithelial cells have been developed in order to inhibit synthesis of mucins . GABAAR = -Amino butyric acid A receptor.
Fig. 6
Chemical structures of drugs intended to inhibit mucin synthesis .
How To Reduce Excess Mucus
Preventing or removing excess mucus is a bit tricky. Even though it may be irritating, mucus does serve a very important and very valuable purpose in your body. Your body may also compensate if it thinks it’s not making enough mucus, so even if there was something you could take to remove mucus altogether, chances are it would come back even stronger in order to make sure your body has the protection it thinks it needs. The best thing to do is try the following:
- Drink Water Since so many people with anxiety are dehydrated, drinking water should be your first step. It won’t remove the phlegm right away, but it should drastically cut down on its creation.
- Drink Hot Teas A hot tea – especially one with herbal remedies for throat health – is one of the best things you can do to remove mucus. Hot teas are naturally soothing to your throat, and the act of drinking tea can be calming to your anxiety.
- Breathe Slower You should also try to regain control of your breathing. Breathe slower, so that you’re able to stop hyperventilating. Once you stop hyperventilating, you should notice some of the mucus start to go away.
- Gargle Warm Salt Water This is a basic remedy for getting rid of mucus that has nothing to do with anxiety, but it’s still effective. Some warm salt water gargling should clear up some of that mucus without coughing, and soothe your throat in a way that makes breathing easier.
Was this article helpful?
This Article Has Been Updated
The evidence in this article is no longer current. to see an updated and expanded article
Abstract
VOL: 99, ISSUE: 23, PAGE NO: 63
Marion Richardson, BD, CertEd, DipN, RGN, RNT, is senior lecturer and programme leader, emergency nursing, University of Hertfordshire
This blood supplies the cells of the body with oxygen and removes the waste products of metabolism. Tissues of the respiratory tract are thin and delicate, and become thinnest at the surfaces of the aveoli, where gaseous exchange occurs. The body has a number of mechanisms which protect these tissues and ensure that debris and bacteria do not reach them.
Tiny hairs called cilia trap large pieces of debris and waft them out of the airways; the reflexes of sneezing and coughing help to expel particles from the respiratory system and the production of mucus keeps the tissues moist and helps to trap small particles of foreign matter.
