Q: Whats The Difference Between Asthma And Copd
Asthma occurs frequently in people with a family history of the disease and often begins in childhood. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, and these symptoms flare up during an asthma attack. At other times, symptoms may fade or become minimal.
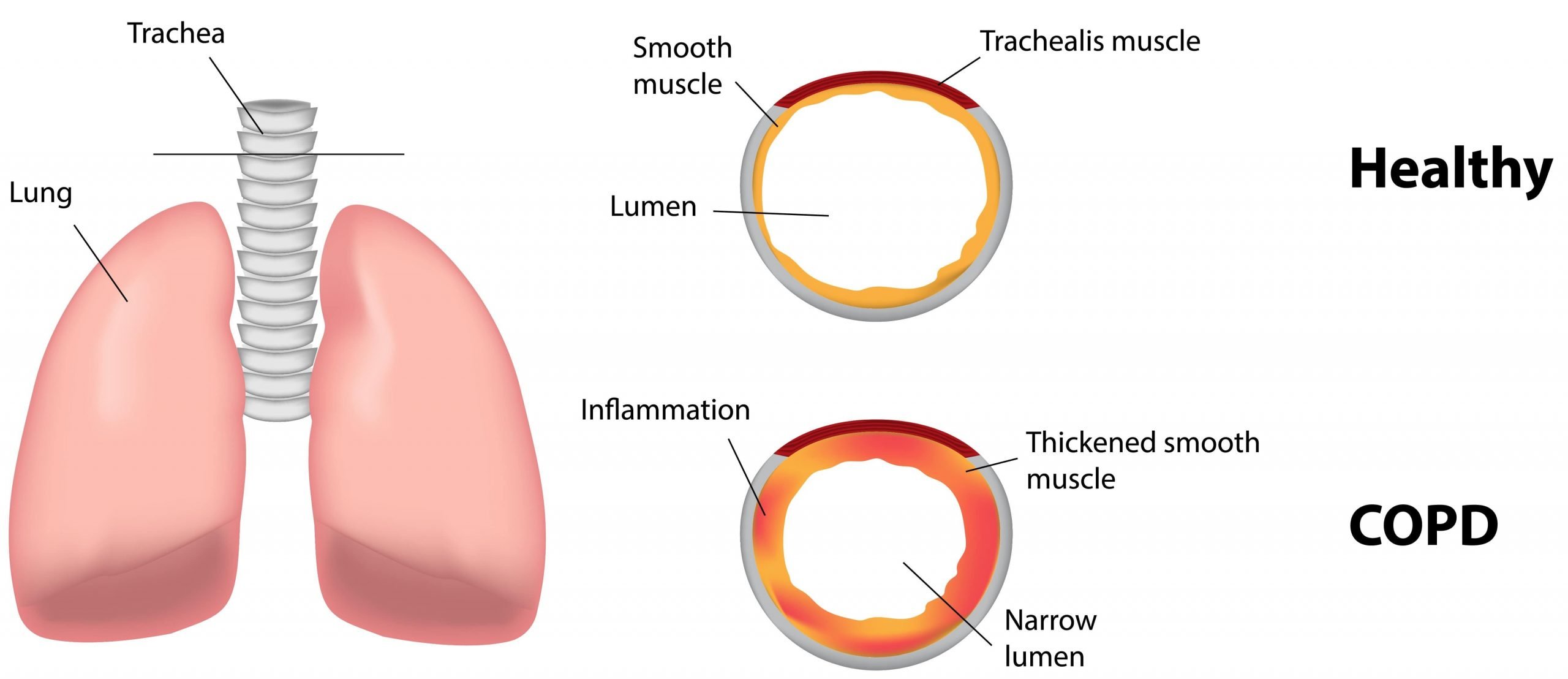
COPD is different and usually strikes later in life. Most people diagnosed with COPD either used to smoke, or still do. Some symptomssuch as chest tightness and coughingare similar to asthma. Other symptoms, such as mucus production, are distinct to COPD. Unlike asthma, symptoms rarely ever fade completely.
Airflow Limitation In Copd
The chronic airflow limitation of COPD is caused by a mixture of small airway disease and parenchymal destruction , the relative contributions of which vary from person to person . Chronic inflammation causes structural changes and narrowing of small airways. Destruction of the lung parenchyma, also by inflammatory processes, leads to the loss of alveolar attachments to the small airways and decreases lung elastic recoil in turn these changes diminish the ability of the airways to remain open during expiration .
