What Triggers An Asthma Attack
Numerous triggers can cause asthma attacks, including:
Tobacco smoke;While smoking is unhealthy for anyone, its particularly dangerous for people with asthma. If you smoke, you should quit.
Secondhand;smoke can also trigger an asthma attack. Avoid situations in which people around you smoke. Also don’t let people smoke in a place where you spend a lot of time, such as your home or car even if you’re not present when they smoke.
Smoke from wood or grass;Even though it may seem natural, smoke from these sources contains harmful gases and particles.
Avoid burning wood in your home. If you live in an area where wildfires occur, monitor air quality forecasts and try to stay inside when particle levels are at their worst.
Outdoor air pollution
Certain foods and food additives;While almost any food can cause an allergic reaction, a few additives are widely believed to cause adverse reactions in some people.
Acid reflux;can also trigger an asthma attack in some people, so any food that aggravates this condition may also be responsible for symptoms.
Respiratory infections;These include;influenza , the common cold, respiratory syncytial virus , and;sinus infections.
Strong emotional statesCertain medications
Other Tests For Conditions That May Mimic Asthma
There are some medical conditions that often make asthma harder to treat and control, in addition to being asthma mimics. These include allergies and GERD. If you are diagnosed with asthma, your doctor might also test you for these conditions, or treat them for several weeks to see if your asthma symptoms also improve.
For more information on allergies, GERD, and other triggers, see Causes of Asthma.
How Is Asthma Treated
Take your medicine exactly as your doctor tells you and stay away from things that can trigger an attack to control your asthma.
Everyone with asthma does not take the same medicine.
You can breathe in some medicines and take other medicines as a pill. Asthma medicines come in two typesquick-relief and long-term control. Quick-relief medicines control the symptoms of an asthma attack. If you need to use your quick-relief medicines more and more, visit your doctor to see if you need a different medicine. Long-term control medicines help you have fewer and milder attacks, but they dont help you while you are having an asthma attack.
Asthma medicines can have side effects, but most side effects are mild and soon go away. Ask your doctor about the side effects of your medicines.
Remember you can control your asthma. With your doctors help, make your own asthma action plan. Decide who should have a copy of your plan and where he or she should keep it. Take your long-term control medicine even when you dont have symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Does Marijuana Affect Asthma
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Asthma
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including information about your parents and siblings. Your provider will also ask you about your symptoms. Your provider will need to know any history of allergies, eczema and other lung diseases.
Your healthcare provider may order a chest X-ray, blood test or skin test. Your provider may order spirometry. This test measures airflow through your lungs.
Is Asthma An Autoimmune Disease
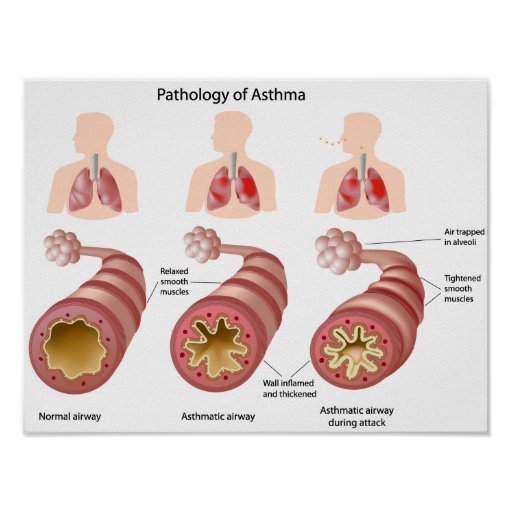
Asthma is caused by an overactive immune response. But asthma is not considered an autoimmune disease. The processes that cause the asthma immune response are different from the ones that cause autoimmune diseases.3
Most people with asthma have allergic asthma. This is sometimes called extrinsic asthma. In extrinsic asthma, the immune system is triggered by allergens. This causes the immune system to overreact. The reaction causes inflammation in the lungs, which then causes trouble breathing. This immune reaction is mainly driven by an antibody called IgE.3
Some people with asthma are not triggered by allergens. Instead, things like exercise, stress, extreme hot or cold temperatures, or infections trigger their asthma. This type of asthma is called nonallergic, or intrinsic, asthma. It makes up 10 to 33 percent of all asthma cases. The immune response in intrinsic asthma is very similar to the response in extrinsic asthma. However, intrinsic asthma is more likely to cause severe asthma.4
Read Also: How To Deal With Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
How Do My Airways React To Triggers
If you have asthma you have sensitive airways that are inflamed and ready to react when they come into contact with something they don’t like.
