What Can Go Wrong With The Immune System
Sometimes a person may have an immune response even though there is no real threat. This can lead to problems such as allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases. If you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake.
Other immune system problems happen when your immune system does not work correctly. These problems include immunodeficiency diseases. If you have an immunodeficiency disease, you get sick more often. Your infections may last longer and can be more serious and harder to treat. They are often genetic disorders.
There are other diseases that can affect your immune system. For example, HIV is a virus that harms your immune system by destroying your white blood cells. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS . People with AIDS have badly damaged immune systems. They get an increasing number of severe illnesses.
An Integrative Approach To Autoimmune Disease Treatment
Autoimmune diseases are chronic conditions that require life-long management. The traditional approach to treatment involves the use of immunosuppressive medications, such as TNF inhibitors. Despite being considered the gold standard for the treatment of autoimmune conditions, a significant number of individuals do not respond adequately to treatment. Additionally, long-term use of these medications can lead to severe side effects and leave patients vulnerable to opportunistic infections and an increased risk of cancer.
An integrative approach to treatment may incorporate dietary and nutrient therapy, as well as lifestyle interventions, such as strategies for better sleep, mindfulness, and avoidance of environmental triggers.
When To See A Doctor
See a doctor if you have symptoms of an autoimmune disease. You might need to visit a specialist, depending on the type of disease you have.
- Rheumatologists treat joint diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis as well as other autoimmune diseases like Sjögrens syndrome and SLE.
- Gastroenterologists treat diseases of the GI tract, such as celiac and Crohns disease.
- Endocrinologists treat conditions of the glands, including Graves disease, Hashimotos thyroiditis, and Addisons disease.
- Dermatologists treat skin conditions, such as psoriasis.
The Healthline FindCare tool can provide options in your area if you need help finding a specialist.
Don’t Miss: How Does Dupixent Help Asthma
S Everyone Can Take To Lower The Risk Of Getting And Spreading Covid
- Practice social distancing/self-monitoring/self-isolation/isolation as directed by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and often with soap and warm water for at least 30 seconds.
- Wear a non-medical grade face mask when you are in public places and in situations where you are not able to maintain physical distancing, like on public transportation or the grocery store.
- Avoid closed spaces, crowded places, and close contact.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces, such as toys, phones and door handles.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, ears or mouth.
- Stay home if you are sick. Encourage those you know who are sick to stay home until they no longer have symptoms.
- Avoid contact with people who are unwell.
- Make sure that you get high-quality information about COVID-19 from reliable sources. The Public Health Agency of Canada is a reliable source of information, as are provincial and territorial public health authorities.
Autoimmune Disease And Your Health

Having lupus, rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis raises your risk for heart disease. While taking steps to reduce heart disease is always a good idea, it is even more essential if you have one of these conditions. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to keep your heart healthy and strong. For example, keeping your blood pressure and cholesterol levels within healthy ranges, eating a nutritious diet and exercising regularly can be lifesaving.
These steps can also help reduce the symptoms of autoimmune disease. Orbai admits that making time for healthy living can be hard, given womens fast-paced lives, but she insists that finding the balance is key to living with autoimmune disease.
Its something thats going to involve commitment, and sometimes its going to be tough, she says. But learning to listen to your body and being smart about what triggers your disease is important. Its something you do for yourself.
Sign Up for Our Free Newsletter
One of the best things you can do to protect and improve your health is to stay informed. Your Health is a FREE e-newsletter that serves as your smart, simple connection to the world-class expertise of Johns Hopkins.
Also Check: When Was Dupixent Approved For Asthma
Association Between Ad And Crohns Disease
Pooling result of five studies estimated an elevated prevalence of Crohns disease in AD compared to controls, with an average OR of 1.66 . Three cohort studies further detected an increased incidence of Crohns disease in AD, with a pooled RR of 1.38 , indicating that patients with AD had higher risk of developing Crohns disease .
Autoimmune Phenomena In Asthma: Evidence From Immunological Studies
Autoantibodies are a hallmark of autoimmunity. However, the mere presence of autoantibodies does not clinically justify the presence of an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune involvement in the pathogenesis of asthma has been proposed based on the numerous studies that report the presence of circulating autoantibodies against diverse self-antigens/structures .
Read Also: How Long Does An Asthma Flare Up Last
Infections Impact On Asthma
Asthma can be triggered by a variety of things. One of the most common triggers are infections, including respiratory viruses and, to a lesser degree, bacterial and fungal infections of the respiratory tract.
Respiratory viruses are the predominant infectious cause of asthma attacks. As the viruses attach to receptors on the lining of the airways, they effectively trip the alarms for the immune system to attack, leading to inflammation and the onset of acute asthma symptoms.