So in COPD inflammation causes small airway disease and parenchymal destruction that all lead to airflow limitation .
Treatment Options For Obstructive Vs Restrictive Lung Disease
Treatment options will be somewhat different for these two types of respiratory illness.1 With obstructive lung disease, the goal is to reduce inflammation and relax the airways. So, treatments might include bronchodilators and/or inhaled steroids. Some medications are long-acting and some are shorter-acting.1
In addition, with COPD, supplemental oxygen therapy might be helpful. This is not generally prescribed in people who have asthma. Changes in lifestyle may also be helpful. For example, with asthma, learning to avoid your triggers can help keep your asthma under control.1
With restrictive lung disease, the treatment options are often more limited. They may also vary greatly, depending on the specific type of restrictive disease. Steroids and bronchodilators are sometimes used. Medications that suppress the immune system may also be helpful.1 Other options might include supportive oxygen therapy and even lung transplants.1
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Contact Post Acute Medical Today
If you have asthma or COPD, learn more about the cardiopulmonary health services available to you by contacting Post Acute Medical today. At Post Acute Medical, we concentrate on quality care, patient satisfaction and long-term positive outcomes. Providing high-quality care to our patients is our top priority.
Find out how Post Acute Medical can help you manage your COPD or asthma by locating the facility nearest you and calling for more information.
Inflammatory Mediators Involved In Copd
Chemotactic factors: Lipid mediators: e.g., leukotriene B4 attracts neutrophils and T lymphocytes, Chemokines: e.g., interleukin-8 attracts neutrophils and monocytes. Proinflammatory cytokines: e.g., tumor necrosis factor- , IL-1 , and IL-6 amplify the inflammatory process and may contribute to some of the systemic effects of COPD. Growth factors: e.g., transforming growth factor-ß may induce fibrosis in small airways .
You May Like: Are Chihuahuas Good For Asthma Patients
Defining Obstructive Vs Restrictive
Obstructive lung disease is a condition where the airflow into and out of the lungs is impeded.1 This occurs when inflammation causes the airways to swell, making them narrower. Because of that, breathing well becomes harder and air often gets trapped in the lungs. This results in something known as hyperinflation of the lungs. Exhaling becomes slower and shallower than in a person with a healthy respiratory system.1
Examples of obstructive lung disease include:1
Restrictive lung disease is a condition where the lungs don’t function effectively. People with this cannot take a full, deep breath and fill their lungs with air. This can be due to problems within the lungs themselves or due to some kind of damage from external forces .1
With intrinsic disorders, the lungs’ restriction is related to weak muscles, stiffness in the chest wall or damaged nerves.1 Examples of these diseases include:1
- Interstitial lung disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Pneumoconiosis
With extrinsic disorders, other non-respiratory diseases end up causing problems with the function of the airways and lungs. These can include:1
- Obesity
Also, both obstructive and restrictive disease will be diagnosed by using a careful medical history and a variety of pulmonary function tests. The results of those tests and your history will help a doctor determine which type of lung disease you might have.1
Difference Between Asthma And Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
July 21, 2017 by Rachna C
The respiratory disease which is diagnosed during childhood, resulting in shortness of breathing, dryness of a cough, chest tightening is called asthma. On the other hand, COPD also known as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is also one of the respiratory disease, which occurs after the age of 4o, and the condition gets progressively worse with age.
The cells of our body need oxygen to work and grow, and this oxygen is taken by the lungs through the simple process of breathing. Usually, in a day, we breathe 25,000 times a day. But people suffering from any lungs infection experience the problem in breathing.
Lung diseases are one of the most common medical conditions existing in the world. There are many kinds of lungs infections like bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, emphysema, COPD, asthma, pneumonia, tuberculosis, etc. pollutions, infections, allergens, smoking or genetics can be the major cause of all these problems.