If you come into contact with one of your;asthma triggers;it causes your airways to react in three ways:
These reactions in the airways make it difficult to breathe and lead to asthma symptoms, such as chest tightness, wheezing, or coughing. It can also lead to an asthma attack.
Why Asthma Is Not Considered As Autoimmune Disease
There are several reasons for which asthma is not considered as an autoimmune disease to date. The reasons are the following
You May Like: Can Someone With Asthma Take Cough Medicine
How Is Asthma Connected To The Immune System
Scientists are still studying exactly how asthma is connected to the immune system. They think the immune system has a role in the asthma response and the development of asthma.1
Scientists do not know exactly why some people develop asthma. Some think asthma could be caused by an immune response to viruses. They believe standard viruses could cause the immune system to develop the behavior that leads to asthma in some people.5,6
The causes of intrinsic asthma are not well understood. This is because it can be triggered by so many things. But some scientists also think an autoimmune response may have a role in causing it. This potential link could help people with intrinsic asthma, who are sometimes more difficult to treat. It is possible that intrinsic asthma could respond to treatment with medicine used for autoimmune conditions.1
What Is An Asthma Action Plan
Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop an asthma action plan. This plan tells you how and when to use your medicines. It also tells you what to do if your asthma gets worse and when to seek emergency care. Understand the plan and ask your healthcare provider about anything you dont understand.
Don’t Miss: What’s An Asthma Attack Feel Like
Emerging Issues In Respiratory Diseases
There are other important respiratory diseases not included in this topic area, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, respiratory distress syndromes, and upper airway conditions such as rhinitis and chronic sinusitis. In some cases, effective preventive interventions do not exist. In others, nationally representative trend data for disease prevalence and/or incidence, causative exposures, and other preventable risk factors are not available for tracking of measurable goals. It is hoped that, as preventive interventions and surveillance for respiratory hazards and diseases continue to improve, future versions of Healthy People will include measurable goals for at least some of these additional respiratory hazards and diseases.
Other emerging issues in the Respiratory Diseases topic area include:
Staging And Treatment Of Asthma
The goals of long-term management of asthma should include the following: 1) achievement and maintenance of control of symptoms; 2) prevention of asthma exacerbations; 3) maintenance of pulmonary function as close to normal levels as possible; 4) maintenance of normal activity levels, including exercise; 5) avoidance of adverse effects from asthma medications; 6) prevention of the development of irreversible airflow limitation; and 7) prevention of asthma mortality.
The recommended GINA treatment algorithm, together with the clinical features and staging of severity of asthma, are available on the GINA website . It is important to note that the forced expiratory volume in one second levels are before treatment, i.e. in the unmedicated state.
Until the advent of anti-inflammatory drugs, asthma was treated on an as-needed basis and treated as an acute disease rather than a chronic disease. With the recognition that asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease, there has been a gradual move towards treating it more aggressively and earlier in the hope that this may change the natural history of asthma and prevent some of the remodelling that sometimes occurs.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Someone With Asthma
Managing Your Asthma During The Pandemic
- Keep taking your controller medication daily or as prescribed. This will help cut your risk of an asthma attack being triggered by any respiratory virus, including COVID-19.
- Carry your reliever inhaler with you every day, in case your asthma symptoms flare up.
- Monitor your asthma symptoms closely and follow your Asthma Action Plan to help you recognize and manage asthma symptoms, and know when to seek advice from your healthcare provider or emergency help.
- If you must travel, pack all asthma medications in your carry-on luggage so it is easily accessible. Pack extra asthma medication in case your travel plans change or are delayed. Be sure to check travel advice and advisories from the;Government of Canadas website.
