Potential For Endothelial Based Treatments
COPD
It is possible that some of the treatments already available for COPD might be able to improve endothelial functioning. For example, one study observing endothelial function in COPD patients demonstrated that patients with improved 6MWT scores had improved FMD levels . Therefore, it is possible that pulmonary rehabilitation courses could provide one way of improving endothelial function. In vitro studies have also demonstrated treating the increased level of 2AR on EPCs with 2 antagonists improves the proliferation and migratory capacity of these cells . One RCT looking at endothelial function in COPD patients observed an improvement in FMD after lung volume reduction surgery . It is not clear why LVRS improves endothelial functioning but one possibility is that improved cardiac function seen after LVRS might stimulate the endothelium, thus improving FMD .
Table 1 Potential endothelial based treatments in COPD
Symptoms Complaints And Signs
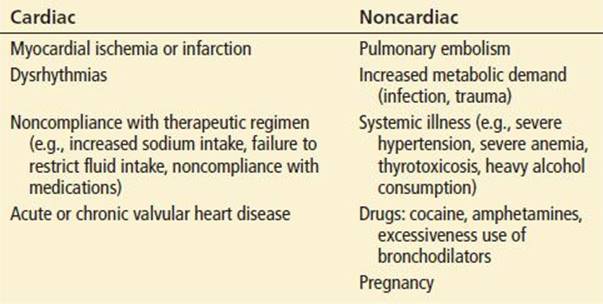
The symptoms of cor pulmonale must again be distinguished between the acute and chronic forms. Acute cor pulmonale develops very rapidly. There is a sudden onset of severe shortness of breath. Without treatment, the right heart fails within a very short time. The result is sudden cardiac death. Chronic cor pulmonale develops over years. As the right heart becomes weaker and weaker due to the pressure load, it can no longer adequately pump venous blood out of the body. This results in a backflow into the veins of the large systemic circulation. As a result, the pressure in the veins increases and fluid is forced into the surrounding tissue. This process is visible, for example, in leg and ankle edema. Blood also backs up in the organs. Enlargement of the spleen and liver can be the result. Furthermore, gastrointestinal problems can occur as a result of the backlog. One speaks then for example of a stasis gastritis. Possibly a congestion of the neck veins is visible. Because the right heart can pump less blood, less blood reaches the lungs and consequently less oxygen-rich blood reaches the left heart. This results in an undersupply of oxygen to the body. The skin of the affected person may turn blue . Patients also suffer from shortness of breath. They are no longer able to work hard physically and quickly become exhausted.
Emphysema Part 10 Of 17
Definition
Permanent loss of alveolar parenchyma distal to the terminal bronchiole.
Aetiology
- Smoking usually older patients as emphysema develops slower
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency usually younger patients as emphysema develops quickly
- Rarely connective tissue diseases e.g. Marfans
Clinical features
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Asthma Attack Without Inhaler
What Is Cor Pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a Latin word that means pulmonary heart, its definition varies, and presently, there is no consensual definition 1), 2). Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail from long-standing pulmonary artery high blood pressure . Long-term high blood pressure in the arteries of the lung and right ventricle of the heart can lead to cor pulmonale. Cor pulmonale can be defined as an alteration in the structure and function of the right ventricle of the heart caused by a primary disorder of the lungs resulting in pulmonary hypertension 3).
The exact prevalence of cor pulmonale is difficult to determine, as physical examination and routine tests are relatively insensitive for the detection of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricle dysfunction. Cor pulmonale is estimated to account for 6% to 7% percent of all types of adult heart disease in the United States;4). Globally, the incidence of cor pulmonale varies widely among countries, depending on the prevalence of cigarette smoking, air pollution, and other risk factors for various lung diseases.
Right-sided heart failure secondary to left-sided heart failure, or congenital heart disease is not considered cor pulmonale 17).
How To Prevent Leg Swelling With Copd
If you want to prevent leg swelling with COPD, your best bet will be to follow your COPD treatment plan. Pulmonary rehabilitation is extremely important for preventing swelling because not only will it improve your endurance, but it will also strengthen your heart muscle, improve circulation, and reduce body fat which is a known contributor to peripheral edema. To combat leg swelling, your doctor may advise that you increase the amount of time spent doing pulmonary rehab, or he/she might advise that you split your exercise routines into shorter, more frequent intervals.