Mucus production in the airways is normal. Without it, airways become dry and malfunction. But sometimes the mucus is produced in excess and changes in nature. This results in the urge to cough and expectorate this mucus as sputum. Sputum expectoration is not normal and there is always an underlying pathological cause.
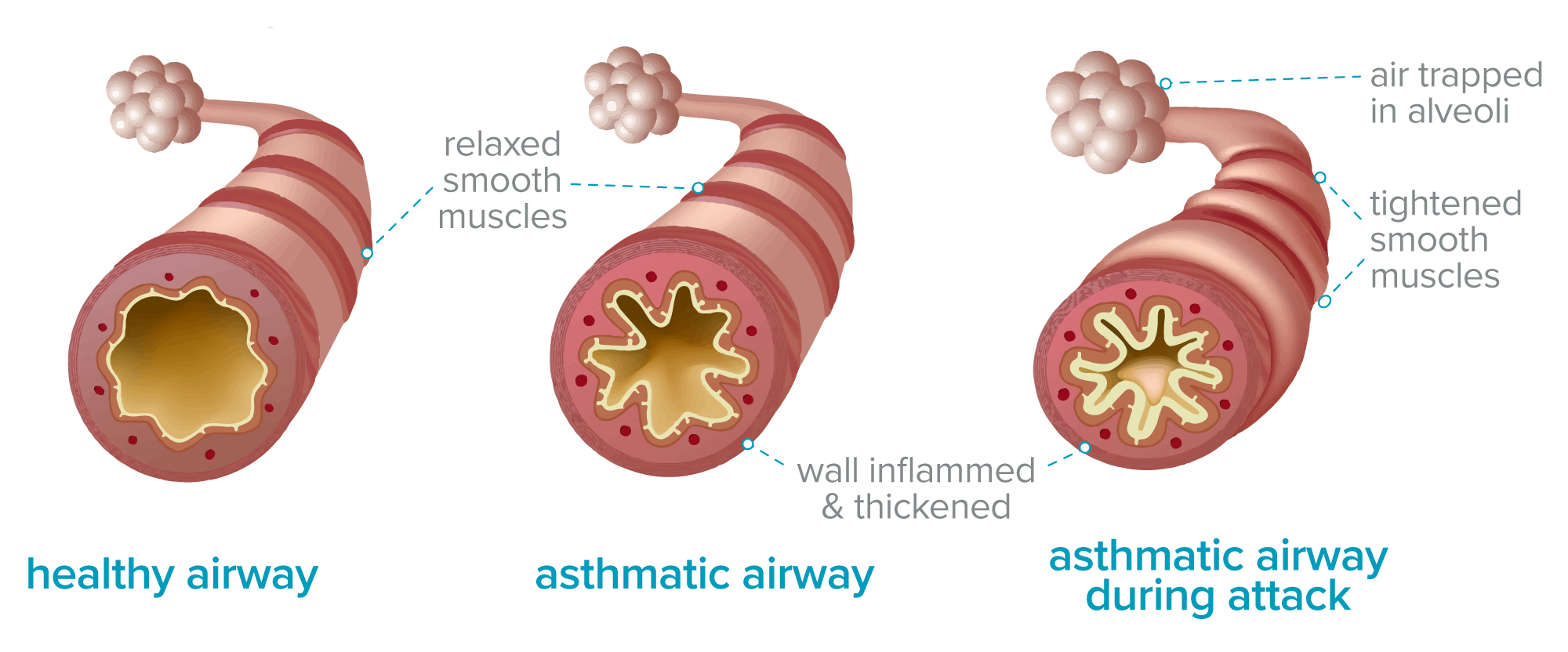
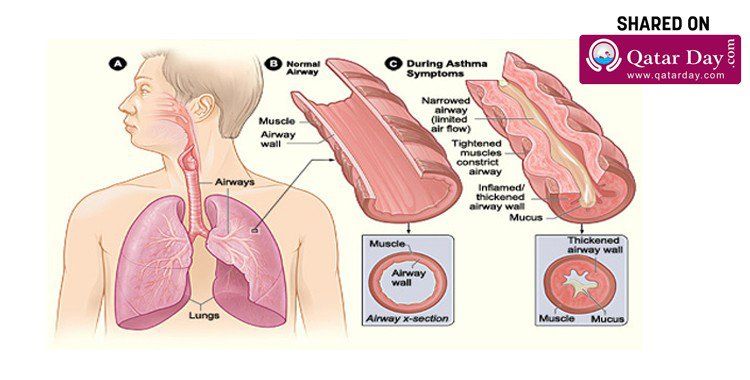
How Does Inflammation Cause Asthma Airway Sensitivity And Obstruction
Many different types of inflammatory cells and signaling chemicals play a role in the cause of asthma. Allergens turn on mast cells and dendritic cells.7 These cells tell Th2 cells to send out signaling chemicals called interleukins. Interleukins turn on other signals that are responsible for some allergy symptoms, mucus production, airway narrowing, and increasing the number of eosinophils. About half the people with severe asthma have high eosinophils, which are a type of white blood cell.8 Signals from other cells increase the inflammation, making the airways more sensitive. The most important cell types are described in the Table.3,7,9
Will It Ever Go Away
Asthma has a variable course. Many children with asthma see it improve or appear to go away as they get older. This can happen any time in childhood or adolescence. If asthma was only intermittent in nature and triggered by viral respiratory infections , there is an excellent likelihood that asthma will be much less of a problem as the child gets older. Sometimes the nature of the asthma changes with age. A young child may have asthma initially only from viral infections. As the child ages, asthma may occur less from viral infections , but inhalant allergy may become an important contributor to the asthma. If asthma persists into adult life, or returns later in adult life after a period of remission, persisting asthmatic symptoms may not be readily explainable by any environmental factors.
Whatever the course, however, asthma is virtually always controllable with acceptably safe measures. While ongoing medical evaluation of asthma should assess whether the disease is still active and continues to need treatment, it is not wise to withhold treatment in the hope that asthma will go away by itself. That may indeed occur, but it may not, and there can be considerable avoidable suffering and disability in the interim.