In this article, we will mark the vital difference between the two common respiratory disease asthma and the COPD. We will also discuss their causes, symptoms, and treatment.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop An Asthma Attack Without Medication
Staging And Treatment Of Asthma
The goals of long-term management of asthma should include the following: 1) achievement and maintenance of control of symptoms 2) prevention of asthma exacerbations 3) maintenance of pulmonary function as close to normal levels as possible 4) maintenance of normal activity levels, including exercise 5) avoidance of adverse effects from asthma medications 6) prevention of the development of irreversible airflow limitation and 7) prevention of asthma mortality.
The recommended GINA treatment algorithm, together with the clinical features and staging of severity of asthma, are available on the GINA website . It is important to note that the forced expiratory volume in one second levels are before treatment, i.e. in the unmedicated state.
Until the advent of anti-inflammatory drugs, asthma was treated on an as-needed basis and treated as an acute disease rather than a chronic disease. With the recognition that asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease, there has been a gradual move towards treating it more aggressively and earlier in the hope that this may change the natural history of asthma and prevent some of the remodelling that sometimes occurs.
Information Sources And Selection Criteria
Occupational respiratory irritants
To identify the evidence of irritants of the respiratory tract, all agents denoted as may cause respiratory irritation by the phrase H335 and may cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled H334 and/or as irritants by American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists were initially listed later this list was compared with results of our database search .
Database search.
We searched for publications reporting investigations exclusively in humans . To be included, the publications had to deal with subjects occupationally exposed to airway irritants.
MEDLINE®-Database was searched with PubMed® from its inception up to December 2007 with the following medical subject headings combinations for each single agent:
Agent AND Humans AND OR Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive OR Lung Diseases, Obstructive/*chemically induced OR Respiratory Function Tests) AND ).
If more than 20 publications per agent were found, the search was more specified:
Agent AND Humans AND AND adverse effects AND OR Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive OR Lung Diseases, Obstructive/*chemically induced OR Respiratory Function Tests) AND ).
Reference list screening
We also considered references in the identified already existing 13 systematic reviews or overviews of causes of work-related asthma or COPD and tried to combine results of both approaches.
Don’t Miss: Can You Join The Army If You Have Asthma
How Different Lung Diseases Affect The Lung
An analysis of how different lung diseases affect the lungs functionsThe lungs are essential respiratory organs in humans which enable us to breathe. Our lungs are specialised structures that allow us to exchange gases. We require oxygen from the air to enter our blood, as all cells need it to function. We also need to get rid of carbon dioxide which is a product of many metabolic reactions within our cells. Our lungs allow this gas exchange so we can get rid of carbon dioxide and acquire oxygen
Basis And Quality Of Data
Irritant-induced obstructive airways diseases cannot usually be diagnosed in one clinical visit and, instead, follow-up and/or detailed clinical investigations are necessary. The diagnostic gold standard for OA is SIC using a specific occupational agent in an exposure chamber. SIC is particularly indicated in the clinical setting where new causative substances with still unknown adverse respiratory sensitization potential are suspected. This gold standard is not applicable for large studies so, it was used mainly in case series or reports.The evidence levels to confirm irritant-induced work-relaated asthma or occupational COPD for the listed irritant agents, professions or worksites are frequently low with the major reasons being that high quality studies were missing and the quality of the available studies was low. Nevertheless, this knowledge is the best available and may help physicians to identify a suspected irritant agent as causative in irritant-induced work-related asthma and / or occupational COPD. As also recently stressed by Quint et al., implementing an evidence-based identification and regulatory process for OA will help to ensure primary prevention of OA. In cases of low evidence level of an agent that does not exclude a causative role, caution should be exercised and a more detailed diagnostic testing of relevant exposure should be performed.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Q: How Is Acos Treated
