Exercises For People With Asthma
Some exercises and sports are better for you than others if you have exercise-induced bronchoconstriction or asthma. Activities that need short bursts of energy are less likely to induce symptoms, such as:
- Hiking and walking
Its best to avoid sports that demand continuous exertion, such as:
- Running
- Basketball
- Netball
Winter sports can be especially challenging and cause symptoms because of the cold, dry air at that time of year skiing, snowboarding, ice skating, ice hockey etc
Swimming can be fine because the warm, humid pool environment does not irritate the airways. However you may find that chlorine or other water-additives may trigger your symptoms so try different pools if that affects you.
Your doctor or nurse can advise the best ways to manage your symptoms when exercising. This may include using breathing exercises or avoiding exercise in certain climates.
How Can I Manage And Treat My Eib
With proper management, you can enjoy exercise and achieve your full potential. Proper management requires that you:
- Take steps to prevent symptoms
- Take medicine before exercising
- Do a proper warm up for 6 to 10 minutes before periods of exercise or vigorous activity
- Carefully watch your respiratory status before, during and after exercise
Children With EIB Inform teachers and coaches if you have a child with EIB. Kids with EIB should be able to take part in activities they just may need medication before an activity.
Athletes With EIB If you are an athlete, disclose your medicines and adhere to standards set by the U.S. Olympic Committee. Request a list of approved and prohibited medications from the Committee hotline at 1-800-233-0393.
Which Activities Are Ok For Kids With Eia
Exercise is a great idea for everyone, including kids with exercise-induced asthma. Besides keeping kids fit, exercise can improve lung function by strengthening the breathing muscles in the chest.
Encourage your child to be active while also keeping asthma symptoms under control by following the asthma action plan. Ask your doctor which exercises, sports, and activities are safe for your child.
These activities usually are OK for people with EIA:
- easy walking, jogging, or hiking
- golf
- gymnastics
- shorter track and field events
Endurance sports and those requiring extended energy output can be more challenging. So can cold-weather sports, like cross-country skiing and ice hockey.
But that doesn’t mean kids can’t play these sports if they enjoy them. In fact, many athletes with asthma have found that with proper training and medicine, they can do any sport they choose.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Asthma Cough
What Exams And Tests Diagnose Exercise
If you are having an asthma attack, your health-care professional will ask you questions about your symptoms, medical history, and medications. Answer as completely as you can. He or she will also examine you and observe you as you breathe.
He or she will assess the severity of the attack. Attacks are usually classified as mild, moderately severe, or severe. This assessment is based on several factors.
- Symptom severity and duration
- Degree of airway obstruction
- Extent to which the attack is interfering with regular activities
If you have had symptoms and are seeking medical care afterward, the health-care professional will ask questions and perform tests to search for and rule out or exclude other causes of the symptoms. The evaluation will almost certainly include tests of how well you can breathe at rest and may include tests during exertion. These tests are done at rest, after six to eight minutes of exercise, and then at regular intervals until at least 30 minutes after you have stopped exercising. Proper diagnosis is essential to ensure that the most appropriate treatment is given.
Measurements of how well you are breathing can be assessed using the following methods:
No blood test can pinpoint the cause of asthma.
- Your blood may be checked for signs of an infection that might be contributing to the symptoms.
- In severe attacks, it may be necessary to sample blood from an artery to determine exactly how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are present in your bloodstream.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Exercise

The goal of asthma treatment is that you can participate fully in any activity you choose.4 If you have underlying asthma outside of exercise, a long-term control medication may be needed. This medication reduces inflammation and airway sensitivity.
Your health care provider may suggest taking a medication before you begin exercise. Short-acting beta-agonists are often recommended for exercise-induced asthma.1 These medications relax the airway and allow it to open up. They are taken five to 20 minutes before starting to exercise. They are effective for two to four hours.
If you are using a SABA every day, your provider may recommend adding another medication.1 Your provider may prescribe a daily inhaled corticosteroid or leukotriene receptor antagonist.1 For athletes with allergies, an antihistamine may be recommended.1
You May Like: Role Of Eosinophils In Allergy
What Can I Do To Reduce My Symptoms
For some athletes, a ten-minute warm-up can reduce exercise-induced asthma for about two hours.1 The best warm-ups include high-intensity intervals.
