Asthma May Raise Risk Of Copd Emphysema
Asthma Patients May Be Up to 17 Times More Likely to Develop Incurable Lung Diseases
July 12, 2004 Adults with asthma may face dramatically higher risks of developing potentially deadly lung diseases later in life, according to a new study.
Researchers found asthmatic people were 12 times more likely to be diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease than people without asthma.
COPD is a group of lung diseases for which there is no cure. COPD causes permanent damage to the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. It includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, it is the fourth leading cause of death in the U.S. and the world.
Our study shows a strong link between asthma diagnosis and the development of COPD, which suggests they may share a common background, says researcher Graciela E. Silva, MPH, of the University of Arizonas College of Medicine in Tucson, in a news release. It is possible that factors such as smoking and repeated episodes of acute bronchitis may facilitate the evolution of asthma into COPD, but the process by which asthma and COPD become comorbid conditions is not clear.
Who Gets Severe Asthma
Severe asthma affects both adults and children. It can develop at any age. Most people who are diagnosed with severe asthma already have an asthma diagnosis: perhaps their asthma changed over time, or developed into severe asthma because of hormonal changes, or pneumonia for example.
Some people are diagnosed right away with severe asthma, but its likely that they had asthma for some time before without it being diagnosed as severe. And it can take time to get a diagnosis of severe asthma.
I was diagnosed with asthma at 35, but my GP said Ive probably always had it. I spent a lot of time in hospital with chest infections and croup as a child. In the lead-up to my severe asthma diagnosis, aged 40, I had pneumonia and started getting a lot of infections. My asthma changed and I could barely walk or move.
We Asked Allergists And Pulmonologists What Patients Need To Know About The Two Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Q: What are similarities and differences between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ?
Asthma and COPD share similar symptoms persistent cough, wheezing, labored breathing during exercise, chest tightness and shortness of breath.
COPD involves several progressive lung diseases that develop over time, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Factors that point to a COPD diagnosis include:
- increased mucus or phlegm
- a greater frequency of respiratory tract infections
- history of smoking cigarettes
- exposure to secondhand smoke or environmental pollutants.
Most people with COPD develop symptoms after the age of 40 following years of exposure to lung irritation, particularly smoking. Other signs that could suggest COPD include fatigue, weight loss and morning headaches.
Q: Is one more common than the other?
Approximately 24 million people in the United States have asthma, including 6.2 million children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
More than 11 million Americans have COPD, but some 12-14 million more people may have the disease and not know it. COPD is sometimes misdiagnosed as asthma.
Q: Which is more serious?
Asthma and COPD are both serious, potentially life-threatening conditions. Both are treated with quick-relief inhalers for respiratory emergencies and daily controller medications that help keep airways open, reduce mucus and improve breathing.
Asthma
Q: Can asthma progress to COPD?
Reviewed by Purvi Parikh, MD
Also Check: Can Hayfever Cause Asthma Symptoms
Similaraties And Differences In Acute Exacerbation Of Asthma And Copd
-
Pathology is different in exacerbation of asthma and COPD
-
Causes of acute exacerbation of asthma and COPD are different.
-
Different role of LABA and ICS in prophylaxis of exacerbation of asthma and COPD.
-
Treatment of acute exacerbation is similar in asthma and COPD.
Acute exacerbation of Asthma
Triggers of acute exacerbation of asthma are usually: allergens, infections , GE reflux, other triggers, sometimes and co-morbidity .
Pharmacotherapy of acute asthma exacerbation
-
Bronchodilators
-
non -invasive mechanical ventilation .
The Differences Between Copd And Asthma

and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are both respiratory diseases involving chronic inflammation that leads to airflow obstruction. While they share similar symptoms, their causes and treatments differ. In some cases, asthma and COPD may overlap in what is termed asthma-COPD overlap syndrome, or ACOS.
However, the frequency and predominating symptoms in asthma and COPD are different. With COPD, you are more likely to experience a morning cough, increased amounts of sputum, and persistent symptoms. If you have asthma, you are more likely to experience episodic symptoms during and/or at night.
Another difference between asthma and COPD is the intermittent symptoms seen with asthma versus the chronic, progressive symptoms seen in COPD. Asthma symptoms are likely to occur after exposure to specific triggers, whereas COPD symptoms occur more regularly.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Spirometry Test For Asthma
Q: How Can I Improve My Lung Health On My Own
No matter which lung condition you have, working closely with your healthcare team can control its effects on your everyday life. But there are other steps you can take as well. For instance, if you smoke, its never too late to quit. Make sure that youre current with all vaccinations, especially the pneumococcal and annual flu vaccine. These viruses can be very harmful to people with a lung disease. In addition, consider asking your provider about pulmonary rehabilitation if you have consistent breathing problems. This type of rehabilitation focuses on managing symptoms, exercising, and eating a nutritious diet.