- Take care of yourself. Get plenty of rest and fluids, and eat good nutritious food.
- Ensure that you speak with your healthcare provider about recommended vaccinations. Getting both the influenza vaccination and pneumococcal disease vaccinationare important steps people with asthma can take to help stay healthy.
- Reach out to Asthma Canadas Asthma & Allergy HelpLinecall-back service to connect with a Certified Respiratory Educator if you have questions about managing your asthma. Call 1-866-787-4050 or email;
How Long Asthma Lasts For
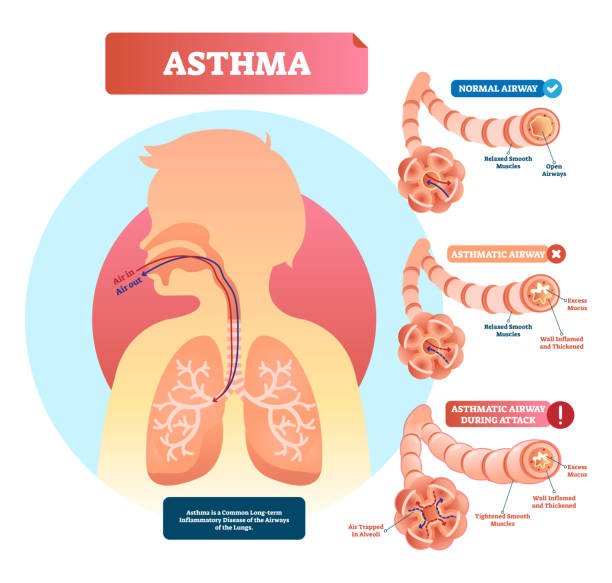
Asthma is a long-term condition;for many people, particularly if it first develops when you’re an adult.
In children, it sometimes goes away or improves during the teenage years, but can come back later in life.
The;symptoms can usually be controlled with treatment. Most people will have normal, active lives, although some people with more severe asthma may;have ongoing problems.
Read Also: How Do You Know If You Have Asthma
Treatment And Medication Options For Asthma
There is no cure for asthma, but you can alleviate and prevent your symptoms through quick-relief and long-term control medication. Long-term control medication works to reduce inflammation to make your airways less sensitive to asthma triggers. Its usually taken daily through an inhaler or as an oral pill. Quick-relief medicines help to relieve symptoms when they happen, relaxing the tight muscles around your airways and easing the flow of air.
Is It Asthma Or Heart Disease
Dr. T Ask Doctor T
I have a question about my father a 74 year old man in relatively good health. Hes fairly active but has asthma and is about 20 pounds overweight. His breathing has been declining rapidly and the PA at his asthma doctors office put him on Prednisone and antibiotics for one week and wants him to see a cardiologist if hes not better. He had a physical 2 months ago told his doctor that he was feeling tired all the time and the doctor told him he was just getting old. Would a heart condition causing breathing issues be picked up during a normal physical? How quickly should we get him to a cardiologist? Im scared to leave him alone.
- Acute episodes of asthma are often treated with steroids
- Difficulty breathing can certainly have a cardiac origin
- New onset of fatigue
Asthma is a chronic disease, and sometimes exacerbated by infections, colds etc. If it is indeed just asthma, a short course of steroids to break the bronchial spam often helps. Likewise, antibiotics may treat an associated infection. However, your dad should have responded by now. Also, this extra weight means additional work for his heart & lungs, so weight loss should be part of his treatment recommendations!
Questions:
- Does It hurt to take deep breaths, and if so, where?
- Is he more short of breath when laying down?
- Is he coughing a lot, and if so, is his sputum production increased. Normal/abnormal?
- Is his weight gain sudden or getting worse?
Some tests:
- EKG
- Blood tests
Also Check: Can You Get Ssi For A Child With Asthma
S Everyone Can Take To Lower The Risk Of Getting And Spreading Covid
- Practice social distancing/self-monitoring/self-isolation/isolation as directed by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and often with soap and warm water for at least 30 seconds.