Hydration is another key treatment for leg swelling caused by COPD. Plasma, the primary component of your blood is made up of 90 percent water. And water is what keeps blood flowing freely throughout your body without clotting or pooling. So, it goes without saying that drinking more water will improve your circulation and keep you healthy. Most doctors will recommend around 8 to 12 glasses of water a day for the average COPD patient.
Read Also: What To Do During An Asthma Attack No Inhaler
What Causes Acute Cor Pulmonale
4.5/5pulmonary hypertension
Cor pulmonale is right ventricular enlargement secondary to a lung disorder that causes pulmonary artery hypertension. Cor pulmonale is usually chronic but may be acute and reversible. Primary pulmonary hypertension is discussed elsewhere.
Beside above, how long can you live with Cor pulmonale? For example, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who develop cor pulmonale have a 30% chance of surviving 5 years.
Considering this, is Cor pulmonale the same as congestive heart failure?
When the right heart fails because of chronic lung disease, pulmonary artery hypertension, or pulmonic valve stenosis, it hypertrophies and results in chronic diastolic failure of the right ventricle. This is chronic cor pulmonale. If a physician documents these diagnoses as “CHF,” all you have is code 428.0.
Is Pulmonary Hypertension same as cor pulmonale?
Pulmonary hypertension is elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries 20 mm Hg at rest. If these changes are secondary to diseases of the lungs or the pulmonary artery system, the condition is referred to as cor pulmonale.
These tests may help diagnose cor pulmonale as well as its cause:
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Cor Pulmonale
3.9/5Symptoms you may have are:
- Fainting spells during activity.
- Chest discomfort, usually in the front of the chest.
- Chest pain.
- Swelling of the feet or ankles.
- Symptoms of lung disorders, such as wheezing or coughing or phlegm production.
- Bluish lips and fingers
Cor pulmonale is a condition that most commonly arises out of complications from high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries . Cor pulmonale causes the right ventricle to enlarge and pump blood less effectively than it should. The ventricle is then pushed to its limit and ultimately fails.
Similarly, what is the difference between cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension? Pulmonary hypertension is elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries 20 mm Hg at rest. If these changes are secondary to diseases of the lungs or the pulmonary artery system, the condition is referred to as cor pulmonale.
Regarding this, can cor pulmonale be cured?
Cor Pulmonale. Cor pulmonale is right ventricular enlargement secondary to a lung disorder that causes pulmonary artery hypertension. Cor pulmonale is usually chronic but may be acute and reversible.
How long can you live with Cor pulmonale?
For example, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who develop cor pulmonale have a 30% chance of surviving 5 years.
These tests may help diagnose cor pulmonale as well as its cause:
You May Like: Small Airway Disease Vs Asthma
Additional Things To Consider If You Have A Hard Time Breathing With Scoliosis
Comorbidities: Comorbidities are multiple health problems that contribute to the patients singular symptom or complaint. More than 1 in 12 people have asthma according to the American Lung Association that leads to chronic breathing problems. Adulthood asthma combined with a degenerative moderate-to-severe scoliosis may gradually create a physical and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease process, leading to significant breathing problems.
What Are The Symptoms Of Peripheral Edema
The primary symptom of peripheral edema is swelling in the extremities. This swelling is usually drastic enough that it will be noticeable by you or your loved ones, and as the swelling increases, youll likely have trouble putting on your shoes or clothing without having to force them on.
Another symptom of peripheral edema is reduced mobility. If youre like most COPD patients, youre probably trying to stay active in order to preserve your lung function and keep your muscles strong and efficient. If youre developing peripheral edema, you may feel your legs becoming heavier or you may notice that you lose your sense of balance more easily than you did before.
In some, but not all cases, people with peripheral edema may experience pain and tightness in their legs or feet. As the amount of fluid increases in the affected area, you may notice the skin becoming shiny and red. You might also experience something called pitting. This is when you press on an area of your skin and the indentation remains there longer than it would on a healthier part of your body. Since the fluids that your legs or feet are retaining would normally be flushed out of the body, you might also see an increase in your body weight.