Whats The Outlook For People With Copd
With COPD, you might experience flare-ups of your condition . This is where breathing and other symptoms get worse suddenly over a short period of time. As the underlying COPD gets more severe, some people may not be able to cope with this at home and may need to go to hospital for treatment. Sadly, despite treatment, a severe flare-up can be fatal. Its thought that around 4% of people admitted to hospital with an acute COPD exacerbation will die.
In the UK there are 1.3 million people with a diagnosis of COPD. And each year, around 30,000 people die in the UK from COPD. Its important to talk to your doctor or nurse about longer-term treatments and advance care planning. This means thinking about what you would like to happen if your condition gets worse, or you experience more severe flare-ups, to help your family and your doctor to understand your wishes. Read more information on advance care planning and taking control of your choices.
Read Also: How Long Can An Asthma Attack Last
Q: Whats The Difference Between Asthma And Copd
Asthma occurs frequently in people with a family history of the disease and often begins in childhood. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, and these symptoms flare up during an asthma attack. At other times, symptoms may fade or become minimal.
COPD is different and usually strikes later in life. Most people diagnosed with COPD either used to smoke, or still do. Some symptomssuch as chest tightness and coughingare similar to asthma. Other symptoms, such as mucus production, are distinct to COPD. Unlike asthma, symptoms rarely ever fade completely.
What Is The Most Serious Asthma Or Copd
COPD symptoms get progressively worse. COPD produces more mucus and phlegm than asthma.
Can asthma turn into COPD?
Most people with asthma will not develop COPD, and many people with COPD do not have asthma. However, it is possible to have both. Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome occurs when a person has these two conditions at the same time.
What is the difference between treating asthma and treating COPD?
The key difference is that treatment in asthma is driven by the need to suppress chronic inflammation, whereas in COPD treatment is driven by the need to reduce symptoms. The treatment algorithm is based on the severity of asthma and COPD.
Read Also: Is Asthma An Inflammatory Disease
What Are The Types Of Copd
COPD includes two main types:
- affects the air sacs in your lungs, as well as the walls between them. They become damaged and are less elastic.
- Chronic bronchitis, in which the lining of your airways is constantly irritated and inflamed. This causes the lining to swell and make mucus.
Most people with COPD have both emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but how severe each type is can be different from person to person.
When Can Asthma Become Copd
Check out these statistics. About 90-95% of asthmatics can obtain good asthma control. Most asthmatics should have normal lung function between asthma attacks. This means their FEV1 should reach 80% or greater.2,3
But, this is not always the case. About 5-10% of asthmatics have what is called refractory asthma. This is asthma that does not improve with treatment. They continue to have airflow limitation and respiratory symptoms despite treatment. These asthmatics are now classified as having Severe Asthma.2,3
Some of these asthmatics may also be diagnosed with COPD.2
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Asthma And Emphysema
Airway Inflammation In Asthma
The airway inflammation in asthma is persistent even though symptoms are episodic, and the relationship between the severity of asthma and the intensity of inflammation is not clearly established .The inflammation affects all airways including in most patients the upper respiratory tract and nose but its physiological effects are most pronounced in medium sized bronchi . The pattern of inflammation in the airways appears to be similar in all clinical form of asthma, whether allergic, non-allergic, or aspirin-induced and at all ages .
Read Also: Can Smoking Weed Cause Asthma
Global Alliance Against Chronic Respiratory Diseases

The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases contributes to WHOs work to prevent and control chronic respiratory diseases. GARD is a voluntary alliance of national and international organizations and agencies from many countries committed to the vision of a world where all people breathe freely.