- Wear a non-medical grade face mask when you are in public places and in situations where you are not able to maintain physical distancing, like on public transportation or the grocery store.
- Avoid closed spaces, crowded places, and close contact.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces, such as toys, phones and door handles.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, ears or mouth.
- Stay home if you are sick. Encourage those you know who are sick to stay home until they no longer have symptoms.
- Avoid contact with people who are unwell.
- Make sure that you get high-quality information about COVID-19 from reliable sources. The Public Health Agency of Canada is a reliable source of information, as are provincial and territorial public health authorities.
Adjusting To The New Normal
Is asthma an autoimmune disease? The short answer is no, its not. If you get an asthma diagnosis, its not the end of the world. You can still live a fulfilling life. You just need to learn how to identify your triggers and get on the best treatment to stay on top of your symptoms.
Be sure to check out our blog to learn more about managing your asthma flare-up.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Diagnosed With Asthma
Vaccine Distribution In Canada
As part of the Canadian Thoracic Societys COVID-19 Respiratory Roundtable panel representing Canadians living with lung disease, Asthma Canada signed a joint statement titled Prioritization of Canadians with Lung Disease in COVID-19 Vaccination Rollout. Alongside other lung health organizations, Asthma Canada is urging;federal, provincial and territorial governments to prioritize people living with lung disease who are at higher risk for more serious COVID-19 complications in the vaccination rollout.;From Canadians living with a lung disease such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , cystic fibrosis, lung cancer, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, and pre- and post-lung transplant, there is widespread concern regarding when in the vaccine rollout in the provinces and territories they will have the opportunity to receive the vaccine.
We will continue to advocate for our community on this subject and will share more information as it becomes available.
Read the full statement here:English | French
How Long Does Asthma Take To Develop
There is no fixed period of time in which asthma can develop. Asthma as a disease may develop from a few weeks to many years after the initial exposure. Analysis of the respiratory responses of sensitized workers has established three basic patterns of asthmatic attacks, as follows:
Immediate â typically develops within minutes of exposure and is at its worst after approximately 20 minutes; recovery takes about 2 hours.
Late â can occur in different forms. It usually starts several hours after exposure and is at its worst after about 4 to 8 hours with recovery within 24 hours. However, it can start 1 hour after exposure with recovery in 3 to 4 hours. In some cases, it may start at night, with a tendency to recur at the same time for a few nights following a single exposure.
Dual or Combined â is the occurrence of both immediate and late types of asthma.
You May Like: What Steroids Are In Asthma Inhalers
Compounding Effects Of Fatigue
The symptoms of celiac disease and asthma are different. But when you have both celiac disease and asthma, you can experience substantial fatigue, especially if neither of them is well controlled.
Asthma is characterized by shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and a chronic cough. When your asthma symptoms worsen, you can feel tired due to the increased effort of breathing, sleep disturbance, and low oxygen.
Celiac disease symptoms include abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, weight loss, and more. Aside from feeling depleted as a result of these symptoms, celiac disease can cause poor absorption of nutrients, leading to fatigue from malnutrition.
Add to this the burden of dealing with severe asthma or refractory celiac disease while managing other aspects of your health and it’s easy to picture just how significant the resulting fatigue can be.
Feeling tired and out of energy can be a sign that your celiac disease, your asthma, or both are either flaring and/or poorly controlled.
How Are Asthma And Copd Linked
Adults with asthma are more likely to develop COPD than adults without asthma.3 One 20-year study showed that people with asthma were:6
- 10 times more likely have symptoms of chronic bronchitis
- 17 times more likely be diagnosed with emphysema
- 5 times more likely to have COPD
In fact, features of asthma and COPD start to overlap over time.6
- Airway sensitivity is typical of asthma, but some people with COPD have sensitive airways.
- One hallmark of asthma is that the airway obstruction can be reverse with medication. However, reversibility can decline over time for people with moderate or severe asthma.
It can be hard to get the diagnosis right, especially in older adults. Overlap between the two conditions is so common, that the term Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome is sometimes used.7
Recommended Reading: What Happens To The Alveoli During An Asthma Attack