Your provider can begin treatment if you have COPD or asthma alone. But if you have ACOS, you may want to see a pulmonologista specialist in lung health. People with ACOS often experience more severe symptoms than those with a single lung disease, but working with a specialist can help you feel better. Treatment for ACOS usually includes medicine.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Due To Occupational Exposure
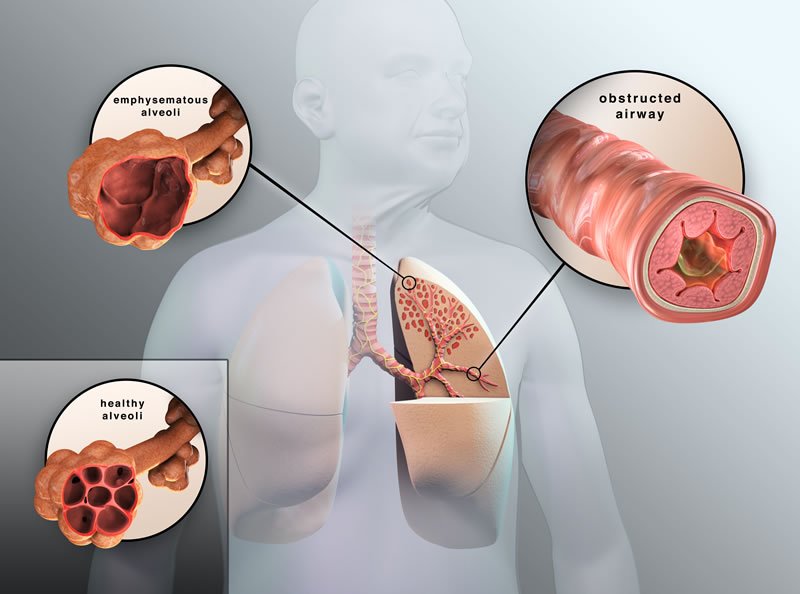
The diagnosis of COPD is based on chronic productive cough, airflow limitation that is usually not fully reversible, and a progressive, abnormal inflammative response of the lungs mostly caused by long-term smoking and by other noxious particles or gases.
During ongoing causative exposures , airflow limitation is usually progressive and associated with an abnormal inflammatory response of the lungs. Patients with COPD have greater number of neutrophils and alveolar macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid than healthy non-smokers. Sites of emphysema, which are frequently found in COPD patients, contain large numbers of lymphocytes, and the extent of lymphocyte accumulation correlates with reduction of FEV1.
In their summaries of the literature, Hnizdo et al., Trupin et al. and Balmes et al. found an occupational contribution in about 15% of COPD cases.
Occupational COPD is identified on epidemiological basis, by observing increased frequencies of COPD among certain working groups, e.g. in construction workers. Some occupational exposures may cause COPD associated with emphysema.
At later stages of OA, the condition of some subjects does not improve over weekends or during holidays and coincides with symptoms of COPD patients. This observation also applies to non-occupational obstructive airways diseases and indicates that a group with changing diagnoses as well as with some overlap between OA and occupational COPD, does exist.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Asthma Without Inhaler
Lifestyle Factors For Copd
If you have COPD it can help to make a number of important lifestyle changes, including:
- quitting smoking techniques can include cold turkey, counselling, nicotine replacement therapy and medications that work on brain receptors. Evidence shows that counselling, together with medical therapy, is most effective
- being as physically active as possible. If possible, attend pulmonary rehabilitation
Expanding Access To Intensive Self
Teaching people how to manage asthma on their own is one of the most important parts of controlling the disease nationwide. Everyone with asthma should develop an individualized asthma action plan with a doctor. In general, people with asthma arent getting action plans from their doctors. Intensive asthma self-management education can improve asthma symptom control for individuals whose asthma is not well-controlled with medical management based upon the NAEPP Guidelines.
Don’t Miss: Nasal Inhaler Recipes
Inflammatory Cells In Asthmatic Airways
Mast cells -activated mucosal mast cells release bronchoconstrictor mediatorshistamine, cysteinyl leukotriens, prostaglandin D2. They are activated by allergens through IgE receptors or by osmotic stimuli . Eosinophils are in increased number in airways, release basic proteins that may damage epithelial cells, and have a role in releasing a growth factors and airway remodeling , T lymphocytes are in increased number and release specific cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 that orchestrate eosinophilic inflammation and IgE production by B lymphocytes . There may also be an increase in inKT cells which release large amounts of T helper: Th1 and Th2 cytokines . Dendritic cells,Macrophages are in increased number, and release inflammatory mediators and cytokines that amplify the inflammatory response . Nutrophils are in increased number in airways and sputum of patients with severe asthma and in smoking asthmatics, but the role of these cells is uncertain and their increase may even be due to steroid therapy .
Is It Asthma Or Copd
A spirometry test, or pulmonary function test, can measure how well the lungs work. Individuals blow into the device as hard and as long as they can, providing information about how much air the lungs take in and expel. Many doctors use spirometry tests to measure airway problems associated with COPD and asthma.
