Asthma Nursing Care Plan
Patients with asthma suffer mainly from respiratory symptoms, and the nurse should address these symptoms as soon as they are identified. Nursing diagnoses for patients with asthma center mostly on airway clearance, breathing patterns, and gas exchange but also include other issues involving endurance, anxiety, and even nutritional status. In this section, some of the most common nursing diagnoses and their care plan will be presented to help better care for patients with asthma. The following nursing diagnoses were more commonly seen among patients with asthma:
- Ineffective airway clearance
Nursing Interventions With Rationales For Bronchial Asthma Ineffective Airway Clearance
| Nursing Interventions | Rationales |
| Administer short-acting beta-2-adrenergic agonist. | These drugs are bronchodilators that relax the airway muscles, allowing air to pass more easily. Examples include Albuterol and Levalbuterol. |
| Administer inhaled corticosteroids. | These drugs work by decreasing inflammation and mucous production in the airways. They should be given after bronchodilators. Examples include Budesonide and Fluticasone. |
| If airway swelling persists despite bronchodilators or corticosteroids, anticipate alternate medication administration. | Magnesium sulfate, Helium, and different types of anesthesia are alternate medications that can be used to decrease inflammation and lessen airway resistance. |
| Administer oxygen as needed. | Oxygen should be provided based on patient needs and requirements. Intubation may be required for airway protection. |
| Monitor vital signs, breath sounds, and mucous membranes for the presence of cyanosis. | The patient must be closely monitored for signs of impending hypoxia or respiratory failure. |
| Monitor ABGs as needed. | A patient experiencing an asthma attack will first exhibit respiratory alkalosis. As the condition worsens the patient will then exhibit respiratory acidosis. ABGs should be monitored to guide treatment. |
Nursing interventions with rationales for Asthma Ineffective airway clearance
Types Of School Health Care Plans
A school health care plan is a written set of documents that outlines your childs medical condition and needs. The plan usually lists information about your childs asthma or allergies, how they should be managed, and what to do in an emergency. It may also include school staff responsibilities, training, and services needed to help keep your child safe. A school health care plan often includes several forms and documents.
Three common types of school care plans are:
- Emergency care plan This is a medical plan from your childs doctor for the school to follow to treat asthma while the student is at school.
- Individual health care plan This is a type of nursing care plan. For a student with asthma, this would also include an emergency care plan. An IHCP addresses what the school will do to establish and maintain a safe school environment for the student with asthma.2
- 504 plan This is a legally binding plan written by the school in collaboration with a student and their family.3 Similar to an IHCP, this plan provides guidelines for changes in the classroom or other school locations to achieve the goal of providing a safe education.
Emergency Care Plans
An ECP is the medical plan your childs doctor writes for the school nurse to follow. ECPs usually use terms people with a non-medical background can also understand and follow.
Your childs ECP should have:
Individual Health Care Plans
The school nurse will work with you, your child, and their doctor to write the IHCP.1
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Asthma
Shortness Of Breath Nursing Care Plan 2
Ineffective Airway Clearance
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Airway Clearance related to copious and persistent bronchial secretions secondary to pertussis, as evidenced by dyspnea, increased mucus secretions, and productive cough.
Desired Outcome:
- The patient will be able to maintain clear and open airways as evidenced by normal breath sounds, normal depth, and rate of respirations.
- The patient will demonstrate the ability to effectively cough up secretions after treatments and deep breathing exercises.
- The patient will demonstrate increased air exchange.
- The patient will be able to classify methods to improve the removal of secretions.
- The patient will recognize the significance in changes of sputum such as the color, characteristics, and amount.
- The patient will be able to identify and avoid necessary factors that limit effective airway clearance.
What To Do If The School Will Not Work With You
Public or private schools that get funds from the federal government have to follow Section 504 and the ADA. Public schools must provide a free and appropriate education in the least restrictive environment.6
Also, all non-religious private schools must abide by the ADA, regardless if they receive federal funding. While they do not have to provide a free and appropriate education, private schools are public accommodations under the ADA, and therefore have to take necessary steps to make sure a child is not excluded, denied services, or treated differently due to their disability .7 As a recent agreement with the Department of Justice indicated, these obligations can include the requirements to administer emergency medicine such as epinephrine auto-injectors.