Read Also: What To Do Asthma Attack No Inhaler
Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors
The PDE5 inhibitors function by preventing the degradation of cyclic GMP and subsequently prolonging the vasodilatory effect of nitric oxide. Of these, sildenafil has been intensively studied and was approved by the FDA for treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Sildenafil promotes selective smooth muscle relaxation in lung vasculature. Tadalafil and vardenafil are other PDE5 inhibitors also approved by the FDA for the treatment of PAH to improve exercise ability.
There are not enough data available yet regarding the efficacy of these drugs in patients with secondary pulmonary hypertension, such as in patients with COPD.
Isotopic Ventriculography And Mri
Isotopic right ventriculography is a technique used to assess right ventricular global function. Studies performed 20yrs ago have shown significant correlation between right ventricular ejection fraction measured with isotopic ventriculography and Ppa, . However, this method does not allow diagnosis of PH, owing to the important overlap of this measurement in COPD patients in a stable disease state, compared with normal subjects . Therefore, isotopic right ventriculogram adds little information compared to echocardiography, and this method is costly.
MRI allows the measurement of volumes and blood flow in the thorax. New generation devices are not hindered by cardiac motion. At present, it is probably the best method for the measurement of right ventricular ejection fraction and right ventricular mass , , but its role in the diagnosis strategy of PH in COPD must be determined.
Recommended Reading: What To Do If Someone Is Having An Asthma Attack
Prevalence Of Ph In Copd
Determination of prevalence of PH in COPD has been hampered by difficulties in obtaining valid data from an adequate population-based sample of COPD. The main reason is that right heart catheterisation cannot be performed on a large scale for ethical reasons and it is well known that echocardiography alone is subject to some error . Only studies of hospitalised subjects are available. Burrows et al. reported 36yrs ago that 50 patients with COPD and severe airflow limitation /vital capacity ratio of 37%) had an average Ppa value of 26mmHg. In a larger sample of 175 patients with a mean FEV1/VC ratio of 40%, Weitzenblum et al. observed a prevalence of PH of 35%.
Prognostic impact of pulmonary hypertension. a) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with a mean pulmonary artery pressure 25mmHg at the beginning of long-term oxygen therapy have a significantly shorter life expectancy compared with patients with Ppa<25mmHg . Reproduced from with permission from the publisher. b) COPD patients with Ppa>18mmHg in a stable state of the disease have an increased risk of hospitalisation for exacerbation compared with patients with Ppa 18mmHg . Reproduced from with permission from the publisher.
What Is The Treatment For Cor Pulmonale
4.9/5Treatmentcor pulmonalecor pulmonaleread more on it
For example, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who develop cor pulmonale have a 30% chance of surviving 5 years.
Beside above, is Cor pulmonale the same as congestive heart failure? When the right heart fails because of chronic lung disease, pulmonary artery hypertension, or pulmonic valve stenosis, it hypertrophies and results in chronic diastolic failure of the right ventricle. This is chronic cor pulmonale. If a physician documents these diagnoses as “CHF,” all you have is code 428.0.
Consequently, what happens in Cor pulmonale?
Cor pulmonale occurs when the blood pressure in the pulmonary arterywhich carries blood from the heart to the lungsincreases and leads to the enlargement and subsequent failure of the right side of the heart. Symptoms of cor pulmonale can include fatigue, swelling, and chest pain.
Is Cor pulmonale fatal?
Cor pulmonale can also cause severe fluid retention, difficulty breathing, and even shock. It’s life-threatening when it’s not treated.
Read Also: How To Fix Asthma Without Inhaler
Prevention Of Copd And Asthma
COPD
COPD is a preventable disease. Although primary prevention hinges on tobacco cessation strategies, secondary prevention of COPD centers on early diagnosis, risk factor modification and treatment. However, early diagnosis of COPD is often delayed. In 2002, the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 7 reported that approximately 24 million adults in the USA have evidence of impaired lung function on spirometry; however, only about 50% of these patients have physician-diagnosed COPD, most of which is moderately advanced disease. At this late stage of disease, only tertiary prevention, aimed at preventing the complications of COPD, is effective. Therefore, primary and secondary prevention strategies need to be improved.