In some cases, the symptoms of the infection will precede the attack in others, the infection and asthma symptoms will co-occur.
Among the respiratory viruses closely link to asthma symptoms are:
- Rhinoviruses, the predominant cause of the common cold
- Coronaviruses, some of which cause colds
- Adenoviruses, associated with colds, bronchitis, and pneumonia
- Influenza viruses, associated with flu
- Parainfluenza viruses, which mainly affect infants and young children
- Respiratory syncytial virus , which most children get by the age of 2
Viral-induced asthma attack is extremely common, affecting roughly 85% of children and 50% of adults with asthma.
Less commonly, bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis have been known to trigger asthma attacks, particularly if a sinus infection is involved.
Fungal infections are more closely associated with poor asthma control rather than the onset of an attack, although it can occur.
Systemic Autoimmune Diseases With Pulmonary Manifestations
Caution needs to be exercised in ascertaining the dose of anti-IL5 mAb therapies in patients presenting with severe asthma and a known systemic autoimmune pathomechanism such as eGPA. If the mAb dose is not adequate, these severe patients with increased IgG load , and increased levels of IL-5 molecules present with a higher probability of falling into the zone of antibody-antigen equivalence leading to heightened inflammation/immune-complex mediated complications. Investigating target specificities of sputum autoantibodies against disease-specific autoantigens or adopting an omics approach can provide a tool for prognosis, diagnosis and monitoring response to biologics for several systemic autoimmune diseases that present with pulmonary complications.
Also Check: What Does An Inhaler Do For Someone Without Asthma
Possible Eosinophil Effector Functions In Autoimmune Diseases
Eosinophils are extremely versatile effector cells that damage tissues or modulate the activity of other immune and stromal cells. One could envision many of these effector functions playing a role in the context of autoimmune diseases as well . Damage of tissues and cells is a feature of many organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Eosinophils are well known for their strong cytotoxic properties, mediated mostly through granule proteins. This could contribute to organ destruction in autoimmune inflammation.
Autoimmune Diseases Include Common And Rare Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are a broad range of more than eighty related disorders, ranging from common to very rare. They affect around 5% of people and are an important health issue in Australia and New Zealand:
Common autoimmune diseases include thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes.
Less commone autoimmune diseases include systemic lupus erythematosus , also known as lupus, and vasculitis disorders .
Don’t Miss: How Does Asthma Affect The Lungs
Australian Researchers Claim Asthma And Autoimmune Breakthrough
Australian researchers say an “incredible” discovery could allow new treatments for asthma and prevent autoimmune diseases and life-threatening anaphylaxis. They have found a natural way the body stops rogue antibodies causing disease through a protein called neuritin.
Allergies and autoimmune diseases, where the body’s defenses turn rogue and target healthy tissue, are increasing in adults and children, but researchers arent quite sure why.
At the Australian National University, scientists have found that humans have their own mechanisms for fighting back against these pathogenic antibodies that can cause autoimmunity or allergies.
Professor Carola Vinuesa said its an exciting discovery.
We found a protein called neuritin that is made by our own immune system, and we never knew before that our immune system could make this protein, and it proves to be quite important to prevent allergies autoimmune diseases, she said.
Neuritin is like a supercharged antihistamine, the type of drug commonly used to treat allergy symptoms.
Vinuesa hopes the research could provide a completely new approach to current treatments for immune conditions, which can have a debilitating effect on patients.
Researchers say there are more than 80 known autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis.
The Australian study began five years ago and used genetically engineered mice and human cells grown in a laboratory. It was published in the science journal Cell.