For people with cross-country skiers asthma, breathing through a face mask warms and humidifies the air. The warm, humid air is easier to breathe.1
Diets for exercise-induced asthma have not been well studied. There is some evidence that a low-salt diet may help.1 A vitamin C supplement or a fish oil supplement might also be helpful. In two studies of vitamin C and one study of fish oil, people who took the supplement had less airway narrowing than people who did not take the supplement.
What Types Of Medicines Treat Or Prevent Eib
There are three types of medicines to prevent or treat the symptoms of EIB. Your health care provider can help you find the best treatment program for you based on your asthma history and the type of activity.
- Short-acting beta agonist / bronchodilator : This medication can prevent symptoms when taken 10 to 15 minutes before exercise. It will help prevent symptoms for up to four hours. This same medication can also treat and reverse the symptoms of EIB should they occur.
- Long-acting bronchodilator: This needs to be taken 30 to 60 minutes before activity and only once within a 12-hour period. Salmeterol can help prevent EIB symptoms for 10 to 12 hours. This medication is for preventing symptoms. It does not offer any quick relief, so it not for treating symptoms once they begin.
- Mast cell stabilizers: Cromolyn sodium or nedocromil sodium need to be taken 15 to 20 minutes before exercise. These medications may also help to prevent the late phase reaction of EIB that some people experience. These medications are only for preventing EIB because they do not relieve symptoms once they begin. Some individuals use one of these medicines in combination with a short-acting bronchodilator.
If you have frequent symptoms with usual activity or exercise, talk to your doctor. An increase in your long-term control medications may help. Long-term control medicines, such as inhaled steroids, can help EIB.
Recommended Reading: Quick Relief Inhaler For Asthma
How Long Can Exercise
Exercise-induced asthma can be chronic, which means that a person may experience it every time they exercise. For others, it can be infrequent, or it may only occur when they do certain types of exercise, such as running.
The actual symptoms are typically fairly short-lived. They usually happen during exercise and for around 1015 minutes after stopping.
In rare cases, a person may have a more serious asthma attack that requires emergency treatment. People with asthma should always carry an inhaler for asthma attacks.
A doctor may suspect EIB based on a persons physical history. For example, if the persons wheezing and breathlessness persist despite getting fitter, they may have exercise-induced asthma.
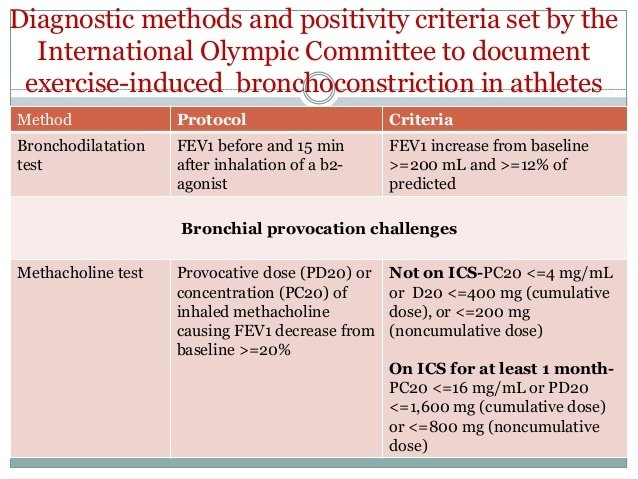
Doctors use two tests to diagnose EIB: spirometry and bronchial provocation tests.
Spirometry measures how much air a person can breathe in and out. A doctor usually performs this test shortly after the person exercises to test for breathing difficulties.
Bronchial provocation tests expose the lungs to an asthma trigger, then use spirometry to see how the lungs react.
According to a 2018 review article , exercise-induced asthma is under-diagnosed and frequently misdiagnosed. Many people assume that wheezing, coughing, and breathlessness are normal parts of exercise and either ignore their symptoms or avoid exercise.