Factors doctors look at when weighing a diagnosis with COPD or asthma include:
- A history of smoking: Most people with COPD are or were smokers.
- Age: Asthma often appears in childhood. If breathing difficulties occur after the age of 40, doctors are more likely to diagnose COPD.
- Symptoms: Coughing in the morning, heavy phlegm, and progressively getting worse suggest COPD. Recurring attacks, particularly if accompanied by allergies or eczema, suggest asthma.
- Family history: Asthma is more likely to run in families.
- Symptom triggers: People with COPD may have symptoms when they are active or at rest, without a known trigger. Asthma attacks may be caused by physical activity or something in the environment.
- Onset of symptoms: COPD tends to get worse over time, while asthma attacks come on suddenly.
- Responsiveness to treatment: Asthma tends to respond better to quick acting rescue inhalers than COPD does.
Diagnosis with either condition doesnt rule out developing another breathing disorder, so patients should report all symptoms to their doctor.
Also Check: Does Weed Cure Asthma
Occupational Copd An Underestimated Category
We identified only 20 out of 474 publications that referred to occupational COPD, with most of them implicating inorganic or organic dust or fumes, such as cement dust, construction work and diesel exhaust, as the causative agents.
As an example, the mixed agent cement dust was investigated in 14 studies but only four studies documented cement dust as the causative agent in occupational COPD . The remaining 10 studies described irritant-induced OA cases or identified significant asthma symptoms/ obstructive ventilation patterns without a clear diagnosis . It can be assumed that if it had been considered on the other 10 studies then occupational COPD caused by cement dust would have been frequently observed.
General acceptance of this statement does not exist, although evidence for an association between individual exposure levels and COPD is accumulating in the latest literature.
Are There Rehabilitation Programs For Copd
The goals of COPD rehabilitation programs include helping the patientreturn to the highest level of function and independence possible, whileimproving the overall quality of the person’s physical, emotional, andsocial life. Attaining these goals help people with COPD live morecomfortably by improving endurance, providing relief of symptoms, andpreventing progression of the disease with minimal side effects.
In order to reach these goals, COPD rehabilitation programs may include thefollowing:
-
Medication management
-
Exercises to decrease respiratory symptoms and improve muscle strength and endurance
-
Respiratory treatments to improve breathing ability
-
Assistance with obtaining respiratory equipment and portable oxygen
-
Methods to increase independence with activities of daily living
-
Exercises for physical conditioning and improved endurance
-
Stress management, relaxation exercises, and emotional support
-
Smoking cessation programs
Don’t Miss: Asthma And Humidifier Use
Asthma And Copd: What’s The Difference And Is There A Link
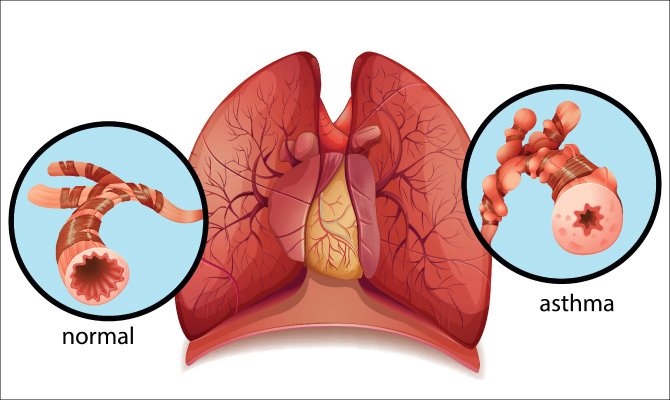
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are lung diseases. Both cause swelling in your airways that makes it hard to breathe.
With asthma, the swelling is often triggered by something youâre allergic to, like pollen or mold, or by physical activity. COPD is the name given to a group of lung diseases that include emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Emphysema happens when the tiny sacs in your lungs are damaged. Chronic bronchitis is when the tubes that carry air to your lungs get inflamed. Smoking is the most common cause of those conditions .
Asthma gets better. Symptoms can come and go, and you may be symptom-free for a long time. With COPD, symptoms are constant and get worse over time, even with treatment.
Key Differences Between Asthma And Copd
The following points will target on the fundamental differences between both kinds of reparatory diseases:
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do When You Have An Asthma Attack