References
Also Check: Pulmonologist Or Allergist For Asthma
Inflammatory Mediators Involved In Asthma
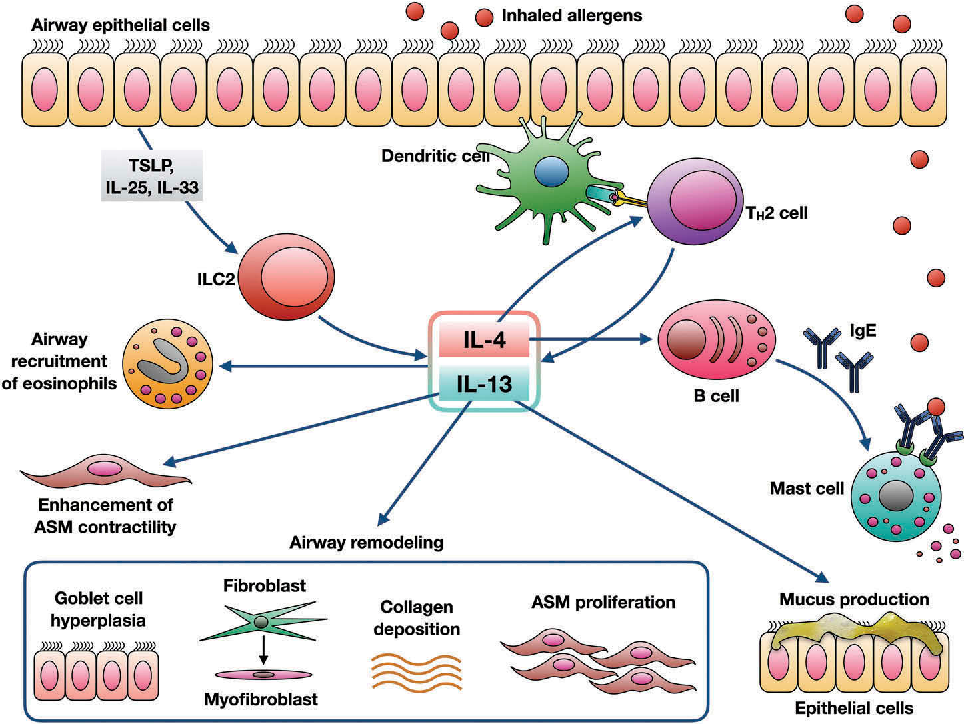
Chemokines are important in the recruitment of inflammatory cells into the airways and are mainly expressed in airway epithelial cells . Eotaxin is selective for eosinophils, whereas thymus and activationregulated chemokines and macrophage-derived chemokines recruit Th2 cells . Cysteinyl leukotrienes are potent bronchoconstrictors and proinflammatory mediators mainly derived from mast cells and eosinophils . Cytokines orchestrate the inflammatory response in asthma. Key cytokines include IL-1 and TNF, and GM-CSF. Th2-derived cytokines include IL-5, which is required for eosinophil differentiation and survival IL-4, which is important for Th2 cell differentiation and IL-13, needed for IgE formation . Histamine is released from mast cells and contributes to bronchoconstriction and inflammation . Nitric oxide , a potent vasodilator, is produced from syntheses in airway epithelial cells . Exhaled NO is increasingly being used to monitor the effectiveness of asthma treatment . Prostaglandin D2 is a bronchoconstrictor derived predominantly from mast cells and is involved in Th2 cell recruitment to the airways .
Airway structural cells involved in the pathogenesis of asthma are: airway epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts and airway nerves .
Why Does Overlap Happen
Having already analyzed all the potentially important common risk factors for overlapping asthma and COPD, such as increasing age, smoking, BHR, inflammation, remodeling and exacerbations, the big question is why does overlap happen. Dutch hypothesis tries to answer the question, stating that asthma and BHR predispose to COPD later in life and that asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema are different expressions of a single airway disease. Furthermore, the presence of these expressions is influenced by host and environmental factors . Epidemiological studies, on the other hand, proved a correlation between respiratory illnesses during childhood and impaired adult lung function . Knowing that airway growth starts in utero, fetal or childhood exposures may contribute to adult asthma or COPD .
Also Check: Can Asthma Ever Go Away
Response Rates And Sample Characteristics
The response rate was minimum in the elderly and maximum in people aged 4564 . The distribution of sex and smoking habits showed a statistically significant variation across age groups. The percentage of women was 53.6%, 52.2% and 42.7% in the 2044, 4564 and 6584 yrs age groups, respectively. In these age groups, 26.6%, 23.4% and 9.6% of the subjects were current smokers, while 55.4%, 42.2% and 53.0% of the subjects never smoked.
Why Can Copd And Asthma Co
An important distinction to make is that COPD doesnt necessarily cause asthma, nor does asthma cause someone to develop COPD. In fact, a person can live with either lung disease and never experience symptoms of the other.