If a public school is not willing to accommodate your child, contact your school districts superintendent or 504 coordinator in writing. If you continue to be unhappy with the plan as implemented by the school district, you can contact the Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights or file a suit in a federal court.3
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Asthma Test
Nursing Interventions With Rationales For Bronchial Asthma Anxiety
| Nursing Interventions | |
| Stay with the patient and encourage slow, deep breaths. | Consistent presence and coaching can help lessen feelings of anxiety during an asthma exacerbation. |
| Provide a calm environment and decrease stimuli. | A calm environment will decrease anxiety, thus decreasing oxygen consumption. |
| Educate the patient on pursed-lip breathing. | Pursed lip breathing is an intentional breathing technique that encourages slow, deep, effective breaths. |
| Help the patient develop an emergency plan for asthma attacks. | The patient should always have their rescue inhaler on hand. During an asthma exacerbation, the patient should sit upright and administer their rescue inhaler. If no relief is felt within 4 minutes, the patient should seek immediate medical attention, and continue administering the rescue inhaler every 4 minutes. |
Nursing interventions with rationales for Asthma Anxiety
Nursing Interventions With Rationales For Bronchial Asthma Knowledge Deficit
| Nursing Interventions | Rationales |
| Educate the patient about rescue inhalers vs. controller inhalers. | Rescue inhalers are meant to be used in case of emergency and should not be used every day. Controller or maintenance inhalers can be used every day to decrease symptoms of asthma. Examples of maintenance inhalers are Symbicort and Advair. |
| Educate the patient about environmental asthma triggers. | Examples of environmental triggers include smoke, allergens, mold, and air pollution. |
| Educate the patient on how to effectively manage asthma when exercising. | Sometimes asthma can be exacerbated by exercise. Walking, swimming, or hiking are asthma-friendly alternatives, and exercise with short bursts of activity is better than prolonged exercise. Sometimes a physician can prescribe a rescue inhaler to be used before exercise. |
| Show the patient how to use a spacer. | A spacer is a tube between the inhaler and the patients mouth which gives the patient more time to inhale the medication. |
| Advise the patient to rinse their mouth following administration of an inhaled corticosteroid. | If the mouth is not properly rinsed after administration of inhaled corticosteroids the patient can develop thrush, a fungal infection in the mouth, which looks like white patches on the mucous membranes and tongue. |
Nursing interventions with rationales for Asthma Knowledge deficit
Recommended Readings & References
Don’t Miss: Can Muscle Relaxers Help Asthma
Signs And Symptoms Of Shortness Of Breath
Shortness of Breath is characterized by difficult breathing. After strenuous activity, it may last for 1 or 2 minutes. A person may feel like there is not enough air into the lungs in mild cases.
In severe circumstances, however, it can be like the feeling of suffocating. Overexertion, time spent at high altitude, or a symptom of a variety of illnesses can all cause dyspnea.
Shortness of Breath can be identified by observing the following symptoms:
- Dyspnea caused by physical activity or a medical condition
- As a result of breathing issues, feeling suffocated or smothered
- A struggle to breathe
- Wheezing
- Coughing
Its understandable if someone experiences shortness of breath after a vigorous workout. However, It is advised to seek medical help if any of the following symptoms are present:
- After strenuous activity, I took a short breath sooner than usual.
- Out of breath after an activity that used to be easy before.
- Dyspnea for no apparent reason.
Signs And Symptoms Of Asthma Attacks
- Non-stop coughing
- Severe wheezing
- Rapid breathing
- Retractions tightened neck and chest muscles
- Difficulty talking
- Feelings of anxiety or panic
- Pale, sweaty face
- Cyanosis blue lips or fingernails
Asthma may be worsening if the patient experiences the signs and symptoms or has asthma attacks more frequently.
He/she may have more shortness of breath based on peak flow meter readings and may have to alleviate the symptoms using a quick-relief inhaler more frequently than usual.
Recommended Reading: Can You Join The Air Force With Asthma
How To Create A School Health Care Plan For Asthma Or Allergies
Your childs school may already have a process in place for creating care plans.
Start by contacting the school to ask who the point of contact is for creating a school health care plan for your child. Then request a meeting with the school representative to talk about your childs needs and to ask questions about the schools policies.
Use a positive tone when approaching the school. You are part of the team that will work together to keep your child healthy and safe at school. Communicate often, calmly, and confidently.
Make contact well before the school year starts such as in the spring before. The first few days of school are very busy for staff. Youll want to have everything in place before the first day of school.
Here are some questions you may want to ask at your meeting:
- Does the school or school district have a nurse?
- When can I meet with school staff responsible for my child, such as their teacher, coach, and dietary staff ?
- Where will my childs medicines be kept? Will they be easily accessible?
- Are staff trained on how to manage asthma and allergies?
- How does the school staff handle asthma episodes or attacks and allergic reactions?