Pearls And Other Issues
It is important to consider the anti-doping regulations present in many athletic programs. Some medications utilized for Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction may require a therapeutic use exemption . ICS, LTRA’s, MCSA’s, inhaled anticholinergics, SABA , antibiotics, 1st generation antihistamines with or without oral decongestant, nasal ipratropium, dextromethorphan, nasal corticosteroids, topical decongestants, and proton pump inhibitors in appropriate doses do not enhance performance and therefore do not require a TUE. Oral steroids and terbutaline are banned and require TUE.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Smoke Weed With Asthma
Clinical Signs And Symptoms
EIB was a disease classically diagnosed and treated on the basis of self-reported symptoms. Recent studies have shown a lack of diagnosis specificity and sensitivity based on symptoms.- These studies have demonstrated that athletes with presumed symptoms of EIB did not have EIB with testing. Testing also found a number of athletes that fit criteria for EIB but did not have symptoms, emphasizing a need for objective testing in athletes. Therefore, although a history and a physical examination are important, they should not be relied on to diagnose or exclude the diagnosis of EIB.
The presentation of EIB can vary the most common symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, chest pain , cough , early fatigue, and poor performance. Symptoms are similar to those that occur in an acute asthma attack, but they are induced by 10 to 15 minutes of intense exercise and are much shorter in duration. Symptoms often dissipate when the activity stops. A late-phase response can occur 4 to 8 hours after exercise.
Physical examination immediately after exercising may reveal wheezing, which usually dissipates with rest. Athletes with wheezing at rest should be suspected of having asthma rather than EIB. Dermatologic examination may demonstrate atopic disease such as eczema. Nasal examination may show enlarged, boggy turbinates. The throat may have posterior pharynx cobblestoning and enlarged tonsils, which are both signs of allergic rhinitis.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Exercise
Your provider will ask about your symptoms, including when you have them and how long they last. After listening to your lungs, your provider will ask you to perform an activity that usually triggers your symptoms . Then your provider will measure your lung function with a spirometry test.
During spirometry, you exhale as much air as you can as fast as possible. You breathe into a tube attached to a machine called a spirometer. The machine measures how well your lungs work after exercise.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Asthma Attacks Last
Can Exercise Induced Asthma In Kids Be Prevented And Treated Effectively
Whenever cold weather sets in, exercises must be performed indoors and care should be taken to use a scarf or some other material to cover the mouth and nose.
Before starting an exercise a prescribed drug must be inhaled to prevent symptoms of asthma.
Perform exercises at a comfortable level, which does not exert you too much.
Use proper techniques, warm-up, and cool-down exercises after each exercise session.
Perform exercises at a lower level in case of viral infection.
Take necessary outdoor precautions during seasons like summer or spring when pollen count is high or a high level of pollution is observed. It is better to avoid outdoor activity, especially if you suffer from allergies.
Exercise should not be avoided or used as an excuse to take part in physical activity. Proper diagnosis and treatment will enable children to lead a full life participating in a sport or physical activity they like without suffering from the symptoms of asthma in kids.
Fish Oil For Exercise Induced Asthma
The choking of the airways causes different symptoms including hacking, snugness over the chest, wheezing and shortness of breath. These symptoms for the most part start to back off over a time of thirty minutes or somewhere in the vicinity emulating exercise.
When you exercise or move strenuously, you have a tendency to breathe faster and through your mouth. When you breathe in through your mouth, the air that you breathe in does not experience the humidifying and warming process that happens when you breathe gradually through your nose. All things considered, the air that enters your lungs is colder.
Individuals with exercise-induced asthma have lungs that are exceptionally touchy to this sharp change in temperature, which bothers the airways and reasons different asthma symptoms. The seriousness of symptoms and the affectability of the lungs change from individual to individual.
Recommended Reading: Can Weed Cause Asthma
How Do You Treat Exercise
- Is struggling to breathe
- Canââ¬â¢t walk or talk
- Shows other signs of a severe attack
1. Stop the activity.
- Have the person sit down and rest.
2. Follow the personââ¬â¢s asthma plan, if possible.
- Find out if the person has an individualized asthma action plan from a doctor.
- If so, follow its directions.
3. Give asthma first aid.
- If the person doesn’t have an asthma plan:
- For a child, follow directions for first aid and using an inhaler in Acute Asthma Attack Treatment for Children.