However, when your condition is left untreated, or youre experiencing a worsening of symptoms, you risk damaging your lungs, which could lead to other serious lung issues.
As mentioned earlier, asthma can cause mucus buildup in the lungs, creating the onset of a respiratory infection. With each cycle of infection, the lungs become more damaged, putting the person at greater risk of developing bronchiectasis.
In this scenario, asthma doesnt directly cause bronchiectasis. The repeated damage to your lungs, caused by infection, does. The same is true for asthma and COPD and vise versa:
Asthma does not necessarily lead to COPD, but a person whose lungs have been damaged by poorly controlled asthma and continued exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke is at increased risk of developing COPD .
One condition doesnt replace the other, either. This is why ACOS is not considered a separate disease . Instead, it refers to someone who is living with a mix of asthma and COPD symptoms. This, of course, requires a different diagnosis and treatment plan than if you were living with only one of these conditions.
You May Like: How Do You Know You Have Asthma
Outlook For People With Severe Asthma
Because severe asthma is so unpredictable in the treatments it responds to, and the course it takes, the long-term outlook is different for everyone, says Dr Andy.
There are lots of treatments around for people with severe asthma and your team of healthcare professionals will work with you to find the right ones for you so you can have the best quality of life possible in the long term.
Airway remodelling
One of the possible long-term effects of severe asthma is something called airway remodelling.
This is where your airways become thicker over time, so the airway itself is narrower, making it harder to breathe.
Airway remodelling can happen if people have frequent asthma attacks. If you have severe asthma, your risk increases because youll probably have asthma attacks more often. Long-term exposure to pollutants including tobacco smoke can play a part too.
Whatever the reason, if youre continually having lots of symptoms over a long period of time then theres a risk your airways will become permanently narrowed, scarred and inflamed, which can mean your symptoms get worse.
For most people, changes to the structure of your airways can be avoided with good asthma management.
Airway remodelling can be treated with bronchial thermoplasty, but this treatment is not recommended for everyone with severe asthma.
COPD and Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome
Long term severe asthma can sometimes lead to a chronic lung condition called COPD or ACO .
Similarities And Differences In Regular Standard Treatment Of Asthma And Copd
-
In both diseases the adequate treatment may reduce symptoms and number of exacerbations and improve the quality of life.
-
Treatment of asthma is characterized by suppression of inflammation.
-
Treatment of COPD is characterized by decreasing of symptoms.
The GOAL of treatment in ASTHMA is to: reduce inflammation and to achieve¸total control . The GOAL of treatment in COPD is to: reduce symptoms, prevent exacerbations and decrease mortality . In both asthma and COPD almost the same drugs are used, but not in the same order and the same efficiency in treatment.
Recommended Reading: How To Diagnose Asthma In Child
Differences Between Copd And Asthma
There are a number of other differences between COPD and asthma as well.
-
Often diagnosed during childhood or adolescence
-
Symptoms more likely to occur episodically and/or at night
-
Commonly triggered by allergens, cold air, exercise
-
People who have asthma are more commonly nonsmokers
-
Comorbid conditions include eczema and allergic rhinitis
-
Treatment usually involves inhaled steroids
-
Airflow restriction mostly reversible
-
Likely to cause morning cough, increased sputum, and persistent symptoms
-
Exacerbations commonly triggered by pneumonia and flu or pollutants
-
Most people who have COPD have smoked or had significant secondhand smoke exposure
-
Comorbid conditions include coronary heart disease or osteoporosis
-
Treatment usually involves pulmonary rehabilitation
-
Airflow restriction is permanent or only partially reversible
Once you develop COPD, your symptoms will generally be chronic. Over time, with COPD, you are likely to experience symptoms that are not typical for asthmalosing weight, decreased strength, and diminished endurance, functional capacity, and quality of life.
How The Body Handles Hot Temperatures
As a means of reducing the temperature of the body to maintain the optimal core temperature 37oC, the body performs the following:
1. The thyroid gland reduces hormones into the body to reduce heating in the body and releasing as much heat as possible by doing the following.
2. Decreasing heart rate,
3. Decreasing blood pressure,
4. Decreasing metabolism,
5. Increasing the size of the blood vessels in the skin to increase heat loss and water loss through sweating,
6. Increasing water loss from the kidneys to again increase heat loss from the water excretion
The issue is that as the temperature increase above 32 oC, the bodys ability to reduce and increase heat loss has reached its limits . This is where it becomes dangerous for the body and normal bodily functions start to fail.
You May Like: What To Do After An Asthma Attack