- How is bullying handled?
If you feel your child needs a 504 plan, also contact the school districts 504 coordinator. Ask to have your child evaluated for a 504 plan.
Your childs school health care plan may include:
Personalised Care In Asthma
A primary care nurses quick guide to
Personalised care in asthma
Key learning points:
1. Personalised care planning, in the form of an individual written action plan, is a key feature of best practice for asthma management in primary care
2. Personalised asthma action plans may improve patientsknowledge, confidence, symptom control, and reduce hospital admission and readmission
3. Despite these benefits, personalised asthma action plans are under-utilised primary care nurses can aid effective implementation
Asthma is the most common long-term condition in the UK, affecting up to 5.4 million people. Many asthma patients are managed in primary care therefore nurses in the setting have a role in ensuring best practice, a key feature of which is personalised care.1,2,3,4
What is personalised care in asthma?
Personalised care planning involvesa conversation- or series of conversations between a patient and health professionals, to agree how to manage the patients condition. The Kings Fund stresses that this is a continuous process, not a one-off event.5,6
It has been recommended in asthma management for a quarter of a century, and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence states that healthcare professionals should ensure that every asthma patient has a written, personalised plan.1,7,8
Why are written asthma action plans important?
What does an action plan contain?
· Specific advice about recognising loss of asthma control.
Monitor their asthma.
Resources
You May Like: How To Avoid Asthma Triggers At Home
Cystic Fibrosis Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
Cystic fibrosis is a rare, genetic, and progressive disease that damages the lungs, digestive system, and causes further complications to other organs. Cystic fibrosis is normally diagnosed as a newborn. There is no cure for CF and patients usually do not live past their 50s. Mutations to the CFTR Read more
A Stepwise Management Approach
There is no National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance for asthma management. However, a quality standard outlines 11 high-priority areas for quality improvement linked to British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network guidance on asthma management .
In most patients, asthma is effectively managed with inhaled corticosteroids and inhaled ß2-agonists according to steps 1-3 of the BTS/SIGN stepwise management plan . However, a minority of patients have poorly controlled asthma despite the prescription of optimal inhaled medication. These patients require additional maintenance therapies such as leukotriene receptor antagonists, sustained-release theophylline, oral ß2 agonists, or intermittent or regular oral corticosteroids . All patients at step 4 or 5 require referral to specialist asthma services for assessment and evaluation of their suitability for individualised therapy .
Read Also: Is Warm Mist Humidifier Good For Asthma
Risk Factors Of Asthma
A number of factors are thought to increase your chances of developing asthma. They include:
Nursing Care Plan For Asthma 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance related to imbalance between oxygen supply and demand secondary to asthma as evidenced by fatigue, overwhelming lack of energy, verbalization of tiredness, generalized weakness, and shortness of breath upon exertion
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to demonstrate active participation in necessary and desired activities and demonstrate an increase in activity levels.
Don’t Miss: Is Asthma Acute Or Chronic
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is an umbrella term that also includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD causes the airways of the lungs to become narrow due to inflammation, mucus, or other damage. This affects the ability to breathe normally and often results in shortness of breath, especially on exertion. COPD often occurs from smoking Read more
Sample Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care Plans
Here we have formulated a sample nursing care plan for Acute Exacerbation of Bronchial Asthma based on a hypothetical case scenario.
It will include three sample nursing care plans with NANDA nursing diagnoses, nursing assessment, expected outcome, and nursing interventions with rationales.
You May Like: How To Cure Asthma Naturally Permanently
Shortness Of Breath Nursing Care Plan 3
Impaired Gas Exchange
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange related to changes in oxygen supply, destruction of the alveoli, and changes in the alveolar-capillary membrane, secondary to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , as evidenced by dyspnea, SpO2 level of 78%, confusion, and restlessness.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to demonstrate improved breathing and will show normal oxygenation of tissues as measured by normal arterial blood gasses results, and will have no signs of respiratory distress.
- The patient will be able to participate in the treatment plan to the best of his/her ability.