New Drug Target For Asthma Autoimmune Disorders Identified
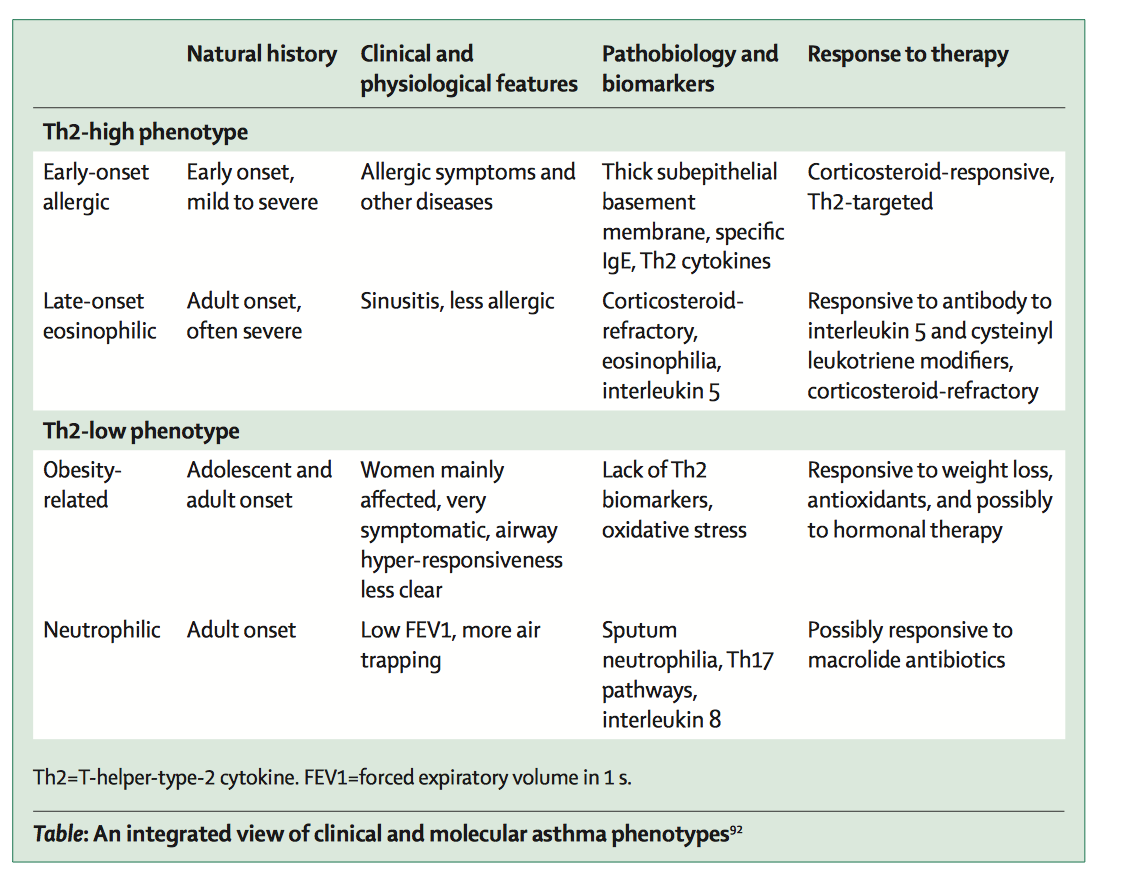
Using a new tool for probing the molecular makeup of cells, researchers have discovered that PD-1 a marker that already serves as a drug target for some cancers may also serve as a drug target for asthma and other autoimmune disorders.
The researchers, led by a group from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in the United Kingdom, report their work in the journal Nature.
Immune disorders arise because the immune system either fails such as by not removing unwanted cells during infection or cancer or becomes too active.
When it is too active, the immune system attacks healthy cells and tissue, giving rise to autoimmune diseases or allergies such as asthma, where the airways become swollen or inflamed.
In the new study, the researchers examine a recently discovered group of cells in the immune system called innate lymphoid cells . Within this group, there is a subgroup called ILC2 cells that influences immune responses during infections and asthma.
Scientists have observed that levels of ILC2 cells shoot up when triggered by pollen or toxins, causing lung inflammation.
However, as yet, they know little about how ILC2 cells develop from ILC progenitor cells in bone marrow, and whether they sport distinguishing markers once activated.
For the first time, the study team used a new tool called single-cell RNA sequencing to investigate ILC cells.
- There is no cure for asthma, but it can be managed with drugs and by avoiding triggers
- Asthma
Also Check: How Is Asthma Diagnosed In Toddlers
Foods That Contain Certain Additives
Many food items, especially ultra-processed foods, contain additives to improve shelf life, texture, and taste. Some of these may negatively affect your immune response.
For example, some emulsifiers, which are added to processed foods to improve texture and shelf life, can alter gut bacteria, harm your gut lining, and induce inflammation, all of which can cause immune dysfunction .
Carboxymethylcellulose and polysorbate-80 are commonly used emulsifiers that have been linked to immune dysfunction in rodent studies (
Choosing nutritious, high fiber carb sources like starchy vegetables, oats, fruit, and legumes over refined carbs is smart to support immune health.
Summary
A diet high in refined carbs may adversely affect your immune system. Choosing more nutritious carb sources like fruits and starchy vegetables is a better choice for your overall health.
Recommended Reading: Asthma Symptoms In Adults Bronchitis
Limit Exposure To Environmental Toxins
Research has identified a number of possible environmental toxins associated with immune dysfunction and autoimmunity, including:
- Asbestos
- Heavy metals
- Mineral oil
- Pesticides and fungicides
- Trichloroethylene
While a direct correlation between exposure to toxins and the manifestation of autoimmune conditions has not been established, limiting exposure to potential harmful toxins at home and in the workplace may help reduce the risk of autoimmune conditions.