4. Resume activity when itââ¬â¢s safe.
- Wait until the person can breathe easily and is symptom-free before resuming exercise.
- If symptoms return when person starts exercise again, repeat treatment and stop exercise for rest of day.
5. Follow up.
Risk Factors And Triggers
Risk factors for EIB and potential inciting factors include a family or personal history of atopy to environmental factors . Oral breathing does not warm the air, thus making it more likely to provoke airway cooling and EIB. Allergens, high pollen counts, pollution, and dry air can trigger symptoms. Intense exercise is more likely to cause bronchospasm because of the increased ventilation. Last, chemicals, insecticides, pesticides, and fertilizers can all trigger symptoms of EIB.,
Don’t Miss: How To Calm Down Asthma Symptoms
A Possible Reason For Exercise Induced Asthma
A respiratory disorder that is often chronic, asthma is a condition that is not pleasant and which is also known to cause many discomforts including inflammation in the airways. This blocks air from getting to your lungs and results in mild to severe breathing problems which are commonly referred to as asthma. An asthma attack is also known to onset suddenly and it is often also caused by allergens present in the environment that an asthma sufferer finds themselves in.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- I have trouble breathing when I exercise? Do I have EIB?
- How does EIB differ from regular asthma?
- Is it safe for me to exercise? What kinds of exercise can I do?
- Are there medicines I can take to prevent and treat my symptoms?
- How long do I have to take the medicines and what are the side effects?
- Are there other lifestyle changes I can make to relieve my symptoms?
- Will I always have EIB or can it go away?
Recommended Reading: Peer Reviewed Articles On Asthma
What Is Exercised Induced Bronchoconstriction
Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction , is a temporary narrowing of the lower airways, occurring after vigorous exercise. It may occur in people with asthma or in people without asthma.
In people with asthma who experience EIB, exercise is an asthma trigger. This means that for some people during vigorous exercise the small airways in the lungs become red, swollen, and may become blocked with mucus. This narrows the airways and makes it more difficult to breathe.
Not everybody that has asthma has EIB and some people with EIB may not have asthma
What About Exercise Induced Asthma
Are you one of the people that only gets asthma attacks when you run or exercise? If so, you are one of the few to suffer from what is known as exercise induced asthma.
In past years, medical professionals used to think that this exercise induced condition was a completely different form of asthma. But nowadays its a well known fact that asthmatics have a worsening of their symptoms right after heavy exercise, even to the point of triggering an attack.
This asthma from exercise is a problem that is very heavily slanted towards children and young people in general, something which also used to puzzle doctors in the past, but of course, children and teenagers exercise a lot more than adults do, so the adults dont really get the symptoms from exercise in the first place!
So what is exercise induced asthma really? Its simply a regular form of the disease which is just too mild to show up in most conditions, and needs that extra big provocation, like an unusually intense and long bout of running or biking, to come into view.
If the air you breathe while you are taking exercise if dry and cold, then the attack will be even worse, while if it is warm and moist air, the symptoms will be less pronounced. What happens is, the increased breathing in and out that happens during exercise dries up the lining in your lungs, and if they cool down at the same time, they will try to swell with blood to warm up and rehydrate again, and this will definitely worsen any asthma condition.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Medication And Competitive Sport
For elite, professional, and semi-professional athletes this is a very significant concern as the issue of drugs in sport and any medications or supplementstaken, may have serious implications.
Many sporting bodies require elite, professional, and semi-professional athletes to provide evidence of EIB, such as Bronchial Challenge Test results before they are permitted to use EIB medicines during competition. So for any athlete competing at this level before you take any medication or supplement, even if prescribed by your doctor, always check with relevant authorities.
Don’t Rely Only On Quick

You can also use pre-exercise drugs as a quick-relief treatment for symptoms. However, you shouldn’t need to use your pre-exercise inhaler more often than your doctor recommends.
Keep a record of how many puffs you use each week, how often you use your pre-exercise inhaler for prevention and how often you use it to treat symptoms. If you use it daily or you frequently use it for symptom relief, your doctor might adjust your long-term control medication.
Recommended Reading: Asthma Statistics Worldwide