Better prevention of COPD can be achieved through compliance with guidelines. Numerous guidelines exist to assist physicians in early diagnosis, prevention of disease progression and management of COPD, including those of GOLD, the American Thoracic Society, the National Collaborating Center for Chronic Conditions and the Canadian Thoracic Society.
Asthma
Numerous guidelines are also available to aid physicians and other healthcare professionals to better prevent and manage asthma. Two frequently referenced guidelines are those of the NAEPP and the Global Initiative for Asthma .
Outlook For People With Cor Pulmonale
The outlook for people with cor pulmonale ultimately depends on the management of pulmonary hypertension. Cor pulmonale can also cause severe fluid retention, difficulty breathing, and even shock. Its life-threatening when its not treated.
Talk to your doctor if you notice any changes in the way you feel, especially if youre currently being treated for pulmonary hypertension. Your doctor may need to adjust your treatment plan to help prevent cor pulmonale.
Recommended Reading: How Can U Get Asthma
Prostacyclin Analogues And Receptor Agonists
Epoprostenol, treprostinil, and bosentan are prostacyclin analogues and have potent vasodilatory properties. Epoprostenol is administered intravenously . Treprostinil can be administered IV and subcutaneously ; the FDA has approved oral and inhaled formulations. Iloprost is commonly inhaled but requires frequent dosing.
Of these prostacyclin analogues, epoprostenol has been the most studied; it has been shown to improve survival in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension as well as some benefit in other types of World Health Organization classification group 1 pulmonary hypertension, particularly in patients with more severe functional status.
Selexipag is a prostacyclin receptor agonist, which acts to vasodilate the pulmonary vasculature. It is administered orally and has been shown to reduce disease progression in PAH.
Treating Pulmonary Hypertension And Cor Pulmonale
Your doctor will need to treat the causes of pulmonary hypertension to treat cor pulmonale. Prescription medications can help decrease blood pressure and help encourage oxygen flow back into the lungs. Diuretics may also be used to get rid of fluid retention and to keep your blood sodium levels down. You may also take blood thinners to prevent blood clots.
Severe or advanced cases of cor pulmonale require more aggressive treatments such as a heart or lung transplant. Others may need to take oxygen therapy.
Read Also: What Helps Asthma Attacks Without An Inhaler
Heres What You Can Do Yourself
When cor pulmonale occurs, the underlying condition must first be treated. If heart failure is already present, the doctor will also recommend a low-salt diet and dehydrating medications. Sometimes dietary supplements and digitalis are also prescribed. Smokers should stop consuming cigarettes immediately, as the symptoms are usually caused by severe lung disease. It is advisable to work out these measures together with the doctor in charge. Long-time smokers often need therapeutic support to quit, but can also make it easier to give up by using nicotine patches and the like. In any case, the trigger of the causative disease must be identified and remedied immediately. If the symptoms persist, treatment in hospital is required. Acute cor pulmonale is a medical emergency that must be treated immediately. First responders should immediately alert the emergency physician and place the affected person in the recovery position. Sometimes, life-sustaining measures must also be performed. Appropriate precautions must also be taken for prolonged hospitalization. In the long term, then, cor pulmonale always requires medical treatment. Everyday measures such as a healthy diet, exercise, and abstaining from stimulants can be used as a supplement.
More articles that may interest you:
How Does Swelling Occur
People with cor pulmonale do not have enough oxygen flowing through their body in their bloodstreams. Also, the heart is not able to pump the amount of blood through the body that is needed for organs like the liver and kidneys to function well.4
In healthy people, the liver and kidneys help remove fluids from the body. But without enough blood supply, those organs are not able to do their usual jobs. This causes too much fluid to collect and build up in areas like the ankles, legs, and feet. These kinds of swelling are common symptoms of cor pulmonale.4
Don’t Miss: What Is The Blood Test For Eosinophilic Asthma