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Asthma
Tips For Wearing A Face Mask With Asthma
The Public Health Agency of Canada currently recommends that Canadians wear non-medical face masks while in public spaces where physical distancing cannot be maintained such as on public transit, or at the grocery store.
Be sure to check your provincial or territorial authority for up-to-date guidance.
Wearing a face mask is NOT a substitute for physical distancing or frequent handwashing. Wearing a non-medical face mask is an extra measure that can be taken to protect those around you. When worn properly, a person wearing a non-medical mask can reduce the spread of their own infectious respiratory droplets.
Make sure you wear your mask properly. It should cover both your nose and mouth. If your mask gets soiled or wet, be sure to wash and dry it before wearing it again. You can read information about appropriate use of non-medical masks, and how to properly place, remove and clean a non-medical mask from the Public Health Agency of Canada.
The vast majority of people with asthma can wear a non-medical mask safely. If you are unable to wear a non-medical mask without experiencing breathing issues, do not wear a mask. Instead, make sure you are practicing physical distancing by maintaining a 2-metre distance. Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider as soon as possible to go over your Asthma Action Plan and review your asthma symptoms and control. Your healthcare provider may suggest or ask you to consider other options to protect yourself.
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis was first described by Churg and Strauss in 1951 . The disease progresses through three overlapping phases: adult-onset asthma, peripheral and tissue eosinophilia, and necrotizing vasculitis with tissue infiltration of eosinophils . EGPA is an idiopathic type of small vessel vasculitis and is also part of the hypereosinophilic syndromes . It is associated with HLA and IL-10 polymorphisms . About 40% of EGPA patients have perinuclear ANCA antibodies against myeloperoxidase , resulting in the classification of EGPA as an ANCA-associated vasculitis . The presence or absence of ANCA in EGPA may indicate two clinical subtypes with different organ involvement. ANCA-positive patients have more frequent vasculitis and glomerulonephritis, whereas ANCA-negative patients have more frequent heart and lung involvement .
Blood eosinophils in EGPA show an activated phenotype expressing high levels of CD69 and CD11b . Moreover, they express IL-25, a cytokine that increases release of IL-4, -5, and -13 from T cells. Serum IL-25 is increased in patients with active EGPA compared to inactive disease or healthy controls. It is also detectable in eosinophils from lesional biopsies. T cells in these biopsies and in the blood express the IL-25 receptor IL-17RB . This suggests a feed-forward loop between eosinophils and Th2 cells in EGPA.
Also Check: How To Deal With Asthma Flare Ups
Immunologic And Autoimmune Lung Disease
Respiratory problems are common and can be serious in patients who have a connective tissue or autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. With an autoimmune disease, a persons own immune system attacks the lungs, causing inflammation and scarring that can impair lung function and breathing. Rheumatoid arthritis may lead to a group of lung conditions categorized as rheumatoid lung disease. These include shortness of breath or dyspnea caused when the lung lining gets inflamed and filled with fluid . Common lung problems for people with connective tissue disease are interstitial lung disease , including pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary sarcoidosis, and pulmonary hypertension. Patients with autoimmune disease may also present with bronchiectasis and lung nodules.
Board-certified pulmonologists and thoracic surgeons at the Brigham and Womens Hospital Lung Center provide specialized medical and surgical services for immunologic and autoimmune lung diseases. They collaborate with a multidisciplinary team that crosses many specialties: rheumatology, radiology, pathology and pulmonary rehabilitation. Together with our diagnostic microbiology and rheumatology laboratories, we provide patients with accurate diagnosis and comprehensive disease treatment and management.
Antibodies Against Bronchial Epithelial Cells
In the following years, circulating IgG autoantibodies to cytokeratin 18 were more frequently detected in patients with non-atopic asthma compared to those with atopic asthma or healthy controls.,, IgG autoantibodies to alpha enolase were more frequently detected in patients with severe asthma compared with those with mild-to-moderate asthma or healthy controls. The subclass was confirmed to be predominantly IgG, indicating a possible complement-mediated cytotoxicity. Though the cytotoxicity of the detected IgGs against the bronchial antigens were confirmed in vitro, involvement of the complement cascade was not determined. Although a clinical correlation was reported with a decline in lung function, the use of immortalised cell-lines might have restricted the translational merit of these studies.
You May Like: Which Is Better For Asthma Humidifier Or Vaporizer
Association Between Ad And Systematic Lupus Erythematosus
The prevalence of systematic lupus erythematosus in AD and controls was reported in four studies . Patients with AD had a higher prevalence of systematic lupus erythematosus compared to controls, with an OR of 1.74 . Similarly, the incidence of systematic lupus erythematosus in AD and controls was reported in two cohort studies, with an average RR of 2.20 , indicating an increased risk of developing systematic lupus erythematosus in AD patients .