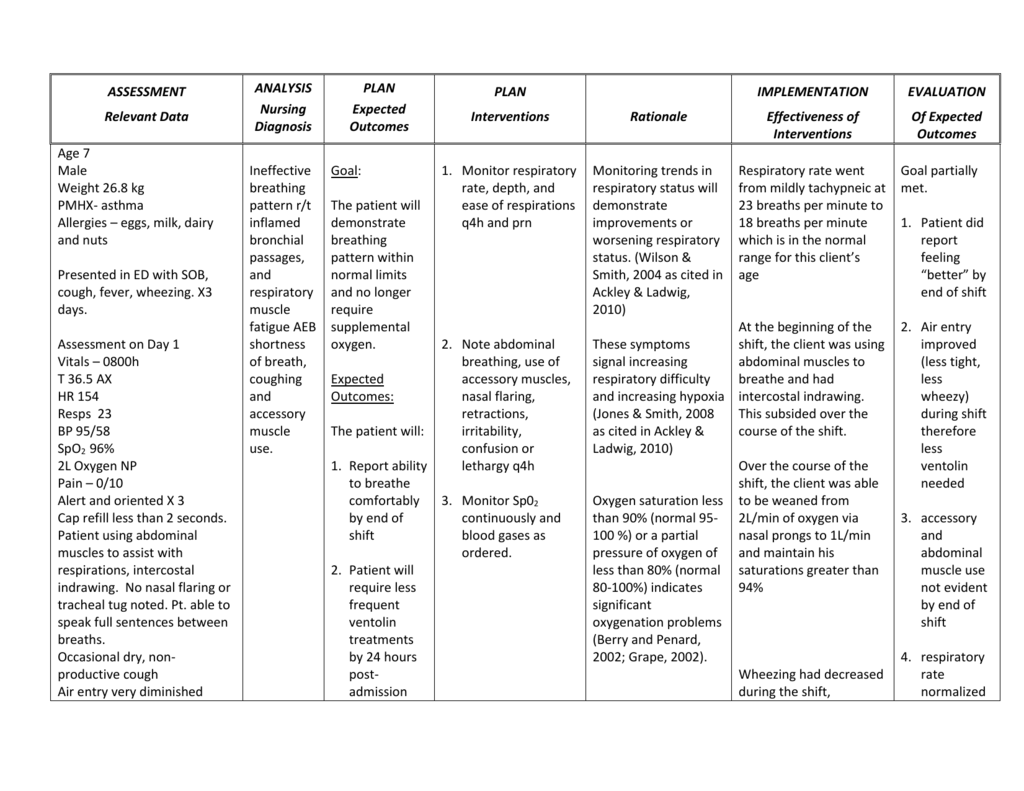
Nursing Care Plans For Shortness Of Breath 1
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Nursing Diagnosis:Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to airway obstruction, secondary to asthma, as evidenced by dyspnea, bradypnea, nasal flaring, and use of accessory muscles when breathing.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will be able to demonstrate calm breathing at a normal rate and depth and the absence of dyspnea.
- The patient will be able to maintain an effective breathing pattern.
- The patient will have respiratory rates within the normal range.
- The patient will be able to verbalize comfort when breathing.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Cough
Treatment For Shortness Of Breath
Nursing Care Plan For Asthma 3
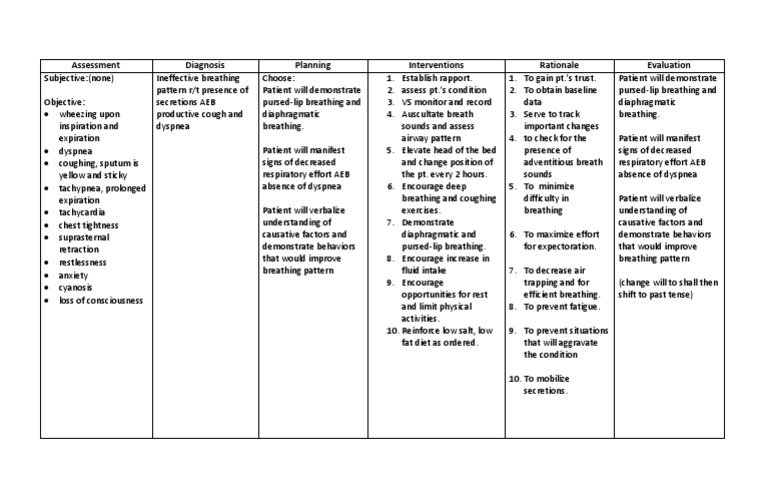
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to inadequate pulmonary ventilation, secondary to asthma, as evidenced by shortness of breath, coughing, cyanosis, nasal flaring, changes in the depth of breathing, excessive use of accessory muscles, presence of respiratory noise, and tachypnea.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patients abnormal breathing pattern will be corrected, as evidenced by a normal respiratory pattern, with no evidence of dyspnea noted.
- The nurse will note that the use of diaphragmatic compression is evident, ABG values are within the prescribed ranges, and there is evidence of comfortable breathing, either vocally or by the patients conduct.
You May Like: Can Cold Air Cause Asthma
